The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation Post COVID-19 Infection and Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16223794, PROSPERO CRD42023469826, Nov 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
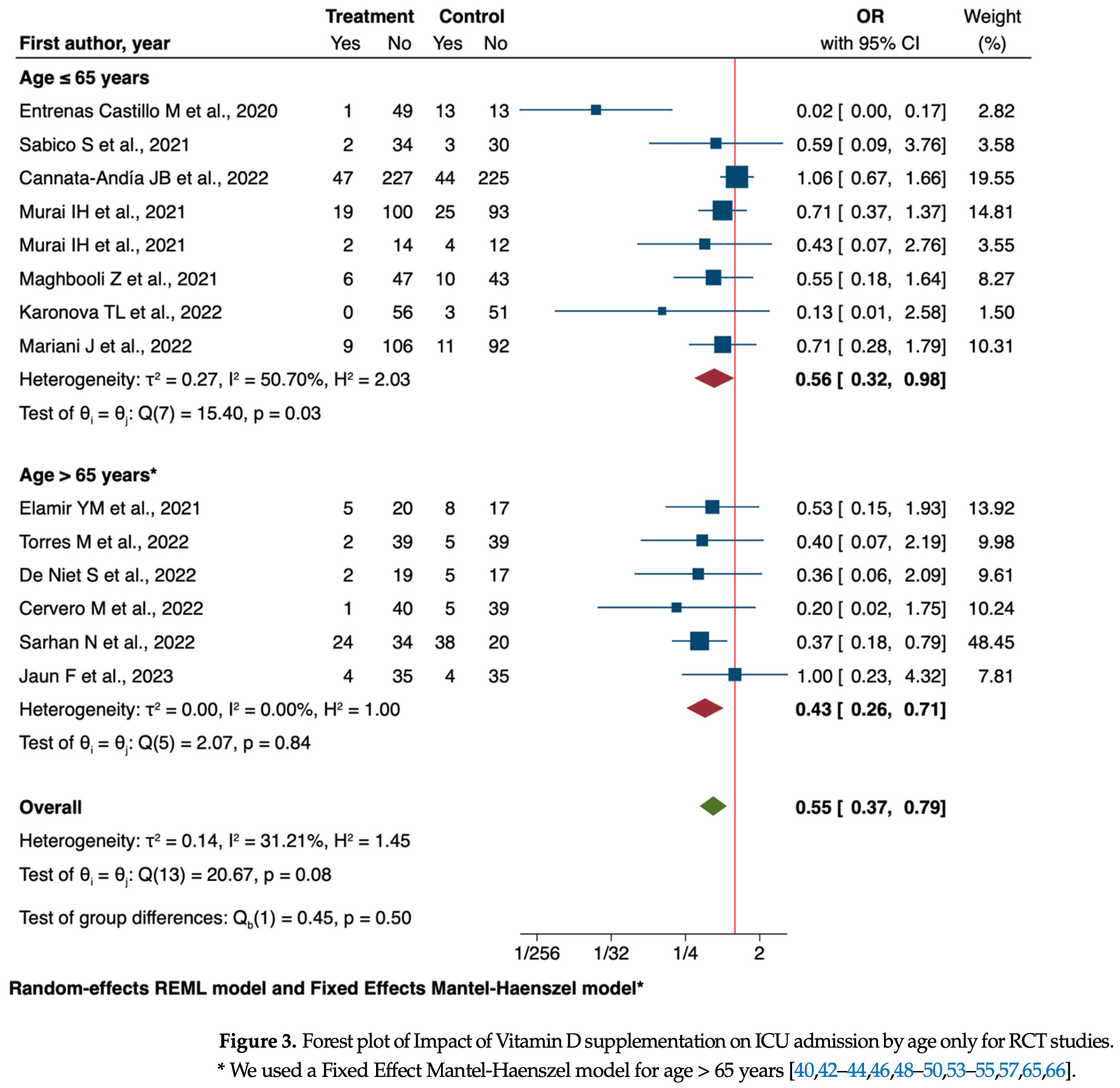
Meta analysis of 29 studies showing significantly lower ICU admission and intubation rates with vitamin D treatment in COVID-19 patients. Mortality was significantly reduced in observational studies but without statistical significance in RCTs. Subgroup analyses revealed more pronounced effects in older patients and severe COVID-19 cases. Authors include Murai et al. twice (the second study analyzes a subgroup of the same patients), and only include 29 studies from the current 72 studies (33 RCTs).
20 meta-analyses show significant improvements with vitamin D treatment for mortality1-14,
mechanical ventilation1,5,6,11,15-17 ,
ICU admission1,3,5,6,9,11,13,15-19 ,
hospitalization11,
severity2,4,5,10,20 , and
cases7,19,20 .
Currently there are 135 vitamin D treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 39% lower mortality [32‑45%], 17% lower ventilation [-5‑35%], 45% lower ICU admission [28‑57%], 22% lower hospitalization [13‑30%], and 17% fewer cases [9‑25%].
1.
Shah et al., Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? - a systematic review, QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040.
2.
Nikniaz et al., The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.34172/PS.2021.13.
3.
Hosseini et al., Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134.
4.
D’Ecclesiis et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396.
5.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
6.
Hariyanto et al., Vitamin D supplementation and Covid‐19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269.
7.
Begum et al., The Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Survival and Prevention: A Meta-analysis, Sudan Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.18502/sjms.v19i1.15776.
8.
Jamilian et al., The role of vitamin D in outcomes of critical care in COVID-19 patients: Evidence from an umbrella meta-analysis of interventional and observational studies, Public Health Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S1368980024000934.
9.
Sobczak et al., Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Severe COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16101402.
10.
Petrelli et al., Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883.
11.
Asla et al., Vitamin D on COVID-19 Patients During the Pandemic, 2022. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science Journal, doi:10.12944/CRNFSJ.11.1.3.
12.
Kow et al., The impact of vitamin D administration on mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01564-2.
13.
Zhang et al., The impact of supplementing vitamin D through different methods on the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1441847.
14.
Doustmohammadian et al., Impact of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme, doi:10.1016/j.nupar.2025.12.001.
15.
Meng et al., The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.09.008.
16.
Yang et al., Therapeutic effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 aggravation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1367686.
17.
Szarpak et al., Vitamin D supplementation to treat SARS-CoV-2 positive patients. Evidence from meta-analysis, Cardiology Journal, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2021.0122.
18.
Tentolouris et al., The effect of vitamin D supplementation on mortality and intensive care unit admission of COVID-19 patients. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3517.
Sartini et al., 5 Nov 2024, Italy, peer-reviewed, 9 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD42023469826.
Contact: sartini@unige.it (corresponding author), alessio.carbone@galliera.it, elisa.schinca@unige.it, gianluca.ottria@unige.it, martino.oliva@galliera.it, maria.luisa.cristina@galliera.it, lioa@unige.it, carolina.piccinini@libero.it, filippo.del.puente@galliera.it.
The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation Post COVID-19 Infection and Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16223794
Background: Vitamin D's role in COVID-19 management remains controversial. This metaanalysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, focusing on mortality, intensive care unit (ICU) admissions, intubation rates, and hospital length of stay (LOS). Methods: A systematic review of PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Cochrane, and Google Scholar databases was conducted. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and analytical studies investigating vitamin D supplementation in COVID-19 patients were included. The metaanalysis was performed using STATA MP 18.5, employing random-effect or fixed-effect models based on heterogeneity. Results: Twenty-nine studies (twenty-one RCTs, eight analytical) were analyzed. Vitamin D supplementation significantly reduced ICU admissions (OR = 0.55, 95% CI: 0.37 to 0.79) in RCTs and analytical studies (OR = 0.35, 95% CI: 0.18 to 0.66). Intubation rates were significantly reduced in RCTs (OR = 0.50, 95% CI: 0.27 to 0.92). Mortality reduction was significant in analytical studies (OR = 0.45, 95% CI: 0.24 to 0.86) but not in RCTs (OR = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.61 to 1.04). Subgroup analyses revealed more pronounced effects in older patients and severe COVID-19 cases. LOS showed a non-significant reduction (mean difference = -0.62 days, 95% CI: -1.41 to 0.18). Conclusions: This meta-analysis suggests potential benefits of vitamin D supplementation in COVID-19 patients, particularly in reducing ICU admissions. However, the evidence varies across outcomes and patient subgroups. Discrepancies between RCTs and analytical studies highlight the need for further large-scale, well-designed trials accounting for baseline vitamin D status, standardized supplementation protocols, and patient characteristics to inform clinical guidelines for vitamin D use in COVID-19 management.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www. mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu16223794/s1 . File S1: PRISMA Checklist (Reference [71] is cited in the supplementary materials). Figure S1 : Summary plot of the risk of bias for analytical studies (a) and RCT Studies (b). Table S1 : Characteristics of studies included in the meta-analysis. Table S2 : Characteristics of the study outcomes included in the meta-analysis. Table S3 : Risk ratio (RR) and 95% CI for all meta-analyses carried out (mortality, ICU admission, and intubation). Table S4 : Mean difference and 95% CI for all meta-analyses carried out (LOS).
References
Aiello, Lombardo, Baldelli, Exploring Vitamin D Synthesis and Function in Cardiovascular Health: A Narrative Review, Appl. Sci, doi:10.3390/app14114339
Alcala-Diaz, Limia-Perez, Gomez-Huelgas, Martin-Escalante, Cortes-Rodriguez et al., Calcifediol Treatment and Hospital Mortality Due to COVID-19: A Cohort Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061760
Annweiler, Beaudenon, Gautier, Gonsard, Boucher et al., High-dose versus standard-dose vitamin D supplementation in older adults with COVID-19 (COVIT-TRIAL): A multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled superiority trial, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003999
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubée, Legrand et al., Vitamin D Supplementation Associated to Better Survival in Hospitalized Frail Elderly COVID-19 Patients: The GERIA-COVID Quasi-Experimental Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377
Annweiler, Hanotte, Grandin De L'eprevier, Sabatier, Lafaie et al., Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: A quasi-experimental study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771
Argano, Mallaci Bocchio, Natoli, Scibetta, Lo Monaco et al., Protective Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19-Related Intensive Care Hospitalization and Mortality: Definitive Evidence from Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph16010130
Bignardi, De Andrade Castello, De Matos Aquino, Delfino, Is the vitamin D status of patients with COVID-19 associated with reduced mortality? A systematic review and meta-analysis, Arch. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.20945/2359-3997000000588
Bouillon, Marcocci, Carmeliet, Bikle, White et al., Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions, Endocr. Rev, doi:10.1210/er.2018-00126
Bover, Ruiz, Pilz, Dasilva, Díaz et al., Vitamin D Receptor and Interaction with DNA: From Physiology to Chronic Kidney Disease, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-32507-1_4
Bychinin, Klypa, Mandel, Yusubalieva, Baklaushev et al., Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on cellular immunity and inflammatory markers in COVID-19 patients admitted to the ICU, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-22045-y
Cannata-Andía, Díaz-Sottolano, Fernández, Palomo-Antequera, Herrero-Puente et al., A single-oral bolus of 100,000 IU of cholecalciferol at hospital admission did not improve outcomes in the COVID-19 disease: The COVID-VIT-D-a randomised multicentre international clinical trial, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-022-02290-8
Castillo, Entrenas Costa, Vaquero Barrios, Alcalá Díaz, López Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Cervero, López-Wolf, Casado, Novella-Mena, Ryan-Murua et al., Beneficial Effect of Short-Term Supplementation of High Dose of Vitamin D3 in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Multicenter, Single-Blinded, Prospective Randomized Pilot Clinical Trial, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.863587
Chiodini, Gatti, Soranna, Merlotti, Mingiano et al., Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.736665
Christakos, Deluca, Minireview, Vitamin D: Is there a role in extraskeletal health?, Endocrinology, doi:10.1210/en.2011-0243
Cutolo, Paolino, Smith, Evidences for a protective role of vitamin D in COVID-19, RMD Open, doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001454
Dawson-Hughes, Staten, Knowler, Nelson, Vickery et al., Intratrial Exposure to Vitamin D and New-Onset Diabetes Among Adults with Prediabetes: A Secondary Analysis From the Vitamin D and Type 2 Diabetes (D2d) Study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1765
De Niet, Trémège, Coffiner, Rousseau, Calmes et al., Positive Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14153048
Delvin, Souberbielle, Viard, Salle, Role of vitamin D in acquired immune and autoimmune diseases, Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci, doi:10.3109/10408363.2014.901291
Dilokpattanamongkol, Yan, Jayanama, Ngamjanyaporn, Sungkanuparph et al., Impact of vitamin D supplementation on the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 pneumonia patients: A single-center randomized controlled trial, BMC Complement. Med. Ther, doi:10.1186/s12906-024-04393-6
Domazet Bugarin, Dosenovic, Ilic, Delic, Saric et al., Vitamin D Supplementation and Clinical Outcomes in Severe COVID-19 Patients-Randomized Controlled Trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15051234
Dzik, Kaczor, Mechanisms of vitamin D on skeletal muscle function: Oxidative stress, energy metabolism and anabolic state, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol, doi:10.1007/s00421-019-04104-x
Elamir, Amir, Lim, Rana, Lopez et al., A randomized pilot study using calcitriol in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Bone, doi:10.1016/j.bone.2021.116175
Fernandes, Murai, Reis, Sales, Santos et al., Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on cytokines, chemokines, and growth factor in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab426
Fiore, De Vito, Bagella, Princic, Mariani et al., Effectiveness of Vitamin D Supplements among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: Results from a Monocentric Matched-Cohort Study, Healthcare, doi:10.3390/healthcare10050956
Gallagher, Vitamin D and respiratory infections, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30403-4
Gaudet, Plesa, Mogas, Jalaleddine, Hamid et al., Recent advances in vitamin D implications in chronic respiratory diseases, Respir. Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-022-02147-x
Giannini, Passeri, Tripepi, Sella, Fusaro et al., Effectiveness of In-Hospital Cholecalciferol Use on Clinical Outcomes in Comorbid COVID-19 Patients: A Hypothesis-Generating Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13010219
Girgis, Clifton-Bligh, Hamrick, Holick, Gunton, The roles of vitamin D in skeletal muscle: Form, function, and metabolism, Endocr. Rev, doi:10.1210/er.2012-1012
Güven, Gültekin, The effect of high-dose parenteral vitamin D3 on COVID-19-related inhospital mortality in critical COVID-19 patients during intensive care unit admission: An observational cohort study, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-021-00984-5
Haussler, Haussler, Bartik, Whitfield, Hsieh et al., Vitamin D receptor: Molecular signaling and actions of nutritional ligands in disease prevention, Nutr. Rev, doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2008.00093.x
Jaun, Boesing, Luethi-Corridori, Abig, Bloch et al., Effect of Single High Dose Vitamin D Substitution in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with Vitamin D Deficiency on Length of Hospital Stay, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines11051277
Jevalikar, Mithal, Singh, Sharma, Farooqui et al., Lack of association of baseline 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with disease severity and mortality in Indian patients hospitalized for COVID-19, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-85809-y
Jolliffe, Ganmaa, Wejse, Raqib, Haq et al., Adjunctive vitamin D in tuberculosis treatment: Meta-analysis of individual participant data, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.02003-2018
Jolliffe, Greenberg, Hooper, Mathyssen, Rafiq et al., Vitamin D to prevent exacerbations of COPD: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials, Thorax, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-212092
Karonova, Golovatyuk, Kudryavtsev, Chernikova, Mikhaylova et al., Effect of Cholecalciferol Supplementation on the Clinical Features and Inflammatory Markers in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Open-Label, Single-Center Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132602
Kow, Ramachandram, Hasan, Wong, Thiruchelvam, The impact of vitamin D administration on mortality in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01564-2
Louis, Kannan, Shanmugham, Balakrishnan, Nagarajan, Vitamin D and Immune Function: Unraveling the Connections, doi:10.1007/978-3-031-55489-6_16
Luo, Wan, Liu, Tong, Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range, Stat. Methods Med. Res, doi:10.1177/0962280216669183
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Jamalimoghadamsiahkali, Asadi, Zarei et al., Treatment with 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (Calcifediol) Is Associated with a Reduction in the Blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Marker of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Pilot Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial, Endocr. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016
Mariani, Antonietti, Tajer, Ferder, Inserra et al., High-dose vitamin D versus placebo to prevent complications in COVID-19 patients: Multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0267918
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Molina, Carrero, Bover, Chauveau, Mazzaferro et al., European Renal Nutrition (ERN) and Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Working Groups of the European Renal Association-European Dialysis Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA). Vitamin D, a modulator of musculoskeletal health in chronic kidney disease, J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, doi:10.1002/jcsm.12218
Murai, Fernandes, Antonangelo, Gualano, Pereira, Effect of a Single High-Dose Vitamin D3 on the Length of Hospital Stay of Severely 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-Deficient Patients with COVID-19, Clinics, doi:10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Muñoz, Grant, Vitamin, Cancer: An Historical Overview of the Epidemiology and Mechanisms, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14071448
Nicolae, Mihai, Chisnoiu, Balasa, Frecus et al., Immunomodulatory Effects of Vitamin D in Respiratory Tract Infections and COVID-19 in Children, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15153430
Nogues, Ovejero, Pineda-Moncusí, Bouillon, Arenas et al., Calcifediol Treatment and COVID-19-Related Outcomes, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab405
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ
Page, Moher, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n160
Papagni, Pellegrino, Di Gennaro, Patti, Ricciardi et al., Impact of Vitamin D in Prophylaxis and Treatment in Tuberculosis Patients, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23073860
Reuter, Furin, The problem with vitamin D supplementation for tuberculosis, Lancet HIV, doi:10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30114-4
Sabico, Enani, Sheshah, Aljohani, Aldisi et al., Effects of a 2-Week 5000 IU versus 1000 IU Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Recovery of Symptoms in Patients with Mild to Moderate Covid-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072170
Sarhan, Abou Warda, Sarhan, Boshra, Mostafa-Hedeab et al., Evidence for the Efficacy of a High Dose of Vitamin D on the Hyperinflammation State in Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina58101358
Sartini, Del Puente, Oliva, Carbone, Blasi Vacca et al., Riding the COVID Waves: Clinical Trends, Outcomes, and Remaining Pitfalls of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: An Analysis of Two High-Incidence Periods at a Hospital in Northern Italy, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10225239
Sartini, Del Puente, Oliva, Carbone, Bobbio et al., Preventive Vitamin D Supplementation and Risk for COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16050679
Shirvani, Kalajian, Song, Holick, Disassociation of Vitamin D's Calcemic Activity and Non-calcemic Genomic Activity and Individual Responsiveness: A Randomized Controlled Double-Blind Clinical Trial, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-53864-1
Sirajudeen, Shah, Al Menhali, A Narrative Role of Vitamin D and Its Receptor: With Current Evidence on the Gastric Tissues, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms20153832
Soliman, Abdelaziz, Fathy, Impact of Vitamin D Therapy on the Progress COVID-19: Six Weeks Follow-Up Study of Vitamin D Deficient Elderly Diabetes Patients, Proc. Singap. Healthc, doi:10.1177/20101058211041405
Tan, Ho, Kalimuddin, Cherng, Teh et al., Cohort study to evaluate the effect of vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 in combination on progression to severe outcomes in older patients with coronavirus (COVID-19), Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017
Torres, Casado, Vigón, Rodríguez-Mora, Mateos et al., Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D, Biomed. Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965
Umar, Sastry, Chouchane, Role of Vitamin D Beyond the Skeletal Function: A Review of the Molecular and Clinical Studies, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms19061618
Van De Peppel, Van Leeuwen, Vitamin D and gene networks in human osteoblasts, Front. Physiol, doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00137
Vassalle, Editorial: Vitamin D: From pathophysiology to clinical impact, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1506137
Voltan, Cannito, Ferrarese, Ceccato, Camozzi et al., An Overview of Gene Regulation, Ranging from Metabolism to Genomic Effects, Genes, doi:10.3390/genes14091691
Wan, Wang, Liu, Tong, Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range, BMC Med. Res. Methodol, doi:10.1186/1471-2288-14-135
Wu, Xiong, Zhu, Wei, Zhuo et al., Effects of vitamin D supplementation on the outcomes of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis, BMC Pulm. Med, doi:10.1186/s12890-018-0677-6
Yang, Sun, Yang, Zhang, Li et al., Therapeutic effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 aggravation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1367686
Zhang, Zhang, Wen, Zhang, Wei et al., Vitamin D Deficiency and Increased Risk of Bladder Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis, Cell. Physiol. Biochem, doi:10.1159/000438534
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16223794",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu16223794",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: Vitamin D’s role in COVID-19 management remains controversial. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, focusing on mortality, intensive care unit (ICU) admissions, intubation rates, and hospital length of stay (LOS). Methods: A systematic review of PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Cochrane, and Google Scholar databases was conducted. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and analytical studies investigating vitamin D supplementation in COVID-19 patients were included. The meta-analysis was performed using STATA MP 18.5, employing random-effect or fixed-effect models based on heterogeneity. Results: Twenty-nine studies (twenty-one RCTs, eight analytical) were analyzed. Vitamin D supplementation significantly reduced ICU admissions (OR = 0.55, 95% CI: 0.37 to 0.79) in RCTs and analytical studies (OR = 0.35, 95% CI: 0.18 to 0.66). Intubation rates were significantly reduced in RCTs (OR = 0.50, 95% CI: 0.27 to 0.92). Mortality reduction was significant in analytical studies (OR = 0.45, 95% CI: 0.24 to 0.86) but not in RCTs (OR = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.61 to 1.04). Subgroup analyses revealed more pronounced effects in older patients and severe COVID-19 cases. LOS showed a non-significant reduction (mean difference = −0.62 days, 95% CI: −1.41 to 0.18). Conclusions: This meta-analysis suggests potential benefits of vitamin D supplementation in COVID-19 patients, particularly in reducing ICU admissions. However, the evidence varies across outcomes and patient subgroups. Discrepancies between RCTs and analytical studies highlight the need for further large-scale, well-designed trials accounting for baseline vitamin D status, standardized supplementation protocols, and patient characteristics to inform clinical guidelines for vitamin D use in COVID-19 management.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu16223794"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7127-2893",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Operating Unit Hospital Hygiene, Galliera Hospital, 16128 Genoa, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Department of Health Sciences, University of Genoa, 16132 Genoa, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sartini",
"given": "Marina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0080-5493",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Galliera Hospital, 16128 Genoa, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Del Puente",
"given": "Filippo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0008-9907-3299",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Operating Unit Hospital Hygiene, Galliera Hospital, 16128 Genoa, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Carbone",
"given": "Alessio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0008-1999-8786",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Operating Unit Hospital Hygiene, Galliera Hospital, 16128 Genoa, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Department of Health Sciences, University of Genoa, 16132 Genoa, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Schinca",
"given": "Elisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Operating Unit Hospital Hygiene, Galliera Hospital, 16128 Genoa, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Department of Health Sciences, University of Genoa, 16132 Genoa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Ottria",
"given": "Gianluca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Sciences, University of Genoa, 16132 Genoa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Dupont",
"given": "Chiara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Sciences, University of Genoa, 16132 Genoa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Piccinini",
"given": "Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0004-5913-9258",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Operating Unit Hospital Hygiene, Galliera Hospital, 16128 Genoa, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Oliva",
"given": "Martino",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7926-7108",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Operating Unit Hospital Hygiene, Galliera Hospital, 16128 Genoa, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Department of Health Sciences, University of Genoa, 16132 Genoa, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cristina",
"given": "Maria Luisa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-05T13:25:14Z",
"timestamp": 1730813114000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-05T14:04:17Z",
"timestamp": 1730815457000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-06T05:28:06Z",
"timestamp": 1730870886673,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "22",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "22",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1730764800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/16/22/3794/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3794",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcsm.12218",
"article-title": "Vitamin D, a modulator of musculoskeletal health in chronic kidney disease",
"author": "Molina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "686",
"journal-title": "J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19061618",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "Umar, M., Sastry, K.S., and Chouchane, A.I. (2018). Role of Vitamin D Beyond the Skeletal Function: A Review of the Molecular and Clinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-319-32507-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_3",
"unstructured": "Ureña Torres, P., Cozzolino, M., and Vervloet, M. (2016). Vitamin D Receptor and Interaction with DNA: From Physiology to Chronic Kidney Disease. Vitamin D in Chronic Kidney Disease, Springer."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1753-4887.2008.00093.x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor: Molecular signaling and actions of nutritional ligands in disease prevention",
"author": "Haussler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S98",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Rev.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms20153832",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "Sirajudeen, S., Shah, I., and Al Menhali, A. (2019). A Narrative Role of Vitamin D and Its Receptor: With Current Evidence on the Gastric Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 20."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-53864-1",
"article-title": "Disassociation of Vitamin D’s Calcemic Activity and Non-calcemic Genomic Activity and Individual Responsiveness: A Randomized Controlled Double-Blind Clinical Trial",
"author": "Shirvani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17685",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/genes14091691",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_7",
"unstructured": "Voltan, G., Cannito, M., Ferrarese, M., Ceccato, F., and Camozzi, V. (2023). Vitamin D: An Overview of Gene Regulation, Ranging from Metabolism to Genomic Effects. Genes, 14."
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and gene networks in human osteoblasts",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "Front. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/er.2018-00126",
"article-title": "Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions",
"author": "Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1109",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Rev.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/en.2011-0243",
"article-title": "Minireview: Vitamin D: Is there a role in extraskeletal health?",
"author": "Christakos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2930",
"journal-title": "Endocrinology",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/er.2012-1012",
"article-title": "The roles of vitamin D in skeletal muscle: Form, function, and metabolism",
"author": "Girgis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Rev.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00421-019-04104-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of vitamin D on skeletal muscle function: Oxidative stress, energy metabolism and anabolic state",
"author": "Dzik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "825",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Appl. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14071448",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_13",
"unstructured": "Muñoz, A., and Grant, W.B. (2022). Vitamin D and Cancer: An Historical Overview of the Epidemiology and Mechanisms. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000438534",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Deficiency and Increased Risk of Bladder Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1686",
"journal-title": "Cell. Physiol. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1765",
"article-title": "Intratrial Exposure to Vitamin D and New-Onset Diabetes Among Adults with Prediabetes: A Secondary Analysis From the Vitamin D and Type 2 Diabetes (D2d) Study",
"author": "Staten",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2916",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/app14114339",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Aiello, G., Lombardo, M., and Baldelli, S. (2024). Exploring Vitamin D Synthesis and Function in Cardiovascular Health: A Narrative Review. Appl. Sci., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-022-02147-x",
"article-title": "Recent advances in vitamin D implications in chronic respiratory diseases",
"author": "Gaudet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Respir. Res.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-031-55489-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Tappia, P.S., Shah, A.K., and Dhalla, N.S. (2024). Vitamin D and Immune Function: Unraveling the Connections. Lipophilic Vitamins in Health and Disease. Advances in Biochemistry in Health and Disease, Springer."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23073860",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "Papagni, R., Pellegrino, C., Di Gennaro, F., Patti, G., Ricciardi, A., Novara, R., Cotugno, S., Musso, M., Guido, G., and Ronga, L. (2022). Impact of Vitamin D in Prophylaxis and Treatment in Tuberculosis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/10408363.2014.901291",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in acquired immune and autoimmune diseases",
"author": "Delvin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "232",
"journal-title": "Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12890-018-0677-6",
"article-title": "Effects of vitamin D supplementation on the outcomes of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "BMC Pulm. Med.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.02003-2018",
"article-title": "Adjunctive vitamin D in tuberculosis treatment: Meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1802003",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30114-4",
"article-title": "The problem with vitamin D supplementation for tuberculosis",
"author": "Reuter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e450",
"journal-title": "Lancet HIV",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30403-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and respiratory infections",
"author": "Gallagher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "54",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-212092",
"article-title": "Vitamin D to prevent exacerbations of COPD: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "337",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2024.1506137",
"article-title": "Editorial: Vitamin D: From pathophysiology to clinical impact",
"author": "Vassalle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1506137",
"journal-title": "Front. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.736665",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes",
"author": "Chiodini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "736665",
"journal-title": "Front. Public Health",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001454",
"article-title": "Evidences for a protective role of vitamin D in COVID-19",
"author": "Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e001454",
"journal-title": "RMD Open",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16050679",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_30",
"unstructured": "Sartini, M., Del Puente, F., Oliva, M., Carbone, A., Bobbio, N., Schinca, E., Giribone, L., and Cristina, M.L. (2024). Preventive Vitamin D Supplementation and Risk for COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10225239",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Sartini, M., Del Puente, F., Oliva, M., Carbone, A., Blasi Vacca, E., Parisini, A., Boni, S., Bobbio, N., Feasi, M., and Battistella, A. (2021). Riding the COVID Waves: Clinical Trends, Outcomes, and Remaining Pitfalls of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: An Analysis of Two High-Incidence Periods at a Hospital in Northern Italy. J. Clin. Med., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15153430",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_32",
"unstructured": "Nicolae, M., Mihai, C.M., Chisnoiu, T., Balasa, A.L., Frecus, C.E., Mihai, L., Lupu, V.V., Ion, I., Pantazi, A.C., and Nelson Twakor, A. (2023). Immunomodulatory Effects of Vitamin D in Respiratory Tract Infections and COVID-19 in Children. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n160",
"article-title": "PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews",
"author": "Page",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "n160",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0962280216669183",
"article-title": "Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1785",
"journal-title": "Stat. Methods Med. Res.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2288-14-135",
"article-title": "Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "135",
"journal-title": "BMC Med. Res. Methodol.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "ref_36",
"unstructured": "National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (2024, March 04). Study Quality Assessment Tools, Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools."
},
{
"key": "ref_37",
"unstructured": "(2024, March 04). JBI’s Critical Appraisal Tools Assist in Assessing the Trustworthiness, Relevance and Results of Published Papers. JBI Critical Appraisal Tool for Quasi-Experimental Studies. Available online: https://jbi.global/critical-appraisal-tools."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: A quasi-experimental study",
"author": "Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105771",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_39",
"unstructured": "Annweiler, G., Corvaisier, M., Gautier, J., Dubée, V., Legrand, E., Sacco, G., and Annweiler, C. (2020). Vitamin D Supplementation Associated to Better Survival in Hospitalized Frail Elderly COVID-19 Patients: The GERIA-COVID Quasi-Experimental Study. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"article-title": "Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study",
"author": "Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105751",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-85809-y",
"article-title": "Lack of association of baseline 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with disease severity and mortality in Indian patients hospitalized for COVID-19",
"author": "Jevalikar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6258",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016",
"article-title": "Treatment with 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (Calcifediol) Is Associated with a Reduction in the Blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Marker of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Pilot Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial",
"author": "Maghbooli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1242",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Pract.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"article-title": "Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Murai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1053",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549",
"article-title": "Effect of a Single High-Dose Vitamin D3 on the Length of Hospital Stay of Severely 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-Deficient Patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Murai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e3549",
"journal-title": "Clinics",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab405",
"article-title": "Calcifediol Treatment and COVID-19-Related Outcomes",
"author": "Nogues",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e4017",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072170",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_46",
"unstructured": "Sabico, S., Enani, M.A., Sheshah, E., Aljohani, N.J., Aldisi, D.A., Alotaibi, N.H., Alshingetti, N., Alomar, S.Y., Alnaami, A.M., and Amer, O.E. (2021). Effects of a 2-Week 5000 IU versus 1000 IU Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Recovery of Symptoms in Patients with Mild to Moderate Covid-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003999",
"article-title": "High-dose versus standard-dose vitamin D supplementation in older adults with COVID-19 (COVIT-TRIAL): A multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled superiority trial",
"author": "Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1003999",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.863587",
"article-title": "Beneficial Effect of Short-Term Supplementation of High Dose of Vitamin D3 in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Multicenter, Single-Blinded, Prospective Randomized Pilot Clinical Trial",
"author": "Cervero",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "863587",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14153048",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_49",
"unstructured": "De Niet, S., Trémège, M., Coffiner, M., Rousseau, A.F., Calmes, D., Frix, A.N., Gester, F., Delvaux, M., Dive, A.F., and Guglielmi, E. (2022). Positive Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bone.2021.116175",
"article-title": "A randomized pilot study using calcitriol in hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Elamir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "116175",
"journal-title": "Bone",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "154",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqab426",
"article-title": "Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on cytokines, chemokines, and growth factor in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19",
"author": "Fernandes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "790",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/healthcare10050956",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_52",
"unstructured": "Fiore, V., De Vito, A., Bagella, P., Princic, E., Mariani, A.A., Denti, L., Fois, A.G., Madeddu, G., Babudieri, S., and Maida, I. (2022). Effectiveness of Vitamin D Supplements among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: Results from a Monocentric Matched-Cohort Study. Healthcare, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0267918",
"article-title": "High-dose vitamin D versus placebo to prevent complications in COVID-19 patients: Multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Mariani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0267918",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina58101358",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_54",
"unstructured": "Sarhan, N., Abou Warda, A.E., Sarhan, R.M., Boshra, M.S., Mostafa-Hedeab, G., ALruwaili, B.F., Ibrahim, H.S.G., Schaalan, M.F., and Fathy, S. (2022). Evidence for the Efficacy of a High Dose of Vitamin D on the Hyperinflammation State in Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Medicina, 58."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965",
"article-title": "Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D",
"author": "Torres",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112965",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Pharmacother.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15051234",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_56",
"unstructured": "Domazet Bugarin, J., Dosenovic, S., Ilic, D., Delic, N., Saric, I., Ugrina, I., Stojanovic Stipic, S., Duplancic, B., and Saric, L. (2023). Vitamin D Supplementation and Clinical Outcomes in Severe COVID-19 Patients-Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines11051277",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_57",
"unstructured": "Jaun, F., Boesing, M., Luethi-Corridori, G., Abig, K., Bloch, N., Giezendanner, S., Grillmayr, V., Haas, P., Leuppi-Taegtmeyer, A.B., and Muser, J. (2023). Effect of Single High Dose Vitamin D Substitution in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with Vitamin D Deficiency on Length of Hospital Stay. Biomedicines, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12906-024-04393-6",
"article-title": "Impact of vitamin D supplementation on the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 pneumonia patients: A single-center randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Dilokpattanamongkol",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "97",
"journal-title": "BMC Complement. Med. Ther.",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017",
"article-title": "Cohort study to evaluate the effect of vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 in combination on progression to severe outcomes in older patients with coronavirus (COVID-19)",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111017",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "79–80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061760",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_60",
"unstructured": "Alcala-Diaz, J.F., Limia-Perez, L., Gomez-Huelgas, R., Martin-Escalante, M.D., Cortes-Rodriguez, B., Zambrana-Garcia, J.L., Entrenas-Castillo, M., Perez-Caballero, A.I., López-Carmona, M.D., and Garcia-Alegria, J. (2021). Calcifediol Treatment and Hospital Mortality Due to COVID-19: A Cohort Study. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13010219",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_61",
"unstructured": "Giannini, S., Passeri, G., Tripepi, G., Sella, S., Fusaro, M., Arcidiacono, G., Torres, M.O., Michielin, A., Prandini, T., and Baffa, V. (2021). Effectiveness of In-Hospital Cholecalciferol Use on Clinical Outcomes in Comorbid COVID-19 Patients: A Hypothesis-Generating Study. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-021-00984-5",
"article-title": "The effect of high-dose parenteral vitamin D3 on COVID-19-related inhospital mortality in critical COVID-19 patients during intensive care unit admission: An observational cohort study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1383",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/20101058211041405",
"article-title": "Impact of Vitamin D Therapy on the Progress COVID-19: Six Weeks Follow-Up Study of Vitamin D Deficient Elderly Diabetes Patients",
"author": "Soliman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20101058211041405",
"journal-title": "Proc. Singap. Healthc.",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-22045-y",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on cellular immunity and inflammatory markers in COVID-19 patients admitted to the ICU",
"author": "Bychinin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18604",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-022-02290-8",
"article-title": "A single-oral bolus of 100,000 IU of cholecalciferol at hospital admission did not improve outcomes in the COVID-19 disease: The COVID-VIT-D-a randomised multicentre international clinical trial",
"author": "Mouzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "83",
"journal-title": "BMC Med.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14132602",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_66",
"unstructured": "Karonova, T.L., Golovatyuk, K.A., Kudryavtsev, I.V., Chernikova, A.T., Mikhaylova, A.A., Aquino, A.D., Lagutina, D.I., Zaikova, E.K., Kalinina, O.V., and Golovkin, A.S. (2022). Effect of Cholecalciferol Supplementation on the Clinical Features and Inflammatory Markers in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Open-Label, Single-Center Study. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-024-01564-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_67",
"unstructured": "Kow, C.S., Ramachandram, D.S., Hasan, S.S., Wong, Z., and Thiruchelvam, K. (2024). The impact of vitamin D administration on mortality in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Inflammopharmacology, advance online publication."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph16010130",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_68",
"unstructured": "Argano, C., Mallaci Bocchio, R., Natoli, G., Scibetta, S., Lo Monaco, M., and Corrao, S. (2023). Protective Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19-Related Intensive Care Hospitalization and Mortality: Definitive Evidence from Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2024.1367686",
"article-title": "Therapeutic effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 aggravation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1367686",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "Is the vitamin D status of patients with COVID-19 associated with reduced mortality? A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Bignardi",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Arch. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n71",
"article-title": "The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews",
"author": "Page",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "n71",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 71,
"references-count": 71,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/16/22/3794"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation Post COVID-19 Infection and Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "16"
}
