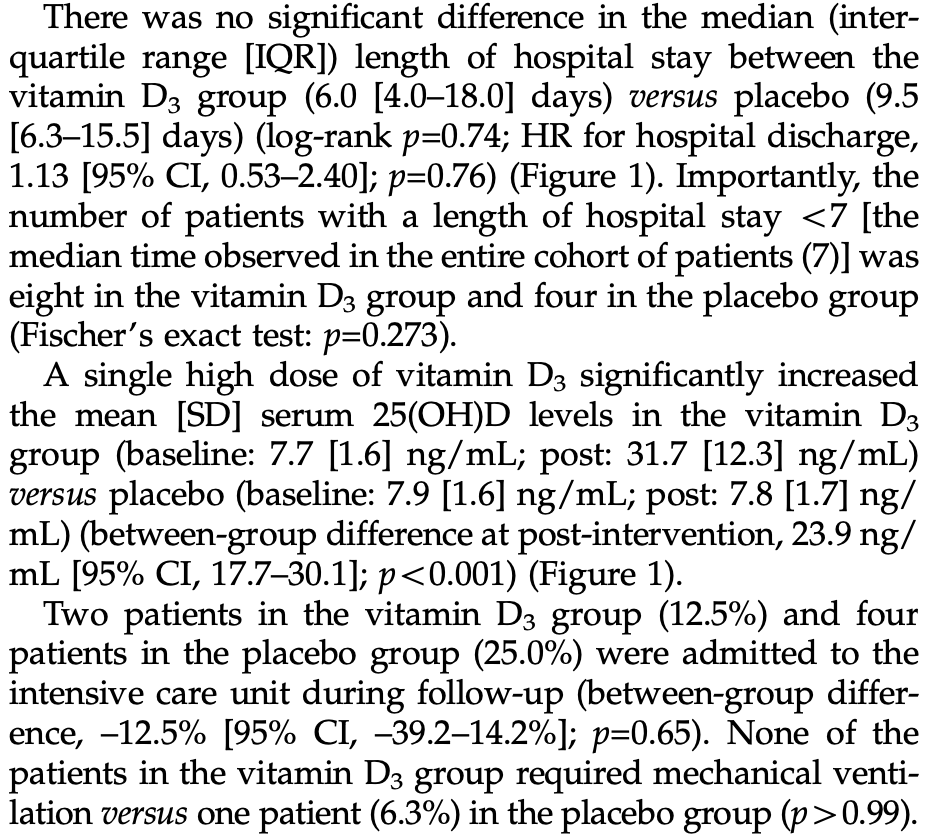
Effect of a Single High-Dose Vitamin D3 on the Length of Hospital Stay of Severely 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-Deficient Patients with COVID-19
et al., Clinics, doi:10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549, NCT04449718, Dec 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Analysis of a subset of patients from Murai et al. with vitamin D < 10 ng/mL, showing improved results with vitamin D treatment, without statistical significance in the small sample.
|
risk of death, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 16 (0.0%), control 1 of 16 (6.2%), NNT 16, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 16 (0.0%), control 1 of 16 (6.2%), NNT 16, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.65, treatment 2 of 16 (12.5%), control 4 of 16 (25.0%), NNT 8.0.
|
|
hospitalization time, 36.8% lower, relative time 0.63, p = 0.27, treatment median 6.0 IQR 14.0 n=16, control median 9.5 IQR 9.2 n=16.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 33.3% lower, RR 0.67, p = 0.27, treatment 8 of 16 (50.0%), control 12 of 16 (75.0%), NNT 4.0, hospitalization ≥7 days.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 11.5% lower, HR 0.88, p = 0.76, treatment 16, control 16, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Murai et al., 31 Dec 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, trial NCT04449718 (history).
Contact: rosamariarp@yahoo.com.
Effect of a Single High-Dose Vitamin D3 on the Length of Hospital Stay of Severely 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-Deficient Patients with COVID-19
Clinics, doi:10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549
Leila Antonangelo 0 0 0 0 -0
References
Amrein, Scherkl, Hoffmann, Neuwersch-Sommeregger, Köstenberger et al., Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide, Eur J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y
Bassatne, Basbous, Chakhtoura, El Zein, Rahme et al., The link between COVID-19 and VItamin D (VIVID): A systematic review and meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753
Bilezikian, Bikle, Hewison, Lazaretti-Castro, Formenti et al., MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: Vitamin D and COVID-19, Eur J Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-20-0665
Carpagnano, Lecce, Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico et al., Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, J Endocrinol Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x
Hernández, Nan, Fernandez-Ayala, García-Unzueta, Hernández-Hernández et al., Vitamin D Status in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa733
Jevalikar, Mithal, Singh, Sharma, Farooqui et al., Lack of association of baseline 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with disease severity and mortality in Indian patients hospitalized for COVID-19, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-85809-y
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Reis, Fernandes, Sales, Santos, Santos et al., Influence of vitamin D status on hospital length of stay and prognosis in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a multicenter prospective cohort study, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab151
Stroehlein, Wallqvist, Iannizzi, Mikolajewska, Metzendorf et al., Vitamin D supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: a living systematic review, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD015043
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549",
"ISSN": [
"1807-5932"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549",
"alternative-id": [
"S1807593222002654"
],
"article-number": "e3549",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0077-5004",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Murai",
"given": "Igor H.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6786-3922",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fernandes",
"given": "Alan L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8634-5100",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Antonangelo",
"given": "Leila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7100-8681",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gualano",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3723-5028",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pereira",
"given": "Rosa Maria Rodrigues",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinics",
"container-title-short": "Clinics",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T10:07:56Z",
"timestamp": 1638353276000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-16T16:59:48Z",
"timestamp": 1657990788000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-16T17:18:54Z",
"timestamp": 1726507134169
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 20,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 329,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1637884800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1807593222002654?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1807593222002654?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e3549",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-20-0665",
"article-title": "MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: Vitamin D and COVID-19",
"author": "Bilezikian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R133",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur J Endocrinol",
"key": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549_bib1",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549_bib2",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19",
"author": "Carpagnano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "765",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Endocrinol Invest",
"key": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549_bib3",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgaa733",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Status in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Hernández",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1343",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549_bib4",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-85809-y",
"article-title": "Lack of association of baseline 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with disease severity and mortality in Indian patients hospitalized for COVID-19",
"author": "Jevalikar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549_bib5",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753",
"article-title": "The link between COVID-19 and VItamin D (VIVID): A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Bassatne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549_bib6",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"article-title": "Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Murai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1053",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549_bib7",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqab151",
"article-title": "Influence of vitamin D status on hospital length of stay and prognosis in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a multicenter prospective cohort study",
"author": "Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "598",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549_bib8",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide",
"author": "Amrein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1498",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549_bib9",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: a living systematic review",
"author": "Stroehlein",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549_bib10",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 10,
"references-count": 10,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1807593222002654"
},
"secondary": [
{
"URL": "https://www.scielo.br/j/clin/a/nZ7krC3zP3VVTcCdzNdq7mF/?lang=em",
"label": "SCIELO"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8595591/",
"label": "PMC"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.clinicsjournal.com/article/effect-of-a-single-high-dose-vitamin-d3-on-the-length-of-hospital-stay-of-severely-25-hydroxyvitamin-d-deficient-patients-with-covid-19/",
"label": "CLINICS"
}
]
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"special_numbering": "C",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of a Single High-Dose Vitamin D3 on the Length of Hospital Stay of Severely 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-Deficient Patients with COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "76"
}
