Effectiveness of Vitamin D Supplements among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: Results from a Monocentric Matched-Cohort Study
et al., Healthcare, doi:10.3390/healthcare10050956, May 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 116 patients with D levels < 30ng/mL, 58 treated with vitamin D 100,000IU daily for two days, and 58 matched controls, showing significantly lower mortality with treatment.
This is the 82nd of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
risk of death, 92.7% lower, RR 0.07, p = 0.01, treatment 3 of 58 (5.2%), control 11 of 58 (19.0%), NNT 7.2, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.36, treatment 4 of 58 (6.9%), control 8 of 58 (13.8%), NNT 14.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.36, treatment 4 of 58 (6.9%), control 8 of 58 (13.8%), NNT 14.
|
|
NIV, 47.8% lower, RR 0.52, p = 0.04, treatment 12 of 58 (20.7%), control 23 of 58 (39.7%), NNT 5.3.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Fiore et al., 22 May 2022, retrospective, matched cohort, Italy, peer-reviewed, mean age 62.5, 10 authors, dosage 100,000IU days 1-2.
Contact: vitofiore30010516@gmail.com (corresponding author), andreadevitoaho@gmail.com, paola.bagella@tiscali.it, princic_e@hotmail.com, annaanto82@gmail.com, dentilucia@outlook.it, giordano@uniss.it, babuder@uniss.it, imaida@uniss.it, agfois@uniss.it.
Effectiveness of Vitamin D Supplements among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: Results from a Monocentric Matched-Cohort Study
Healthcare, doi:10.3390/healthcare10050956
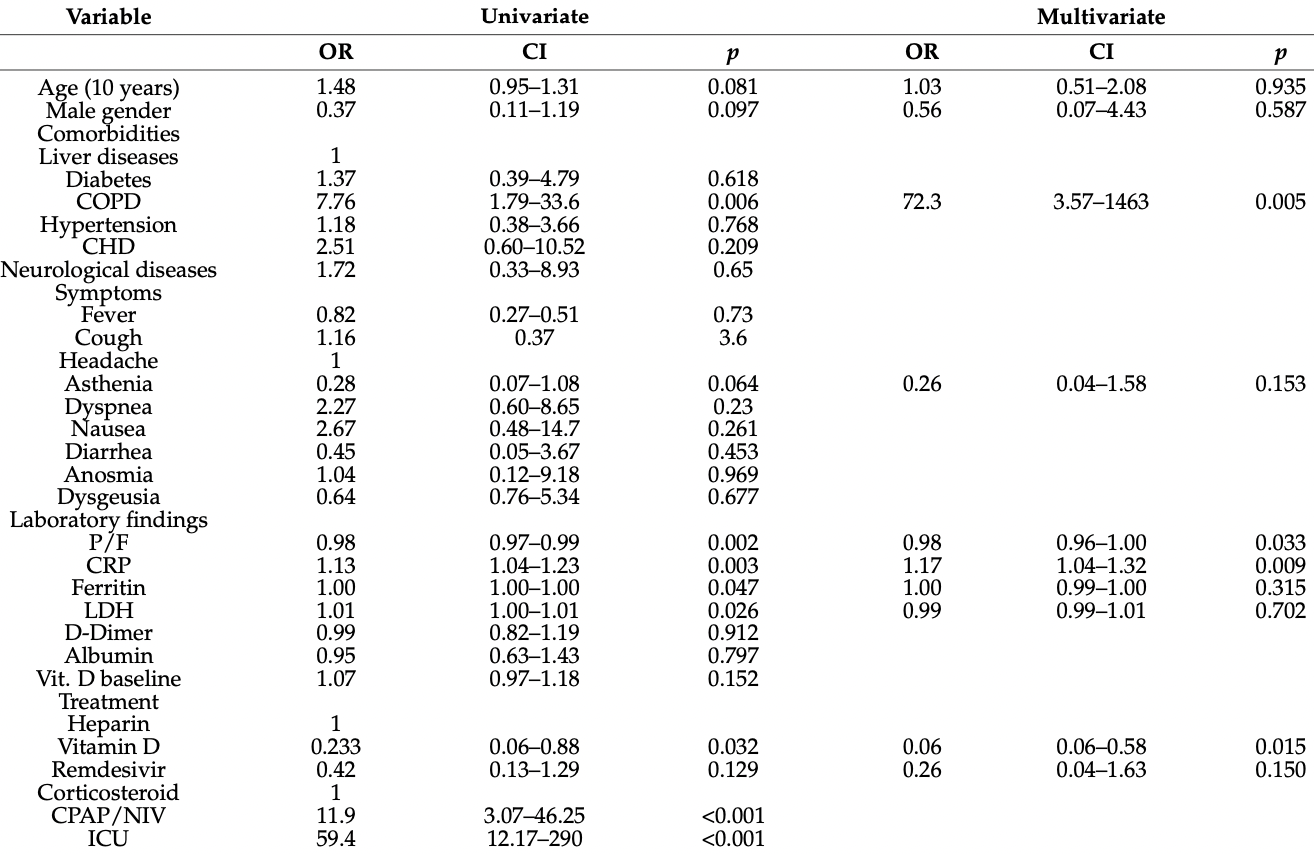
Objectives: Our study aimed to evaluate the usefulness of Vitamin D3 (VitD3) among patients hospitalized for COVID-19. The primary endpoint was to evaluate the difference in survival rates between patients receiving and not VitD3. The secondary endpoints were to evaluate clinical outcomes, such as needing non-invasive ventilation (NIV), ICU transfer, and laboratory findings (inflammatory parameters). Methods: We conducted a retrospective, monocentric matched-cohort study, including patients attending our ward for COVID-19. Patients were divided into two groups depending on VitD3 administration (Group A) or not (Group B) among patients with low VitD levels (defined as blood levels < 30 ng/mL), which depended on physicians' judgment. Our internal protocol provides VitD3 100,000 UI/daily for two days. Findings: 58 patients were included in Group A, and 58 in Group B. Patients were matched for age, sex, comorbidities, COVID-19-related symptoms, PaO2/FiO2 ratio, blood exams, and medical treatments. Regarding the principal endpoint, there was a statistically significant difference between the two groups in survival rates [Group A vs. Group B = 3 vs. 11 (p = 0.042)]. When considering secondary endpoints, Group A patients were less likely to undergo NIV [Group A vs. Group B = 12 vs. 23 (p = 0.026)] and showed an improvement in almost all inflammatory parameters. Conclusions: The link between VitD3 deficiency and the clinical course of COVID-19 during hospitalization suggests that VitD3 level is a useful prognostic marker. Considering the safety of supplementation and the low cost, VitD3 replacement should be considered among SARS-CoV-2 infected patients needing hospitalization.
Author Contributions: V.F. and I.M. conceived the study. V.F., I.M., A.D.V., A.G.F., G.M., S.B., P.B., E.P., A.A.M. and L.D. organized the database. V.F. and A.D.V. performed statistical analysis. A.G.F., G.M., S.B. and I.M. supervised the study. V.F., A.D.V., P.B. and E.P. produced the manuscripts' first draft. All authors contributed to manuscript revision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Ali, Vijayan, Dynamics of the ACE2-SARS-CoV-2/SARS-CoV spike protein interface reveal unique mechanisms, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71188-3
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubée, Legrand et al., Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: The GERIA-COVID quasi-experimental study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377
Annweiler, Hanotte, Grandin De L'eprevier, Sabatier, Lafaie et al., Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: A quasi-experimental study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771
Barlow, Svoboda, Mackellar, Nash, York et al., Antiviral activity and increased host defense against influenza infection elicited by the human cathelicidin LL-37, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025333
Bouillon, Marcocci, Carmeliet, White, Dawson-Hughes et al., Skeletal and extraskeletal actions of Vitamin D: Current evidence and outstanding questions, Endocr. Rev, doi:10.1210/er.2018-00126
Castillo, Entrenas Costa, Vaquero Barrios, Alcalá Díaz, López Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Chiodini, Gatti, Soranna, Merlotti, Mingiano et al., Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.736665
Covino, De Matteis, Santoro, Sabia, Simeoni et al., Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors in COVID-19 patients aged ≥80 years, Geriatr. Gerontol. Int, doi:10.1111/ggi.13960
De, Vito, Fiore, Princic, Geremia et al., Predictors of infection, symptoms development, and mortality in people with SARS-CoV-2 living in retirement nursing homes, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0248009
De, Vito, Geremia, Fiore, Princic et al., Clinical features, laboratory findings and predictors of death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Sardinia, Italy, Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci
De, Vito, Geremia, Princic, Fanelli et al., Does Angiotensin II receptor blockers increase the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection? A real-life experience, Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci
Dror, Morozov, Daoud, Namir, Yakir et al., Pre-infection 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels and association with severity of COVID-19 illness, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0263069
Du, Liang, Yang, Wang, Cao et al., Predictors of mortality for patients with COVID-19 pneumonia caused by SARSCoV-2: A prospective cohort study, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00524-2020
Fiore, Beretta, De Vito, Barac, Maida et al., Emerging Clinical Features of COVID-19 Related Pancreatitis: Case Reports and Review of the Literature, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.779118
Fiore, De Vito, Fanelli, Geremia, Princic et al., Mood Reactive Disorders among COVID-19 Inpatients: Experience from a Monocentric Cohort, Med. Princ. Pract, doi:10.1159/000518490
Imai, Kuba, Rao, Huan, Guo et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature03712
Jaun, Boesing, Lüthi-Corridori, Abig, Makhdoomi et al., High-dose vitamin D substitution in patients with COVID-19: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center study-VitCov Trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-022-06016-2
Kim, Yang, Jang, Jang, Human beta-defensin 2 plays a regulatory role in innate antiviral immunity and is capable of potentiating the induction of antigen-specific immunity, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/s12985-018-1035-2
Liu, Chen, Lin, Han, Clinical features of COVID-19 in elderly patients: A comparison with young and middle-aged patients, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.005
Liu, Stenger, Li, Wenzel, Tan et al., Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1123933
Martha, Wibowo, Pranata, Prognostic value of elevated lactate dehydrogenase in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139542
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a single high dose of Vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Niu, Tian, Lou, Kang, Zhang et al., Clinical characteristics of older patients infected with COVID-19: A descriptive study, Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr, doi:10.1016/j.archger.2020.104058
Quesada-Gomez, Entrenas-Castillo, Bouillon, Vitamin D receptor stimulation to reduce acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in patients with coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infections, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105719
Rodriguez-Guerra, Jadhav, Vittorio, Current treatment in COVID-19 disease: A rapid review, Drugs Context, doi:10.7573/dic.2020-10-3
Saravolatz, Depcinski, Sharma, Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir: Oral COVID Antiviral Drugs, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac180
Ul Afshan, Nissar, Chowdri, Ganai, Relevance of vitamin D3 in COVID-19 infection, Gene Rep, doi:10.1016/j.genrep.2021.101270
Vaira, Hopkins, Salzano, Petrocelli, Melis et al., Olfactory and gustatory function impairment in COVID-19 patients: Italian objective multicenter-study, Head Neck, doi:10.1002/hed.26269
Wang, Nestel, Bourdeau, Nagai, Wang et al., Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.2909
Xu, Yang, Chen, Luo, Zhang et al., Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system, Mol. Med. Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.7546
Yang, Petitjean, Koehler, Zhang, Dumitru et al., Molecular interaction and inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptor, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23498-x
Yu, Qin, Chen, Wang, Tian, D-dimer level is associated with the severity of COVID-19, Thromb. Res, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.07.047
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
Zinellu, De Vito, Scano, Paliogiannis, Fiore et al., The PaO2/FiO2 ratio on admission is independently associated with prolonged hospitalization in COVID-19 patients, J. Infect. Dev. Ctries, doi:10.3855/jidc.13288
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/healthcare10050956",
"ISSN": [
"2227-9032"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10050956",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Objectives: Our study aimed to evaluate the usefulness of Vitamin D3 (VitD3) among patients hospitalized for COVID-19. The primary endpoint was to evaluate the difference in survival rates between patients receiving and not VitD3. The secondary endpoints were to evaluate clinical outcomes, such as needing non-invasive ventilation (NIV), ICU transfer, and laboratory findings (inflammatory parameters). Methods: We conducted a retrospective, monocentric matched-cohort study, including patients attending our ward for COVID-19. Patients were divided into two groups depending on VitD3 administration (Group A) or not (Group B) among patients with low VitD levels (defined as blood levels < 30 ng/mL), which depended on physicians’ judgment. Our internal protocol provides VitD3 100,000 UI/daily for two days. Findings: 58 patients were included in Group A, and 58 in Group B. Patients were matched for age, sex, comorbidities, COVID-19-related symptoms, PaO2/FiO2 ratio, blood exams, and medical treatments. Regarding the principal endpoint, there was a statistically significant difference between the two groups in survival rates [Group A vs. Group B = 3 vs. 11 (p = 0.042)]. When considering secondary endpoints, Group A patients were less likely to undergo NIV [Group A vs. Group B = 12 vs. 23 (p = 0.026)] and showed an improvement in almost all inflammatory parameters. Conclusions: The link between VitD3 deficiency and the clinical course of COVID-19 during hospitalization suggests that VitD3 level is a useful prognostic marker. Considering the safety of supplementation and the low cost, VitD3 replacement should be considered among SARS-CoV-2 infected patients needing hospitalization.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"healthcare10050956"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7444-1920",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fiore",
"given": "Vito",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8265-5400",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "De Vito",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bagella",
"given": "Paola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Princic",
"given": "Elija",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1697-3694",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mariani",
"given": "Anna Antonella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Denti",
"given": "Lucia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5330-572X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fois",
"given": "Alessandro Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6099-2273",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Madeddu",
"given": "Giordano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7291-8687",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Babudieri",
"given": "Sergio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maida",
"given": "Ivana",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Healthcare",
"container-title-short": "Healthcare",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-22T11:13:57Z",
"timestamp": 1653218037000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-22T11:23:43Z",
"timestamp": 1653218623000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-22T11:41:28Z",
"timestamp": 1653219688059
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
22
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1653177600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9032/10/5/956/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "956",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "New-Type Coronavirus Causes Pneumonia in Wuhan: Expert—Xinhua|English.news.cn\nhttp://www.xinhuanet.com/english/2020-01/09/c_138690570.htm"
},
{
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19), Report 191\nhttps://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200729-covid-19-sitrep-191.pdf?sfvrsn=2c327e9e_2"
},
{
"article-title": "Does Angiotensin II receptor blockers increase the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection? A real-life experience",
"author": "De Vito",
"first-page": "523",
"journal-title": "Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci.",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-23498-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-71188-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hed.26269",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical features, laboratory findings and predictors of death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Sardinia, Italy",
"author": "De Vito",
"first-page": "7861",
"journal-title": "Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci.",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.archger.2020.104058",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ggi.13960",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000518490",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.779118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00524-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0248009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.07.047",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3855/jidc.13288",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7573/dic.2020-10-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac180",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2017.7546",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature03712",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.736665",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0263069",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1123933",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.2909",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-018-1035-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0025333",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.genrep.2021.101270",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139542",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/er.2018-00126",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105719",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-022-06016-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9032/10/5/956"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Health Information Management",
"Health Informatics",
"Health Policy",
"Leadership and Management"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effectiveness of Vitamin D Supplements among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: Results from a Monocentric Matched-Cohort Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "10"
}
