Positive Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14153048, NCT04636086, Jul 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
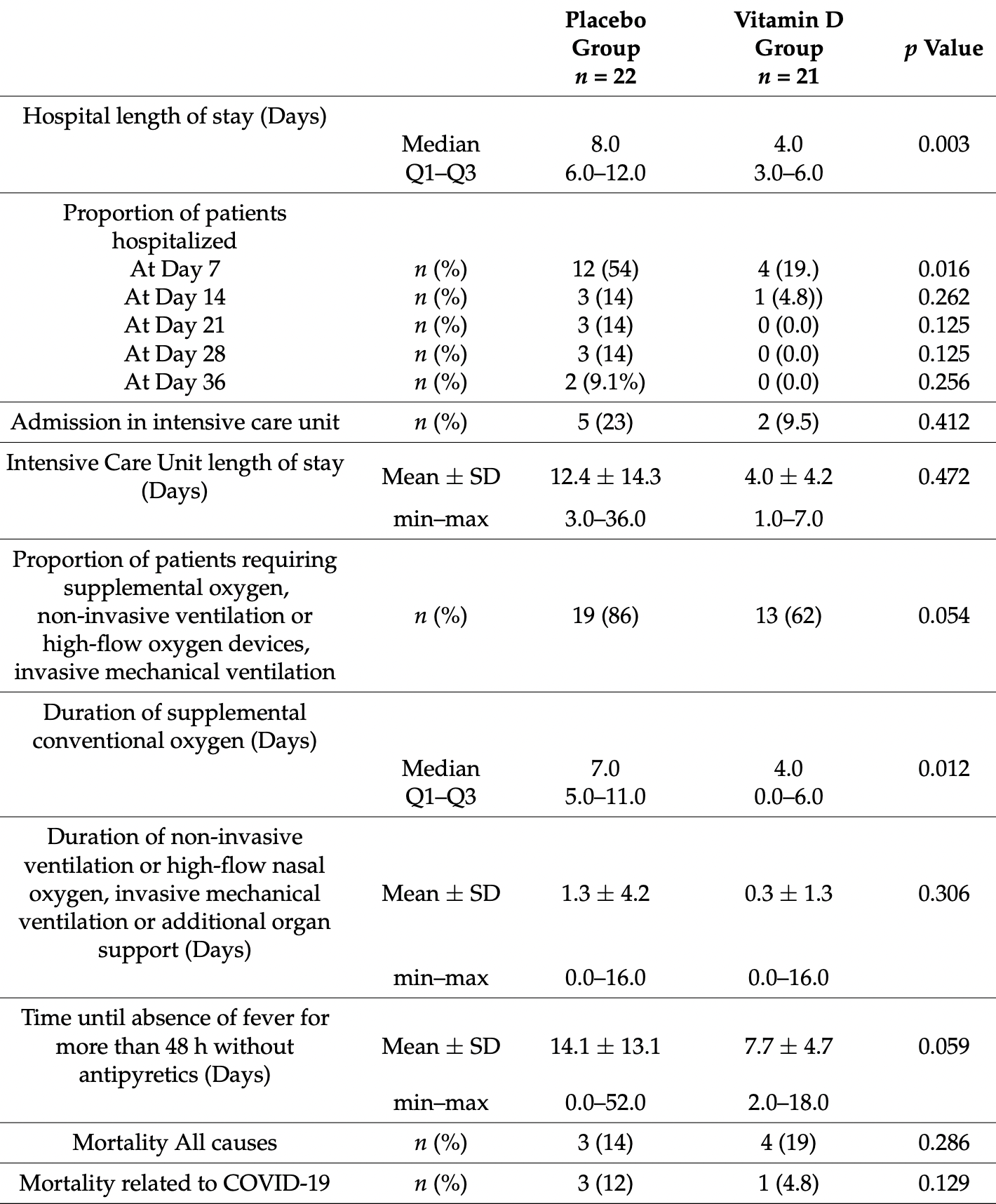
RCT with 21 vitamin D and 22 placebo hospitalized patients in Belgium with vitamin D deficiency, showing significantly shorter hospitalization and improved clinical recovery with treatment.
Cholecalciferol was used in this study.
Meta-analysis shows that late stage treatment with calcitriol / calcifediol (or
paricalcitol, alfacalcidol, etc.) is more effective than cholecalciferol: 66% [47‑78%] lower risk vs. 45% [34‑54%] lower risk.
Cholecalciferol requires two hydroxylation steps to become activated - first
in the liver to calcifediol, then in the kidney to calcitriol. Calcitriol,
paricalcitol, and alfacalcidol are active vitamin D analogs that do not
require conversion. This allows them to have more rapid onset of action
compared to cholecalciferol. The time delay for cholecalciferol to increase
serum calcifediol levels can be 2-3 days, and the delay for converting
calcifediol to active calcitriol can be up to 7 days.
This is the 25th of 40 COVID-19 RCTs for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
This is the 93rd of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of death, 65.1% lower, RR 0.35, p = 0.61, treatment 1 of 21 (4.8%), control 3 of 22 (13.6%), NNT 11, COVID-19 mortality.
|
|
risk of death, 39.7% higher, RR 1.40, p = 0.70, treatment 4 of 21 (19.0%), control 3 of 22 (13.6%), all cause including after discharge and non-COVID-19.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 58.1% lower, RR 0.42, p = 0.41, treatment 2 of 21 (9.5%), control 5 of 22 (22.7%), NNT 7.6.
|
|
ICU time, 67.7% lower, relative time 0.32, p = 0.47, treatment 21, control 22.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 79.6% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.49, treatment 0 of 21 (0.0%), control 2 of 22 (9.1%), NNT 11, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 36.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 85.4% lower, RR 0.15, p = 0.23, treatment 0 of 21 (0.0%), control 3 of 22 (13.6%), NNT 7.3, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 28.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 85.4% lower, RR 0.15, p = 0.23, treatment 0 of 21 (0.0%), control 3 of 22 (13.6%), NNT 7.3, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 21.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 65.1% lower, RR 0.35, p = 0.61, treatment 1 of 21 (4.8%), control 3 of 22 (13.6%), NNT 11, day 14.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 65.1% lower, RR 0.35, p = 0.03, treatment 4 of 21 (19.0%), control 12 of 22 (54.5%), NNT 2.8, day 7.
|
|
recovery time, 45.4% lower, relative time 0.55, p = 0.06, treatment 21, control 22, fever.
|
|
hospitalization time, 50.0% lower, relative time 0.50, p = 0.003, treatment 21, control 22.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
De Niet et al., 26 Jul 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Belgium, peer-reviewed, 16 authors, study period August 2020 - August 2021, dosage 25,000IU days 1-4, 11, 18, 25, trial NCT04636086 (history).
Contact: sdeni@smb.be (corresponding author), mtrem@smb.be, mcoff@smb.be, afrouseau@chuliege.be, d.calmes@chuliege.be, affrix@chuliege.be, f.gester@chuliege.be, muriel.delvaux@chuliege.be, af.dive@chuliege.be, elora.guglielmi@chuliege.be, monique.henket@chuliege.be, alicia.staderoli@chuliege.be, renaud.louis@chuliege.be, j.guiot@chuliege.be, dmaesen@chuliege.be, etienne.cavalier@chu.ulg.ac.be.
Positive Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14153048
Retrospective studies showed a relationship between vitamin D status and COVID-19 severity and mortality, with an inverse relation between SARS-CoV-2 positivity and circulating calcifediol levels. The objective of this pilot study was to investigate the effect of vitamin D supplementation on the length of hospital stay and clinical improvement in patients with vitamin D deficiency hospitalized with COVID-19. The study was randomized, double blind and placebo controlled. A total of 50 subjects were enrolled and received, in addition to the best available COVID therapy, either vitamin D (25,000 IU per day over 4 consecutive days, followed by 25,000 IU per week up to 6 weeks) or placebo. The length of hospital stay decreased significantly in the vitamin D group compared to the placebo group (4 days vs. 8 days; p = 0.003). At Day 7, a significantly lower percentage of patients were still hospitalized in the vitamin D group compared to the placebo group (19% vs. 54%; p = 0.0161), and none of the patients treated with vitamin D were hospitalized after 21 days compared to 14% of the patients treated with placebo. Vitamin D significantly reduced the duration of supplemental oxygen among the patients who needed it (4 days vs. 7 days in the placebo group; p = 0.012) and significantly improved the clinical recovery of the patients, as assessed by the WHO scale (p = 0.0048). In conclusion, this study demonstrated that the clinical outcome of COVID-19 patients requiring hospitalization was improved by administration of vitamin D.
References
Amrein, Schnedl, Holl, Riedl, Christopher et al., Effect of high-dose vitamin D 3 on hospital length of stay in critically ill patients with vitamin D deficiency: The VITdAL-ICU randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2014.13204
Angelidi, Belanger, Lorinsky, Karamanis, Chamorro-Pareja et al., Vitamin D Status Is Associated With In-Hospital Mortality and Mechanical Ventilation: A Cohort of COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients, Mayo Clin. Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001
Barnett, Zhao, Koyama, Janz, Wang et al., Vitamin D deficiency and risk of acute lung injury in severe sepsis and severe trauma: A case-control study, Ann. Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/2110-5820-4-5
Beard, Bearden, Striker, Vitamin D and the anti-viral state, J. Clin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006
Braun, Gibbons, Litonjua, Giovannucci, Christopher, Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at critical care initiation is associated with increased mortality, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31822d74f3
Cannata-Andía, Díaz-Sottolano, Fernández, Palomo-Antequera, Herrero-Puente et al., A single-oral bolus of 100,000 IU of cholecalciferol at hospital admission did not improve outcomes in the COVID-19 disease: The COVID-VIT-D-a randomised multicentre international clinical trial, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-022-02290-8
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Díaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Cavalier, Faché, Souberbielle, Randomised, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel Study of Vitamin D 3 Supplementation with Different Schemes Based on Multiples of 25,000 IU Doses, Int. J. Endocrinol, doi:10.1155/2013/327265
Cavalier, Fraser, Bhattoa, Heijboer, Makris et al., Analytical Performance Specifications for 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Examinations, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020431
Cavalier, Lukas, Bekaert, Peeters, Le Goff et al., Analytical and clinical evaluation of the new Fujirebio Lumipulse ® G non-competitive assay for 25(OH)-vitamin D and three immunoassays for 25(OH)D in healthy subjects, osteoporotic patients, third trimester pregnant women, healthy African subjects, hemodialyzed and intensive care patients, Clin. Chem. Lab. Med, doi:10.1515/cclm-2015-0923
Cavalier, Lukas, Crine, Peeters, Carlisi et al., Evaluation of automated immunoassays for 25(OH)-vitamin D determination in different critical populations before and after standardization of the assays, Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.cca.2014.01.026
Coussens, The role of UV radiation and vitamin D in the seasonality and outcomes of infectious disease, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci, doi:10.1039/c6pp00355a
De Niet, Coffiner, Da Silva, Jandrain, Souberbielle et al., A Randomized Study to Compare a Monthly to a Daily Administration of Vitamin D 3 Supplementation, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10060659
Dijkman, Jebbink, Deijs, Milewska, Pyrc et al., Replication-dependent downregulation of cellular angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protein expression by human coronavirus NL63, J. Gen. Virol, doi:10.1099/vir.0.043919-0
Dopico, Evangelou, Ferreira, Guo, Pekalski et al., Widespread seasonal gene expression reveals annual differences in human immunity and physiology, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/ncomms8000
Fabbri, Infante, Ricordi, Editorial-Vitamin D status: A key modulator of innate immunity and natural defense from acute viral respiratory infections, Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci, doi:10.26355/eurrev_202004_20876
Golpour, Bereswill, Heimesaat, Antimicrobial and Immune-Modulatory Effects of Vitamin D Provide Promising Antibiotics-Independent Approaches to Tackle Bacterial Infections-Lessons Learnt from a Literature Survey, Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol, doi:10.1556/1886.2019.00014
Gombart, Pierre, Maggini, A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System-Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12010236
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu7064240
Gruber-Bzura, Vitamin D and Influenza-Prevention or Therapy?, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms19082419
Han, Jones, Tangpricha, Brown, Hao et al., High Dose Vitamin D Administration in Ventilated Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Pilot Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/j.jcte.2016.04.004
Hansdottir, Monick, Hinde, Lovan, Look et al., Respiratory epithelial cells convert inactive vitamin D to its active form: Potential effects on host defense, J. Immunol. Baltim. Md, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.7090
Hewison, Vitamin D and immune function: An overview, Proc. Nutr. Soc, doi:10.1017/S0029665111001650
Higgins, Wischmeyer, Queensland, Sillau, Sufit et al., Relationship of vitamin D deficiency to clinical outcomes in critically ill patients, JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr, doi:10.1177/0148607112444449
Holick, Vitamin, Deficiency, None, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMra070553
Jolliffe, Camargo, Sluyter, Aglipay, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6
Jolliffe, Griffiths, Martineau, Vitamin D in the prevention of acute respiratory infection: Systematic review of clinical studies, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.11.017
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, Bi, Holick, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239252
Kempker, West, Kempker, Siwamogsatham, Alvarez et al., Vitamin D status and the risk for hospital-acquired infections in critically ill adults: A prospective cohort study, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122136
Lang, Aspinall, Vitamin D Status and the Host Resistance to Infections: What It Is Currently (Not) Understood, Clin. Ther, doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.04.004
Mcnally, Menon, Chakraborty, Fisher, Williams et al., The association of vitamin D status with pediatric critical illness, Pediatrics, doi:10.1542/peds.2011-3059
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics With COVID-19 Test Results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Milani, Simonetti, Edefonti, Lava, Agostoni et al., Seasonal variability of the vitamin D effect on physical fitness in adolescents, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-80511-x
Moromizato, Litonjua, Braun, Gibbons, Giovannucci et al., Association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and sepsis in the critically ill, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31829eb7af
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D 3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Nair, Lee, Reynolds, Nguyen, Myburgh et al., Significant perturbation of vitamin Dparathyroid-calcium axis and adverse clinical outcomes in critically ill patients, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-012-2713-y
Olliver, Spelmink, Hiew, Meyer-Hoffert, Henriques-Normark et al., Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D on innate and adaptive immune responses to Streptococcus pneumoniae, J. Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jit355
Quraishi, Litonjua, Moromizato, Gibbons, Camargo et al., Association between prehospital vitamin D status and hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile infections, JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr, doi:10.1177/0148607113511991
Rondanelli, Miccono, Lamburghini, Avanzato, Riva et al., Self-Care for Common Colds: The Pivotal Role of Vitamin D, Vitamin C, Zinc, and Echinacea in Three Main Immune Interactive Clusters (Physical Barriers, Innate and Adaptive Immunity) Involved during an Episode of Common Colds-Practical Advice on Dosages and on the Time to Take These Nutrients/Botanicals in order to Prevent or Treat Common Colds, Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM, doi:10.1155/2018/5813095
Schleck, Souberbielle, Jandrain, Da Silva, De Niet et al., Double-Blind, Parallel Study to Evaluate the Dose-Response of Three Different Vitamin D Treatment Schemes on the 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Serum Concentration in Patients with Vitamin D Deficiency, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu7075227
Teymoori-Rad, Marashi, Vitamin D and COVID-19: From potential therapeutic effects to unanswered questions, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2159
Thickett, Moromizato, Litonjua, Amrein, Quraishi et al., Association between prehospital vitamin D status and incident acute respiratory failure in critically ill patients: A retrospective cohort study, BMJ Open Respir. Res, doi:10.1136/bmjresp-2014-000074
Wei, Christakos, Mechanisms Underlying the Regulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity by Vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu7105392
Who, Working Group on the Clinical Characterisation and Management of COVID-19 infection. A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7
Wise, Camara, Sempos, Lukas, Le Goff et al., Vitamin D Standardization Program (VDSP) intralaboratory study for the assessment of 25-hydroxyvitamin D assay variability and bias, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105917
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14153048",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu14153048",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Retrospective studies showed a relationship between vitamin D status and COVID-19 severity and mortality, with an inverse relation between SARS-CoV-2 positivity and circulating calcifediol levels. The objective of this pilot study was to investigate the effect of vitamin D supplementation on the length of hospital stay and clinical improvement in patients with vitamin D deficiency hospitalized with COVID-19. The study was randomized, double blind and placebo controlled. A total of 50 subjects were enrolled and received, in addition to the best available COVID therapy, either vitamin D (25,000 IU per day over 4 consecutive days, followed by 25,000 IU per week up to 6 weeks) or placebo. The length of hospital stay decreased significantly in the vitamin D group compared to the placebo group (4 days vs. 8 days; p = 0.003). At Day 7, a significantly lower percentage of patients were still hospitalized in the vitamin D group compared to the placebo group (19% vs. 54%; p = 0.0161), and none of the patients treated with vitamin D were hospitalized after 21 days compared to 14% of the patients treated with placebo. Vitamin D significantly reduced the duration of supplemental oxygen among the patients who needed it (4 days vs. 7 days in the placebo group; p = 0.012) and significantly improved the clinical recovery of the patients, as assessed by the WHO scale (p = 0.0048). In conclusion, this study demonstrated that the clinical outcome of COVID-19 patients requiring hospitalization was improved by administration of vitamin D.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu14153048"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4393-2636",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "De Niet",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trémège",
"given": "Mickaël",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coffiner",
"given": "Monte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4157-6570",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rousseau",
"given": "Anne-Francoise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Calmes",
"given": "Doriane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frix",
"given": "Anne-Noelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gester",
"given": "Fanny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Delvaux",
"given": "Muriel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dive",
"given": "Anne-Francoise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guglielmi",
"given": "Elora",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Henket",
"given": "Monique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Staderoli",
"given": "Alicia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maesen",
"given": "Didier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Louis",
"given": "Renaud",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7800-1730",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Guiot",
"given": "Julien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0947-2226",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cavalier",
"given": "Etienne",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-26T04:17:27Z",
"timestamp": 1658809047000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-26T04:31:50Z",
"timestamp": 1658809910000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-26T05:15:04Z",
"timestamp": 1658812504951
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "15",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "15",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1658793600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/15/3048/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3048",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra070553",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7064240",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/c6pp00355a",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.04.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19082419",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/5813095",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12010236",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665111001650",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7105392",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26355/eurrev_202004_20876",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2159",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/vir.0.043919-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.11.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.7090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jit355",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1556/1886.2019.00014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0b013e31829eb7af",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjresp-2014-000074",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0148607112444449",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-012-2713-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0b013e31822d74f3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0148607113511991",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/2110-5820-4-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2014.13204",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2011-3059",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0122136",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.01.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcte.2016.04.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2013/327265",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7075227",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10060659",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"key": "ref39",
"unstructured": "Diagnostic Testing for SARS-CoV-2\nhttps://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/diagnostic-testing-for-sars-cov-2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105917",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13020431",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2015-0923",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cca.2014.01.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-022-02290-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-80511-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms8000",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref47"
}
],
"reference-count": 47,
"references-count": 47,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/15/3048"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Positive Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}
