The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2—an extensive review
et al., The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6, Dec 2021
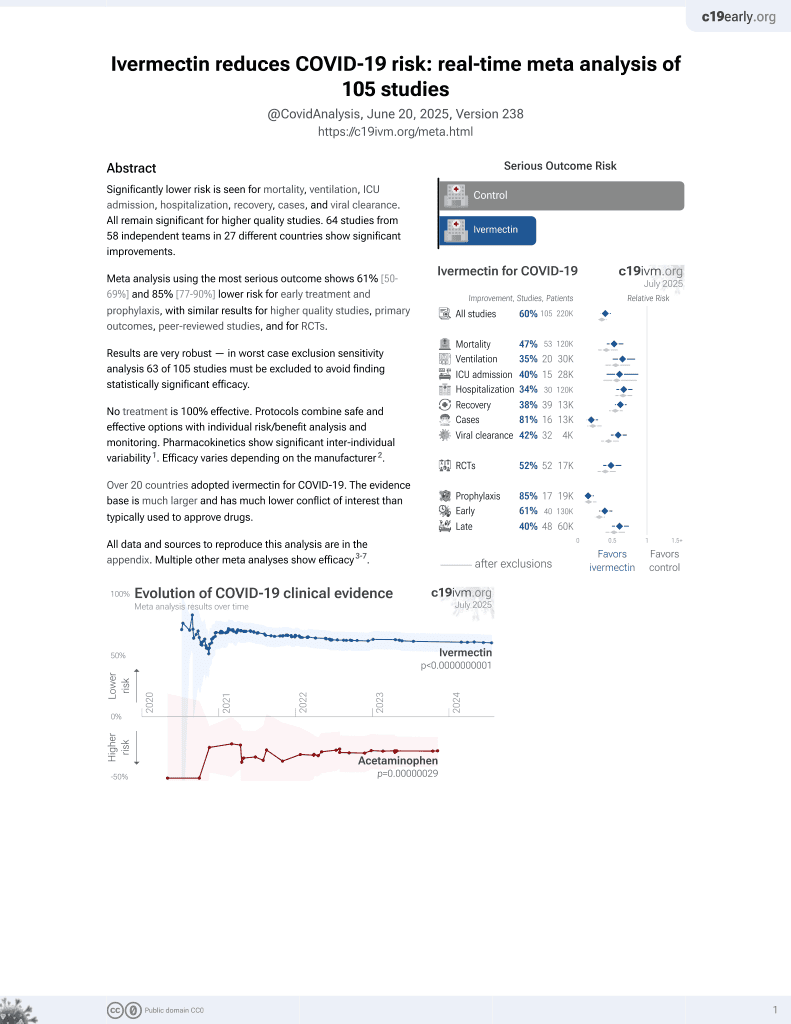
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Extensive review of 20 mechanisms of action of ivermectin for SARS-CoV-2.
1.
Reich, S., Methodological Analysis of Bias Risks in Adaptive Multi-Arm Platform Trials: A Case-Series from Three COVID-19 Studies, Center for Open Science, doi:10.31222/osf.io/h5kc8_v1.
2.
Mothae et al., SARS-CoV-2 host-pathogen interactome: insights into more players during pathogenesis, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2025.110607.
3.
Zhang et al., Rho-GTPases subfamily: cellular defectors orchestrating viral infection, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-025-00722-w.
4.
Saha et al., Inhaled Dry Powder of Antiviral Agents: A Promising Approach to Treating Respiratory Viral Pathogens, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17020252.
5.
Ulloa-Aguilar et al., The Nucleolus and Its Interactions with Viral Proteins Required for Successful Infection, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13181591.
6.
Enyeji et al., Effective Treatment of COVID-19 Infection with Repurposed Drugs: Case Reports, Viral Immunology, doi:10.1089/vim.2024.0034.
7.
Wimalawansa, S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
8.
Shouman et al., SARS-CoV-2-associated lymphopenia: possible mechanisms and the role of CD147, Cell Communication and Signaling, doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01718-3.
9.
Mehraeen et al., Treatments for Olfactory Dysfunction in COVID-19: A Systematic Review, International Archives of Otorhinolaryngology, doi:10.1055/s-0044-1786046.
10.
Scheim et al., Back to the Basics of SARS-CoV-2 Biochemistry: Microvascular Occlusive Glycan Bindings Govern Its Morbidities and Inform Therapeutic Responses, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16040647.
11.
Yagisawa et al., Global trends in clinical trials of ivermectin for COVID-19—Part 2, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.11553/antibiotics.77.1_45.
12.
Liu et al., Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and immune regulation: insights into pathobiology and therapeutic implications of transfusion-related acute lung injury, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021.
13.
Scheim (B) et al., Sialylated Glycan Bindings from SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Blood and Endothelial Cells Govern the Severe Morbidities of COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242317039.
14.
Yemeke et al., Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of medical products in Zimbabwe: a qualitative study based on key informant interviews with health system stakeholders, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068923.
15.
Kory, P., The Global War on Ivermectin, International Covid Summit III, European Parliament, Brussels, covid19criticalcare.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/GLOBAL-WAR-ON-IVERMECTIN-PARLIAMENT.pdf.
16.
Babalola et al., The Place of Ivermectin in the Management of Covid-19: State of the Evidence, Medical Research Archives, doi:10.18103/mra.v11i4.3778.
17.
Loo et al., Recent Advances in Inhaled Nanoformulations of Vaccines and Therapeutics Targeting Respiratory Viral Infections, Pharmaceutical Research, doi:10.1007/s11095-023-03520-1.
18.
Scheim (C), D., From Cold to Killer: How SARS-CoV-2 Evolved without Hemagglutinin Esterase to Agglutinate and Then Clot Blood Cells, Center for Open Science, doi:10.31219/osf.io/sgdj2.
19.
Kory (B), P., The Criminal Censorship of Ivermectin's Efficacy By The High-Impact Medical Journals - Part 1, Pierre Kory’s Medical Musings, pierrekory.substack.com/p/the-criminal-censorship-of-ivermectins.
20.
Al-kuraishy et al., Central effects of Ivermectin in alleviation of Covid-19-induced dysautonomia, Current Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1389450123666220810102406.
21.
Schwartz, E., Does ivermectin have a place in the treatment of mild Covid-19?, New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2022.100989.
22.
Marques et al., Ivermectin as a possible treatment for COVID-19: a review of the 2022 protocols, Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.258325.
23.
Semiz, S., SIT1 transporter as a potential novel target in treatment of COVID-19, Biomolecular Concepts, doi:10.1515/bmc-2021-0017.
24.
Zaidi et al., The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2—an extensive review, The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6.
25.
Behl et al., CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target, Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072.
26.
Low et al., Repositioning Ivermectin for Covid-19 treatment: Molecular mechanisms of action against SARS-CoV-2 replication, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166294.
27.
Fordham et al., The uses and abuses of systematic reviews, OSF Preprints, doi:10.31219/osf.io/mp4f2.
28.
Kow et al., Pitfalls in Reporting Sample Size Calculation Across Randomized Controlled Trials Involving Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001441.
29.
Santin et al., Ivermectin: a multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honored distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19, New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100924.
30.
Adegboro et al., A review of the anti-viral effects of ivermectin, African Journal of Clinical and Experimental Microbiology, doi:10.4314/ajcem.v22i3.2.
31.
Turkia, M., A Continuation of a Timeline of Ivermectin-Related Events in the COVID-19 Pandemic [June 30, 2021], ResearchGate, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.16973.36326.
32.
Jagiasi et al., Variation in therapeutic strategies for the management of severe COVID-19 in India- A nationwide cross-sectional survey, The International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14574.
33.
Lind et al., Increase in Outpatient Ivermectin Dispensing in the US During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Analysis, Journal of General Internal Medicine, doi:10.1007/s11606-021-06948-6.
34.
Wang et al., Minimum manufacturing costs, national prices and estimated global availability of new repurposed therapies for COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.06.01.21258147.
35.
Kory (C) et al., Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001377.
36.
DiNicolantonio et al., Anti-inflammatory activity of ivermectin in late-stage COVID-19 may reflect activation of systemic glycine receptors, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2021-001655.
37.
Turkia (B), M., A timeline of ivermectin-related events in the COVID-19 pandemic, Research Gate, www.researchgate.net/publication/350610718_A_Timeline_of_Ivermectin-Related_Events_in_the_COVID-19_Pandemic_April_3_2021.
38.
Wehbe et al., Repurposing Ivermectin for COVID-19: Molecular Aspects and Therapeutic Possibilities, Front. Immunol., doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586.
39.
Yagisawa (B) et al., Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, 74-1, Mar 2021, jja-contents.wdc-jp.com/pdf/JJA74/74-1-open/74-1_44-95.pdf.
40.
Jans et al., The broad spectrum host-directed agent ivermectin as an antiviral for SARS-CoV-2 ?, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.042.
41.
Kory (D) et al., Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.643369.
42.
Formiga et al., Ivermectin: an award-winning drug with expected antiviral activity against COVID-19, J. Control Release, doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009.
43.
Scheim (D), D., Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-Threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-Mediated Vascular Occlusion, SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3636557.
44.
Turkia (C), M., FLCCC Alliance MATH+ ascorbic acid and I-MASK+ ivermectin protocols for COVID-19 — a brief review, ResearchGate, www.researchgate.net/profile/Mika_Turkia/publication/345694745_FLCCC_Alliance_MATH_ascorbic_acid_and_I-MASK_ivermectin_protocols_for_COVID-19_-_A_Brief_Review/links/5fab010f4585150781078260/FLCCC-Alliance-MATH-ascorbic-acid-and-I-MASK-ivermectin-protocols-for-COVID-19-A-Brief-Review.pdf.
45.
Jans (B) et al., Ivermectin as a Broad-Spectrum Host-Directed Antiviral: The Real Deal?, Cells 2020, 9:9, 2100, doi:10.3390/cells9092100.
46.
Elkholy et al., Ivermectin: A Closer Look at a Potential Remedy, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.10378.
47.
DiNicolantonio (B) et al., Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350.
48.
Vora et al., White paper on Ivermectin as a potential therapy for COVID-19, Indian Journal of Tuberculosis, doi:10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.07.031.
Zaidi et al., 21 Dec 2021, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2—an extensive review
The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6
Considering the urgency of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, detection of new mutant strains and potential re-emergence of novel coronaviruses, repurposing of drugs such as ivermectin could be worthy of attention. This review article aims to discuss the probable mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2 by summarizing the available literature over the years. A schematic of the key cellular and biomolecular interactions between ivermectin, host cell, and SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 pathogenesis and prevention of complications has been proposed.
Conflict of interest The authors declare no competing interests. Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Haverich, Welte et al., Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2015432
Andersson, Ottestad, Tracey, Extracellular HMGB1: a therapeutic target in severe pulmonary inflammation including COVID-19?, Mol Med, doi:10.1186/s10020-020-00172-4pmid
Arshad, Pertinez, Box, Prioritization of anti-SARS-Cov-2 drug repurposing opportunities based on plasma and target site concentrations derived from their established human pharmacokinetics, Clin Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1002/cpt.1909
Bennett, Zhao, Bosard, Imperiale, Role of a nuclear localization signal on the minor capsid proteins VP2 and VP3 in BKPyV nuclear entry, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2014.10.013.
Bharadwaj, Kasembeli, Robinson, Tweardy, Targeting janus kinases and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 to treat inflammation, fibrosis, and cancer: rationale, progress, and caution, Pharm Rev
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDAapproved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787
Canga, The pharmacokinetics and interactions of ivermectin in humans-a mini-review, AAPS J, doi:10.1208/s12248-007-9000-9.
Chandler, Serious neurological adverse events after ivermectin-do they occur beyond the indication of onchocerciasis?, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.17-0042.
Chen, Zheng, Liu, Yan, Xu et al., Plasma CRP level is positively associated with the severity of COVID-19, Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob
Choudhury, Das, Patra, Bhattacharya, Ghosh et al., Exploring the binding efficacy of ivermectin against the key proteins of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: an in silico approach, Future Virol, doi:10.2217/fvl-2020-0342
Ci, Li, Yu, Avermectin exerts anti-inflammatory effect by downregulating the nuclear transcription factor kappa-B and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation pathway, Fundam Clin Pharm
Crump, Ōmura, Ivermectin, 'wonder drug' from Japan: the human use perspective, Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci, doi:10.2183/pjab.87.13.
Diao, Wang, Tan, Chen, Liu et al., Reduction and functional exhaustion of T cells in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Front Immunol
Dominguez-Gomez, Chavez-Blanco, Medina-Franco, Saldivar-Gonzalez, Flores-Torrontegui et al., Ivermectin as an inhibitor of cancer stem-like cells, Mol Med Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.8231.
Dou, Chen, Wang, Yuan, Lei et al., Ivermectin induces cytostatic autophagy by blocking the PAK1/Akt axis in breast cancer, Cancer Res
Dueñas-González, Juárez-Rodríguez, Ivermectin: potential repurposing of a versatile antiparasitic as a novel anticancer, doi:10.5772/intechopen.99813
Edwards, Dingsdale, Helsby, Orme, Breckenridge, The relative systemic availability of ivermectin after administration as capsule, tablet, and oral solution, Eur J Clin Pharm
Eweas, Alhossary, As, Molecular docking reveals ivermectin and remdesivir as potential repurposed drugs against SARS-CoV-2, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.592908
Freedman, Chapter 4-Ionophores in planar lipid bilayers
Frieman, Yount, Heise, Kopecky-Bromberg, Palese et al., Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus ORF6 antagonizes STAT1 function by sequestering nuclear import factors on the rough endoplasmic reticulum/golgi membrane, J Virol
Fulcher, Jans, Regulation of nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of viral proteins; an integral role in pathogenesis?, Biochem Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res
Gharebaghi, Heidary, COVID-19 and Iran: swimming with hands tied!, Swiss Med Wkly, doi:10.4414/smw.2020.20242.
Hadjadj, Yatim, Barnabei, Corneau, Boussier et al., Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients, Science
Heidary, Gharebaghi, Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen, J Antibiot, doi:10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z.
Jiang, Wang, Sun, Wu, Ivermectin reverses the drug resistance in cancer cells through EGFR/ERK/Akt/NF-κB pathway, J Exp Clin Cancer Res, doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1251-7
Juarez, Schcolnik-Cabrera, Dueñas-Gonzalez, The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug, Am J Cancer Res
Kim, Choi, Kim, Lee, The PAK1-Stat3 signaling pathway activates IL-6 gene transcription and human breast cancer stem cell formation, Cancers
Kircik, Rosso, Layton, Schauber, Over 25 years of clinical experience with ivermectin: an overview of safety for an increasing number of indications, J Drugs Dermatol
Klotz, Ogbuokiri, Okonkwo, Ivermectin binds avidly to plasma proteins, Eur J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/BF00316107.
Konno, Kimura, Uriu, Fukushi, Irie et al., SARS-CoV-2 ORF3b is a potent interferon antagonist whose activity is further increased by a naturally occurring elongation variant, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108185
Kumar, Jeyaraman, Jain, Anudeep, A wonder drug in the arsenal against COVID-19: medication evidence from ivermectin, J Adv Med Med Res
Layhadi, Turner, Crossman, Fountain, ATP evokes Ca 2+ responses and CXCL5 secretion via P2X4 receptor activation in human monocyte-derived macrophages, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1700965.
Lehrer, Rheinstein, Ivermectin docks to the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain attached to ACE2, Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.12134
Liu, Zhang, Joo, Sun, NF-κB signaling in inflammation, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
Ma, Wu, Shaw, Gao, Wang et al., Structural basis and functional analysis of the SARS coronavirus nsp14-nsp10 complex, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Martin, Robertson, Choudhary, Ivermectin: an anthelmintic, an insecticide, and much more, Trends Parasitol, doi:10.1016/j.pt.2020.10.005
Matsuyama, Kubli, Yoshinaga, An aberrant STAT pathway is central to COVID-19, Cell Death Differ, doi:10.1038/s41418-020-00633-7.
Melo, Lazarini, Larrous, Attenuation of clinical and immunological outcomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection by ivermectin, EMBO Mol Med, doi:10.15252/emmm.202114122.
Mielech, Kilianski, Baez-Santos, Mesecar, Baker, MERS-CoV papain-like protease has deISGylating and deubiquitinating activities, Virology
Mody, Ho, Wills, Mawri, Lawson et al., Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents, Commun Biol, doi:10.1038/s42003-020-01577-x
Nagai, Satomi, Abiru, Miyamoto, Nagasawa et al., Antihypertrophic effects of small molecules that maintain mitochondrial ATP levels under hypoxia, EBio-Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.09.022
Novac, Challenges and opportunities of drug repositioning, Trends Pharm Sci
Park, Iwasaki, Type I. and type III interferons-induction, signaling, evasion, and application to combat COVID-19, Cell Host Microbe
Priel, Silberberg, Mechanism of ivermectin facilitation of human P2X4 receptor channels, J Gen Physiol, doi:10.1085/jgp.200308986
Principletrial, Join the PRINCIPLE
Raza, Shahin, Zhai, Ivermectin inhibits bovine herpesvirus 1 DNA polymerase nuclear import and interferes with viral replication, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8030409
Rizzo, Ivermectin, antiviral properties and COVID-19: a possible new mechanism of action, Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharm, doi:10.1007/s00210-020-01902-5.
Scheim, Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-Threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-Mediated Vascular Occlusion
Sekimoto, Imamoto, Nakajima, Hirano, Yoneda, Extracellular signal-dependent nuclear import of Stat1 is mediated by nuclear pore-targeting complex formation with NPI-1, but not Rch1, EMBO J
Seth, Mas, Conod, Mueller, Siems et al., LongLasting WNT-TCF response blocking and epigenetic modifying activities of withanolide f in human cancer cells, PLoS ONE
Stokes, Layhadi, Bibic, Dhuna, Fountain, P2X4 receptor function in the nervous system and current breakthroughs in pharmacology, Front Pharm, doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00291.
Swargiary, Ivermectin as a promising RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor and a therapeutic drug against SARS-CoV2: evidence from in silico studies, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-73308/v1
V'kovski, Kratzel, Steiner, Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6.
Verrest, Dorlo, Lack of clinical pharmacokinetic studies to optimize the treatment of neglected tropical diseases: a systematic review, Clin Pharmacokinet
Wagstaff, Rawlinson, Hearps, Jans, An AlphaScreen(R)-based assay for high-throughput screening for specific inhibitors of nuclear import, J Biomol Screen, doi:10.1177/1087057110390360.
Wang, Zhang, Wu, Niu, Song et al., Structural and functional basis of SARS-CoV-2 entry by using human ACE2, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.045.
Wu, Fossali, Hypoalbuminemia in COVID-19: assessing the hypothesis for underlying pulmonary capillary leakage, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13208
Wu, Peng, Huang, Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2020.02.001
Xydakis, Dehgani-Mobaraki, Holbrook, Smell and taste dysfunction in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30293-0
Yagisawa, Foster, Hanaki, Ōmura, Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19, Jpn J Antibiotics
Yan, Ci, Chen, Anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin in mouse model of allergic asthma, Inflamm Res
Yang, Atkinson, Wang, Lee, Bogoyevitch et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer, Antivir Res
Yang, Chu, Hou, Chai, Shuai et al., Attenuated interferon and pro-inflammatory response in SARSCoV-2-infected human dendritic cells is associated with viral antagonism of STAT1 phosphorylation, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa356
Zaidi, Dawoodi, Pirro, Monti, Mobaraki, Key role of annexin A2 and plasmin in COVID-19 pathophysiology, clinical presentation and outcomes-a review, Ital J Prev, Diagn Ther Med, doi:10.30459/2020-24
Zhang, Song, Ci, Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice, Inflamm Res, doi:10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8
Zheng, Ma, Zhang, COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system, Nat Rev Cardiol, doi:10.1038/s41569-020-0360-5.
Zheng, Peng, Xu, Zhao, Liu et al., Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021
Zheng, Yu, Feng, Lou, Zou, Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARSCoV-2 in Zhejiang province, China, January-March 2020: retrospective cohort study, BMJ
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6",
"ISSN": [
"0021-8820",
"1881-1469"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6",
"alternative-id": [
"491"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "20 October 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 2,
"value": "9 November 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 3,
"value": "10 November 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 4,
"value": "21 December 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Compliance with ethical standards",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6510-6365",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zaidi",
"given": "Asiya Kamber",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8339-1868",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dehgani-Mobaraki",
"given": "Puya",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"The Journal of Antibiotics"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-21T04:29:21Z",
"timestamp": 1640060961000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-24T11:04:36Z",
"timestamp": 1643022276000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-25T20:30:42Z",
"timestamp": 1648240242587
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0021-8820"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1881-1469"
}
],
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1640044800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1640044800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41429-021-00491-6.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41429-021-00491-6",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41429-021-00491-6.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "60-71",
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
21
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.4414/smw.2020.20242.",
"author": "R Gharebaghi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "w20242",
"journal-title": "Swiss Med Wkly",
"key": "491_CR1",
"unstructured": "Gharebaghi R, Heidary F. COVID-19 and Iran: swimming with hands tied! Swiss Med Wkly. 2020;150:w20242. https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2020.20242.",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2183/pjab.87.13.",
"author": "A Crump",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci",
"key": "491_CR2",
"unstructured": "Crump A, Ōmura S. Ivermectin, ‘wonder drug’ from Japan: the human use perspective. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2011;87:13–28. https://doi.org/10.2183/pjab.87.13.",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"author": "LH Kircik",
"first-page": "325",
"journal-title": "J Drugs Dermatol",
"key": "491_CR3",
"unstructured": "Kircik LH, Del Rosso JQ, Layton AM, Schauber J. Over 25 years of clinical experience with ivermectin: an overview of safety for an increasing number of indications. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:325–32.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1208/s12248-007-9000-9.",
"author": "A Gonzalez Canga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "42",
"journal-title": "AAPS J",
"key": "491_CR4",
"unstructured": "Gonzalez Canga A, et al. The pharmacokinetics and interactions of ivermectin in humans–a mini-review. AAPS J. 2008;10:42–6. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-007-9000-9.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.9734/jammr/2020/v32i1030512",
"author": "BS Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "30",
"journal-title": "J Adv Med Med Res.",
"key": "491_CR5",
"unstructured": "Kumar BS, Jeyaraman M, Jain R, Anudeep TC. A wonder drug in the arsenal against COVID—19: medication evidence from ivermectin. J Adv Med Med Res. 2020;32:30–7.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tips.2013.03.004",
"author": "N Novac",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "267",
"journal-title": "Trends Pharm Sci",
"key": "491_CR6",
"unstructured": "Novac N. Challenges and opportunities of drug repositioning. Trends Pharm Sci. 2013;34:267–72.",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "491_CR7",
"unstructured": "ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Clinicaltrials.gov. 2021 [cited 10 November 2021]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/home Home - ClinicalTrials.gov."
},
{
"key": "491_CR8",
"unstructured": "Activ6study.org. Activ-6 study. Activ6study.org; 2021. https://activ6study.org/."
},
{
"key": "491_CR9",
"unstructured": "Principletrial.org. Join the PRINCIPLE Trial. Principletrial.org.; 2021. https://www.principletrial.org/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF00637608",
"author": "G Edwards",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "681",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Pharm",
"key": "491_CR10",
"unstructured": "Edwards G, Dingsdale A, Helsby N, Orme ML, Breckenridge AM. The relative systemic availability of ivermectin after administration as capsule, tablet, and oral solution. Eur J Clin Pharm. 1988;35:681–4.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40262-016-0467-3",
"author": "L Verrest",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "583",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacokinet",
"key": "491_CR11",
"unstructured": "Verrest L, Dorlo TPC. Lack of clinical pharmacokinetic studies to optimize the treatment of neglected tropical diseases: a systematic review. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017;56:583–606.",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF00316107.",
"author": "U Klotz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "607",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "491_CR12",
"unstructured": "Klotz U, Ogbuokiri JE, Okonkwo PO. Ivermectin binds avidly to plasma proteins. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1990;39:607–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00316107.",
"volume": "39",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13208",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR13",
"unstructured": "Wu MA, Fossali T, et al. Hypoalbuminemia in COVID-19: assessing the hypothesis for underlying pulmonary capillary leakage. J Intern Med. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.13208."
},
{
"key": "491_CR14",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Application for inclusion of ivermectin on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (EML) and Model List of Essential Medicines for Children (EMLc). World Health Organization; 2016."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pt.2020.10.005",
"author": "RJ Martin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "48",
"journal-title": "Trends Parasitol.",
"key": "491_CR15",
"unstructured": "Martin RJ, Robertson AP, Choudhary S. Ivermectin: an anthelmintic, an insecticide, and much more. Trends Parasitol. 2021;37:48–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2020.10.005.",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.17-0042.",
"author": "RE Chandler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "382",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "491_CR16",
"unstructured": "Chandler RE. Serious neurological adverse events after ivermectin-do they occur beyond the indication of onchocerciasis? Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;98:382–8. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.17-0042.",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.045.",
"author": "Q Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "491_CR17",
"unstructured": "Wang Q, Zhang Y, Wu L, Niu S, Song C, Zhang Z, et al. Structural and functional basis of SARS-CoV-2 entry by using human ACE2. Cell. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.045.",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.02.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR18",
"unstructured": "Wu A, Peng Y, Huang B, et al. Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China. Cell Host Microbe. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2020.02.001."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2013.11.040",
"author": "AM Mielech",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "64",
"journal-title": "Virology.",
"key": "491_CR19",
"unstructured": "Mielech AM, Kilianski A, Baez-Santos YM, Mesecar AD, Baker SC. MERS-CoV papain-like protease has deISGylating and deubiquitinating activities. Virology. 2014;450–451:64–70.",
"volume": "450–451",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "491_CR20",
"unstructured": "Lehigh.edu. BioS 353. Lehigh.edu; 2021. https://www.lehigh.edu/~jas0/V14.html."
},
{
"DOI": "10.21873/invivo.12134",
"author": "S Lehrer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3023",
"journal-title": "In Vivo.",
"key": "491_CR21",
"unstructured": "Lehrer S, Rheinstein PH. Ivermectin docks to the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain attached to ACE2. In Vivo. 2020;34:3023–6. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.12134.",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2020.592908",
"author": "AF Eweas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "592908.",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol.",
"key": "491_CR22",
"unstructured": "Eweas AF, Alhossary AA, Abdel-Moneim AS. Molecular docking reveals ivermectin and remdesivir as potential repurposed drugs against SARS-CoV-2. Front Microbiol. 2021;11:592908. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.592908.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl-2020-0342",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR23",
"unstructured": "Choudhury A, Das NC, Patra R, Bhattacharya M, Ghosh P, Patra BC, et al. Exploring the binding efficacy of ivermectin against the key proteins of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: an in silico approach. Future Virol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.2217/fvl-2020-0342."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.03.019",
"author": "A Fulcher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2176",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.",
"key": "491_CR24",
"unstructured": "Fulcher A, Jans DA. Regulation of nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of viral proteins; an integral role in pathogenesis? Biochem Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2011;1813:2176–90.",
"volume": "1813",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760",
"author": "SNY Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104760",
"journal-title": "Antivir Res.",
"key": "491_CR25",
"unstructured": "Yang SNY, Atkinson SC, Wang C, Lee A, Bogoyevitch MA, Borg NA, et al. The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer. Antivir Res. 2020;177:104760.",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-387738-3.00004-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "491_CR26",
"unstructured": "Freedman JC. Chapter 4—Ionophores in planar lipid bilayers. In: Sperelakis N, editor. Cell physiology sourcebook. Essentials of membrane biophysics, 4th ed. London, UK; Waltham, MA, USA; San Diego, CA, USA: Academic Press; 2012. p. 61–6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00210-020-01902-5.",
"author": "E Rizzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1153",
"journal-title": "Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharm",
"key": "491_CR27",
"unstructured": "Rizzo E. Ivermectin, antiviral properties and COVID-19: a possible new mechanism of action. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharm. 2020;393:1153–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01902-5.",
"volume": "393",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5772/intechopen.99813",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR28",
"unstructured": "Dueñas-González A, Juárez-Rodríguez M. Ivermectin: potential repurposing of a versatile antiparasitic as a novel anticancer. In: Raymond C, Dalgleish A, editors. Repurposed drugs for cancer. IntechOpen; 2021. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.99813."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2017.8231.",
"author": "G Dominguez‑Gomez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3397",
"journal-title": "Mol Med Rep",
"key": "491_CR29",
"unstructured": "Dominguez‑Gomez G, Chavez‑Blanco A, Medina‑Franco JL, Saldivar‑Gonzalez F, Flores‑Torrontegui Y, Juarez M, et al. Ivermectin as an inhibitor of cancer stem‑like cells. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17:3397–403. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.8231.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z.",
"author": "F Heidary",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "593",
"journal-title": "J Antibiot",
"key": "491_CR30",
"unstructured": "Heidary F, Gharebaghi R. Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen. J Antibiot. 2020;73:593–602. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1087057110390360.",
"author": "KM Wagstaff",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "192",
"journal-title": "J Biomol Screen",
"key": "491_CR31",
"unstructured": "Wagstaff KM, Rawlinson SM, Hearps AC, Jans DA. An AlphaScreen(R)-based assay for high-throughput screening for specific inhibitors of nuclear import. J Biomol Screen. 2011;16:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087057110390360.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2014.10.013.",
"author": "SM Bennett",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "491_CR32",
"unstructured": "Bennett SM, Zhao L, Bosard C, Imperiale MJ. Role of a nuclear localization signal on the minor capsid proteins VP2 and VP3 in BKPyV nuclear entry. Virology. 2015;474:110–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2014.10.013.",
"volume": "474",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms8030409",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR33",
"unstructured": "Raza S, Shahin F, Zhai W, et al. Ivermectin inhibits bovine herpesvirus 1 DNA polymerase nuclear import and interferes with viral replication. Microorganisms. 2020;8. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8030409."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR34",
"unstructured": "Caly L, Druce JD, Catton MG, Jans DA, Wagstaff KM. The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antiviral Res. 2020;104787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.1909",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR35",
"unstructured": "Arshad U, Pertinez H, Box H, et al. Prioritization of anti-SARS-Cov-2 drug repurposing opportunities based on plasma and target site concentrations derived from their established human pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.1909."
},
{
"key": "491_CR36",
"unstructured": "Yagisawa M, Foster PJ, Hanaki H, Ōmura S. Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19. Jpn J Antibiotics. 2021;44:74-1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-73308/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR37",
"unstructured": "Swargiary A. Ivermectin as a promising RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor and a therapeutic drug against SARS-CoV2: evidence from in silico studies. Research Square; 2020. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-73308/v1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6.",
"author": "P V’kovski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "491_CR38",
"unstructured": "V’kovski P, Kratzel A, Steiner S, et al. Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19:155–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1508686112",
"author": "Y Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9436",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "491_CR39",
"unstructured": "Ma Y, Wu L, Shaw N, Gao Y, Wang J, Sun Y, et al. Structural basis and functional analysis of the SARS coronavirus nsp14-nsp10 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:9436–41.",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-020-01577-x",
"author": "V Mody",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "93",
"journal-title": "Commun Biol",
"key": "491_CR40",
"unstructured": "Mody V, Ho J, Wills S, Mawri A, Lawson L, Ebert MCCJC, et al. Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents. Commun Biol. 2021;4:93. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-01577-x.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/emboj/16.23.7067",
"author": "T Sekimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7067",
"journal-title": "EMBO J",
"key": "491_CR41",
"unstructured": "Sekimoto T, Imamoto N, Nakajima K, Hirano T, Yoneda Y. Extracellular signal-dependent nuclear import of Stat1 is mediated by nuclear pore-targeting complex formation with NPI-1, but not Rch1. EMBO J. 1997;16:7067–77.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108185",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR42",
"unstructured": "Konno Y, Kimura I, Uriu K, Fukushi M, Irie T, Koyanagi Y, et al. SARS-CoV-2 ORF3b is a potent interferon antagonist whose activity is further increased by a naturally occurring elongation variant. Cell Rep. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108185."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa356",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR43",
"unstructured": "Yang D, Chu H, Hou Y, Chai Y, Shuai H, Lee AC-Y, et al. Attenuated interferon and pro-inflammatory response in SARSCoV-2-infected human dendritic cells is associated with viral antagonism of STAT1 phosphorylation. J Infect Dis. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa356."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-020-00633-7.",
"author": "T Matsuyama",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3209",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ",
"key": "491_CR44",
"unstructured": "Matsuyama T, Kubli SP, Yoshinaga SK, et al. An aberrant STAT pathway is central to COVID-19. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27:3209–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00633-7.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0168170",
"author": "C Seth",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0168170",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "491_CR45",
"unstructured": "Seth C, Mas C, Conod A, Mueller J, Siems K, Kuciak M, et al. LongLasting WNT-TCF response blocking and epigenetic modifying activities of withanolide f in human cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0168170.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.008",
"author": "A Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "870",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "491_CR46",
"unstructured": "Park A, Iwasaki A, Type I. and type III interferons—induction, signaling, evasion, and application to combat COVID-19. Cell Host Microbe. 2020;27:870–8.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8",
"author": "X Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "524",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Res",
"key": "491_CR47",
"unstructured": "Zhang X, Song Y, Ci X, et al. Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice. Inflamm Res. 2008;57:524–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8.",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23",
"author": "T Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "17023",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "491_CR48",
"unstructured": "Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun S-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017;2:17023 https://doi.org/10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23.",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13046-019-1251-7",
"author": "L Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "J Exp Clin Cancer Res",
"key": "491_CR49",
"unstructured": "Jiang L, Wang P, Sun YJ, Wu YJ. Ivermectin reverses the drug resistance in cancer cells through EGFR/ERK/Akt/NF-κB pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:265 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1251-7.",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1443",
"author": "S Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m1443",
"journal-title": "BMJ.",
"key": "491_CR50",
"unstructured": "Zheng S, Fan J, Yu F, Feng B, Lou B, Zou Q, et al. Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARSCoV-2 in Zhejiang province, China, January-March 2020: retrospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1443.",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015432",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR51",
"unstructured": "Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, Haverich A, Welte T, Laenger F, et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2015432."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR52",
"unstructured": "Zheng Z, Peng F, Xu B, Zhao J, Liu H, Peng J, et al. Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Infect. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.00827",
"author": "B Diao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "827",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "491_CR53",
"unstructured": "Diao B, Wang C, Tan Y, Chen X, Liu Y, Ning L, et al. Reduction and functional exhaustion of T cells in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Front Immunol. 2020;11:827.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc6027",
"author": "J Hadjadj",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "718",
"journal-title": "Science.",
"key": "491_CR54",
"unstructured": "Hadjadj J, Yatim N, Barnabei L, Corneau A, Boussier J, Smith N, et al. Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Science. 2020;369:718–24.",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12941-020-00362-2",
"author": "W Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob.",
"key": "491_CR55",
"unstructured": "Chen W, Zheng KI, Liu S, Yan Z, Xu C, Qiao Z. Plasma CRP level is positively associated with the severity of COVID-19. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2020;19:18.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/pr.119.018440",
"author": "U Bharadwaj",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "486",
"journal-title": "Pharm Rev",
"key": "491_CR56",
"unstructured": "Bharadwaj U, Kasembeli MM, Robinson P, Tweardy DJ. Targeting janus kinases and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 to treat inflammation, fibrosis, and cancer: rationale, progress, and caution. Pharm Rev. 2020;72:486–526.",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01012-07",
"author": "M Frieman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9812",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "491_CR57",
"unstructured": "Frieman M, Yount B, Heise M, Kopecky-Bromberg SA, Palese P, Baric RS. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus ORF6 antagonizes STAT1 function by sequestering nuclear import factors on the rough endoplasmic reticulum/golgi membrane. J Virol. 2007;81:9812–24.",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cancers11101527",
"author": "J-H Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1527",
"journal-title": "Cancers.",
"key": "491_CR58",
"unstructured": "Kim J-H, Choi HS, Kim S-L, Lee D-S. The PAK1-Stat3 signaling pathway activates IL-6 gene transcription and human breast cancer stem cell formation. Cancers. 2019;11:1527.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2887",
"author": "Q Dou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4457",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res",
"key": "491_CR59",
"unstructured": "Dou Q, Chen H-N, Wang K, Yuan K, Lei Y, Li K, et al. Ivermectin induces cytostatic autophagy by blocking the PAK1/Akt axis in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2016;76:4457–69.",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/emmm.202114122.",
"author": "GD De Melo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e14122",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol Med",
"key": "491_CR60",
"unstructured": "De Melo GD, Lazarini F, Larrous F, et al. Attenuation of clinical and immunological outcomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection by ivermectin. EMBO Mol Med. 2021;13:e14122. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.202114122.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1085/jgp.200308986",
"author": "A Priel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "J Gen Physiol.",
"key": "491_CR61",
"unstructured": "Priel A, Silberberg SD. Mechanism of ivermectin facilitation of human P2X4 receptor channels. J Gen Physiol. 2004;123:281–93. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.200308986.",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2017.00291.",
"author": "L Stokes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "291",
"journal-title": "Front Pharm",
"key": "491_CR62",
"unstructured": "Stokes L, Layhadi JA, Bibic L, Dhuna K, Fountain SJ. P2X4 receptor function in the nervous system and current breakthroughs in pharmacology. Front Pharm. 2017;8:291. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00291.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1700965.",
"author": "JA Layhadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1159",
"journal-title": "J Immunol.",
"key": "491_CR63",
"unstructured": "Layhadi JA, Turner J, Crossman D, Fountain SJ. ATP evokes Ca2+ responses and CXCL5 secretion via P2X4 receptor activation in human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Immunol. 2018;200:1159. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1700965.",
"volume": "200",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s10020-020-00172-4pmid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR64",
"unstructured": "Andersson U, Ottestad W, Tracey KJ. Extracellular HMGB1: a therapeutic target in severe pulmonary inflammation including COVID-19? Mol Med. 2020;26:42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-020-00172-4pmid."
},
{
"author": "M Juarez",
"first-page": "317",
"journal-title": "Am J Cancer Res.",
"key": "491_CR65",
"unstructured": "Juarez M, Schcolnik-Cabrera A, Dueñas-Gonzalez A. The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug. Am J Cancer Res. 2018;8:317–31.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30293-0",
"author": "MS Xydakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1015",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis.",
"key": "491_CR66",
"unstructured": "Xydakis MS, Dehgani-Mobaraki P, Holbrook EH, et al. Smell and taste dysfunction in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20:1015–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30293-0.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1472-8206.2009.00684.x",
"author": "X Ci",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "449",
"journal-title": "Fundam Clin Pharm",
"key": "491_CR67",
"unstructured": "Ci X, Li H, Yu Q. Avermectin exerts anti-inflammatory effect by downregulating the nuclear transcription factor kappa-B and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation pathway. Fundam Clin Pharm. 2009;23:449–55.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00011-011-0307-8",
"author": "S Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "589",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Res",
"key": "491_CR68",
"unstructured": "Yan S, Ci X, Chen N. Anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin in mouse model of allergic asthma. Inflamm Res. 2011;60:589–96.",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.30459/2020-24",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "491_CR69",
"unstructured": "Zaidi AK, Dawoodi S, Pirro M, Monti M, Mobaraki PD. Key role of annexin A2 and plasmin in COVID-19 pathophysiology, clinical presentation and outcomes—a review. Ital J Prev, Diagn Ther Med. 2020;3. https://doi.org/10.30459/2020-24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3636557",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "491_CR70",
"unstructured": "Scheim DE. Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-Threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-Mediated Vascular Occlusion (June 26, 2020). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3636557."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41569-020-0360-5.",
"author": "YY Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "259",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Cardiol",
"key": "491_CR71",
"unstructured": "Zheng YY, Ma YT, Zhang JY, et al. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17:259–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-020-0360-5.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.09.022",
"author": "H Nagai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "147",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine.",
"key": "491_CR72",
"unstructured": "Nagai H, Satomi T, Abiru A, Miyamoto K, Nagasawa K, Maruyama M, et al. Antihypertrophic effects of small molecules that maintain mitochondrial ATP levels under hypoxia. EBioMedicine. 2017;24:147–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.09.022.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2017"
}
],
"reference-count": 72,
"references-count": 72,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"J Antibiot"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Drug Discovery",
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2—an extensive review"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "75"
}