Evidence for the Efficacy of a High Dose of Vitamin D on the Hyperinflammation State in Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina58101358, NCT04738760, Sep 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT comparing 200,000IU IM cholecalciferol and 1mcg/day alfacalcidol, showing lower mortality and improved recovery with high dose treatment.
Cholecalciferol was used in this study.
Meta-analysis shows that late stage treatment with calcitriol / calcifediol (or
paricalcitol, alfacalcidol, etc.) is more effective than cholecalciferol: 66% [47‑78%] lower risk vs. 45% [34‑54%] lower risk.
Cholecalciferol requires two hydroxylation steps to become activated - first
in the liver to calcifediol, then in the kidney to calcitriol. Calcitriol,
paricalcitol, and alfacalcidol are active vitamin D analogs that do not
require conversion. This allows them to have more rapid onset of action
compared to cholecalciferol. The time delay for cholecalciferol to increase
serum calcifediol levels can be 2-3 days, and the delay for converting
calcifediol to active calcitriol can be up to 7 days.
This is the 28th of 40 COVID-19 RCTs for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
This is the 101st of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of death, 18.5% lower, RR 0.81, p = 0.003, treatment 26 of 58 (44.8%), control 30 of 58 (51.7%), NNT 14, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
|
improvement, 74.4% better, OR 0.26, p = 0.03, treatment 58, control 58, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
time to improvement, 28.8% lower, relative time 0.71, p = 0.002, treatment 58, control 58.
|
|
hospitalization time, 31.5% lower, relative time 0.69, p = 0.04, treatment 58, control 58.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sarhan et al., 27 Sep 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Egypt, peer-reviewed, 9 authors, study period December 2020 - June 2021, dosage 200,000IU single dose, trial NCT04738760 (history).
Contact: gomaa@ju.edu.sa (corresponding author).
Evidence for the Efficacy of a High Dose of Vitamin D on the Hyperinflammation State in Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina58101358
Background and Objectives: Vitamin D supplementation plays a key effect in lowering cytokine storms among COVID-19 patients by influencing the activity of the renin-angiotensin system and the production of the angiotensin-2 converting enzyme. The study was conducted to explore the effect of high-dose intramuscular vitamin D in hospitalized adults infected with moderate-tosevere SARS-CoV-2 in comparison with the standard of care in the COVID-19 protocol. Materials and Methods: Two groups of patients were compared in this prospective randomized controlled trial as the vitamin D was administered orally to group 1 (alfacalcidol 1 mcg/day) and intramuscularly to group 2 (cholecalciferol 200,000 IU). One hundred and sixteen participants were recruited in total, with fifty-eight patients in each group. Following the Egyptian Ministry of Health's policy for COVID-19 management, all patients received the same treatment for a minimum of five days. Results: A significant difference was recorded in the length of hospital stay (8.6 versus 6.8 days), need for high oxygen or non-invasive mechanical ventilator (67% versus 33%), need for a mechanical ventilator (25% versus 75%), clinical improvement (45% versus 55%), the occurrence of sepsis (35% versus 65%), and in the monitored laboratory parameters in favor of high-dose vitamin D. Moreover, clinical improvement was significantly associated with the need for low/high oxygen, an invasive/noninvasive mechanical ventilator (MV/NIMV), and diabetes, while mortality was associated with the need for MV, ICU admission, atrial fibrillation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, and the occurrence of secondary infection. Conclusions: Our study showed that high-dose vitamin D was considered a promising treatment in the suppression of cytokine storms among COVID-19 patients and was associated with better clinical improvement and fewer adverse outcomes compared to low-dose vitamin D.
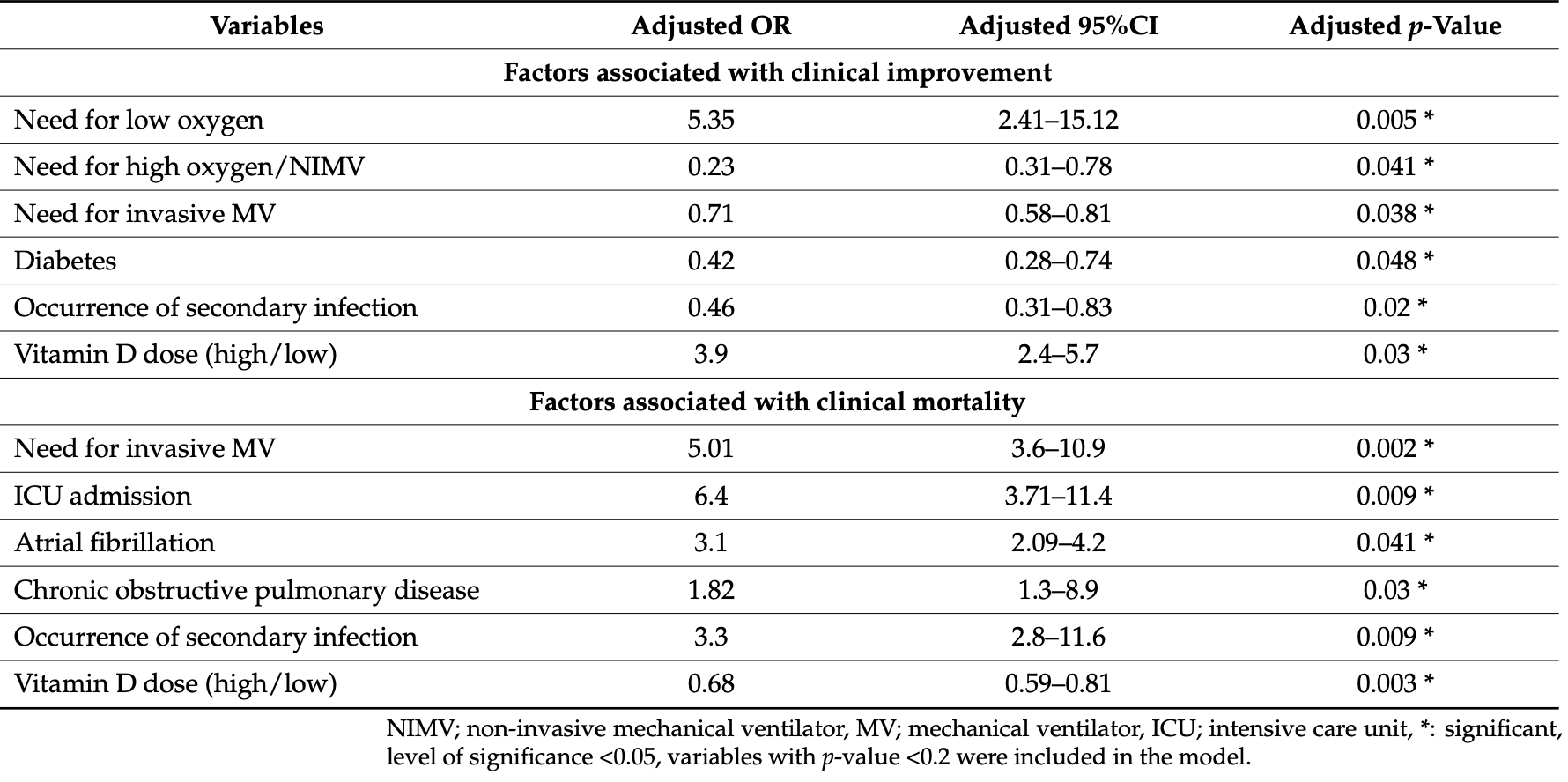
Predictors of Clinical Improvement by Binary Logistic Regression Analysis The binary logistic regression analysis indicated that better clinical improvement and less severe COVID-19 symptoms were associated with the need for low oxygen (OR = 6.67, C.I. = 2.07-21.35, p = 0.001) and inversely associated with the need for high oxygen and NIMV (OR = 6.19, C.I. = 0.41-0.86, p = 0.031), the need for an invasive mechanical ventilator (MV) (OR = 0.83, C.I. = 0.64-0.98, p = 0.012), diabetes (OR = 0.37, C.I. = 0.33-0.56, p = 0.045), atrial fibrillation (OR = 0.41, C.I.= 0.15-0.38, p = 0.008), and the occurrence of secondary infection (OR = 0.33, C.I. = 0.16-0.94, p = 0.004), as shown in Table 3 . However, after conducting a multiple logistic regression with covariates reporting a p-value less than 0.2 in the univariate regression analysis, only the need for low oxygen (adjusted OR = 5.53, C.I. = 2.41-15.12, p = 0.005), the need for high oxygen/NIMV (adjusted OR = 0.23, C.I. = 0.31-0.78, p = 0.041), the need for invasive MV (adjusted OR= 0.71, C.I. = 0.58-0.81, p = 0.038), diabetes (adjusted OR = 0.42, C.I. = 0.28-0.74, p = 0.048), and the occurrence of secondary bacterial infection (adjusted OR = 0.46, C.I.= 0.31-0.83, p = 0.02) remained significant, as shown in Table 4 .
Predictors of Mortality by Binary Logistic Regression Analysis The binary logistic regression analysis revealed that COVID-19 mortality was associated with the need for MV (OR = 4.93, C.I. = 1.1-12.56, p = 0.039),..
References
Annweiler, Beaudenon, Gautier, Simon, Dubée et al., Study Group. COvid-19 and high-dose VITamin D supplementation TRIAL in high-risk older patients (COVIT-TRIAL): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-020-04928-5
Annweiler, Beaudenon, Simon, Guenet, Otekpo et al., Group. Vitamin D supplementation prior to or during COVID-19 associated with better 3-month survival in geriatric patients: Extension phase of the GERIA-COVID study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105958
Annweiler, Legrand, Souberbielle, Vitamin D in adults: Update on testing and supplementation, Geriatr. Psychol. Neuropsychiatr. Vieil, doi:10.1684/pnv.2018.0722
Baktash, Hosack, Patel, Shah, Kandiah et al., Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalized older patients with COVID-19, Postgrad. Med. J
Barrea, Gennari, Merlotti, Mingiano, Frosali et al., A Role Also in Long COVID-19?, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14081625
Bayraktar, Turan, Bayraktar, Ozturk, Erdo Gdu, Analysis of serum cytokine and protective vitamin D levels in severe cases of COVID-19, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27294
Biesalski, Vitamin D deficiency and co-morbidities in COVID-19 patients-A fatal relationship?, Nfs J, doi:10.1016/j.nfs.2020.06.001
Campi, Gennari, Merlotti, Mingiano, Frosali et al., Vitamin D and COVID-19 severity and related mortality: A prospective study in Italy, BMC Infect. Dis
Castillo, Entrenas Costa, Vaquero Barrios, Díaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol
Charoenngam, Shirvani, Holick, Vitamin D and its potential benefit for the COVID-19 pandemic, Endocr. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.03.006
Chen, Chang, Wu, Yu, Wei et al., Upregulation of the chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 via a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike-ACE2 signaling pathway, J. Virol
Chen, Mei, Xie, Yuan, Ma et al., Low vitamin D levels do not aggravate COVID-19 risk or death, and vitamin D supplementation does not improve outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis and GRADE assessment of cohort studies and RCTs, Nutr. J, doi:10.1186/s12937-021-00744-y
De, Puente-Yagüe, Cuadrado-Cenzual, Ciudad-Cabañas, Hernández-Cabria et al., Vitamin D: And its role in breast cancer, Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.kjms.2018.03.004
Dijkman, Jebbink, Deijs, Milewska, Pyrc et al., Replication-dependent downregulation of cellular angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protein expression by human coronavirus NL63, J. Gen. Virol, doi:10.1099/vir.0.043919-0
Dinicolantonio, O'keefe, Magnesium and vitamin D deficiency as a potential cause of immune dysfunction, cytokine storm, and disseminated intravascular coagulation in COVID-19 patients, Mo. Med
Dissanayake, De Silva, Sumanatilleke, De Silva, Gamage et al., Prognostic and therapeutic role of vitamin D in COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab892
Ghasemian, Shamshirian, Heydari, Malekan, Alizadeh-Navaei et al., The role of vitamin D in the age of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14675
Gil, Plaza-Diaz, Mesa, Vitamin D: Classic and novel actions, Ann. Nutr. Metab, doi:10.1159/000486536
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hossein-Nezhad, Holick, Vitamin D for health: A global perspective, Mayo Clin. Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.05.011
Infante, Buoso, Pieri, Lupisella, Nuccetelli et al., Low Vitamin D status at admission as a risk factor for poor survival in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: An Italian retrospective study, J. Am. Coll. Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.2021.1877580
Jain, Chaurasia, Sengar, Singh, Mahor et al., Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z
Ji, Zhang, Zhai, Zhang, Zhang et al., an automated topic-wise inference method based on massive literature, suggests a possible mechanism via ACE2 for the pathological changes in the human host after coronavirus infection, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.02.27.967588
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, Bi, Holick, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239252
Kong, Zhu, Shi, Liu, Chen et al., VDR attenuates acute lung injury by blocking Ang-2-Tie-2 pathway and renin-angiotensin system, Mol. Endocrinol, doi:10.1210/me.2013-1146
Lakkireddy, Gadiga, Malathi, Karra, Raju et al., Impact of daily high dose oral vitamin D therapy on the inflammatory markers in patients with COVID 19 disease, Sci. Rep
Ling, Broad, Murphy, Pappachan, Pardesi-Newton et al., High-dose cholecalciferol booster therapy is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: A cross-sectional multi-centre observational study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12123799
Mariani, Tajer, Antonietti, Inserra, Ferder et al., High-dose vitamin D versus placebo to prevent complications in COVID-19 patients: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial (CARED-TRIAL), Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-021-05073-3
Medical, Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2013.281053
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D levels, race/ethnicity, and clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4117
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Pereira, Dantas Damascena, Galvão Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da Mota Santana, Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090
Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Suri, Yaddanapudi et al., Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: A randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study), Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065
Remmelts, Van De Garde, Meijvis, Peelen, Damoiseaux et al., Addition of vitamin D status to prognostic scores improves the prediction of outcome in community-acquired pneumonia, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/cis751
Sarhan, Mohammad, Boshra, Differential clinical diagnosis and prevalence rate of allergic rhinitis, asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among COVID-19 patients, Int. J. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14532
Schaalan, Warda, Osman, Fathy, Sarhan et al., The Impact of Sociodemographic, Nutritional, and Health Factors on the Incidence and Complications of COVID-19 in Egypt: A Cross-Sectional Study, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14030448
Serdar, Cihan, Yücel, Serdar, Sample size, power and effect size revisited: Simplified and practical approaches in pre-clinical, clinical and laboratory studies, Biochem. Med, doi:10.11613/BM.2021.010502
Sharma, Tiwari, Deb, Marty, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): A global pandemic and treatment strategies, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106054
Singh, Nimavat, Singh, Ahmad, Sinha, Prevalence of Low Level of Vitamin D Among COVID-19 Patients and Associated Risk Factors in India-A Hospital-Based Study, Int. J. Gen. Med, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S309003
Tan, Ho, Kalimuddin, Cherng, Teh et al., Cohort study to evaluate the effect of vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 in combination on progression to severe outcomes in older patients with coronavirus (COVID-19), Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017
Viechtbauer, Smits, Kotz, Budé, Spigt et al., A simple formula for the calculation of sample size in pilot studies, J. Clin. Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2015.04.014
Yang, Zhang, Xu, Effect of vitamin D on ACE2 and vitamin D receptor expression in rats with LPS-induced acute lung injury, Chin. J. Emerg. Med
Yuan, Pan, Kong, Zheng, Szeto et al., 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses renin gene transcription by blocking the activity of the cyclic AMP response element in the renin gene promoter, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M705495200
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina58101358",
"ISSN": [
"1648-9144"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101358",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background and Objectives: Vitamin D supplementation plays a key effect in lowering cytokine storms among COVID-19 patients by influencing the activity of the renin-angiotensin system and the production of the angiotensin-2 converting enzyme. The study was conducted to explore the effect of high-dose intramuscular vitamin D in hospitalized adults infected with moderate-to-severe SARS-CoV-2 in comparison with the standard of care in the COVID-19 protocol. Materials and Methods: Two groups of patients were compared in this prospective randomized controlled trial as the vitamin D was administered orally to group 1 (alfacalcidol 1 mcg/day) and intramuscularly to group 2 (cholecalciferol 200,000 IU). One hundred and sixteen participants were recruited in total, with fifty-eight patients in each group. Following the Egyptian Ministry of Health’s policy for COVID-19 management, all patients received the same treatment for a minimum of five days. Results: A significant difference was recorded in the length of hospital stay (8.6 versus 6.8 days), need for high oxygen or non-invasive mechanical ventilator (67% versus 33%), need for a mechanical ventilator (25% versus 75%), clinical improvement (45% versus 55%), the occurrence of sepsis (35% versus 65%), and in the monitored laboratory parameters in favor of high-dose vitamin D. Moreover, clinical improvement was significantly associated with the need for low/high oxygen, an invasive/non-invasive mechanical ventilator (MV/NIMV), and diabetes, while mortality was associated with the need for MV, ICU admission, atrial fibrillation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, and the occurrence of secondary infection. Conclusions: Our study showed that high-dose vitamin D was considered a promising treatment in the suppression of cytokine storms among COVID-19 patients and was associated with better clinical improvement and fewer adverse outcomes compared to low-dose vitamin D.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"medicina58101358"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4067-5518",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sarhan",
"given": "Neven",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4434-6217",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Abou Warda",
"given": "Ahmed E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0781-6454",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sarhan",
"given": "Rania M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4916-4359",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Boshra",
"given": "Marian S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4947-0495",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mostafa-Hedeab",
"given": "Gomaa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2034-7709",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "ALruwaili",
"given": "Bashayer F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3584-1953",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "Haytham Soliman Ghareeb",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8569-689X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Schaalan",
"given": "Mona F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3626-3040",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fathy",
"given": "Shaimaa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicina",
"container-title-short": "Medicina",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-28T05:51:49Z",
"timestamp": 1664344309000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-28T07:51:08Z",
"timestamp": 1664351468000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"DSR-2021-01-0379"
],
"name": "the Deanship of Scientific Research at Jouf University"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-29T05:16:15Z",
"timestamp": 1664428575330
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1664236800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/58/10/1358/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1358",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106054",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14030448",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalized older patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Baktash",
"first-page": "442",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.kjms.2018.03.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1684/pnv.2018.0722",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.05.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000486536",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27294",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"article-title": "Magnesium and vitamin D deficiency as a potential cause of immune dysfunction, cytokine storm, and disseminated intravascular coagulation in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "DiNicolantonio",
"first-page": "68",
"journal-title": "Mo. Med.",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/me.2013-1146",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M705495200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/vir.0.043919-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.02.27.967588",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02560-09",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin D on ACE2 and vitamin D receptor expression in rats with LPS-induced acute lung injury",
"author": "Yang",
"first-page": "1284",
"journal-title": "Chin. J. Emerg. Med.",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.03.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2013.281053",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.11613/BM.2021.010502",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2015.04.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.14532",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S309003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"key": "ref26",
"series-title": "Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D.",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nfs.2020.06.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12123799",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14081625",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06281-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.14675",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab892",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12937-021-00744-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105958",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/cis751",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.2021.1877580",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-90189-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04928-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-021-05073-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
}
],
"reference-count": 45,
"references-count": 45,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/58/10/1358"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Evidence for the Efficacy of a High Dose of Vitamin D on the Hyperinflammation State in Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "58"
}
