A review of the anti-viral effects of ivermectin
et al., African Journal of Clinical and Experimental Microbiology, doi:10.4314/ajcem.v22i3.2, Jul 2021
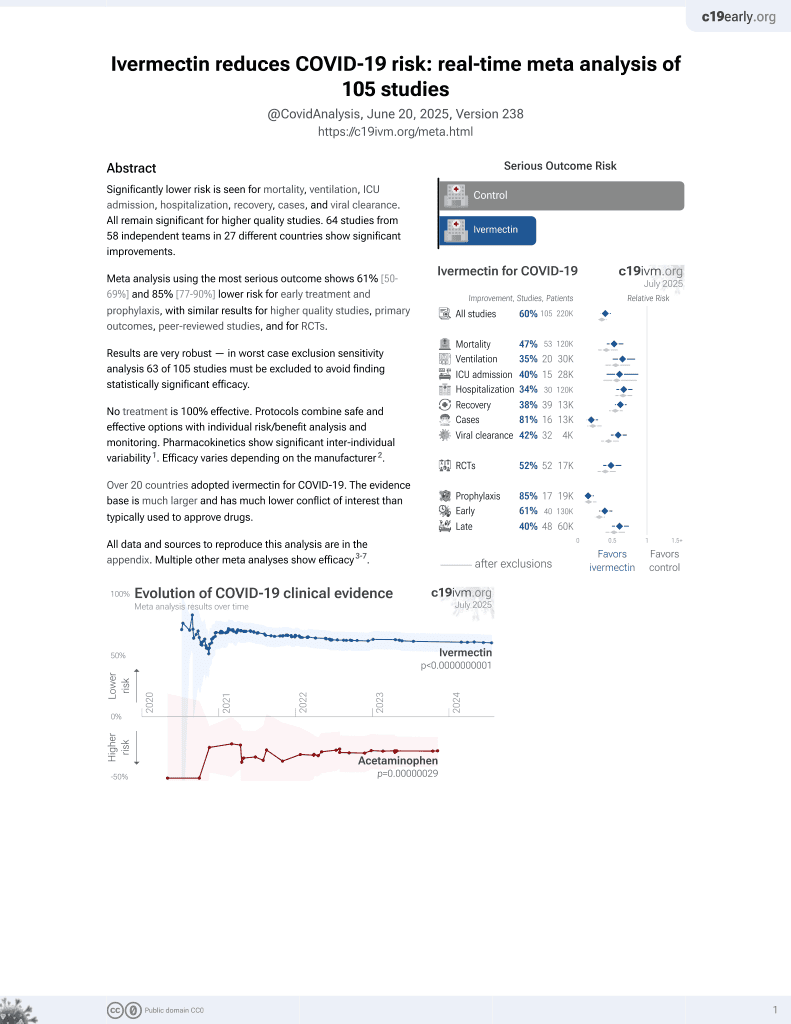
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of the antiviral effects of ivermectin.
1.
Reich, S., Methodological Analysis of Bias Risks in Adaptive Multi-Arm Platform Trials: A Case-Series from Three COVID-19 Studies, Center for Open Science, doi:10.31222/osf.io/h5kc8_v1.
2.
Mothae et al., SARS-CoV-2 host-pathogen interactome: insights into more players during pathogenesis, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2025.110607.
3.
Zhang et al., Rho-GTPases subfamily: cellular defectors orchestrating viral infection, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-025-00722-w.
4.
Saha et al., Inhaled Dry Powder of Antiviral Agents: A Promising Approach to Treating Respiratory Viral Pathogens, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17020252.
5.
Ulloa-Aguilar et al., The Nucleolus and Its Interactions with Viral Proteins Required for Successful Infection, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13181591.
6.
Enyeji et al., Effective Treatment of COVID-19 Infection with Repurposed Drugs: Case Reports, Viral Immunology, doi:10.1089/vim.2024.0034.
7.
Wimalawansa, S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
8.
Shouman et al., SARS-CoV-2-associated lymphopenia: possible mechanisms and the role of CD147, Cell Communication and Signaling, doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01718-3.
9.
Mehraeen et al., Treatments for Olfactory Dysfunction in COVID-19: A Systematic Review, International Archives of Otorhinolaryngology, doi:10.1055/s-0044-1786046.
10.
Scheim et al., Back to the Basics of SARS-CoV-2 Biochemistry: Microvascular Occlusive Glycan Bindings Govern Its Morbidities and Inform Therapeutic Responses, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16040647.
11.
Yagisawa et al., Global trends in clinical trials of ivermectin for COVID-19—Part 2, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.11553/antibiotics.77.1_45.
12.
Liu et al., Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and immune regulation: insights into pathobiology and therapeutic implications of transfusion-related acute lung injury, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021.
13.
Scheim (B) et al., Sialylated Glycan Bindings from SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Blood and Endothelial Cells Govern the Severe Morbidities of COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242317039.
14.
Yemeke et al., Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of medical products in Zimbabwe: a qualitative study based on key informant interviews with health system stakeholders, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068923.
15.
Kory, P., The Global War on Ivermectin, International Covid Summit III, European Parliament, Brussels, covid19criticalcare.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/GLOBAL-WAR-ON-IVERMECTIN-PARLIAMENT.pdf.
16.
Babalola et al., The Place of Ivermectin in the Management of Covid-19: State of the Evidence, Medical Research Archives, doi:10.18103/mra.v11i4.3778.
17.
Loo et al., Recent Advances in Inhaled Nanoformulations of Vaccines and Therapeutics Targeting Respiratory Viral Infections, Pharmaceutical Research, doi:10.1007/s11095-023-03520-1.
18.
Scheim (C), D., From Cold to Killer: How SARS-CoV-2 Evolved without Hemagglutinin Esterase to Agglutinate and Then Clot Blood Cells, Center for Open Science, doi:10.31219/osf.io/sgdj2.
19.
Kory (B), P., The Criminal Censorship of Ivermectin's Efficacy By The High-Impact Medical Journals - Part 1, Pierre Kory’s Medical Musings, pierrekory.substack.com/p/the-criminal-censorship-of-ivermectins.
20.
Al-kuraishy et al., Central effects of Ivermectin in alleviation of Covid-19-induced dysautonomia, Current Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1389450123666220810102406.
21.
Schwartz, E., Does ivermectin have a place in the treatment of mild Covid-19?, New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2022.100989.
22.
Marques et al., Ivermectin as a possible treatment for COVID-19: a review of the 2022 protocols, Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.258325.
23.
Semiz, S., SIT1 transporter as a potential novel target in treatment of COVID-19, Biomolecular Concepts, doi:10.1515/bmc-2021-0017.
24.
Zaidi et al., The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2—an extensive review, The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6.
25.
Behl et al., CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target, Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072.
26.
Low et al., Repositioning Ivermectin for Covid-19 treatment: Molecular mechanisms of action against SARS-CoV-2 replication, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166294.
27.
Fordham et al., The uses and abuses of systematic reviews, OSF Preprints, doi:10.31219/osf.io/mp4f2.
28.
Kow et al., Pitfalls in Reporting Sample Size Calculation Across Randomized Controlled Trials Involving Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001441.
29.
Santin et al., Ivermectin: a multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honored distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19, New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100924.
30.
Adegboro et al., A review of the anti-viral effects of ivermectin, African Journal of Clinical and Experimental Microbiology, doi:10.4314/ajcem.v22i3.2.
31.
Turkia, M., A Continuation of a Timeline of Ivermectin-Related Events in the COVID-19 Pandemic [June 30, 2021], ResearchGate, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.16973.36326.
32.
Jagiasi et al., Variation in therapeutic strategies for the management of severe COVID-19 in India- A nationwide cross-sectional survey, The International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14574.
33.
Lind et al., Increase in Outpatient Ivermectin Dispensing in the US During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Analysis, Journal of General Internal Medicine, doi:10.1007/s11606-021-06948-6.
34.
Wang et al., Minimum manufacturing costs, national prices and estimated global availability of new repurposed therapies for COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.06.01.21258147.
35.
Kory (C) et al., Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001377.
36.
DiNicolantonio et al., Anti-inflammatory activity of ivermectin in late-stage COVID-19 may reflect activation of systemic glycine receptors, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2021-001655.
37.
Turkia (B), M., A timeline of ivermectin-related events in the COVID-19 pandemic, Research Gate, www.researchgate.net/publication/350610718_A_Timeline_of_Ivermectin-Related_Events_in_the_COVID-19_Pandemic_April_3_2021.
38.
Wehbe et al., Repurposing Ivermectin for COVID-19: Molecular Aspects and Therapeutic Possibilities, Front. Immunol., doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586.
39.
Yagisawa (B) et al., Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, 74-1, Mar 2021, jja-contents.wdc-jp.com/pdf/JJA74/74-1-open/74-1_44-95.pdf.
40.
Jans et al., The broad spectrum host-directed agent ivermectin as an antiviral for SARS-CoV-2 ?, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.042.
41.
Kory (D) et al., Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.643369.
42.
Formiga et al., Ivermectin: an award-winning drug with expected antiviral activity against COVID-19, J. Control Release, doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009.
43.
Scheim (D), D., Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-Threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-Mediated Vascular Occlusion, SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3636557.
44.
Turkia (C), M., FLCCC Alliance MATH+ ascorbic acid and I-MASK+ ivermectin protocols for COVID-19 — a brief review, ResearchGate, www.researchgate.net/profile/Mika_Turkia/publication/345694745_FLCCC_Alliance_MATH_ascorbic_acid_and_I-MASK_ivermectin_protocols_for_COVID-19_-_A_Brief_Review/links/5fab010f4585150781078260/FLCCC-Alliance-MATH-ascorbic-acid-and-I-MASK-ivermectin-protocols-for-COVID-19-A-Brief-Review.pdf.
45.
Jans (B) et al., Ivermectin as a Broad-Spectrum Host-Directed Antiviral: The Real Deal?, Cells 2020, 9:9, 2100, doi:10.3390/cells9092100.
46.
Elkholy et al., Ivermectin: A Closer Look at a Potential Remedy, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.10378.
47.
DiNicolantonio (B) et al., Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350.
48.
Vora et al., White paper on Ivermectin as a potential therapy for COVID-19, Indian Journal of Tuberculosis, doi:10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.07.031.
Adegboro et al., 2 Jul 2021, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
A review of the anti-viral effects of ivermectin
African Journal of Clinical and Experimental Microbiology, doi:10.4314/ajcem.v22i3.2
Ivermectin is an avermectin which is a group of pentacyclic sixteen-membered lactone (macrocyclic lactone disaccharide) derived from the soil bacterium Streptomyces avermitilis. It is a semi-synthetic broad-spectrum antihelminthic, anti-viral and anti-cancer agent. It has a wide safety margin with low adverse effects when it is used orally. It has, however, so far only been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a broad spectrum anti-parasitic agent. Because ivermectin also has broad activities as an anti-viral agent, we herein review its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic activities, as well as the in vitro and in vivo studies conducted on the drug. It is hoped that this work will pave way for ivermectin being seriously considered as an addition to the drugs available for the management of patients with COVID-19.
References
Azeem, Ashraff, Rasheed, Anjum, Hameed, Evaluation of cytotoxic and antiviral activity of ivermectin against Newcastle disease virus, Pak J Pharm Sci
Banerjee, Nandy, Dalai, Ahmed, The battle against COVID-19 pandemic: What we need to know before we "test fire" ivermectin, Drug Res (Stuttg.)
Barrows, Campos, Powell, A screen of FDA-drugs, for inhibitors of Zika virus infection, Cell Host Microbe
Basanez, Pion, Boakes, Effect of single-dose ivermectin on Onchocerca volvulus: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet Infect Dis
Bennet, Zhao, Bosard, Imperiale, Role of a nuclear localization signal on the minor capsid proteins VP2 and VP3 in BKPyV nuclear entry, Virology
Berthomme, Monahan, Parris, Jacquemont, Epstein, Cloning, sequencing, and functional characterization of the two subunits of the pseudorabies virus DNA polymerase holoenzyme: evidence for specificity of interaction, J Virol
Borst, Schinkel, What have learnt thus far from mice with disrupted p-glycoprotein genes?, Eur J Cancer
Bray, Rayner, Noel, Jans, None
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA approved drug Ivermectin inhibit replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-COV-2 in vitro, Antivir Res
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antivir Res
Caly, Wagstaff, Jans, Nuclear trafficking of proteins from RNA viruses: Potential target for antivirals?, Antivir Res
Canga, Prieto, Liebana, Martinez, Vega, The pharmacokinetics and interactions of ivermectin-a minireview, AAPS J
Carmona-Guttierrez, Bauer, Zimmermann, Digesting the crisis: Autophagy and coronavirus, Microb Cell, doi:.10.15698/.05.715
Didier, Loor, The abamectin derivative ivermectin is a potent p-glycoprotein inhibitor, Anti-Cancer Drugs
Dou, Chen, Wang, Ivermectin induces cytostatic autophagy by blocking the PAK/AKT axis in breast cancer, Cancer Res
González Canga, Sahagún Prieto, Diez Liébana, The pharmacokinetics and interaction of ivermectin in humans: a mini-review, AAPS J, doi:10.1208/s12248-007-9000-9
Gotz, Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Sci Rep
Gotz, Magar, Dornfeld, Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Sci Rep
Heidary, Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen, J Antibiot, doi:10.1038/s41429-%09020-0336-z
Juarez, Schcolnik-Cabrera, Duenas-Gonzalez, The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug, Am J Cancer Res
Laing, Gillan, Daveney, Ivermectin-Old Drug, New Tricks?, Trends Parasitol, doi:10.1016/j.pt.2017.02.004
Lundberg, Pinkham, Baer, Nuclear import and export inhibitors alter capsid protein distribution in mammalian cells and reduce Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus replication, Antivir Res
Lv, Liu, Wang, Ivermectin inhibits DNA polymerase UL42 of pseudorabies virus entrance into the nucleus and proliferation of the virus in vitro and vivo, Antivir Res
Lv, Liu, Wang, Ivermectin inhibits DNA polymerase UL42 of pseudorabies virus entrance into the nucleus and proliferation of the virus in vitro and vivo, Antivir Res
Mudatsir, Yufika, Nainu, Antiviral activity of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2: An old-fashioned dog with a new trick -a literature review, Scientia Pharmaceutica, doi:10.3390/scipharm88030036
Nicolas, Maia, Bassat, Safety of oral ivermectin during pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet Glob Health
Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Ivermectin in COVID Nineteen) study: Use of ivermectin is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.06.2012446
Raza, Shahin, Zhai, Ivermectin inhibits bovine herpesvirus-1 DNA polymerase nuclear import and interferes with viral replication, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8030409
Rizzo, Ivermectin, antiviral properties and COVID-19: A possible new mechanism of action, Nauyn-Schmeid Acta Pharmacol
Schmith, Zhou, Lohmer, The approved dose of ivermectin alone is not the ideal dose for the treatment of COVID-19, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Slonska, Cymerys, Skwarska, Golke, Banbura, Influence of importin alpha/beta and exportin 1 on Equine herpesvirus type 1 (EHV-1) replication in primary murine neurons, Pol J Vet Sci
Tay, Fraser, Chan, Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1-4 non -structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin, Antivir Res
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Zn 2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathol
Wagstaff, Ivermectin and COVID-19: A report in Antiviral Research, widespread interest, an FDA warning, two letters to the editor and the authors' responses, Antivir. Res
Wagstaff, Rawlinson, Hearps, Jans, An Alpha Screen (R)-based assay for high throughput screening for specific inhibitor of nuclear import, J Biomol Screen
Wagstaff, Sivakumaran, Heaton, Harrich, Jans, Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin α/β-mediated nuclear import to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus, Biochem J
Wagstaff, Sivakumaran, Heaton, Harrich, Jans, Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importinα/β -mediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus, Biochem J
Wang, Du, Huang, The pseudorabies virus DNA polymerase accessory subunit UL42 directs nuclear transport of the holoenzyme, Front Microbiol
Yang, Atkinson, Wang, The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport import α/β1 heterodimer, Antivir Res
Yang, Atkinson, Wang, The broad-spectrum anti-viral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/βI heterodimer, Antivir Res
Yang, Qi, Farias-Pereira, Permethrin and ivermectin modulate lipid metabolism in steatosis-induced HepG2 hepatocyte, Food Chem Toxicol
Yates, Wolstenholme, An ivermectin sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel subunit from Dirafilaria immitis, Int J Parasitol
Zhang, Ni, Zhang, Ivermectin confers its cytostatic effect by inducing AMPK/ mTOR-mediated autophagy and DNA damage, Chemosph
Ōmura, Crump, The life and times of ivermectin: A success story, Nat Rev Microbiol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4314/ajcem.v22i3.2",
"ISSN": [
"1595-689X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/ajcem.v22i3.2",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Ivermectin is an avermectin which is a group of pentacyclic sixteen-membered lactone (macrocyclic lactone disaccharide) derived from the soil bacterium Streptomyces avermitilis. It is a semi-synthetic broad-spectrum anti-helminthic, anti-viral and anti-cancer agent. It has a wide safety margin with low adverse effects when it is used orally. It has, however, so far only been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a broad spectrum anti-parasitic agent. Because ivermectin also has broad activities as an anti-viral agent, we herein review its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic activities, as well as the in vitro and in vivo studies conducted on the drug. It is hoped that this work will pave way for ivermectin being seriously considered as an addition to the drugs available for the management of patients with COVID-19.
\nKeywords: ivermectin; pharmacokinetics; pharmacodynamics; broad-spectrum anti-viral; COVID-19</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adegboro",
"given": "B.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawani",
"given": "O.A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oriaifo",
"given": "S.E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abayomi",
"given": "S.A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "African Journal of Clinical and Experimental Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "Af J Clin Exp Micro",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-05T14:41:18Z",
"timestamp": 1625496078000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-05T14:41:32Z",
"timestamp": 1625496092000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-01T15:51:26Z",
"timestamp": 1711986686424
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
]
}
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajcem/article/download/209853/197857",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajcem/article/download/209853/197857",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "2895",
"original-title": [],
"page": "322-329",
"prefix": "10.4314",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "African Journals Online (AJOL)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajcem/article/view/209853"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A review of the anti-viral effects of ivermectin",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "22"
}