Structural Deformability Induced in Proteins of Potential Interest Associated with COVID-19 by binding of Homologues present in Ivermectin: Comparative Study Based in Elastic Networks Models
et al., Journal of Molecular Liquids, doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284, Aug 2021
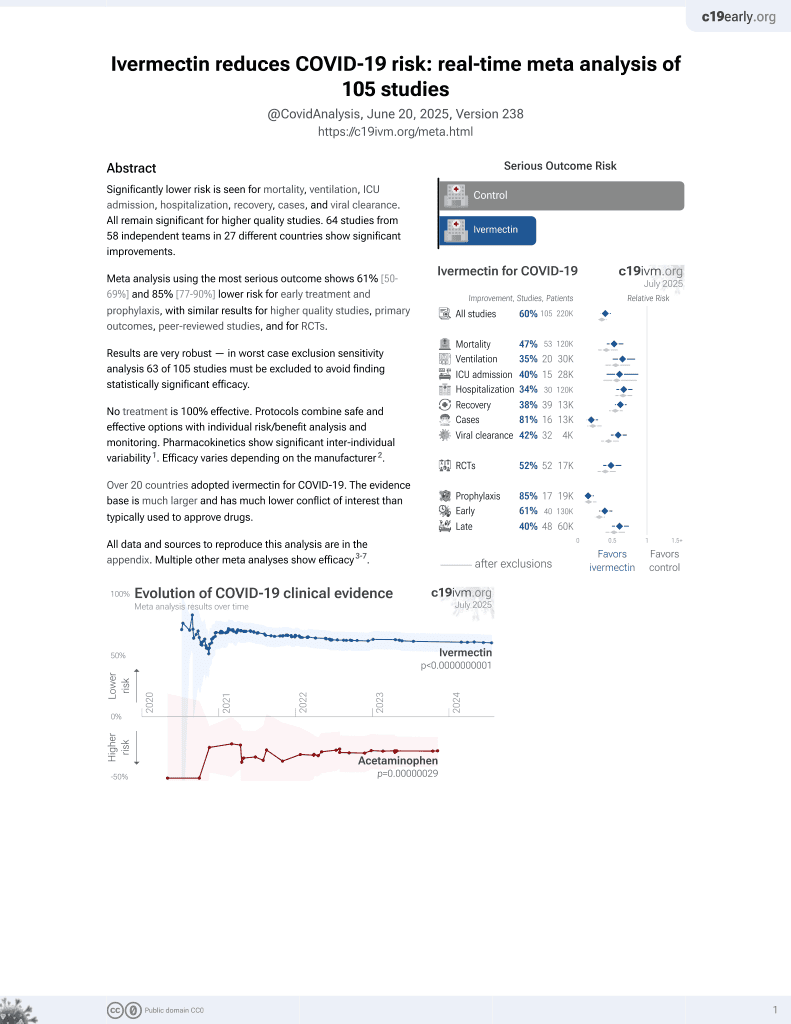
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In silico elastic network model analysis of ivermectin components (avermectin-B1a and avermectin-B1b) providing a biophysical and computational perspective of proposed multi-target activity of ivermectin for COVID-19.
74 preclinical studies support the efficacy of ivermectin for COVID-19:
Ivermectin, better known for antiparasitic activity, is a broad spectrum antiviral with activity against many viruses including H7N771, Dengue37,72,73 , HIV-173, Simian virus 4074, Zika37,75,76 , West Nile76, Yellow Fever77,78, Japanese encephalitis77, Chikungunya78, Semliki Forest virus78, Human papillomavirus57, Epstein-Barr57, BK Polyomavirus79, and Sindbis virus78.
Ivermectin inhibits importin-α/β-dependent nuclear import of viral proteins71,73,74,80 , shows spike-ACE2 disruption at 1nM with microfluidic diffusional sizing38, binds to glycan sites on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein preventing interaction with blood and epithelial cells and inhibiting hemagglutination41,81, shows dose-dependent inhibition of wildtype and omicron variants36, exhibits dose-dependent inhibition of lung injury61,66, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 via IMPase inhibition37, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 induced formation of fibrin clots resistant to degradation9, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro54, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RdRp activity28, may minimize viral myocarditis by inhibiting NF-κB/p65-mediated inflammation in macrophages60, may be beneficial for COVID-19 ARDS by blocking GSDMD and NET formation82, may interfere with SARS-CoV-2's immune evasion via ORF8 binding4, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by disrupting CD147 interaction83-86, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 attachment to lipid rafts via spike NTD binding2, shows protection against inflammation, cytokine storm, and mortality in an LPS mouse model sharing key pathological features of severe COVID-1959,87, may be beneficial in severe COVID-19 by binding IGF1 to inhibit the promotion of inflammation, fibrosis, and cell proliferation that leads to lung damage8, may minimize SARS-CoV-2 induced cardiac damage40,48, may counter immune evasion by inhibiting NSP15-TBK1/KPNA1 interaction and restoring IRF3 activation88, may disrupt SARS-CoV-2 N and ORF6 protein nuclear transport and their suppression of host interferon responses1, reduces TAZ/YAP nuclear import, relieving SARS-CoV-2-driven suppression of IRF3 and NF-κB antiviral pathways35, increases Bifidobacteria which play a key role in the immune system89, has immunomodulatory51 and anti-inflammatory70,90 properties, and has an extensive and very positive safety profile91.
1.
Gayozo et al., Binding affinities analysis of ivermectin, nucleocapsid and ORF6 proteins of SARS-CoV-2 to human importins α isoforms: A computational approach, Biotecnia, doi:10.18633/biotecnia.v27.2485.
2.
Lefebvre et al., Characterization and Fluctuations of an Ivermectin Binding Site at the Lipid Raft Interface of the N-Terminal Domain (NTD) of the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16121836.
3.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
4.
Bagheri-Far et al., Non-spike protein inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by natural products through the key mediator protein ORF8, Molecular Biology Research Communications, doi:10.22099/mbrc.2024.50245.2001.
5.
de Oliveira Só et al., In Silico Comparative Analysis of Ivermectin and Nirmatrelvir Inhibitors Interacting with the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202404.1825.v1.
6.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
7.
Oranu et al., Validation of the binding affinities and stabilities of ivermectin and moxidectin against SARS-CoV-2 receptors using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation, GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.30574/gscbps.2024.26.1.0030.
8.
Zhao et al., Identification of the shared gene signatures between pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension using bioinformatics analysis, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1197752.
9.
Vottero et al., Computational Prediction of the Interaction of Ivermectin with Fibrinogen, Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms241411449.
10.
Chellasamy et al., Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors, Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277.
11.
Umar et al., Inhibitory potentials of ivermectin, nafamostat, and camostat on spike protein and some nonstructural proteins of SARS-CoV-2: Virtual screening approach, Jurnal Teknologi Laboratorium, doi:10.29238/teknolabjournal.v11i1.344.
12.
Alvarado et al., Interaction of the New Inhibitor Paxlovid (PF-07321332) and Ivermectin With the Monomer of the Main Protease SARS-CoV-2: A Volumetric Study Based on Molecular Dynamics, Elastic Networks, Classical Thermodynamics and SPT, Computational Biology and Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2022.107692.
13.
Aminpour et al., In Silico Analysis of the Multi-Targeted Mode of Action of Ivermectin and Related Compounds, Computation, doi:10.3390/computation10040051.
14.
Parvez et al., Insights from a computational analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Host–pathogen interaction, pathogenicity, and possible drug therapeutics, Immunity, Inflammation and Disease, doi:10.1002/iid3.639.
15.
Francés-Monerris et al., Microscopic interactions between ivermectin and key human and viral proteins involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, doi:10.1039/D1CP02967C.
16.
González-Paz et al., Comparative study of the interaction of ivermectin with proteins of interest associated with SARS-CoV-2: A computational and biophysical approach, Biophysical Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677.
17.
González-Paz (B) et al., Structural Deformability Induced in Proteins of Potential Interest Associated with COVID-19 by binding of Homologues present in Ivermectin: Comparative Study Based in Elastic Networks Models, Journal of Molecular Liquids, doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284.
18.
Rana et al., A Computational Study of Ivermectin and Doxycycline Combination Drug Against SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-755838/v1.
19.
Muthusamy et al., Virtual Screening Reveals Potential Anti-Parasitic Drugs Inhibiting the Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein, Journal of Virology & Antiviral Research, www.scitechnol.com/abstract/virtual-screening-reveals-potential-antiparasitic-drugs-inhibiting-the-receptor-binding-domain-of-sarscov2-spike-protein-16398.html.
20.
Qureshi et al., Mechanistic insights into the inhibitory activity of FDA approved ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2: old drug with new implications, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1906750.
21.
Schöning et al., Highly-transmissible Variants of SARS-CoV-2 May Be More Susceptible to Drug Therapy Than Wild Type Strains, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-379291/v1.
22.
Bello et al., Elucidation of the inhibitory activity of ivermectin with host nuclear importin α and several SARS-CoV-2 targets, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1911857.
23.
Udofia et al., In silico studies of selected multi-drug targeting against 3CLpro and nsp12 RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase proteins of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV, Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics, doi:10.1007/s13721-021-00299-2.
24.
Choudhury et al., Exploring the binding efficacy of ivermectin against the key proteins of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: an in silico approach, Future Medicine, doi:10.2217/fvl-2020-0342.
25.
Kern et al., Modeling of SARS-CoV-2 Treatment Effects for Informed Drug Repurposing, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.625678.
26.
Saha et al., The Binding mechanism of ivermectin and levosalbutamol with spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, Structural Chemistry, doi:10.1007/s11224-021-01776-0.
27.
Eweas et al., Molecular Docking Reveals Ivermectin and Remdesivir as Potential Repurposed Drugs Against SARS-CoV-2, Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.592908.
28.
Parvez (B) et al., Prediction of potential inhibitors for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 using comprehensive drug repurposing and molecular docking approach, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.098.
29.
Francés-Monerris (B) et al., Has Ivermectin Virus-Directed Effects against SARS-CoV-2? Rationalizing the Action of a Potential Multitarget Antiviral Agent, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12782258.v1.
30.
Kalhor et al., Repurposing of the approved small molecule drugs in order to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 S protein and human ACE2 interaction through virtual screening approaches, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1824816.
31.
Swargiary, A., Ivermectin as a promising RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor and a therapeutic drug against SARS-CoV2: Evidence from in silico studies, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-73308/v1.
32.
Maurya, D., A Combination of Ivermectin and Doxycycline Possibly Blocks the Viral Entry and Modulate the Innate Immune Response in COVID-19 Patients, American Chemical Society (ACS), doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12630539.v1.
33.
Lehrer et al., Ivermectin Docks to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-binding Domain Attached to ACE2, In Vivo, 34:5, 3023-3026, doi:10.21873/invivo.12134.
34.
Suravajhala et al., Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin with COVID-19 Proteins, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v3.
35.
Kofler et al., M-Motif, a potential non-conventional NLS in YAP/TAZ and other cellular and viral proteins that inhibits classic protein import, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2025.112105.
36.
Shahin et al., The selective effect of Ivermectin on different human coronaviruses; in-vitro study, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4180797/v1.
37.
Jitobaom et al., Identification of inositol monophosphatase as a broad‐spectrum antiviral target of ivermectin, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29552.
38.
Fauquet et al., Microfluidic Diffusion Sizing Applied to the Study of Natural Products and Extracts That Modulate the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD/ACE2 Interaction, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28248072.
39.
García-Aguilar et al., In Vitro Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Ivermectin Interaction, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242216392.
40.
Liu et al., SARS-CoV-2 viral genes Nsp6, Nsp8, and M compromise cellular ATP levels to impair survival and function of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, Stem Cell Research & Therapy, doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03485-3.
41.
Boschi et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induces Hemagglutination: Implications for COVID-19 Morbidities and Therapeutics and for Vaccine Adverse Effects, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.11.24.517882.
42.
De Forni et al., Synergistic drug combinations designed to fully suppress SARS-CoV-2 in the lung of COVID-19 patients, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0276751.
43.
Saha (B) et al., Manipulation of Spray-Drying Conditions to Develop an Inhalable Ivermectin Dry Powder, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14071432.
44.
Jitobaom (B) et al., Synergistic anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of repurposed anti-parasitic drug combinations, BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology, doi:10.1186/s40360-022-00580-8.
45.
Croci et al., Liposomal Systems as Nanocarriers for the Antiviral Agent Ivermectin, International Journal of Biomaterials, doi:10.1155/2016/8043983.
46.
Zheng et al., Red blood cell-hitchhiking mediated pulmonary delivery of ivermectin: Effects of nanoparticle properties, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121719.
47.
Delandre et al., Antiviral Activity of Repurposing Ivermectin against a Panel of 30 Clinical SARS-CoV-2 Strains Belonging to 14 Variants, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15040445.
48.
Liu (B) et al., Genome-wide analyses reveal the detrimental impacts of SARS-CoV-2 viral gene Orf9c on human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, Stem Cell Reports, doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.01.014.
49.
Segatori et al., Effect of Ivermectin and Atorvastatin on Nuclear Localization of Importin Alpha and Drug Target Expression Profiling in Host Cells from Nasopharyngeal Swabs of SARS-CoV-2- Positive Patients, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13102084.
50.
Jitobaom (C) et al., Favipiravir and Ivermectin Showed in Vitro Synergistic Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-941811/v1.
51.
Munson et al., Niclosamide and ivermectin modulate caspase-1 activity and proinflammatory cytokine secretion in a monocytic cell line, British Society For Nanomedicine Early Career Researcher Summer Meeting, 2021, web.archive.org/web/20230401070026/https://michealmunson.github.io/COVID.pdf.
52.
Mountain Valley MD, Mountain Valley MD Receives Successful Results From BSL-4 COVID-19 Clearance Trial on Three Variants Tested With Ivectosol™, 5/18, www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2021/05/18/2231755/0/en/Mountain-Valley-MD-Receives-Successful-Results-From-BSL-4-COVID-19-Clearance-Trial-on-Three-Variants-Tested-With-Ivectosol.html.
53.
Yesilbag et al., Ivermectin also inhibits the replication of bovine respiratory viruses (BRSV, BPIV-3, BoHV-1, BCoV and BVDV) in vitro, Virus Research, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198384.
54.
Mody et al., Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents, Communications Biology, doi:10.1038/s42003-020-01577-x.
55.
Jeffreys et al., Remdesivir-ivermectin combination displays synergistic interaction with improved in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2022.106542.
56.
Surnar et al., Clinically Approved Antiviral Drug in an Orally Administrable Nanoparticle for COVID-19, ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci., doi:10.1021/acsptsci.0c00179.
57.
Li et al., Quantitative proteomics reveals a broad-spectrum antiviral property of ivermectin, benefiting for COVID-19 treatment, J. Cellular Physiology, doi:10.1002/jcp.30055.
58.
Caly et al., The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787.
59.
Zhang et al., Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice, Inflammation Research, doi:10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8.
60.
Gao et al., Ivermectin ameliorates acute myocarditis via the inhibition of importin-mediated nuclear translocation of NF-κB/p65, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112073.
61.
Abd-Elmawla et al., Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome by ivermectin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis, Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B, doi:10.1631/jzus.B2200385.
62.
Uematsu et al., Prophylactic administration of ivermectin attenuates SARS-CoV-2 induced disease in a Syrian Hamster Model, The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-023-00623-0.
63.
Albariqi et al., Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Inhaled Ivermectin in Mice as a Potential COVID-19 Treatment, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121688.
64.
Errecalde et al., Safety and Pharmacokinetic Assessments of a Novel Ivermectin Nasal Spray Formulation in a Pig Model, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2021.01.017.
65.
Madrid et al., Safety of oral administration of high doses of ivermectin by means of biocompatible polyelectrolytes formulation, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05820.
66.
Ma et al., Ivermectin contributes to attenuating the severity of acute lung injury in mice, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113706.
67.
de Melo et al., Attenuation of clinical and immunological outcomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection by ivermectin, EMBO Mol. Med., doi:10.15252/emmm.202114122.
68.
Arévalo et al., Ivermectin reduces in vivo coronavirus infection in a mouse experimental model, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-86679-0.
69.
Chaccour et al., Nebulized ivermectin for COVID-19 and other respiratory diseases, a proof of concept, dose-ranging study in rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-74084-y.
70.
Yan et al., Anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin in mouse model of allergic asthma, Inflammation Research, doi:10.1007/s00011-011-0307-8.
71.
Götz et al., Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/srep23138.
72.
Tay et al., Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1–4 non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002.
73.
Wagstaff et al., Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin α/β-mediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus, Biochemical Journal, doi:10.1042/BJ20120150.
74.
Wagstaff (B) et al., An AlphaScreen®-Based Assay for High-Throughput Screening for Specific Inhibitors of Nuclear Import, SLAS Discovery, doi:10.1177/1087057110390360.
75.
Barrows et al., A Screen of FDA-Approved Drugs for Inhibitors of Zika Virus Infection, Cell Host & Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2016.07.004.
76.
Yang et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760.
77.
Mastrangelo et al., Ivermectin is a potent inhibitor of flavivirus replication specifically targeting NS3 helicase activity: new prospects for an old drug, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dks147.
78.
Varghese et al., Discovery of berberine, abamectin and ivermectin as antivirals against chikungunya and other alphaviruses, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.12.012.
79.
Bennett et al., Role of a nuclear localization signal on the minor capsid Proteins VP2 and VP3 in BKPyV nuclear entry, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2014.10.013.
80.
Kosyna et al., The importin α/β-specific inhibitor Ivermectin affects HIF-dependent hypoxia response pathways, Biological Chemistry, doi:10.1515/hsz-2015-0171.
81.
Scheim et al., Sialylated Glycan Bindings from SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Blood and Endothelial Cells Govern the Severe Morbidities of COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242317039.
82.
Liu (C) et al., Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and immune regulation: insights into pathobiology and therapeutic implications of transfusion-related acute lung injury, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021.
83.
Shouman et al., SARS-CoV-2-associated lymphopenia: possible mechanisms and the role of CD147, Cell Communication and Signaling, doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01718-3.
84.
Scheim (B), D., Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-Threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-Mediated Vascular Occlusion, SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3636557.
85.
Scheim (C), D., From Cold to Killer: How SARS-CoV-2 Evolved without Hemagglutinin Esterase to Agglutinate and Then Clot Blood Cells, Center for Open Science, doi:10.31219/osf.io/sgdj2.
86.
Behl et al., CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target, Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072.
87.
DiNicolantonio et al., Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350.
88.
Mothae et al., SARS-CoV-2 host-pathogen interactome: insights into more players during pathogenesis, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2025.110607.
89.
Hazan et al., Treatment with Ivermectin Increases the Population of Bifidobacterium in the Gut, ACG 2023, acg2023posters.eventscribe.net/posterspeakers.asp.
González-Paz et al., 17 Aug 2021, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Structural deformability induced in proteins of potential interest associated with COVID-19 by binding of homologues present in ivermectin: Comparative study based in elastic networks models
Journal of Molecular Liquids, doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
The Z-Score showed conformational fluctuations between free protein and lowenergy ligand-protein complexes. Starting from this model, it was observed that all the Avermectins-Protein complexes presented differences in the distances of their Cα atoms, as well as in their energetics at 100 ns of simulation and with respect to their corresponding free protein subjected to the same dynamic conditions. In ProSA-web, the most extreme Z-Score values were related to more dynamic and distant conformations of the free protein. This applies both for very negative values and for values very close to 0, since they tend to fall outside the Z-Score obtained from all the protein chains determined experimentally in the Protein Data Bank (PDB). In fact, the Z-Score for proteins such as the Multidrug ABC transporter (PDB: 2HYD) has been reported to be -8.29, which is in the range of native conformations. Whereas according to the ProSA-web results obtained for the homologous ABC transporter protein of multiple drugs (PDB: 1JSQ), the Z-Score of this model is −0.60, a value too high for a typical native structure [52] . In IMPα1, the complexes with the homologues presented the most distant conformational fluctuation from the free protein one with a Z-Score more negative than that obtained for the ligand-free protein, which suggests unfolding of this protein with both stereoisomers. On the contrary, although a similar trend towards unfolding against Mpro was predicted, especially with compound..
References
Ahmed, Rippmann, Barnickel, Gohlke, A normal modebased geometric simulation approach for exploring biologically relevant conformational transitions in proteins, Journal of chemical information and modeling, doi:10.1021/ci100461k
Atilgan, Durrell, Jernigan, Demirel, Keskin et al., Anisotropy of fluctuation dynamics of proteins with an elastic network model, Biophys. J, doi:10.1016/S0006-3495
Azam, Taban, Eid, Iqbal, Alam et al., An in-silico analysis of ivermectin interaction with potential SARS-CoV-2 targets and host nuclear importin α, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1841028
Bahar, Cheng, Lee, Kaya, Zhang, Structureencoded global motions and their role in mediating protein-substrate interactions, Biophysical Journal, doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.004
Bernardes, Fukuda, Da Silva, De Oliveira, De Barros et al., Comparative study of the interactions between fungal transcription factor nuclear localization sequences with mammalian and fungal importin-alpha, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-58316-9
Bhattacharya, Sharma, Patra, Ghosh, Sharma et al., A SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate: In-silico cloning and validation, Informatics in medicine unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2020.100394
Bope, Tong, Li, Lu, Fluctuation matching approach for elastic network model and structure-based model of biomacromolecules, Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2016.12.006
Calligari, Gerolin, Abergel, Polimeno, Decomposition of proteins into dynamic units from atomic cross-correlation functions, Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, doi:10.1021/acs.jctc.6b00702
Chhetri, Chettri, Rai, Sinha, Brahman, Exploration of inhibitory action of Azo imidazole derivatives against COVID-19 main protease (M pro ): A computational study, Journal of molecular structure, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129178
Culletta, Gulotta, Perricone, Zappalà, Almerico et al., Exploring the SARS-CoV-2 Proteome in the Search of Potential Inhibitors via Structure-Based Pharmacophore Modeling/Docking Approach, Computation, doi:10.3390/computation8030077
De Oliveira, Rocha, Paluch, Costa, Repurposing approved drugs as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 S-protein from molecular modeling and virtual screening, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1772885
Doruker, Atilgan, Bahar, Dynamics of proteins predicted by molecular dynamics simulations and analytical approaches: application to alphaamylase inhibitor, Proteins, doi:10.1002/1097-0134(20000815
Dubanevics, Mcleish, Computational analysis of dynamic allostery and control in the SARS-CoV-2 main protease, Journal of the Royal Society Interface, doi:10.1098/rsif.2020.0591
Dykeman, Sankey, Normal mode analysis and applications in biological physics, Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, doi:10.1088/0953-8984/22/42/423202
Elmezayen, Al-Obaidi, Şahin, Yelekçi, Drug repurposing for coronavirus (COVID-19): in silico screening of known drugs against coronavirus 3CL hydrolase and protease enzymes, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1758791
Emekli, Schneidman-Duhovny, Wolfson, Nussinov, Haliloglu, HingeProt: automated prediction of hinges in protein structures, Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, doi:10.1002/prot.21613
Fatoki, Ibraheem, Ogunyemi, Akinmoladun, Ugboko et al., Network analysis, sequence and structure dynamics of key proteins of coronavirus and human host, and molecular docking of selected phytochemicals of nine medicinal plants, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1794971
Felline, Seeber, Fanelli, webPSN v2. 0: a webserver to infer fingerprints of structural communication in biomacromolecules, Nucleic acids research, doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa397
Fleming, Fleming, HullRad: Fast calculations of folded and disordered protein and nucleic acid hydrodynamic properties, Biophysical journal, doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2018.01.002
González-Paz, Lossada, Fernández-Materán, Paz, Vera-Villalobos et al., Can Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Affect the Interaction Between Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-COV-2 Spike and the Human ACE2 Receptor? A Computational Biophysical Study, Frontiers in Physics, doi:10.3389/fphy.2020.587606
González-Paz, Lossada, Moncayo, Romero, Paz et al., A Bioinformatics Study of Structural Perturbation of 3CL-Protease and the HR2-Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Induced by Synergistic Interaction with Ivermectins, Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, doi:10.33263/BRIAC112.98139826
Goyal, Goyal, Targeting the dimerization of the main protease of coronaviruses: a potential broad-spectrum therapeutic strategy, ACS Combinatorial Science, doi:10.1021/acscombsci.0c00058
Greene, Protein structure networks, Briefings in Functional Genomics, doi:10.1093/bfgp/els039
Guedes, Barreto, Marinho, Krempser, Kuenemann et al., New machine learning and physics-based scoring functions for drug discovery, Scientific reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-82410-1
Guedes, Costa, Dos Santos, Karl, Rocha et al., Drug Design and Repurposing with DockThor-VS Web Server: Virtual Screening focusing on SARS-CoV-2
Gurung, In silico structure modelling of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp13 helicase and Nsp14 and repurposing of FDA approved antiviral drugs as dual inhibitors, Gene Reports, doi:10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100860
Halder, Dölker, Van, Gregor, Dickmanns et al., MD simulations and FRET reveal an environment-sensitive conformational plasticity of importin-β, Biophysical Journal, doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.014
Heidary, Gharebaghi, Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen, The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z
Heidary, Gharebaghi, Lateef, Mohammed, Alshmailawi et al., Antiviral Vector Effects of Ivermectin on COVID-19: An Update, Journal of Cellular & Molecular Anesthesia, doi:10.22037/jcma.v6i1.33827
Hollup, Saelensminde, Reuter, WEBnm@: a web application for normal mode analysis of proteins, BMC Bioinformatics, doi:10.1186/1471-2105-6-52
Hosseini, Chen, Xiao, Wang, Computational molecular docking and virtual screening revealed promising SARS-CoV-2 drugs, Precision Clinical Medicine, doi:10.1093/pcmedi/pbab001
Hu, Di Paola, Liang, Giuliani, Comparative study of elastic network model and protein contact network for protein complexes: the hemoglobin case, BioMed research international, doi:10.1155/2017/2483264
Jayaram, Bhushan, Shenoy, Narang, Bose et al., Bhageerath: an energy based web enabled computer software suite for limiting the search space of tertiary structures of small globular proteins, Nucleic Acids Research, doi:10.1093/nar/gkl789
Jia, Yan, Ren, Wu, Wang et al., Delicate structural coordination of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus Nsp13 upon ATP hydrolysis, Nucleic acids research, doi:10.1093/nar/gkz409
Kapoor, Ghorai, Kushwaha, Shukla, Aggarwal et al., Plausible mechanisms explaining the role of cucurbitacins as potential therapeutic drugs against coronavirus 2019, Informatics In Medicine Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2020.100484
Kasahara, Terazawa, Itaya, Goto, Nakamura et al., myPresto/omegagene 2020: a molecular dynamics simulation engine for virtual-system coupled sampling, Biophysics and Physicobiology, doi:10.2142/biophysico.BSJ-2020013
Kow, Merchant, Mustafa, Hasan, The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a metaanalysis, Pharmacological Reports, doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z
Lakhani, Thayer, Black, Beveridge, Spectral analysis of molecular dynamics simulations on PDZ: MD sectors, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2019
Lewis, Chaudhuri, Alshamsi, Carayannopoulos, Dearness et al., The efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 prophylaxis: A systematic review and metaanalysis of randomized trials, PloS one, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0244778
Lin, Chou, Chang, Hsu, Chang, Correlation between dissociation and catalysis of SARS-CoV main protease, Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, doi:10.1016/j.abb.2008.01.023
López-Blanco, Aliaga, Quintana-Ortí, Chacón, iMODS: internal coordinates normal mode analysis server, Nucleic acids research, doi:10.1093/nar/gku339
Magalhães, Barbosa, Dardenne, A genetic algorithm for the ligand-protein docking problem, Genetics and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1590/S1415-47572004000400022
Martin, Jans, Antivirals that target the host IMPα/β1-virus interface, Biochemical Society Transactions, doi:10.1042/BST20200568
Mirza, Froeyen, Structural elucidation of SARS-CoV-2 vital proteins: Computational methods reveal potential drug candidates against main protease, Nsp12 polymerase and Nsp13 helicase, Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2020.04.008
Mitrousis, Olia, Walker-Kopp, Cingolani, Molecular basis for the recognition of snurportin 1 by importin β, Journal of Biological Chemistry, doi:10.1074/jbc.M709093200
Mosquera-Yuqui, Lopez-Guerra, Moncayo-Palacio, Targeting the 3CLpro and RdRp of SARS-CoV-2 with phytochemicals from medicinal plants of the Andean Region: molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1835716
Neupane, Karn, Mukeri, Pathak, Sharma et al., Molecular dynamics analysis of phytochemicals from Ageratina adenophora against COVID-19 main protease (Mpro) and human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, doi:10.1016/j.bcab.2021.101924
Ng, Salim, Chu, Drug repurposing for COVID-19: Approaches, challenges and promising candidates, Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107930
O'boyle, Banck, James, Morley, Vandermeersch et al., Open babel: an open chemical toolbox, J. Chem, doi:10.1186/1758-2946-3-33
Oany, Pervin, Moni, Pharmacoinformatics based elucidation and designing of potential inhibitors against Plasmodium falciparum to target importin α/β mediated nuclear importation, Infection, Genetics and Evolution, doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104699
Panikar, Shoba, Arun, Sahayarayan, Nanthini et al., Essential oils as an effective alternative for the treatment of COVID-19: Molecular interaction analysis of protease (Mpro) with pharmacokinetics and toxicological properties, Journal of Infection and Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.12.037
Ponzoni, Polles, Carnevale, Micheletti, SPECTRUS: A dimensionality reduction approach for identifying dynamical domains in protein complexes from limited structural datasets, Structure, doi:10.1016/j.str.2015.05.022
Pott-Junior, Bastos, Constantino, Da Cunha, De Melo et al., Use of ivermectin in the treatment of Covid-19: A pilot trial, Toxicology Reports, doi:10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.03.003
Rawal, Khurana, Sharma, Verma, Gupta et al., An extensive survey of molecular docking tools and their applications using text mining and deep curation strategies, PeerJ Preprints, doi:10.7287/peerj.preprints.27538v1
Santos, Guedes, Karl, Dardenne, Highly flexible ligand docking: benchmarking of the DockThor program on the LEADS-PEP protein-peptide data set, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00905
Schmith, Zhou, Lohmer, The approved dose of ivermectin alone is not the ideal dose for the treatment of COVID-19, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.1889
Seeber, Felline, Raimondi, Muff, Friedman et al., Wordom: a user-friendly program for the analysis of molecular structures, trajectories, and free energy surfaces, Journal of computational chemistry, doi:10.1002/jcc.21688
Shah, Chaple, Arora, Yende, Mehta et al., Prospecting for Cressa cretica to treat COVID-19 via in silico molecular docking models of the SARS-CoV-2, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1872419
Skjaerven, Hollup, Reuter, Normal mode analysis for proteins, Journal of Molecular Structure THEOCHEM, doi:10.1016/j.theochem.2008.09.024
Smith, Di Antonio, Bellucci, Thomas, Caporuscio et al., Contribution of the residue at position 4 within classical nuclear localization signals to modulating interaction with importins and nuclear targeting, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Molecular Cell Research, doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.05.006
Sánchez-Tejeda, Sánchez-Ruiz, Salazar, Loza-Mejía, A definition of "multitargeticity": identifying potential multitarget and selective ligands through a vector analysis, Frontiers in chemistry, doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.00176
Thurakkal, Singh, Roy, Kar, Sadhukhan et al., An in-silico study on selected organosulfur compounds as potential drugs for SARS-CoV-2 infection via binding multiple drug targets, Chemical Physics Letters, doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2020.138193
Tiwari, Fuglebakk, Hollup, Skjaerven, Cragnolini et al., WEBnm@ v2. 0: Web server and services for comparing protein flexibility, BMC bioinformatics, doi:10.1186/s12859-014-0427-6
Tu, Mccuaig, Melino, Rawle, Le et al., Targeting novel LSD1-dependent ACE2 demethylation domains inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication, Cell Discovery, doi:10.1038/s41421-021-00279-w
Verkhivker, Bouzida, Gehlhaar, Rejto, Arthurs et al., Deciphering common failures in molecular docking of ligand-protein complexes, Journal of computer-aided molecular design, doi:10.1023/a:1008158231558
Wada, Kanamori, Nakamura, Fukunishi, Selection of in silico drug screening results for G-protein-coupled receptors by using universal active probes, Journal of chemical information and modeling, doi:10.1021/ci200236x
Wahedi, Ahmad, Abbasi, Stilbene-based natural compounds as promising drug candidates against COVID-19, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1762743
Yadav, Choudhury, Kumar, Bhatia, Virtual repurposing of ursodeoxycholate and chenodeoxycholate as lead candidates against SARS-Cov2-Envelope protein: A molecular dynamics investigation, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1868339
Yesilbag, Toker, Ates, Ivermectin also inhibits the replication of bovine respiratory viruses (BRSV, BPIV-3, BoHV-1, BCoV and BVDV) in vitro, Virus research, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198384
Yonezawa, Electrostatic properties of water models evaluated by a longrange potential based solely on the Wolf charge-neutral condition, Chemical Physics Letters, doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2012.12.028
Zhou, Pang, Electrostatic interactions in protein structure, folding, binding, and condensation, Chemical reviews, doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00305
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284",
"ISSN": [
"0167-7322"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284",
"alternative-id": [
"S0167732221020080"
],
"article-number": "117284",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Structural deformability induced in proteins of potential interest associated with COVID-19 by binding of homologues present in ivermectin: Comparative study based in elastic networks models"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of Molecular Liquids"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "González-Paz",
"given": "Lenin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hurtado-León",
"given": "María Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lossada",
"given": "Carla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernández-Materán",
"given": "Francelys V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vera-Villalobos",
"given": "Joan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loroño",
"given": "Marcos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paz",
"given": "J.L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffreys",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alvarado",
"given": "Ysaias J.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Molecular Liquids",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Molecular Liquids",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-17T03:54:31Z",
"timestamp": 1629172471000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-09T06:53:11Z",
"timestamp": 1673247191000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-14T14:19:43Z",
"timestamp": 1705241983584
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0167732221020080?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0167732221020080?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "117284",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Drug repurposing for COVID-19: Approaches, challenges and promising candidates",
"author": "Ng",
"issue": "228",
"journal-title": "Pharmacology & Therapeutics",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0005",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0244778",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0010",
"unstructured": "Lewis, K., Chaudhuri, D., Alshamsi, F., Carayannopoulos, L., Dearness, K., Chagla, Z., Alhazzani, W. & GUIDE Group. (2021). The efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 prophylaxis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. PloS one, 16(1), e0244778. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0244778."
},
{
"article-title": "A definition of “multitargeticity”: identifying potential multitarget and selective ligands through a vector analysis",
"author": "Sánchez-Tejeda",
"issue": "176",
"journal-title": "Front. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0015",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1794971",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0020",
"unstructured": "Fatoki, T. H., Ibraheem, O., Ogunyemi, I. O., Akinmoladun, A. C., Ugboko, H. U., Adeseko, C. J., Awofisayo, O., Olusegun, S., & Enibukun, J. (2020). Network analysis, sequence and structure dynamics of key proteins of coronavirus and human host, and molecular docking of selected phytochemicals of nine medicinal plants.Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 20, 1-23. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1794971."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z",
"article-title": "Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen",
"author": "Heidary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "593",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "The Journal of Antibiotics",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0025",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Antiviral Vector Effects of Ivermectin on COVID-19: An Update",
"author": "Heidary",
"first-page": "101",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Journal of Cellular & Molecular Anesthesia",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0030",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198384",
"article-title": "Ivermectin also inhibits the replication of bovine respiratory viruses (BRSV, BPIV-3, BoHV-1, BCoV and BVDV) in vitro",
"author": "Yesilbag",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "198384",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0035",
"volume": "297",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "A Bioinformatics Study of Structural Perturbation of 3CL-Protease and the HR2-Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Induced by Synergistic Interaction with Ivermectins",
"author": "González-Paz",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0040",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1841028",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0045",
"unstructured": "Azam, F., Taban, I.M., Eid, E.E.M., Iqbal, M., Alam, O., Khan, S., Mahmood, D., Anwar, M.J., Khalilullah, H., Khan, M.U. (2020). An in-silico analysis of ivermectin interaction with potential SARS-CoV-2 targets and host nuclear importin α. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, Nov 2:1-14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1841028."
},
{
"article-title": "Repurposing approved drugs as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 S-protein from molecular modeling and virtual screening",
"author": "de Oliveira",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0050",
"volume": "1–10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Targeting the 3CLpro and RdRp of SARS-CoV-2 with phytochemicals from medicinal plants of the Andean Region: molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations",
"author": "Mosquera-Yuqui",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0055",
"volume": "1–14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26434/chemrxiv.12237995",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0060",
"unstructured": "Hosseini, M., Chen, W., Xiao, D., & Wang, C. (2020). Computational molecular docking and virtual screening revealed promising SARS-CoV-2 drugs. Precision Clinical Medicine, pbab001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/pcmedi/pbab001."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkaa397",
"article-title": "webPSN v2. 0: a webserver to infer fingerprints of structural communication in biomacromolecules",
"author": "Felline",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W94",
"issue": "W1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0065",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ci100461k",
"article-title": "A normal mode-based geometric simulation approach for exploring biologically relevant conformational transitions in proteins",
"author": "Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1604",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inf. Model.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0070",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/1097-0134(20000815)40:3<512::AID-PROT180>3.0.CO;2-M",
"article-title": "Dynamics of proteins predicted by molecular dynamics simulations and analytical approaches: application to alpha-amylase inhibitor",
"author": "Doruker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "512",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Proteins",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0075",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0006-3495(01)76033-X",
"article-title": "Anisotropy of fluctuation dynamics of proteins with an elastic network model",
"author": "Atilgan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biophys. J .",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0080",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.21688",
"article-title": "Wordom: a user-friendly program for the analysis of molecular structures, trajectories, and free energy surfaces",
"author": "Seeber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1183",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0085",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Normal mode analysis and applications in biological physics",
"author": "Dykeman",
"first-page": "423202",
"issue": "42",
"journal-title": "J. Phys.: Condens. Matter",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0090",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/prot.21613",
"article-title": "HingeProt: automated prediction of hinges in protein structures",
"author": "Emekli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1219",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinf.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0095",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gku339",
"article-title": "iMODS: internal coordinates normal mode analysis server",
"author": "López-Blanco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W271",
"issue": "W1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0100",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.theochem.2008.09.024",
"article-title": "Normal mode analysis for proteins",
"author": "Skjaerven",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "42",
"issue": "1–3",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Struct. (Thoechem)",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0105",
"volume": "898",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"article-title": "WEBnm@: a web application for normal mode analysis of proteins",
"author": "Hollup",
"issue": "52",
"journal-title": "BMC Bioinf.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0110",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bfgp/els039",
"article-title": "Protein structure networks",
"author": "Greene",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "469",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Briefings in Functional Genomics",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0115",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparative study of elastic network model and protein contact network for protein complexes: the hemoglobin case",
"author": "Hu",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Biomed Res. Int.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0120",
"volume": "2017",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-021-00279-w",
"article-title": "Targeting novel LSD1-dependent ACE2 demethylation domains inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication",
"author": "Tu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Cell Discovery",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0125",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.014",
"article-title": "MD simulations and FRET reveal an environment-sensitive conformational plasticity of importin-β",
"author": "Halder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "277",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Biophys. J .",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0130",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.05.006",
"article-title": "Contribution of the residue at position 4 within classical nuclear localization signals to modulating interaction with importins and nuclear targeting",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1114",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0135",
"volume": "1865",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-58316-9",
"article-title": "Comparative study of the interactions between fungal transcription factor nuclear localization sequences with mammalian and fungal importin-alpha",
"author": "Bernardes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1458",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0140",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BST20200568",
"article-title": "Antivirals that target the host IMPα/β1-virus interface",
"author": "Martin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "281",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Soc. Trans.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0145",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cplett.2020.138193",
"article-title": "An in-silico study on selected organosulfur compounds as potential drugs for SARS-CoV-2 infection via binding multiple drug targets",
"author": "Thurakkal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "138193",
"journal-title": "Chem. Phys. Lett.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0150",
"volume": "763",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/computation8030077",
"article-title": "Exploring the SARS-CoV-2 Proteome in the Search of Potential Inhibitors via Structure-Based Pharmacophore Modeling/Docking Approach",
"author": "Culletta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Computation",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0155",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imu.2020.100484",
"article-title": "Plausible mechanisms explaining the role of cucurbitacins as potential therapeutic drugs against coronavirus 2019",
"author": "Kapoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100484",
"journal-title": "Inf. Med. Unlocked",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0160",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Prospecting for Cressa cretica to treat COVID-19 via in silico molecular docking models of the SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Shah",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0165",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.12.037",
"article-title": "Essential oils as an effective alternative for the treatment of COVID-19: Molecular interaction analysis of protease (Mpro) with pharmacokinetics and toxicological properties",
"author": "Panikar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "601",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infection and Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0170",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129178",
"article-title": "Exploration of inhibitory action of Azo imidazole derivatives against COVID-19 main protease (Mpro): A computational study",
"author": "Chhetri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129178",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Struct.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0175",
"volume": "1224",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphy.2020.587606",
"article-title": "Can Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Affect the Interaction Between Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-COV-2 Spike and the Human ACE2 Receptor? A Computational Biophysical Study",
"author": "González-Paz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "526",
"journal-title": "Front. Phys.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0180",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcab.2021.101924",
"article-title": "Molecular dynamics analysis of phytochemicals from Ageratina adenophora against COVID-19 main protease (Mpro) and human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)",
"author": "Neupane",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101924",
"journal-title": "Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0185",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Open babel: an open chemical toolbox",
"author": "O'Boyle",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "33",
"journal-title": "J. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0190",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-84700-0",
"article-title": "Drug Design and Repurposing with DockThor-VS Web Server: Virtual Screening focusing on SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutic Targets and their Non-Synonym Variants",
"author": "Guedes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5543",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0195",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "An extensive survey of molecular docking tools and their applications using text mining and deep curation strategies",
"author": "Rawal",
"first-page": "e27538v1",
"journal-title": "PeerJ Preprints",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0200",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00905",
"article-title": "Highly flexible ligand docking: benchmarking of the DockThor program on the LEADS-PEP protein–peptide data set",
"author": "Santos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "667",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0205",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/S1415-47572004000400022",
"article-title": "A genetic algorithm for the ligand-protein docking problem",
"author": "Magalhães",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "605",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0210",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"article-title": "New machine learning and physics-based scoring functions for drug discovery",
"author": "Guedes",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "3198",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0215",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1008158231558",
"article-title": "Deciphering common failures in molecular docking of ligand-protein complexes",
"author": "Verkhivker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "731",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0220",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"article-title": "Stilbene-based natural compounds as promising drug candidates against COVID-19",
"author": "Wahedi",
"first-page": "3225",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0225",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ci200236x",
"article-title": "Selection of in silico drug screening results for G-protein-coupled receptors by using universal active probes",
"author": "Wada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2398",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inf. Model.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0230",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00305",
"article-title": "Electrostatic interactions in protein structure, folding, binding, and condensation",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1691",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Chem. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0235",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cplett.2012.12.028",
"article-title": "Electrostatic properties of water models evaluated by a long-range potential based solely on the Wolf charge-neutral condition",
"author": "Yonezawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "308",
"journal-title": "Chem. Phys. Lett.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0240",
"volume": "556",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2142/biophysico.BSJ-2020013",
"article-title": "myPresto/omegagene 2020: a molecular dynamics simulation engine for virtual-system coupled sampling",
"author": "Kasahara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "140",
"issue": "0",
"journal-title": "Biophysics and Physicobiology",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0245",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bpj.2018.01.002",
"article-title": "HullRad: Fast calculations of folded and disordered protein and nucleic acid hydrodynamic properties",
"author": "Fleming",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "856",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Biophys. J .",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0250",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkl789",
"article-title": "Bhageerath: an energy based web enabled computer software suite for limiting the search space of tertiary structures of small globular proteins",
"author": "Jayaram",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6195",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0255",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1758791",
"article-title": "Drug repurposing for coronavirus (COVID-19): in silico screening of known drugs against coronavirus 3CL hydrolase and protease enzymes",
"author": "Elmezayen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2980",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0260",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12859-014-0427-6",
"article-title": "WEBnm@ v2. 0: Web server and services for comparing protein flexibility",
"author": "Tiwari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Bioinf.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0265",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.str.2015.05.022",
"article-title": "SPECTRUS: A dimensionality reduction approach for identifying dynamical domains in protein complexes from limited structural datasets",
"author": "Ponzoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1516",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Structure",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0270",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M709093200",
"article-title": "Molecular basis for the recognition of snurportin 1 by importin β",
"author": "Mitrousis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7877",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0275",
"volume": "283",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkz409",
"article-title": "Delicate structural coordination of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus Nsp13 upon ATP hydrolysis",
"author": "Jia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6538",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0280",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acscombsci.0c00058",
"article-title": "Targeting the dimerization of the main protease of coronaviruses: a potential broad-spectrum therapeutic strategy",
"author": "Goyal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "297",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "ACS Comb. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0285",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2008.01.023",
"article-title": "Correlation between dissociation and catalysis of SARS-CoV main protease",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "34",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0290",
"volume": "472",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104699",
"article-title": "Pharmacoinformatics based elucidation and designing of potential inhibitors against Plasmodium falciparum to target importin α/β mediated nuclear importation",
"author": "Oany",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104699",
"journal-title": "Infection, Genetics and Evolution",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0295",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Virtual repurposing of ursodeoxycholate and chenodeoxycholate as lead candidates against SARS-Cov2-Envelope protein: A molecular dynamics investigation",
"author": "Yadav",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0300",
"volume": "1–12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100860",
"article-title": "In silico structure modelling of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp13 helicase and Nsp14 and repurposing of FDA approved antiviral drugs as dual inhibitors",
"author": "Gurung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100860",
"journal-title": "Gene Reports",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0305",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1098/rsif.2020.0591",
"article-title": "Computational analysis of dynamic allostery and control in the SARS-CoV-2 main protease",
"author": "Dubanevics",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20200591",
"issue": "174",
"journal-title": "J. R. Soc. Interface",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0310",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.004",
"article-title": "Structure-encoded global motions and their role in mediating protein-substrate interactions",
"author": "Bahar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1101",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Biophys. J .",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0315",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2016.12.006",
"article-title": "Fluctuation matching approach for elastic network model and structure-based model of biomacromolecules",
"author": "Bope",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100",
"journal-title": "Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0320",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imu.2020.100394",
"article-title": "A SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate: In-silico cloning and validation",
"author": "Bhattacharya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100394",
"journal-title": "Inf. Med. Unlocked",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0325",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jctc.6b00702",
"article-title": "Decomposition of proteins into dynamic units from atomic cross-correlation functions",
"author": "Calligari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "309",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Theory Comput.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0330",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2019.1588169",
"article-title": "Spectral analysis of molecular dynamics simulations on PDZ: MD sectors",
"author": "Lakhani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "781",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0335",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpha.2020.04.008",
"article-title": "Structural elucidation of SARS-CoV-2 vital proteins: Computational methods reveal potential drug candidates against main protease, Nsp12 polymerase and Nsp13 helicase",
"author": "Mirza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "320",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J. Pharm. Anal.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0340",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.1889",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0345",
"unstructured": "Schmith, V. D., Zhou, J., & Lohmer, L. R. (2020). The approved dose of ivermectin alone is not the ideal dose for the treatment of COVID‐19.Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics,108(4), 762-765. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.1889."
},
{
"article-title": "The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Kow",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0350",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.03.003",
"article-title": "Use of ivermectin in the treatment of Covid-19: A pilot trial",
"author": "Pott-Junior",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "Toxicol. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284_b0355",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 71,
"references-count": 71,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0167732221020080"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Structural deformability induced in proteins of potential interest associated with COVID-19 by binding of homologues present in ivermectin: Comparative study based in elastic networks models",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "340"
}