Ivermectin and COVID-19: A report in Antiviral Research, widespread interest, an FDA warning, two letters to the editor and the authors' responses
et al., Antiviral Res., doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104805, Apr 2020
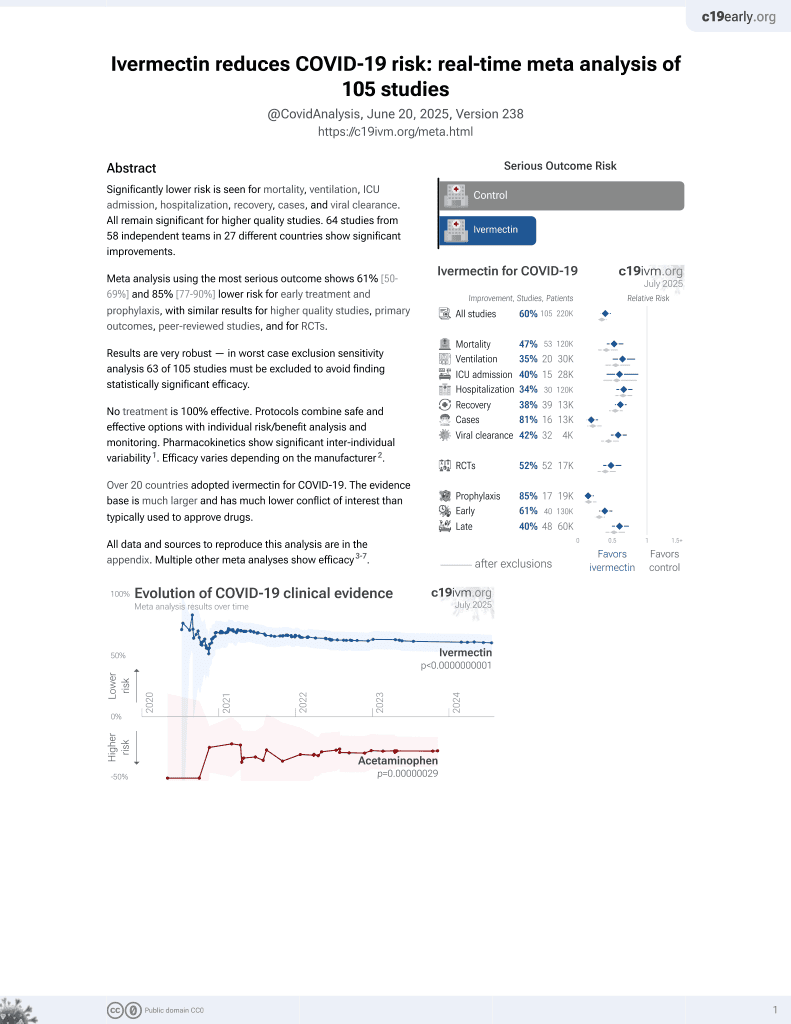
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Responses to Caly et al., and the author's reply. The original authors note that "ivermectin's key direct target in mammalian cells is a not a viral component, but a host protein important in intracellular transport; the fact that it is a host-directed agent (HDA) is almost certainly the basis of its broad-spectrum activity against a number of different RNA viruses in vitro. The way a HDA can reduce viral load is by inhibiting a key cellular process that the virus hijacks to enhance infection by suppressing the host antiviral response. Reducing viral load by even a modest amount by using a HDA at low dose early in infection can be the key to enabling the body's immune system to begin to mount the full antiviral response before the infection takes control."
1.
Reich, S., Methodological Analysis of Bias Risks in Adaptive Multi-Arm Platform Trials: A Case-Series from Three COVID-19 Studies, Center for Open Science, doi:10.31222/osf.io/h5kc8_v1.
2.
Mothae et al., SARS-CoV-2 host-pathogen interactome: insights into more players during pathogenesis, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2025.110607.
3.
Zhang et al., Rho-GTPases subfamily: cellular defectors orchestrating viral infection, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-025-00722-w.
4.
Saha et al., Inhaled Dry Powder of Antiviral Agents: A Promising Approach to Treating Respiratory Viral Pathogens, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17020252.
5.
Ulloa-Aguilar et al., The Nucleolus and Its Interactions with Viral Proteins Required for Successful Infection, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13181591.
6.
Enyeji et al., Effective Treatment of COVID-19 Infection with Repurposed Drugs: Case Reports, Viral Immunology, doi:10.1089/vim.2024.0034.
7.
Wimalawansa, S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
8.
Shouman et al., SARS-CoV-2-associated lymphopenia: possible mechanisms and the role of CD147, Cell Communication and Signaling, doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01718-3.
9.
Mehraeen et al., Treatments for Olfactory Dysfunction in COVID-19: A Systematic Review, International Archives of Otorhinolaryngology, doi:10.1055/s-0044-1786046.
10.
Scheim et al., Back to the Basics of SARS-CoV-2 Biochemistry: Microvascular Occlusive Glycan Bindings Govern Its Morbidities and Inform Therapeutic Responses, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16040647.
11.
Yagisawa et al., Global trends in clinical trials of ivermectin for COVID-19—Part 2, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.11553/antibiotics.77.1_45.
12.
Liu et al., Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and immune regulation: insights into pathobiology and therapeutic implications of transfusion-related acute lung injury, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021.
13.
Scheim (B) et al., Sialylated Glycan Bindings from SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Blood and Endothelial Cells Govern the Severe Morbidities of COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242317039.
14.
Yemeke et al., Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of medical products in Zimbabwe: a qualitative study based on key informant interviews with health system stakeholders, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068923.
15.
Kory, P., The Global War on Ivermectin, International Covid Summit III, European Parliament, Brussels, covid19criticalcare.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/GLOBAL-WAR-ON-IVERMECTIN-PARLIAMENT.pdf.
16.
Babalola et al., The Place of Ivermectin in the Management of Covid-19: State of the Evidence, Medical Research Archives, doi:10.18103/mra.v11i4.3778.
17.
Loo et al., Recent Advances in Inhaled Nanoformulations of Vaccines and Therapeutics Targeting Respiratory Viral Infections, Pharmaceutical Research, doi:10.1007/s11095-023-03520-1.
18.
Scheim (C), D., From Cold to Killer: How SARS-CoV-2 Evolved without Hemagglutinin Esterase to Agglutinate and Then Clot Blood Cells, Center for Open Science, doi:10.31219/osf.io/sgdj2.
19.
Kory (B), P., The Criminal Censorship of Ivermectin's Efficacy By The High-Impact Medical Journals - Part 1, Pierre Kory’s Medical Musings, pierrekory.substack.com/p/the-criminal-censorship-of-ivermectins.
20.
Al-kuraishy et al., Central effects of Ivermectin in alleviation of Covid-19-induced dysautonomia, Current Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1389450123666220810102406.
21.
Schwartz, E., Does ivermectin have a place in the treatment of mild Covid-19?, New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2022.100989.
22.
Marques et al., Ivermectin as a possible treatment for COVID-19: a review of the 2022 protocols, Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.258325.
23.
Semiz, S., SIT1 transporter as a potential novel target in treatment of COVID-19, Biomolecular Concepts, doi:10.1515/bmc-2021-0017.
24.
Zaidi et al., The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2—an extensive review, The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6.
25.
Behl et al., CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target, Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072.
26.
Low et al., Repositioning Ivermectin for Covid-19 treatment: Molecular mechanisms of action against SARS-CoV-2 replication, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166294.
27.
Fordham et al., The uses and abuses of systematic reviews, OSF Preprints, doi:10.31219/osf.io/mp4f2.
28.
Kow et al., Pitfalls in Reporting Sample Size Calculation Across Randomized Controlled Trials Involving Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001441.
29.
Santin et al., Ivermectin: a multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honored distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19, New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100924.
30.
Adegboro et al., A review of the anti-viral effects of ivermectin, African Journal of Clinical and Experimental Microbiology, doi:10.4314/ajcem.v22i3.2.
31.
Turkia, M., A Continuation of a Timeline of Ivermectin-Related Events in the COVID-19 Pandemic [June 30, 2021], ResearchGate, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.16973.36326.
32.
Jagiasi et al., Variation in therapeutic strategies for the management of severe COVID-19 in India- A nationwide cross-sectional survey, The International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14574.
33.
Lind et al., Increase in Outpatient Ivermectin Dispensing in the US During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Analysis, Journal of General Internal Medicine, doi:10.1007/s11606-021-06948-6.
34.
Wang et al., Minimum manufacturing costs, national prices and estimated global availability of new repurposed therapies for COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.06.01.21258147.
35.
Kory (C) et al., Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001377.
36.
DiNicolantonio et al., Anti-inflammatory activity of ivermectin in late-stage COVID-19 may reflect activation of systemic glycine receptors, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2021-001655.
37.
Turkia (B), M., A timeline of ivermectin-related events in the COVID-19 pandemic, Research Gate, www.researchgate.net/publication/350610718_A_Timeline_of_Ivermectin-Related_Events_in_the_COVID-19_Pandemic_April_3_2021.
38.
Wehbe et al., Repurposing Ivermectin for COVID-19: Molecular Aspects and Therapeutic Possibilities, Front. Immunol., doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586.
39.
Yagisawa (B) et al., Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, 74-1, Mar 2021, jja-contents.wdc-jp.com/pdf/JJA74/74-1-open/74-1_44-95.pdf.
40.
Jans et al., The broad spectrum host-directed agent ivermectin as an antiviral for SARS-CoV-2 ?, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.042.
41.
Kory (D) et al., Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.643369.
42.
Formiga et al., Ivermectin: an award-winning drug with expected antiviral activity against COVID-19, J. Control Release, doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.009.
43.
Scheim (D), D., Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-Threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-Mediated Vascular Occlusion, SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3636557.
44.
Turkia (C), M., FLCCC Alliance MATH+ ascorbic acid and I-MASK+ ivermectin protocols for COVID-19 — a brief review, ResearchGate, www.researchgate.net/profile/Mika_Turkia/publication/345694745_FLCCC_Alliance_MATH_ascorbic_acid_and_I-MASK_ivermectin_protocols_for_COVID-19_-_A_Brief_Review/links/5fab010f4585150781078260/FLCCC-Alliance-MATH-ascorbic-acid-and-I-MASK-ivermectin-protocols-for-COVID-19-A-Brief-Review.pdf.
45.
Jans (B) et al., Ivermectin as a Broad-Spectrum Host-Directed Antiviral: The Real Deal?, Cells 2020, 9:9, 2100, doi:10.3390/cells9092100.
46.
Elkholy et al., Ivermectin: A Closer Look at a Potential Remedy, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.10378.
47.
DiNicolantonio (B) et al., Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350.
48.
Vora et al., White paper on Ivermectin as a potential therapy for COVID-19, Indian Journal of Tuberculosis, doi:10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.07.031.
Bray et al., 21 Apr 2020, preprint, 5 authors.
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre -including this research content -immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active.
References
Baraka, Ivermectin distribution in the plasma and tissues of patients infected with Onchocerca volvulus, Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved Drug Ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787
Caly, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787
Crump, Omura, Ivermectin, 'wonder drug' from Japan: the human use perspective, Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci
Guzzo, Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects, J. Clin. Pharmacol
Jans, Kylie, Caly, Druce, Catton et al., The FDA-approved Drug Ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Merck, None, Mectizan NDA
Merck, Stromectol USPI
Navarro, Camprubí, Requena-Méndez, Buonfrate, Giorli et al., Safety of high-dose ivermectin: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Antimicrob. Chemother
Noël, Lima, Pharmacological aspects and clues for the rationale use of Chloroquine/Hydroxychloroquine facing the therapeutic challenges of COVID-19 pandemic, Lat. Am. J. Clin. Sci. Med. Technol
Pimenta, Silva, Noël, Ivermectin is a nonselective inhibitor of mammalian P-type ATPases, Naunyn-Schmied Arch. Pharmacol
Smit, Ochomo, Waterhouse, Kwambai, Abong'o et al., Pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of high dose ivermectin with Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine on mosquitocidal activity and QT-prolongation (IVERMAL), Clin. Pharmacol. Ther
Smit, Pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of high-dose ivermectin with dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine on mosquitocidal activity and QT-prolongation (IVERMAL), Clin. Pharmacol. Ther
Tay, Fraser, Chan, Moreland, Rathore et al., Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1-4 non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.2013Sep
Yang, Atkinson, Wang, Lee, Bogoyevitch et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer
Yao, In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin. Infect. Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104805",
"ISSN": [
"0166-3542"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104805",
"alternative-id": [
"S0166354220302199"
],
"article-number": "104805",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Ivermectin and COVID-19: A report in Antiviral Research, widespread interest, an FDA warning, two letters to the editor and the authors' responses"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Antiviral Research"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104805"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Published by Elsevier B.V."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bray",
"given": "Mike",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rayner",
"given": "Craig",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noël",
"given": "François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jans",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wagstaff",
"given": "Kylie",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Antiviral Research",
"container-title-short": "Antiviral Research",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
4,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2020-04-21T15:26:55Z",
"timestamp": 1587482815000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-13T00:44:34Z",
"timestamp": 1592009074000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-03T08:27:46Z",
"timestamp": 1714724866712
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 87,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1590969600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0166354220302199?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0166354220302199?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "104805",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0166354220302199"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ivermectin and COVID-19: A report in Antiviral Research, widespread interest, an FDA warning, two letters to the editor and the authors' responses",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "178"
}