Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D
et al., Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965, Apr 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
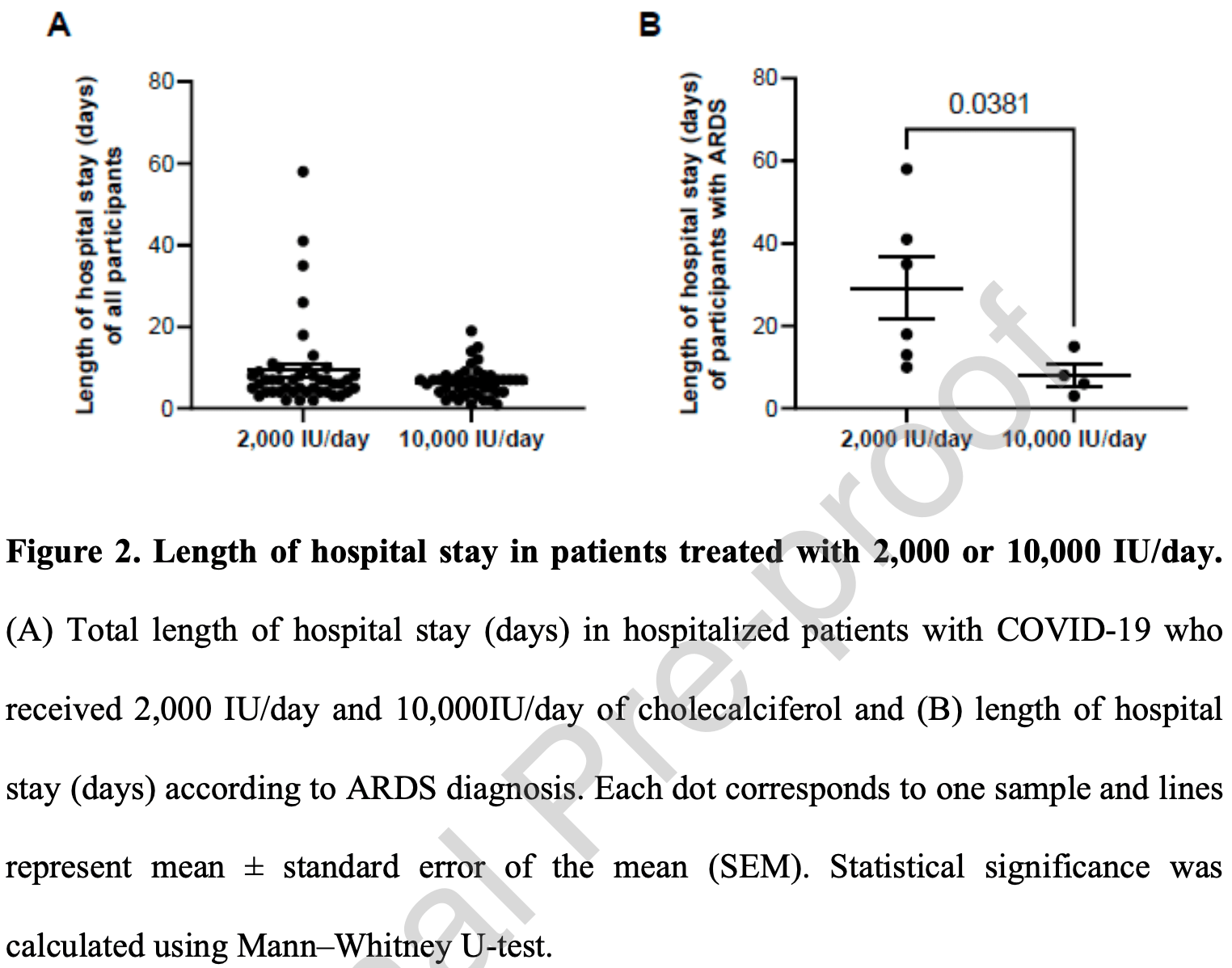
RCT comparing 41 patients treated with 10,000IU/day cholecalciferol and 44 treated with 2,000IU/day in Spain, showing significantly shorter hospitalization for ARDS patients with the higher dose. There was also an increase of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and higher levels of CD4+ T cells. Cytotoxic response against pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 infected cells was over 4-fold higher in patients receiving the higher dose.
Cholecalciferol was used in this study.
Meta-analysis shows that late stage treatment with calcitriol / calcifediol (or
paricalcitol, alfacalcidol, etc.) is more effective than cholecalciferol: 66% [47‑78%] lower risk vs. 45% [34‑54%] lower risk.
Cholecalciferol requires two hydroxylation steps to become activated - first
in the liver to calcifediol, then in the kidney to calcitriol. Calcitriol,
paricalcitol, and alfacalcidol are active vitamin D analogs that do not
require conversion. This allows them to have more rapid onset of action
compared to cholecalciferol. The time delay for cholecalciferol to increase
serum calcifediol levels can be 2-3 days, and the delay for converting
calcifediol to active calcitriol can be up to 7 days.
This is the 15th of 40 COVID-19 RCTs for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
This is the 77th of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of death, 7.3% higher, RR 1.07, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 41 (2.4%), control 1 of 44 (2.3%).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 57.1% lower, RR 0.43, p = 0.44, treatment 2 of 41 (4.9%), control 5 of 44 (11.4%), NNT 15.
|
|
risk of ARDS, 28.5% lower, RR 0.72, p = 0.74, treatment 4 of 41 (9.8%), control 6 of 44 (13.6%), NNT 26.
|
|
hospitalization time, 31.2% lower, relative time 0.69, treatment 41, control 44.
|
|
hospitalization time, 72.6% lower, relative time 0.27, p = 0.04, ARDS patients.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Torres et al., 14 Apr 2022, Single Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Spain, peer-reviewed, median age 65.0, 51 authors, study period June 2020 - March 2021, average treatment delay 7.0 days, dosage 10,000IU days 1-14.
Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965
Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin DImmunomodulatory effect of vitamin D supplementation in patients with COVID-19, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,
Drug Cholecalciferol (vitamin D) used in the study was donated by Italfarmaco Group (Cholecalciferol 25,000IU/2,5ml oral solution). Italfarmaco Group had no role in the design and conduct of the study, in the collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data, or the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author Contributions MCer and MCo conceptualized the project. MT, GC and MCo wrote the manuscript. MT, GC and LV performed the study of cytotoxicity. MT, GC and SRM performed the analysis of cell populations by flow cytometry with technical assistance from EM.
J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f MRLH and GC performed the analysis of cytokines in plasma. FR and EM processed and stored all blood samples. DLW, MNM, PRM, MLTM and MCer identified, selected, and recruited the patients, and also collected the blood samples. MT, MCer and MRLH collected and analyzed the clinical data. All co-authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Author Contributions MCer and MCo conceptualized the project. MT, GC and MCo wrote the manuscript. MT, GC and LV performed the study of cytotoxicity. MT, GC and SRM performed the analysis of cell populations by flow cytometry with technical assistance from EM. MRLH and GC performed the analysis of cytokines in plasma. Anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was significantly increased in 10,000 IU/day group. Individuals who received 10,000..
References
Al-Jaderi, Maghazachi, Effects of Vitamin D3, Calcipotriol and FTY720 on the Expression of Surface Molecules and Cytolytic Activities of Human Natural Killer Cells and Dendritic Cells, Toxins
Annweiler, Vitamin D Supplementation Associated to Better Survival in Hospitalized Frail Elderly COVID-19 Patients: The GERIA-COVID Quasi-Experimental Study, Nutrients
Antonelli, Kushner, Low Serum Levels of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Accompany Severe COVID-19 Because it is a Negative Acute Phase Reactant, Am. J. Med. Sci
Bae, Choe, Holick, Lim, Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 and its severity, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-021-09705-6
Baeke, Takiishi, Korf, Gysemans, Mathieu, Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol
Bendix-Struve, Vitamin D3 treatment of Crohn's disease patients increases stimulated T cell IL-6 production and proliferation, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther
Bishop, Ismailova, Dimeloe, Hewison, White, Vitamin D and immune regulation: antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, JBMR Plus, doi:10.1002/jbm4.10405
Borsche, Glauner, Von Mendel, COVID-19 Mortality Risk Correlates Inversely with Vitamin D3 Status, and a Mortality Rate Close to Zero Could Theoretically Be Achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D3: Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients
Bouillon, Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions, Endocr. Rev
Cantorna, Snyder, Lin, Yang, Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D Regulation of T cells, Nutrients
Chen, Cytokine Storm: The Primary Determinant for the Pathophysiological Evolution of COVID-19 Deterioration, Front. Immunol
Chen, Potential impact of maternal vitamin D status on peripheral blood and endometrium cellular immunity in women with recurrent implantation failure, Am. J. Reprod. Immunol
Chiodini, Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes, Front. Public Health
Cifaldi, Inhibition of Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity by Interleukin-6: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Macrophage Activation Syndrome, Arthritis Rheumatol
Couzin-Frankel, Antiviral pills could change pandemic's course, Science
Da Rocha, Insufficient evidence for vitamin D use in COVID-19: A rapid systematic review, Int. J. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14649
Dankers, Colin, Van Hamburg, Lubberts, Vitamin D in autoimmunity: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential, Front. Immunol
Diao, Reduction and Functional Exhaustion of T Cells in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Front. Immunol
Diao, Reduction and Functional Exhaustion of T Cells in Patients With Coronavirus Disease, Front. Immunol
Fakhoury, Lung-Centric Inflammation of COVID-19: Potential Modulation by Vitamin D, Nutrients
Feng, COVID-19 with Different Severities: A Multicenter Study of Clinical Features, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med
Garcia-Perez, Sanchez-Palomino, Perez-Olmeda, Fernandez, Alcami, A new strategy based on recombinant viruses as a tool for assessing drug susceptibility of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, J. Med. Virol
Group, Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Group, Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Guaraldi, Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol
Gustine, Jones, Immunopathology of Hyperinflammation in COVID-19, Am. J. Pathol
Hastie, Pell, Sattar, Vitamin D and COVID-19 infection and mortality in UK Biobank, Eur. J. Nutr
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7
Huang, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet Lond. Engl
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin. Exp. Res
Infante, Influence of Vitamin D on Islet Autoimmunity and Beta-Cell Function in Type 1 Diabetes, Nutrients
Iturricastillo, Ávalos Pérez-Urría, Couñago, Landete, Scientific evidence in the COVID-19 treatment: A comprehensive review, World J. Virol
J O U R N A L P R E, -p r o o f
J O U R N A L P R E, -p r o o f
J O U R N A L P R E, -p r o o f
J O U R N A L P R E, -p r o o f
J O U R N A L P R E, -p r o o f
J O U R N A L P R E, -p r o o f
Karonova, Stepanova, Bystrova, Jude, High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation Improves Microcirculation and Reduces Inflammation in Diabetic Neuropathy Patients, Nutrients
Kvietys, COVID-19: Lung-Centric Immunothrombosis, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol
Lee, Differential effect of dietary vitamin D supplementation on natural killer cell activity in lean and obese mice, J. Nutr. Biochem
Li, Geng, Peng, Meng, Lu, Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19, J. Pharm. Anal
Louw, Blood vitamin concentrations during the acute-phase response, Crit. Care Med
Martineau, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Mehta, COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet Lond. Engl
Mishra, Tripathi, One year update on the COVID-19 pandemic: Where are we now?, Acta Trop
Murai, Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA
Navarro Valverde, Quesada Gómez, Deficiencia de vitamina D en España: ¿realidad o mito?, Rev. Osteoporos. Metab. Miner
Ni, Impaired Cellular Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in Severe COVID-19 Patients, Front. Immunol
Ohaegbulam, Swalih, Patel, Smith, Perrin, Vitamin D Supplementation in COVID-19 Patients: A Clinical Case Series, Am. J. Ther
Olza, Reported Dietary Intake, Disparity between the Reported Consumption and the Level Needed for Adequacy and Food Sources of Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium and Vitamin D in the Spanish Population: Findings from the ANIBES Study †, Nutrients
Ou, Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV, Nat. Commun
Parums, Editorial: Current Status of Oral Antiviral Drug Treatments for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Non-Hospitalized Patients, Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res
Pedersen, Phenotypic and functional markers for 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-modified regulatory dendritic cells, Clin. Exp. Immunol
Raisi-Estabragh, Vitamin D and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): rapid evidence review, Aging Clin. Exp. Res
Ramos-Martínez, Reduction of respiratory infections in asthma patients supplemented with vitamin D is related to increased serum IL-10 and IFNγ levels and cathelicidin expression, Cytokine
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Griffin, Kenny, Perspective: Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 severity -plausibly linked by latitude, ethnicity, impacts on cytokines, ACE2 and thrombosis, J. Intern. Med
Rolf, Vitamin D3 supplementation in multiple sclerosis: Symptoms and biomarkers of depression, J. Neurol. Sci
Sabico, Effects of a 2-Week 5000 IU versus 1000 IU Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Recovery of Symptoms in Patients with Mild to Moderate Covid-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Nutrients
Sani, Reduced CD4+ terminally differentiated effector memory T cells in moderate-severe house dust mites sensitized allergic rhinitis patients, Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol
Sorci, Faivre, Morand, Explaining among-country variation in COVID-19 case fatality rate, Sci. Rep
Tian, Unique phenotypes and clonal expansions of human CD4 effector memory T cells re-expressing CD45RA, Nat. Commun
Vigón, Impaired Cytotoxic Response in PBMCs From Patients With COVID-19 Admitted to the ICU: Biomarkers to Predict Disease Severity, Front. Immunol
Watkins, Preventing a covid-19 pandemic, BMJ
Weiss, Litonjua, Vitamin D in Host Defense: Implications for Future Research, Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol
Yang, Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis
Yuzefpolskiy, Vitamin D Receptor Signals Regulate Effector and Memory CD8 T Cell Responses to Infections in Mice, J. Nutr
Zheng, Functional exhaustion of antiviral lymphocytes in COVID-19 patients, Cell. Mol. Immunol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965",
"ISSN": [
"0753-3322"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965",
"alternative-id": [
"S0753332222003547"
],
"article-number": "112965",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Torres",
"given": "Montserrat",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Casado",
"given": "Guiomar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vigón",
"given": "Lorena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodríguez-Mora",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mateos",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramos-Martín",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "López-Wolf",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanz-Moreno",
"given": "José",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ryan-Murua",
"given": "Pablo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taboada-Martínez",
"given": "María Luisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "López-Huertas",
"given": "María Rosa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cervero",
"given": "Miguel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coiras",
"given": "Mayte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alonso-Menchén",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arévalo Camacho",
"given": "Sandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Avila Calzada",
"given": "Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Antonio Barbado Albaladejo",
"given": "José",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blanca López",
"given": "Natalia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cañamares Orbis",
"given": "Irene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carrillo Blanco",
"given": "Gema",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cascajero Díaz",
"given": "Almudena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teresa Chica Burguillo",
"given": "María",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corrochano García",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corredera García",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Díez Viñas",
"given": "Victor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gómez-Alvarez Domínguez",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patricia Fernández Fernández",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernández Mondelo",
"given": "Yanira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fonseca Aizpuri",
"given": "Eva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "García Lacalle",
"given": "Concepción",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "García-Pérez",
"given": "Javier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Helguera Amezua",
"given": "Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "José Hidalgo Correas",
"given": "Francisco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lucena Campillo",
"given": "Amparo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matarranz del Amo",
"given": "Mariano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martín Sagarra",
"given": "Oriol",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "José Martínez Martín",
"given": "Emilio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Javier Martínez Simón",
"given": "José",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Novella-Mena",
"given": "María",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pardo Guimera",
"given": "Virginia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luisa Pinillos Pardo",
"given": "María",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramírez Fuentes",
"given": "Fr`ancisca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Renuncio García",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Angeles Rodríguez Dávila",
"given": "María",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roger Revilla",
"given": "Almudena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sampablo Valverde",
"given": "Lourdes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanz Moreno",
"given": "José",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Torres Perea",
"given": "Rafael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valencia La Rosa",
"given": "Jorge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Velasco Arribas",
"given": "María",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Villanueva Fernández-Ardavín",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-14T07:13:33Z",
"timestamp": 1649920413000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-14T07:14:18Z",
"timestamp": 1649920458000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-14T07:43:21Z",
"timestamp": 1649922201025
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0753-3322"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1648771200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 10,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1649635200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0753332222003547?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0753332222003547?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "112965",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19",
"author": "Hu",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "China. Lancet Lond. Engl.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib2",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet Lond. Engl",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib3",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202002-0445OC",
"article-title": "COVID-19 with Different Severities: A Multicenter Study of Clinical Features",
"author": "Feng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1380",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib4",
"volume": "201",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.39295",
"article-title": "Inhibition of Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity by Interleukin-6: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Macrophage Activation Syndrome",
"author": "Cifaldi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3037",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheumatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib5",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.08.009",
"article-title": "Immunopathology of Hyperinflammation in COVID-19",
"author": "Gustine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Pathol",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib6",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.603563",
"article-title": "Impaired Cellular Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in Severe COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Ni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib7",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.00827",
"article-title": "Reduction and Functional Exhaustion of T Cells in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Diao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "827",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib8",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Impaired Cytotoxic Response in PBMCs From Patients With COVID-19 Admitted to the ICU: Biomarkers to Predict Disease Severity",
"author": "Vigón",
"first-page": "1901",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.actatropica.2020.105778",
"article-title": "One year update on the COVID-19 pandemic: Where are we now?",
"author": "Mishra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Acta Trop",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib10",
"volume": "214",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001",
"article-title": "Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102",
"journal-title": "J. Pharm. Anal.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib11",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5501/wjv.v10.i5.217",
"article-title": "Scientific evidence in the COVID-19 treatment: A comprehensive review",
"author": "Iturricastillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "217",
"journal-title": "World J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib12",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30173-9",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Guaraldi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e474",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib13",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib14",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Editorial: Current Status of Oral Antiviral Drug Treatments for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Non-Hospitalized Patients",
"author": "Parums",
"journal-title": "Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib15",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.acx9605",
"article-title": "Antiviral pills could change pandemic’s course",
"author": "Couzin-Frankel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "799",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib16",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Yang",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib17",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/er.2018-00126",
"article-title": "Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions",
"author": "Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1109",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib18",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2016.00697",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in autoimmunity: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential",
"author": "Dankers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib19",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11092185",
"article-title": "Influence of Vitamin D on Islet Autoimmunity and Beta-Cell Function in Type 1 Diabetes",
"author": "Infante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2185",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib20",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib21",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072216",
"article-title": "Lung-Centric Inflammation of COVID-19: Potential Modulation by Vitamin D",
"author": "Fakhoury",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2216",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib22",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and immune regulation: antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory",
"author": "Bishop",
"journal-title": "JBMR Plus",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1165/rcmb.2017-0064ED",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in Host Defense: Implications for Future",
"author": "Weiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "692",
"journal-title": "Research. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib24",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m810",
"article-title": "Preventing a covid-19 pandemic",
"author": "Watkins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m810",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib25",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-020-02372-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID-19 infection and mortality in UK Biobank",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "545",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib26",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1195",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib27",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.20770",
"article-title": "A new strategy based on recombinant viruses as a tool for assessing drug susceptibility of human immunodeficiency virus type 1",
"author": "Garcia-Perez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "127",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib28",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-15562-9",
"article-title": "Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV",
"author": "Ou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1620",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib29",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-75848-2",
"article-title": "Explaining among-country variation in COVID-19 case fatality rate",
"author": "Sorci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18909",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib30",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13149",
"article-title": "Perspective: Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 severity – plausibly linked by latitude, ethnicity, impacts on cytokines, ACE2 and thrombosis",
"author": "Rhodes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "97",
"journal-title": "J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib31",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Insufficient evidence for vitamin D use in COVID-19: A rapid systematic review",
"author": "da Rocha",
"first-page": "14649",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib32",
"volume": "e14649",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-021-09705-6",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 and its severity",
"author": "Bae",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib33",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Supplementation Associated to Better Survival in Hospitalized Frail Elderly COVID-19 Patients: The GERIA-COVID Quasi-Experimental Study",
"author": "Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib34",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-021-01894-z",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): rapid evidence review",
"author": "Raisi-Estabragh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2031",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib35",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9020168",
"article-title": "Reported Dietary Intake, Disparity between the Reported Consumption and the Level Needed for Adequacy and Food Sources of Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium and Vitamin D in the Spanish Population: Findings from the ANIBES Study †",
"author": "Olza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "168",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib36",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4321/S1889-836X2014000500002",
"article-title": "Deficiencia de vitamina D en España: ¿realidad o mito?",
"author": "Navarro Valverde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "Rev. Osteoporos. Metab. Miner",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib37",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib38",
"unstructured": "Recomendaciones de la SEIOMM en la prevención y tratamiento del déficit de vitamina D. Revista de Osteoporosis y Metabolismo Mineral · Publicación Oficial SEIOMM 〈http://revistadeosteoporosisymetabolismomineral.com/2021/07/08/recomendaciones-la-seiomm-la-prevencion-tratamiento-del-deficit-vitamina-d/〉 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"article-title": "Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Murai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1053",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib39",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072170",
"article-title": "Effects of a 2-Week 5000 IU versus 1000 IU Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Recovery of Symptoms in Patients with Mild to Moderate Covid-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Sabico",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2170",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib40",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjms.2021.06.005",
"article-title": "Low Serum Levels of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Accompany Severe COVID-19 Because it is a Negative Acute Phase Reactant",
"author": "Antonelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "333",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib41",
"volume": "362",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00003246-199207000-00007",
"article-title": "Blood vitamin concentrations during the acute-phase response",
"author": "Louw",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib42",
"volume": "20",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13103596",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Mortality Risk Correlates Inversely with Vitamin D3 Status, and a Mortality Rate Close to Zero Could Theoretically Be Achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D3: Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Borsche",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3596",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib43",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.736665",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes",
"author": "Chiodini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib44",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Group",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib45",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.001",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system",
"author": "Baeke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "482",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib46",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03961.x",
"article-title": "Phenotypic and functional markers for 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-modified regulatory dendritic cells",
"author": "Pedersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "48",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib47",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"article-title": "Cytokine Storm: The Primary Determinant for the Pathophysiological Evolution of COVID-19 Deterioration",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib48",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2021.679878",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Lung-Centric Immunothrombosis",
"author": "Kvietys",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib49",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2017.04.017",
"article-title": "Vitamin D3 supplementation in multiple sclerosis: Symptoms and biomarkers of depression",
"author": "Rolf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30",
"journal-title": "J. Neurol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib50",
"volume": "378",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092518",
"article-title": "High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation Improves Microcirculation and Reduces Inflammation in Diabetic Neuropathy Patients",
"author": "Karonova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2518",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib51",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2018.01.001",
"article-title": "Reduction of respiratory infections in asthma patients supplemented with vitamin D is related to increased serum IL-10 and IFNγ levels and cathelicidin expression",
"author": "Ramos-Martínez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "239",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib52",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001222",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Supplementation in COVID-19 Patients: A Clinical Case Series",
"author": "Ohaegbulam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e485",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib53",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Reduction and Functional Exhaustion of T Cells in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Diao",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib54",
"volume": "0",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7043011",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D Regulation of T cells",
"author": "Cantorna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3011",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib55",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2036.2010.04463.x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D3 treatment of Crohn’s disease patients increases stimulated T cell IL-6 production and proliferation",
"author": "Bendix-Struve",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1364",
"journal-title": "Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib56",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib57",
"unstructured": "Sani, M. et al. Reduced CD4+ terminally differentiated effector memory T cells in moderate-severe house dust mites sensitized allergic rhinitis patients. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-017-01728-5",
"article-title": "Unique phenotypes and clonal expansions of human CD4 effector memory T cells re-expressing CD45RA",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1473",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib58",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0402-2",
"article-title": "Functional exhaustion of antiviral lymphocytes in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "533",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib59",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.114.202895",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Receptor Signals Regulate Effector and Memory CD8 T Cell Responses to Infections in Mice",
"author": "Yuzefpolskiy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2073",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib60",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/aji.13243",
"article-title": "Potential impact of maternal vitamin D status on peripheral blood and endometrium cellular immunity in women with recurrent implantation failure",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Reprod. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib61",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/toxins5111932",
"article-title": "Effects of Vitamin D3, Calcipotriol and FTY720 on the Expression of Surface Molecules and Cytolytic Activities of Human Natural Killer Cells and Dendritic Cells",
"author": "Al-Jaderi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1932",
"journal-title": "Toxins",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib62",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.01.004",
"article-title": "Differential effect of dietary vitamin D supplementation on natural killer cell activity in lean and obese mice",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "178",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965_bib63",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 63,
"references-count": 63,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0753332222003547"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}
