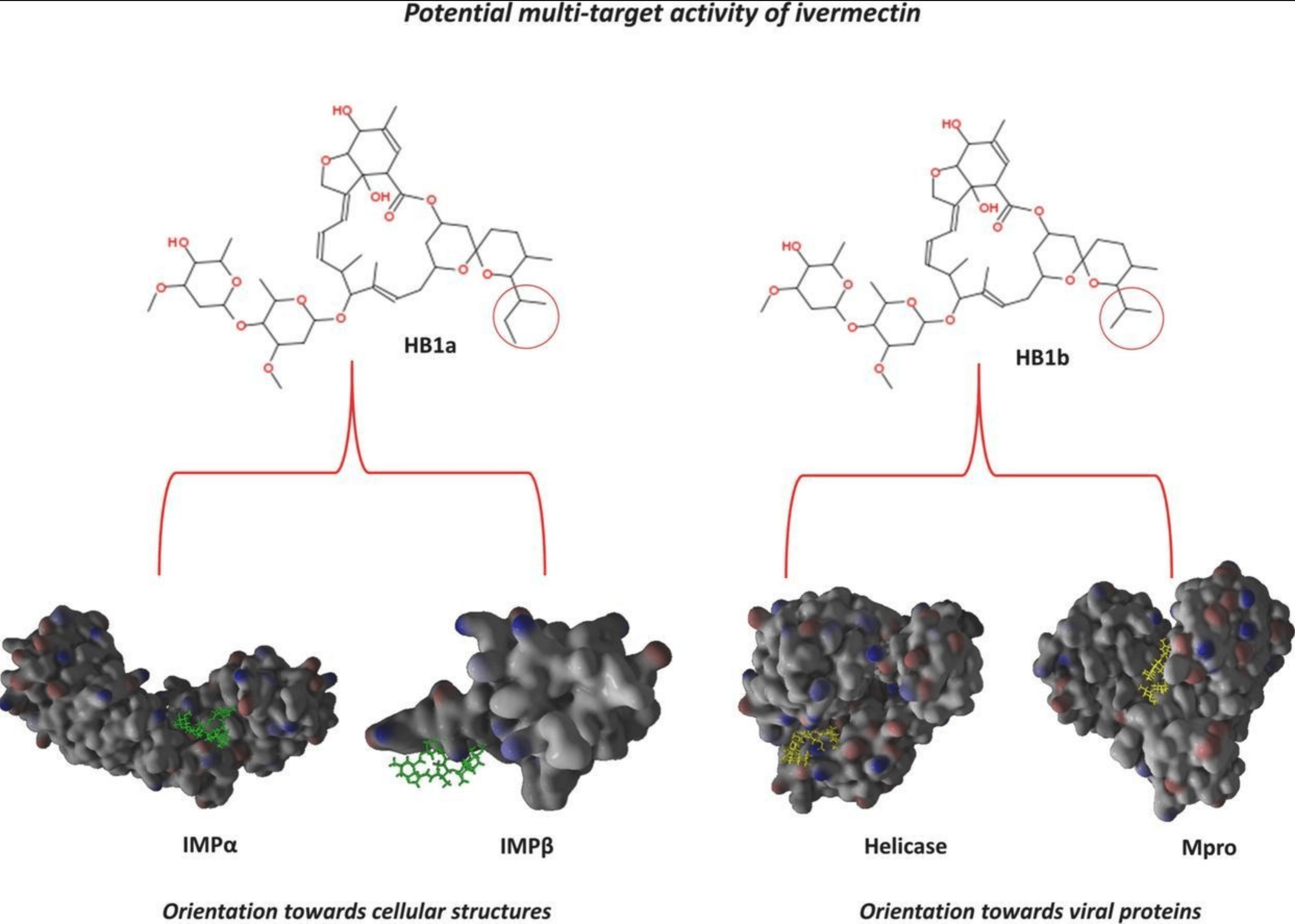
Comparative study of the interaction of ivermectin with proteins of interest associated with SARS-CoV-2: A computational and biophysical approach
et al., Biophysical Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677, Aug 2021
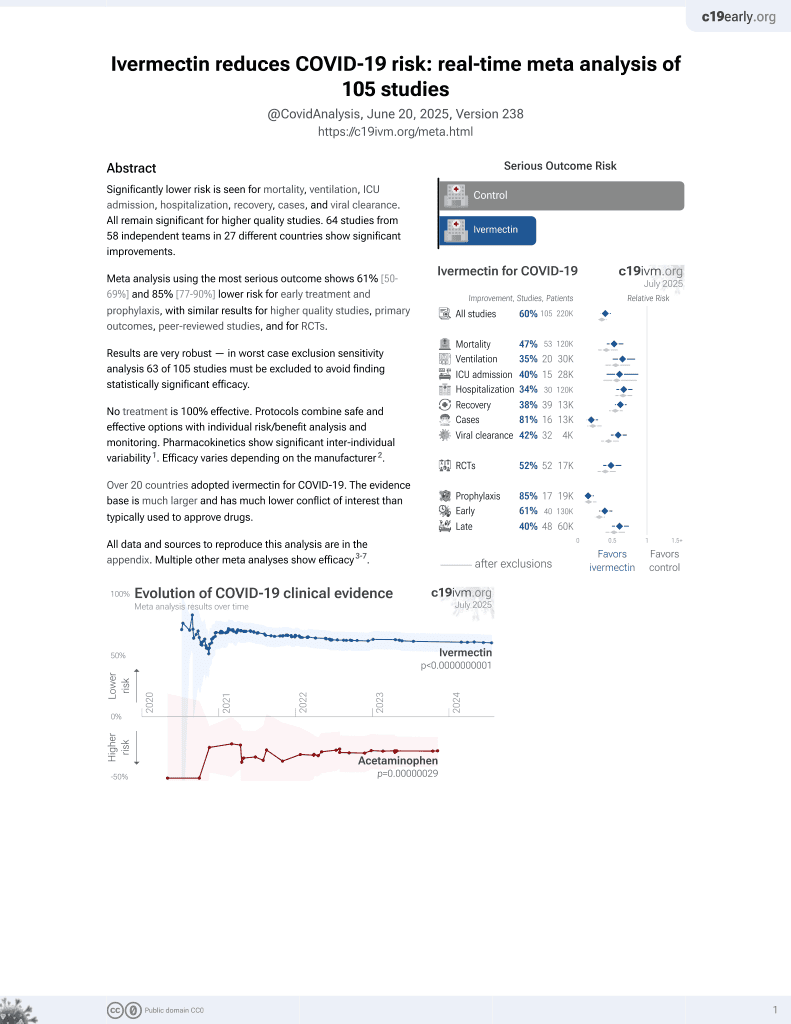
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In silico analysis of the components of ivermectin (avermectin-B1a and avermectin-B1b), suggesting different and complementary inhibitory activity of each component, with an affinity of avermectin-B1b for viral structures, and of avermectin-B1a for host structures.
74 preclinical studies support the efficacy of ivermectin for COVID-19:
Ivermectin, better known for antiparasitic activity, is a broad spectrum antiviral with activity against many viruses including H7N771, Dengue37,72,73 , HIV-173, Simian virus 4074, Zika37,75,76 , West Nile76, Yellow Fever77,78, Japanese encephalitis77, Chikungunya78, Semliki Forest virus78, Human papillomavirus57, Epstein-Barr57, BK Polyomavirus79, and Sindbis virus78.
Ivermectin inhibits importin-α/β-dependent nuclear import of viral proteins71,73,74,80 , shows spike-ACE2 disruption at 1nM with microfluidic diffusional sizing38, binds to glycan sites on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein preventing interaction with blood and epithelial cells and inhibiting hemagglutination41,81, shows dose-dependent inhibition of wildtype and omicron variants36, exhibits dose-dependent inhibition of lung injury61,66, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 via IMPase inhibition37, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 induced formation of fibrin clots resistant to degradation9, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro54, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RdRp activity28, may minimize viral myocarditis by inhibiting NF-κB/p65-mediated inflammation in macrophages60, may be beneficial for COVID-19 ARDS by blocking GSDMD and NET formation82, may interfere with SARS-CoV-2's immune evasion via ORF8 binding4, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by disrupting CD147 interaction83-86, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 attachment to lipid rafts via spike NTD binding2, shows protection against inflammation, cytokine storm, and mortality in an LPS mouse model sharing key pathological features of severe COVID-1959,87, may be beneficial in severe COVID-19 by binding IGF1 to inhibit the promotion of inflammation, fibrosis, and cell proliferation that leads to lung damage8, may minimize SARS-CoV-2 induced cardiac damage40,48, may counter immune evasion by inhibiting NSP15-TBK1/KPNA1 interaction and restoring IRF3 activation88, may disrupt SARS-CoV-2 N and ORF6 protein nuclear transport and their suppression of host interferon responses1, reduces TAZ/YAP nuclear import, relieving SARS-CoV-2-driven suppression of IRF3 and NF-κB antiviral pathways35, increases Bifidobacteria which play a key role in the immune system89, has immunomodulatory51 and anti-inflammatory70,90 properties, and has an extensive and very positive safety profile91.
1.
Gayozo et al., Binding affinities analysis of ivermectin, nucleocapsid and ORF6 proteins of SARS-CoV-2 to human importins α isoforms: A computational approach, Biotecnia, doi:10.18633/biotecnia.v27.2485.
2.
Lefebvre et al., Characterization and Fluctuations of an Ivermectin Binding Site at the Lipid Raft Interface of the N-Terminal Domain (NTD) of the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16121836.
3.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
4.
Bagheri-Far et al., Non-spike protein inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by natural products through the key mediator protein ORF8, Molecular Biology Research Communications, doi:10.22099/mbrc.2024.50245.2001.
5.
de Oliveira Só et al., In Silico Comparative Analysis of Ivermectin and Nirmatrelvir Inhibitors Interacting with the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202404.1825.v1.
6.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
7.
Oranu et al., Validation of the binding affinities and stabilities of ivermectin and moxidectin against SARS-CoV-2 receptors using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation, GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.30574/gscbps.2024.26.1.0030.
8.
Zhao et al., Identification of the shared gene signatures between pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension using bioinformatics analysis, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1197752.
9.
Vottero et al., Computational Prediction of the Interaction of Ivermectin with Fibrinogen, Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms241411449.
10.
Chellasamy et al., Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors, Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277.
11.
Umar et al., Inhibitory potentials of ivermectin, nafamostat, and camostat on spike protein and some nonstructural proteins of SARS-CoV-2: Virtual screening approach, Jurnal Teknologi Laboratorium, doi:10.29238/teknolabjournal.v11i1.344.
12.
Alvarado et al., Interaction of the New Inhibitor Paxlovid (PF-07321332) and Ivermectin With the Monomer of the Main Protease SARS-CoV-2: A Volumetric Study Based on Molecular Dynamics, Elastic Networks, Classical Thermodynamics and SPT, Computational Biology and Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2022.107692.
13.
Aminpour et al., In Silico Analysis of the Multi-Targeted Mode of Action of Ivermectin and Related Compounds, Computation, doi:10.3390/computation10040051.
14.
Parvez et al., Insights from a computational analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Host–pathogen interaction, pathogenicity, and possible drug therapeutics, Immunity, Inflammation and Disease, doi:10.1002/iid3.639.
15.
Francés-Monerris et al., Microscopic interactions between ivermectin and key human and viral proteins involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, doi:10.1039/D1CP02967C.
16.
González-Paz et al., Comparative study of the interaction of ivermectin with proteins of interest associated with SARS-CoV-2: A computational and biophysical approach, Biophysical Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677.
17.
González-Paz (B) et al., Structural Deformability Induced in Proteins of Potential Interest Associated with COVID-19 by binding of Homologues present in Ivermectin: Comparative Study Based in Elastic Networks Models, Journal of Molecular Liquids, doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284.
18.
Rana et al., A Computational Study of Ivermectin and Doxycycline Combination Drug Against SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-755838/v1.
19.
Muthusamy et al., Virtual Screening Reveals Potential Anti-Parasitic Drugs Inhibiting the Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein, Journal of Virology & Antiviral Research, www.scitechnol.com/abstract/virtual-screening-reveals-potential-antiparasitic-drugs-inhibiting-the-receptor-binding-domain-of-sarscov2-spike-protein-16398.html.
20.
Qureshi et al., Mechanistic insights into the inhibitory activity of FDA approved ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2: old drug with new implications, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1906750.
21.
Schöning et al., Highly-transmissible Variants of SARS-CoV-2 May Be More Susceptible to Drug Therapy Than Wild Type Strains, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-379291/v1.
22.
Bello et al., Elucidation of the inhibitory activity of ivermectin with host nuclear importin α and several SARS-CoV-2 targets, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1911857.
23.
Udofia et al., In silico studies of selected multi-drug targeting against 3CLpro and nsp12 RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase proteins of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV, Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics, doi:10.1007/s13721-021-00299-2.
24.
Choudhury et al., Exploring the binding efficacy of ivermectin against the key proteins of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: an in silico approach, Future Medicine, doi:10.2217/fvl-2020-0342.
25.
Kern et al., Modeling of SARS-CoV-2 Treatment Effects for Informed Drug Repurposing, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.625678.
26.
Saha et al., The Binding mechanism of ivermectin and levosalbutamol with spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, Structural Chemistry, doi:10.1007/s11224-021-01776-0.
27.
Eweas et al., Molecular Docking Reveals Ivermectin and Remdesivir as Potential Repurposed Drugs Against SARS-CoV-2, Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.592908.
28.
Parvez (B) et al., Prediction of potential inhibitors for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 using comprehensive drug repurposing and molecular docking approach, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.098.
29.
Francés-Monerris (B) et al., Has Ivermectin Virus-Directed Effects against SARS-CoV-2? Rationalizing the Action of a Potential Multitarget Antiviral Agent, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12782258.v1.
30.
Kalhor et al., Repurposing of the approved small molecule drugs in order to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 S protein and human ACE2 interaction through virtual screening approaches, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1824816.
31.
Swargiary, A., Ivermectin as a promising RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor and a therapeutic drug against SARS-CoV2: Evidence from in silico studies, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-73308/v1.
32.
Maurya, D., A Combination of Ivermectin and Doxycycline Possibly Blocks the Viral Entry and Modulate the Innate Immune Response in COVID-19 Patients, American Chemical Society (ACS), doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12630539.v1.
33.
Lehrer et al., Ivermectin Docks to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-binding Domain Attached to ACE2, In Vivo, 34:5, 3023-3026, doi:10.21873/invivo.12134.
34.
Suravajhala et al., Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin with COVID-19 Proteins, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v3.
35.
Kofler et al., M-Motif, a potential non-conventional NLS in YAP/TAZ and other cellular and viral proteins that inhibits classic protein import, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2025.112105.
36.
Shahin et al., The selective effect of Ivermectin on different human coronaviruses; in-vitro study, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4180797/v1.
37.
Jitobaom et al., Identification of inositol monophosphatase as a broad‐spectrum antiviral target of ivermectin, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29552.
38.
Fauquet et al., Microfluidic Diffusion Sizing Applied to the Study of Natural Products and Extracts That Modulate the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD/ACE2 Interaction, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28248072.
39.
García-Aguilar et al., In Vitro Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Ivermectin Interaction, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242216392.
40.
Liu et al., SARS-CoV-2 viral genes Nsp6, Nsp8, and M compromise cellular ATP levels to impair survival and function of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, Stem Cell Research & Therapy, doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03485-3.
41.
Boschi et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induces Hemagglutination: Implications for COVID-19 Morbidities and Therapeutics and for Vaccine Adverse Effects, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.11.24.517882.
42.
De Forni et al., Synergistic drug combinations designed to fully suppress SARS-CoV-2 in the lung of COVID-19 patients, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0276751.
43.
Saha (B) et al., Manipulation of Spray-Drying Conditions to Develop an Inhalable Ivermectin Dry Powder, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14071432.
44.
Jitobaom (B) et al., Synergistic anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of repurposed anti-parasitic drug combinations, BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology, doi:10.1186/s40360-022-00580-8.
45.
Croci et al., Liposomal Systems as Nanocarriers for the Antiviral Agent Ivermectin, International Journal of Biomaterials, doi:10.1155/2016/8043983.
46.
Zheng et al., Red blood cell-hitchhiking mediated pulmonary delivery of ivermectin: Effects of nanoparticle properties, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121719.
47.
Delandre et al., Antiviral Activity of Repurposing Ivermectin against a Panel of 30 Clinical SARS-CoV-2 Strains Belonging to 14 Variants, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15040445.
48.
Liu (B) et al., Genome-wide analyses reveal the detrimental impacts of SARS-CoV-2 viral gene Orf9c on human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, Stem Cell Reports, doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.01.014.
49.
Segatori et al., Effect of Ivermectin and Atorvastatin on Nuclear Localization of Importin Alpha and Drug Target Expression Profiling in Host Cells from Nasopharyngeal Swabs of SARS-CoV-2- Positive Patients, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13102084.
50.
Jitobaom (C) et al., Favipiravir and Ivermectin Showed in Vitro Synergistic Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-941811/v1.
51.
Munson et al., Niclosamide and ivermectin modulate caspase-1 activity and proinflammatory cytokine secretion in a monocytic cell line, British Society For Nanomedicine Early Career Researcher Summer Meeting, 2021, web.archive.org/web/20230401070026/https://michealmunson.github.io/COVID.pdf.
52.
Mountain Valley MD, Mountain Valley MD Receives Successful Results From BSL-4 COVID-19 Clearance Trial on Three Variants Tested With Ivectosol™, 5/18, www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2021/05/18/2231755/0/en/Mountain-Valley-MD-Receives-Successful-Results-From-BSL-4-COVID-19-Clearance-Trial-on-Three-Variants-Tested-With-Ivectosol.html.
53.
Yesilbag et al., Ivermectin also inhibits the replication of bovine respiratory viruses (BRSV, BPIV-3, BoHV-1, BCoV and BVDV) in vitro, Virus Research, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198384.
54.
Mody et al., Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents, Communications Biology, doi:10.1038/s42003-020-01577-x.
55.
Jeffreys et al., Remdesivir-ivermectin combination displays synergistic interaction with improved in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2022.106542.
56.
Surnar et al., Clinically Approved Antiviral Drug in an Orally Administrable Nanoparticle for COVID-19, ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci., doi:10.1021/acsptsci.0c00179.
57.
Li et al., Quantitative proteomics reveals a broad-spectrum antiviral property of ivermectin, benefiting for COVID-19 treatment, J. Cellular Physiology, doi:10.1002/jcp.30055.
58.
Caly et al., The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787.
59.
Zhang et al., Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice, Inflammation Research, doi:10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8.
60.
Gao et al., Ivermectin ameliorates acute myocarditis via the inhibition of importin-mediated nuclear translocation of NF-κB/p65, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112073.
61.
Abd-Elmawla et al., Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome by ivermectin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis, Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B, doi:10.1631/jzus.B2200385.
62.
Uematsu et al., Prophylactic administration of ivermectin attenuates SARS-CoV-2 induced disease in a Syrian Hamster Model, The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-023-00623-0.
63.
Albariqi et al., Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Inhaled Ivermectin in Mice as a Potential COVID-19 Treatment, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121688.
64.
Errecalde et al., Safety and Pharmacokinetic Assessments of a Novel Ivermectin Nasal Spray Formulation in a Pig Model, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2021.01.017.
65.
Madrid et al., Safety of oral administration of high doses of ivermectin by means of biocompatible polyelectrolytes formulation, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05820.
66.
Ma et al., Ivermectin contributes to attenuating the severity of acute lung injury in mice, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113706.
67.
de Melo et al., Attenuation of clinical and immunological outcomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection by ivermectin, EMBO Mol. Med., doi:10.15252/emmm.202114122.
68.
Arévalo et al., Ivermectin reduces in vivo coronavirus infection in a mouse experimental model, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-86679-0.
69.
Chaccour et al., Nebulized ivermectin for COVID-19 and other respiratory diseases, a proof of concept, dose-ranging study in rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-74084-y.
70.
Yan et al., Anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin in mouse model of allergic asthma, Inflammation Research, doi:10.1007/s00011-011-0307-8.
71.
Götz et al., Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/srep23138.
72.
Tay et al., Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1–4 non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002.
73.
Wagstaff et al., Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin α/β-mediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus, Biochemical Journal, doi:10.1042/BJ20120150.
74.
Wagstaff (B) et al., An AlphaScreen®-Based Assay for High-Throughput Screening for Specific Inhibitors of Nuclear Import, SLAS Discovery, doi:10.1177/1087057110390360.
75.
Barrows et al., A Screen of FDA-Approved Drugs for Inhibitors of Zika Virus Infection, Cell Host & Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2016.07.004.
76.
Yang et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760.
77.
Mastrangelo et al., Ivermectin is a potent inhibitor of flavivirus replication specifically targeting NS3 helicase activity: new prospects for an old drug, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dks147.
78.
Varghese et al., Discovery of berberine, abamectin and ivermectin as antivirals against chikungunya and other alphaviruses, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.12.012.
79.
Bennett et al., Role of a nuclear localization signal on the minor capsid Proteins VP2 and VP3 in BKPyV nuclear entry, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2014.10.013.
80.
Kosyna et al., The importin α/β-specific inhibitor Ivermectin affects HIF-dependent hypoxia response pathways, Biological Chemistry, doi:10.1515/hsz-2015-0171.
81.
Scheim et al., Sialylated Glycan Bindings from SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Blood and Endothelial Cells Govern the Severe Morbidities of COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242317039.
82.
Liu (C) et al., Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and immune regulation: insights into pathobiology and therapeutic implications of transfusion-related acute lung injury, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021.
83.
Shouman et al., SARS-CoV-2-associated lymphopenia: possible mechanisms and the role of CD147, Cell Communication and Signaling, doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01718-3.
84.
Scheim (B), D., Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-Threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-Mediated Vascular Occlusion, SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3636557.
85.
Scheim (C), D., From Cold to Killer: How SARS-CoV-2 Evolved without Hemagglutinin Esterase to Agglutinate and Then Clot Blood Cells, Center for Open Science, doi:10.31219/osf.io/sgdj2.
86.
Behl et al., CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target, Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072.
87.
DiNicolantonio et al., Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350.
88.
Mothae et al., SARS-CoV-2 host-pathogen interactome: insights into more players during pathogenesis, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2025.110607.
89.
Hazan et al., Treatment with Ivermectin Increases the Population of Bifidobacterium in the Gut, ACG 2023, acg2023posters.eventscribe.net/posterspeakers.asp.
González-Paz et al., 19 Aug 2021, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677",
"ISSN": [
"0301-4622"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677",
"alternative-id": [
"S0301462221001599"
],
"article-number": "106677",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Comparative study of the interaction of ivermectin with proteins of interest associated with SARS-CoV-2: A computational and biophysical approach"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Biophysical Chemistry"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "González-Paz",
"given": "Lenin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hurtado-León",
"given": "María Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lossada",
"given": "Carla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernández-Materán",
"given": "Francelys V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vera-Villalobos",
"given": "Joan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loroño",
"given": "Marcos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paz",
"given": "J.L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffreys",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alvarado",
"given": "Ysaias J.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biophysical Chemistry",
"container-title-short": "Biophysical Chemistry",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-19T05:22:24Z",
"timestamp": 1629350544000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-11T07:56:04Z",
"timestamp": 1678521364000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-25T00:24:48Z",
"timestamp": 1706142288626
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 12,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1635724800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1635724800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1635724800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1635724800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1635724800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1635724800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0301462221001599?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0301462221001599?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "106677",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"article-title": "A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"issue": "7816",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0005",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Promising inhibitors targeting M pro: an ideal strategy for anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug discovery",
"author": "Chen",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Therapy",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0010",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fchem.2021.622898",
"article-title": "Structural basis of potential inhibitors targeting SARS-CoV-2 main protease",
"author": "Mengist",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "622898",
"journal-title": "Front. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0015",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117627",
"article-title": "Virtual screening and repurposing of FDA approved drugs against COVID-19 main protease",
"author": "Kandeel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117627",
"journal-title": "Life sciences",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0020",
"volume": "251",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Drug repurposing studies targeting SARS-CoV-2: an ensemble docking approach on drug target 3C-like protease (3CLpro)",
"author": "Koulgi",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0025",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Ivermectin as pre-exposure prophylaxis for COVID-19 among healthcare providers in a selected tertiary hospital in Dhaka – an observational study",
"author": "Alam",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Med. Health Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0030",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-020-01577-x",
"article-title": "Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents",
"author": "Mody",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Commun. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0035",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z",
"article-title": "Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen",
"author": "Heidary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "593",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J. Antibiot.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0040",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/scipharm88030036",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2: an old-fashioned dog with a new trick–a literature review",
"author": "Mudatsir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Sci. Pharm.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0045",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dks147",
"article-title": "Ivermectin is a potent inhibitor of flavivirus replication specifically targeting NS3 helicase activity: new prospects for an old drug",
"author": "Mastrangelo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1884",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J. Antimicrob. Chemother.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0050",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphy.2020.587606",
"article-title": "Can non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs affect the interaction between receptor binding domain of SARS-COV-2 spike and the human ACE2 receptor? A computational biophysical study",
"author": "González-Paz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "526",
"journal-title": "Front. Phys.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0055",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.014",
"article-title": "MD simulations and FRET reveal an environment-sensitive conformational plasticity of importin-β",
"author": "Halder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "277",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Biophys. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0060",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.05.006",
"article-title": "Contribution of the residue at position 4 within classical nuclear localization signals to modulating interaction with importins and nuclear targeting",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1114",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0065",
"volume": "1865",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-58316-9",
"article-title": "Comparative study of the interactions between fungal transcription factor nuclear localization sequences with mammalian and fungal importin-alpha",
"author": "Bernardes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1458",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0070",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BST20200568",
"article-title": "Antivirals that target the host IMPα/β1-virus interface",
"author": "Martin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "281",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Soc. Trans.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0075",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cplett.2020.138193",
"article-title": "An in-silico study on selected organosulfur compounds as potential drugs for SARS-CoV-2 infection via binding multiple drug targets",
"author": "Thurakkal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "138193",
"journal-title": "Chem. Phys. Lett.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0080",
"volume": "763",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/computation8030077",
"article-title": "Exploring the SARS-CoV-2 proteome in the search of potential inhibitors via structure-based pharmacophore modeling/docking approach",
"author": "Culletta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Computation",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0085",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imu.2020.100484",
"article-title": "Plausible mechanisms explaining the role of cucurbitacins as potential therapeutic drugs against coronavirus 2019",
"author": "Kapoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100484",
"journal-title": "Informatics Med. Unlocked",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0090",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Prospecting for Cressa cretica to treat COVID-19 via in silico molecular docking models of the SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Shah",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0095",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.12.037",
"article-title": "Essential oils as an effective alternative for the treatment of COVID-19: molecular interaction analysis of protease (Mpro) with pharmacokinetics and toxicological properties",
"author": "Panikar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Publ. Health.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129178",
"article-title": "Exploration of inhibitory action of Azo imidazole derivatives against COVID-19 main protease (Mpro): a computational study",
"author": "Chhetri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129178",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Struct.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0105",
"volume": "1224",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcab.2021.101924",
"article-title": "Molecular dynamics analysis of phytochemicals from Ageratina adenophora against COVID-19 main protease (Mpro) and human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)",
"author": "Neupane",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101924",
"journal-title": "Biocatalysis Agric. Biotechnol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0110",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkv462",
"article-title": "PockDrug-server: a new web server for predicting pocket druggability on holo and apo proteins",
"author": "Hussein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W436",
"issue": "W1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0115",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173430",
"article-title": "In silico molecular docking analysis for repurposing therapeutics against multiple proteins from SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Deshpande",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "173430",
"issue": "886",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0120",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BSR20201256",
"article-title": "Glecaprevir and Maraviroc are high-affinity inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: possible implication in COVID-19 therapy",
"author": "Shamsi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Biosci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0125",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1134/S0026893313040122",
"article-title": "Search for invisible binding sites of low-molecular-weight compounds on protein molecules and prediction of inhibitory activity",
"author": "Popov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "592",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0130",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkp253",
"article-title": "IC50-to-Ki: a web-based tool for converting IC50 to Ki values for inhibitors of enzyme activity and ligand binding",
"author": "Cer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W441",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0135",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2010470117",
"article-title": "Identify potent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors via accelerated free energy perturbation-based virtual screening of existing drugs",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27381",
"issue": "44",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0140",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ed080p214",
"article-title": "An intuitive look at the relationship of Ki and IC50: a more general use for the Dixon plot",
"author": "Burlingham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "214",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Educ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0145",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13102818.2020.1775118",
"article-title": "Ivermectin as a potential COVID-19 treatment from the pharmacokinetic point of view: antiviral levels are not likely attainable with known dosing regimens",
"author": "Momekov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "469",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0150",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2142/biophysico.BSJ-2020013",
"article-title": "myPresto/omegagene 2020: a molecular dynamics simulation engine for virtual-system coupled sampling",
"author": "Kasahara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "140",
"journal-title": "Biophys. Physicobiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0155",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A bioinformatics study of structural perturbation of 3CL-protease and the HR2-domain of SARS-CoV-2 induced by synergistic interaction with ivermectins",
"author": "González-Paz",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0160",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gks478",
"article-title": "NMSim web server: integrated approach for normal mode-based geometric simulations of biologically relevant conformational transitions in proteins",
"author": "Krüger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W310",
"issue": "Web Server issue",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0165",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkw390",
"article-title": "CSM-lig: a web server for assessing and comparing protein-small molecule affinities",
"author": "Pires",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W557",
"issue": "W1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0170",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkaa397",
"article-title": "webPSN v2. 0: a webserver to infer fingerprints of structural communication in biomacromolecules",
"author": "Felline",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W94",
"issue": "W1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0175",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Binding mechanism and structural insights into the identified protein target of COVID-19 and importin-α with in-vitro effective drug ivermectin",
"author": "Sen Gupta",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130733",
"article-title": "DFT, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation studies on some newly introduced natural products for their potential use against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Erdogan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "130733",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Struct.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0185",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.24703",
"article-title": "SMPBS: Web server for computing biomolecular electrostatics using finite element solvers of size modified Poisson-Boltzmann equation",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "541",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0190",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Repurposing of the approved small molecule drugs in order to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 S protein and human ACE2 interaction through virtual screening approaches",
"author": "Kalhor",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0195",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Mechanistic insights into the inhibitory activity of FDA approved ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2: old drug with new implications",
"author": "Qureshi",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0200",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Repurposing approved drugs as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 S-protein from molecular modeling and virtual screening",
"author": "de Oliveira",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0205",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Network analysis, sequence and structure dynamics of key proteins of coronavirus and human host, and molecular docking of selected phytochemicals of nine medicinal plants",
"author": "Fatoki",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0210",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bpj.2018.01.002",
"article-title": "HullRad: fast calculations of folded and disordered protein and nucleic acid hydrodynamic properties",
"author": "Fleming",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "856",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Biophys. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0215",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Drug repurposing for coronavirus (COVID-19): in silico screening of known drugs against coronavirus 3CL hydrolase and protease enzymes",
"author": "Elmezayen",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0220",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12551-016-0247-1",
"article-title": "Software for molecular docking: a review",
"author": "Pagadala",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Biophys. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0225",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "An in-silico analysis of ivermectin interaction with potential SARS-CoV-2 targets and host nuclear importin α",
"author": "Azam",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0230",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jksus.2020.101315",
"article-title": "Computational investigations of three main drugs and their comparison with synthesized compounds as potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro): DFT, QSAR, molecular docking, and in silico toxicity analysis",
"author": "Mohapatra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101315",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. King Saud Univ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0235",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/D0RA06379G",
"article-title": "Ilimaquinone (marine sponge metabolite) as a novel inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 key target proteins in comparison with suggested COVID-19 drugs: designing, docking and molecular dynamics simulation study",
"author": "Surti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37707",
"journal-title": "RSC Adv.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0240",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/D0NJ03708G",
"article-title": "Two antioxidant 2, 5-disubstituted-1, 3, 4-oxadiazoles (CoViTris2020 and ChloViD2020): successful repurposing against COVID-19 as the first potent multitarget anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs",
"author": "Rabie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "761",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "New J. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0245",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Step toward repurposing drug discovery for COVID-19 therapeutics through in silico approach",
"author": "Marak",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Drug Dev. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0250",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparative docking of SARS-CoV-2 receptors antagonists from repurposing drugs",
"author": "Oliveira",
"journal-title": "ChemRxiv Prepr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0255",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.33263/LIANBS102.23312338",
"article-title": "Repurposing of anthelmintic drugs against SARS-CoV-2 (Mpro and RdRp): novel disease, older therapeutics",
"author": "Cheke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2331",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Letters in Applied NanoBioScience",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0260",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Molecular dynamics simulation perception study of the binding affinity performance for main protease of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Sahu",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0265",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/16583655.2020.1848049",
"article-title": "Molecular docking and dynamic simulations of some medicinal plants compounds against SARS-CoV-2: an in silico study",
"author": "Adejoro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1563",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Taibah Univ. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0270",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00905",
"article-title": "Highly flexible ligand docking: benchmarking of the DockThor program on the LEADS-PEP protein–peptide data set",
"author": "Santos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "667",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inf. Model.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0275",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-84700-0",
"article-title": "Drug design and repurposing with DockThor-VS web server: virtual screening focusing on SARS-CoV-2 therapeutic targets and their non-synonym variants",
"author": "Guedes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5543",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0280",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa579",
"article-title": "Webina: an open-source library and web app that runs AutoDock Vina entirely in the web browser",
"author": "Kochnev",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4513",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0285",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0511",
"article-title": "DINC 2.0: a new protein–peptide docking webserver using an incremental approach",
"author": "Antunes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e55",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0290",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "DINC: a new AutoDock-based protocol for docking large ligands",
"author": "Dhanik",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Struct. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0295",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gky439",
"article-title": "COACH-D: improved protein–ligand binding sites prediction with refined ligand-binding poses through molecular docking",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W438",
"issue": "W1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0300",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms20143558",
"article-title": "Can we still trust docking results? An extension of the applicability of DockBench on PDBbind database",
"author": "Bolcato",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3558",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0305",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb3405",
"article-title": "Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved α-ketoamide inhibitors",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "409",
"issue": "6489",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0310",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Repurposing Ivermectin to inhibit the activity of SARS CoV2 helicase: possible implications for COVID 19 therapeutics",
"author": "Khater",
"journal-title": "OSF Prepr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0315",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0378-4347(87)80248-7",
"article-title": "Determination of 22,23-dihydroavermectin B1a in dog plasma using solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography",
"author": "Kojima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "326",
"journal-title": "J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0320",
"volume": "413",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"article-title": "The metabolism of avermectin-H2B1a and-H2B1b by pig liver microsomes",
"author": "Chiu",
"first-page": "464",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Drug Metab. Dispos.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0325",
"volume": "12",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"article-title": "The metabolism of avermectins B1a, H2B1a, and H2B1b by liver microsomes",
"author": "Miwa",
"first-page": "268",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Drug Metab. Dispos.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0330",
"volume": "10",
"year": "1982"
},
{
"article-title": "Metabolic disposition of ivermectin in tissues of cattle, sheep, and rats",
"author": "Chiu",
"first-page": "590",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Drug Metab. Dispos.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0335",
"volume": "14",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00480169.1981.34836",
"article-title": "An introduction to the avermectins",
"author": "Campbell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "174",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "N. Z. Vet. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0340",
"volume": "29",
"year": "1981"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.6308762",
"article-title": "Ivermectin: a potent new antiparasitic agent",
"author": "Campbell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "823",
"issue": "4613",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0345",
"volume": "221",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104805",
"article-title": "Ivermectin and COVID-19: a report in antiviral research, widespread interest, an FDA warning, two letters to the editor and the authors’ responses",
"author": "Bray",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104805",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0350",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/138920112800399095",
"article-title": "History of avermectin and ivermectin, with notes on the history of other macrocyclic lactone antiparasitic agents",
"author": "Campbell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "853",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0355",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s002280050131",
"article-title": "Ivermectin distribution in the plasma and tissues of patients infected with Onchocerca volvulus",
"author": "Baraka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "407",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0360",
"volume": "50",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.14476",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetic considerations on the repurposing of ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Peña-Silva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1589",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0365",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acscombsci.0c00058",
"article-title": "Targeting the dimerization of the main protease of coronaviruses: a potential broad-spectrum therapeutic strategy",
"author": "Goyal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "297",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "ACS Comb. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0370",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2008.01.023",
"article-title": "Correlation between dissociation and catalysis of SARS-CoV main protease",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "34",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0375",
"volume": "472",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02680-07",
"article-title": "Mechanism for controlling the dimer-monomer switch and coupling dimerization to catalysis of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3C-like protease",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4620",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0380",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444913001315",
"article-title": "Mechanism for controlling the monomer–dimer conversion of SARS coronavirus main protease",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "747",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0385",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "A combination of ivermectin and doxycycline possibly blocks the viral entry and modulate the innate immune response in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Maurya",
"journal-title": "ChemRxiv Prepr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0390",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abe0751",
"article-title": "Structure and inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease reveal strategy for developing dual inhibitors against Mpro and cathepsin L",
"author": "Sacco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "50",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0395",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"article-title": "The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0400",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pt.2017.02.004",
"article-title": "Ivermectin – old drug, new tricks?",
"author": "Laing",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "463",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Trends Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0405",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells9122654",
"article-title": "The role of protein disorder in nuclear transport and in its subversion by viruses",
"author": "Wubben",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2654",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0410",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1316039111",
"article-title": "Molecular-crowding effects on single-molecule RNA folding/unfolding thermodynamics and kinetics",
"author": "Dupuis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8464",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0415",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b01239",
"article-title": "Impact of molecular crowding on translational mobility and conformational properties of biological macromolecules",
"author": "Junker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4477",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "J. Phys. Chem. B",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0420",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13167-020-00209-y",
"article-title": "Anti-parasite drug ivermectin can suppress ovarian cancer by regulating lncRNA-EIF4A3-mRNA axes",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "289",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "EPMA Journal",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0425",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.1889",
"article-title": "The approved dose of ivermectin alone is not the ideal dose for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Schmith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "762",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacolo. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0430",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/fcp.12644",
"article-title": "A systematic review of experimental evidence for antiviral effects of ivermectin and an in-silico analysis of ivermectin’s possible mode of action against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Kinobe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "260",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0435",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/1.3694268",
"article-title": "Dimethyl sulfoxide induced structural transformations and non-monotonic concentration dependence of conformational fluctuation around active site of lysozyme",
"author": "Roy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "115103",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Phys.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0440",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c03716",
"article-title": "Interdiction of protein folding for therapeutic drug development in SARS CoV-2",
"author": "Bergasa-Caceres",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8201",
"issue": "38",
"journal-title": "J. Phys. Chem. B",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0445",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sbi.2020.10.024",
"article-title": "Protein-complex stability in cells and in vitro under crowded conditions",
"author": "Stadmiller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "183",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0450",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl-2020-0342",
"article-title": "Exploring the binding efficacy of ivermectin against the key proteins of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: an in silico approach",
"author": "Choudhury",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "277",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Futur. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0455",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.09.050",
"article-title": "Design, synthesis, characterization, computational study and in-vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of few novel 6-aryl substituted pyrimidine azo dyes",
"author": "Unnisa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8638",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Arab. J. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0460",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00397",
"article-title": "Prediction of drug–target binding kinetics by comparative binding energy analysis",
"author": "Ganotra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1134",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "ACS Med. Chem. Lett.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0465",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11064-019-02852-y",
"article-title": "The binding mechanisms and inhibitory effect of intravenous anesthetics on AChE in vitro and in vivo: kinetic analysis and molecular docking",
"author": "Işık",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2147",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Neurochem. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0470",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Targeting the 3CLpro and RdRp of SARS-CoV-2 with phytochemicals from medicinal plants of the Andean Region: molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations",
"author": "Mosquera-Yuqui",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0475",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Biflavonoids from Rhus succedanea as probable natural inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2: a molecular docking and molecular dynamics approach",
"author": "Lokhande",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0480",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Molecular docking and dynamics simulations reveal the potential of anti-HCV drugs to inhibit COVID-19 main protease",
"author": "Al-Karmalawy",
"first-page": "661230",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceutical Sciences",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0485",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/prot.10031",
"article-title": "Potential of mean force for protein–protein interaction studies",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "190",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0490",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-11-298",
"article-title": "An interaction-motif-based scoring function for protein-ligand docking",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Bioinformatics",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0495",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2020.592908",
"article-title": "Molecular docking reveals ivermectin and remdesivir as potential repurposed drugs against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Eweas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "592908",
"journal-title": "Front. Microbiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0500",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104699",
"article-title": "Pharmacoinformatics based elucidation and designing of potential inhibitors against Plasmodium falciparum to target importin α/β mediated nuclear importation",
"author": "Oany",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104699",
"journal-title": "Infect. Genet. Evol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0505",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Virtual repurposing of ursodeoxycholate and chenodeoxycholate as lead candidates against SARS-Cov2-envelope protein: a molecular dynamics investigation",
"author": "Yadav",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0510",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100860",
"article-title": "In silico structure modelling of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp13 helicase and Nsp14 and repurposing of FDA approved antiviral drugs as dual inhibitors",
"author": "Gurung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100860",
"journal-title": "Gene Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677_bb0515",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 103,
"references-count": 103,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0301462221001599"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Comparative study of the interaction of ivermectin with proteins of interest associated with SARS-CoV-2: A computational and biophysical approach",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "278"
}