Effect of Cholecalciferol Supplementation on the Clinical Features and Inflammatory Markers in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Open-Label, Single-Center Study
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132602, NCT05166005, Jun 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
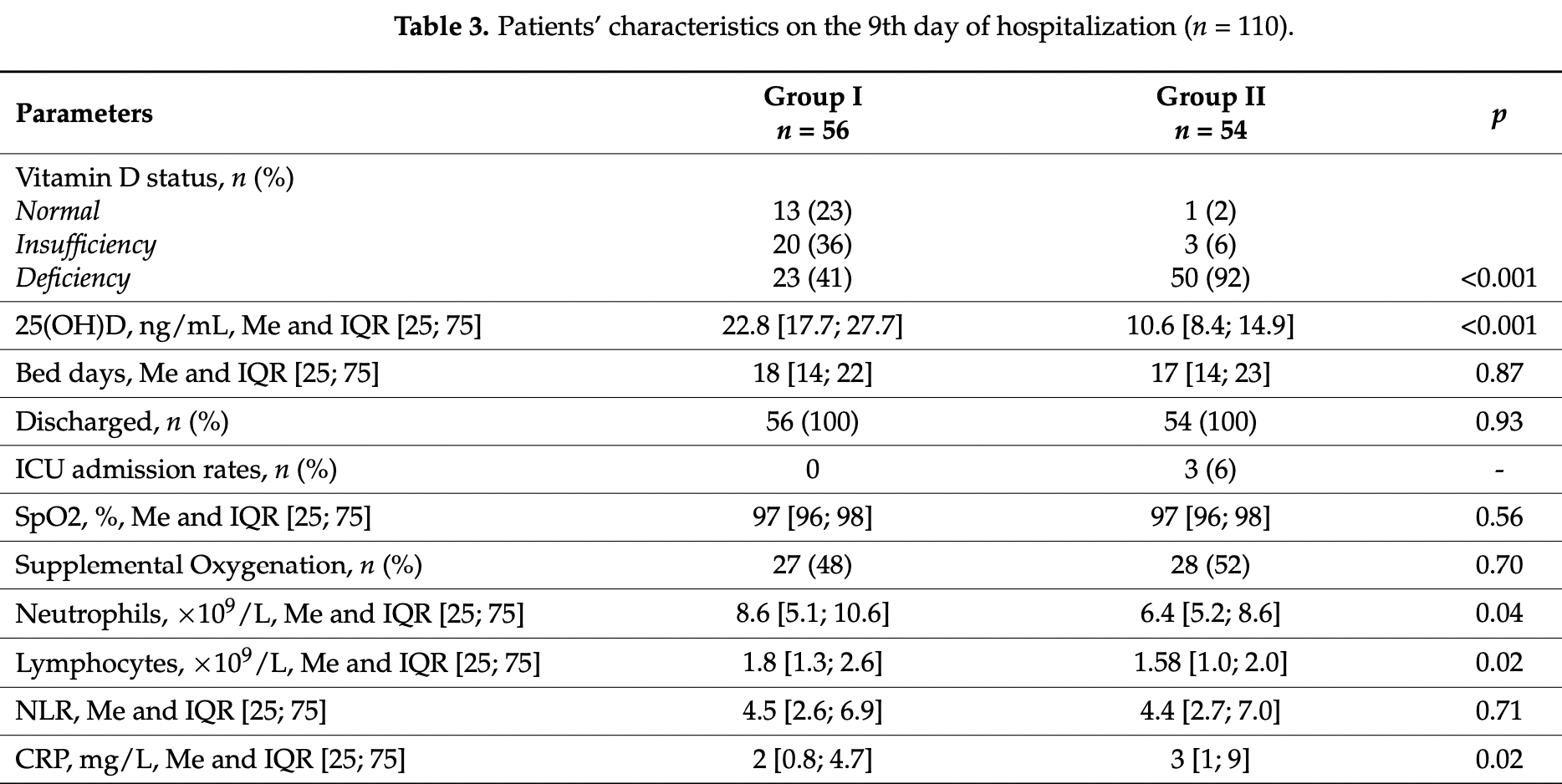
RCT with 56 cholecalciferol and 54 control hospitalized patients with vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency in Russia, showing positive effects on immune status. The median age in the treatment group was 7 years lower and deficiency was less common, while baseline treatment group CT lung involvement and supplemental oxygen use was higher in the treatment group. Treatment increased vitamin D levels and neutrophil and lymphocyte counts, decreased CRP levels, and was associated with a decrease in CD38++CD27 transitional and CD27-CD38+ mature naive B cells and an increase in CD27-CD38- DN B cells.
Cholecalciferol was used in this study.
Meta-analysis shows that late stage treatment with calcitriol / calcifediol (or
paricalcitol, alfacalcidol, etc.) is more effective than cholecalciferol: 66% [47‑78%] lower risk vs. 45% [34‑54%] lower risk.
Cholecalciferol requires two hydroxylation steps to become activated - first
in the liver to calcifediol, then in the kidney to calcitriol. Calcitriol,
paricalcitol, and alfacalcidol are active vitamin D analogs that do not
require conversion. This allows them to have more rapid onset of action
compared to cholecalciferol. The time delay for cholecalciferol to increase
serum calcifediol levels can be 2-3 days, and the delay for converting
calcifediol to active calcitriol can be up to 7 days.
This is the 21st of 40 COVID-19 RCTs for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
This is the 88th of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of ICU admission, 85.9% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.11, treatment 0 of 56 (0.0%), control 3 of 54 (5.6%), NNT 18, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 9.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 7.0% lower, RR 0.93, p = 0.85, treatment 27 of 56 (48.2%), control 28 of 54 (51.9%), NNT 27, baseline oxygen supplementation was higher in the treatment group, 38 vs. 32, day 9.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Karonova et al., 23 Jun 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Russia, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, study period 30 November, 2020 - 20 March, 2021, dosage 50,000IU days 1, 8, trial NCT05166005 (history).
Contact: karonova@mail.ru (corresponding author), ksgolovatiuk@gmail.com, igorek1981@yandex.ru, arabicaa@gmail.com, armikhaylova@yandex.ru, akino97@bk.ru, daria.lagutina.i@yandex.ru, catherine3452@yandex.ru, olgakalinina@mail.ru, golovkin_a@mail.ru, shlyakhto_ev@almazovcentre.ru, williamgrant08@comcast.net.
Effect of Cholecalciferol Supplementation on the Clinical Features and Inflammatory Markers in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Open-Label, Single-Center Study
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132602
Recent studies showed that a low 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) level was associated with a higher risk of morbidity and severe course of COVID-19. Our study aimed to evaluate the effects of cholecalciferol supplementation on the clinical features and inflammatory markers in patients with COVID-19. A serum 25(OH)D level was determined in 311 COVID-19 patients. Among them, 129 patients were then randomized into two groups with similar concomitant medication. Group I (n = 56) received a bolus of cholecalciferol at a dose of 50,000 IU on the first and the eighth days of hospitalization. Patients from Group II (n = 54) did not receive the supplementation. We found significant differences between groups with the preferential increase in serum 25(OH)D level and ∆ 25(OH)D in Group I on the ninth day of hospitalization (p < 0.001). The serum 25(OH)D level on the ninth day was negatively associated with the number of bed days (r = −0.23, p = 0.006); we did not observe other clinical benefits in patients receiving an oral bolus of cholecalciferol. Moreover, in Group I, neutrophil and lymphocyte counts were significantly higher (p = 0.04; p = 0.02), while the C-reactive protein level was significantly lower on the ninth day of hospitalization (p = 0.02). Patients with supplementation of 100,000 IU of cholecalciferol, compared to those without supplementation, showed a decrease in the frequencies of CD38++CD27 transitional and CD27−CD38+ mature naive B cells (p = 0.006 and p = 0.02) and an increase in the level of CD27−CD38− DN B cells (p = 0.02). Thus, the rise in serum 25(OH)D level caused by vitamin D supplementation in vitamin D insufficient and deficient patients may positively affect immune status and hence the course of COVID-19.
References
Agraz-Cibrian, Giraldo, Urcuqui-Inchima, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces formation of neutrophil extracellular trap-like structures and modulates the transcription of genes whose products are neutrophil extracellular trap-associated proteins: A pilot study, Steroids, doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2018.11.001
Alcala-Diaz, Limia-Perez, Gomez-Huelgas, Martin-Escalante, Cortes-Rodriguez et al., Calcifediol Treatment and Hospital Mortality Due to COVID-19: A Cohort Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061760
Amrein, Scherkl, Hoffmann, Neuwersch-Sommeregger, Köstenberger et al., deficiency 2.0: An update on the current status worldwide, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubée, Legrand et al., Vitamin D Supplementation Associated to Better Survival in Hospitalized Frail Elderly COVID-19 Patients: The GERIA-COVID Quasi-Experimental Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377
Ao, Kikuta, Ishii, The Effects of Vitamin D on Immune System and Inflammatory Diseases, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom11111624
Berry, Hesketh, Power, Hypponen, Vitamin D status has a linear association with seasonal infections and lung function in British adults, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114511001991
Bouillon, Marcocci, Carmeliet, Bikle, White et al., Skeletal and extraskeletal actions of Vitamin D: Current evidence and outstanding questions, Endocr. Rev, doi:10.1210/er.2018-00126
Carpagnano, Di Lecce, Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico et al., Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, J. Endocrinol. Investig, doi:10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x
Chen, Sims, Chen, Gu, Chen et al., Modulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on human B cell differentiation, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.179.3.1634
Chinapaka, Baba, Kandakatla, Author Correction: Impact of daily high dose oral vitamin D therapy on the inflammatory markers in patients with COVID-19 disease, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-97181-y
Dankers, Colin, Van Hamburg, Lubberts, Vitamin D in Autoimmunity: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2016.00697
Deluca, Cantorna, Vitamin D: Its role and uses in immunology, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.01-0433rev
Dissanayake, De Silva, Sumanatilleke, De Silva, Gamage et al., Prognostic and therapeutic role of vitamin D in COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab892
Efird, Anderson, Jindal, Redding, Thompson et al., The Interaction of Vitamin D and Corticosteroids: A Mortality Analysis of 26,508 Veterans Who Tested Positive for SARS-CoV-2, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph19010447
Elamir, Amir, Lim, Rana, Lopez et al., A randomized pilot study using calcitriol in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Bone, doi:10.1016/j.bone.2021.116175
Gao, Ding, Dong, Zhang, Kursat Azkur et al., Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: A review, Allergy, doi:10.1111/all.14657
Geldmeyer-Hilt, Heine, Hartmann, Baumgrass, Radbruch et al., 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 impairs NF-κB activation in human naïve B cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.03.078
Golovkin, Kalinina, Bezrukikh, Aquino, Zaikova et al., Imbalanced Immune Response of T-Cell and B-Cell Subsets in Patients with Moderate and Severe COVID-19, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13101966
Gonen, Alaylioglu, Durcan, Ozdemir, Sahin et al., Rapid and Effective Vitamin D Supplementation May Present Better Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Patients by Altering Serum INOS1, IL1B, IFNg, Cathelicidin-LL37, and ICAM1, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13114047
Grant, Anouti, Boucher, Dursun, Gezen-Ak et al., A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health, Nutrients
Gusev, Sarapultsev, Solomatina, Chereshnev, SARS-CoV-2-Specific Immune Response and the Pathogenesis of COVID-19, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23031716
Hanley, Sutter, Goodman, Du, Sekiguchi et al., Circulating B cells in type 1 diabetics exhibit fewer maturation-associated phenotypes, Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2017.09.021
Hayes, Hubler, Moore, Barta, Praska et al., Vitamin D Actions on CD4(+) T Cells in Autoimmune Disease, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2015.00100
Heine, Niesner, Chang, Steinmeyer, Zügel et al., 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) promotes IL-10 production in human B cells, Eur. J. Immunol, doi:10.1002/eji.200838216
Karonova, Andreeva, Golovatuk, Bykova, Simanenkova et al., Low 25(OH)D Level Is Associated with Severe Course and Poor Prognosis in COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13093021
Karonova, Kudryavtsev, Golovatyuk, Aquino, Kalinina et al., Vitamin D Status and Immune Response in Hospitalized Patients with Moderate and Severe COVID-19, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15030305
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, Bi, Holick, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239252
Kaya, Pamukçu, Yakar, The role of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, Epidemiol. Health, doi:10.4178/epih.e2021074
Kazemi, Mohammadi, Aghababaee, Golzarand, Clark et al., Association of Vitamin D status with SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmab012
Khammissa, Fourie, Motswaledi, Ballyram, Lemmer et al., The Biological Activities of Vitamin D and Its Receptor in Relation to Calcium and Bone Homeostasis, Cancer, Immune and Cardiovascular Systems, Skin Biology, and Oral Health, BioMed Res. Int, doi:10.1155/2018/9276380
Kudryavtsev, Arsentieva, Batsunov, Korobova, Khamitova et al., Alterations in B Cell and Follicular T-Helper Cell Subsets in Patients with Acute COVID-19 and COVID-19 Convalescents, Curr. Issues Mol. Biol, doi:10.3390/cimb44010014
Kudryavtsev, Kalinina, Bezrukikh, Melnik, Golovkin, The significance of phenotyping and quantification of plasma extracellular vesicles levels using high-sensitivity flow cytometry during covid-19 treatment, Viruses
Kudryavtsev, Rubinstein, Golovkin, Kalinina, Vasilyev et al., Dysregulated Immune Responses in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Patients: A Comprehensive Overview, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14051082
Lakkireddy, Gadiga, Malathi, Karra, Raju et al., None
Ling, Broad, Murphy, Pappachan, Pardesi-Newton et al., High-Dose Cholecalciferol Booster Therapy is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Multi-Centre Observational Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12123799
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Jamalimoghadamsiahkali, Asadi, Zarei et al., Treatment With 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (Calcifediol) Is Associated With a Reduction in the Blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Marker of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Pilot Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial, Endocr. Pract. Off. J. Am. Coll. Endocrinol. Am. Assoc. Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016
Mangge, Kneihsl, Schnedl, Sendlhofer, Curcio et al., Immune Responses against SARS-CoV-2-Questions and Experiences, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines9101342
Mazziotti, Formenti, Frara, Doga, Giustina, Vitamin D and Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis, Front. Horm. Res, doi:10.1159/000486078
Mercola, Grant, Wagner, Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113361
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Murdaca, Tonacci, Negrini, Greco, Borro et al., Emerging role of vitamin D in autoimmune diseases: An update on evidence and therapeutic implications, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102350
Oristrell, Oliva, Casado, Subirana, Domínguez et al., Vitamin D supplementation and COVID-19 risk: A population-based, cohort study, J. Endocrinol. Investig, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01639-9
Pludowski, Holick, Grant, Konstantynowicz, Mascarenhas et al., Vitamin D supplementation guidelines, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.01.021
Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Suri, Yaddanapudi et al., Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: A randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study), Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065
Rolf, Muris, Hupperts, Damoiseaux, Vitamin D effects on B cell function in autoimmunity, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1111/nyas.12440
Sabico, Enani, Sheshah, Aljohani, Aldisi et al., Effects of a 2-Week 5000 IU versus 1000 IU Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Recovery of Symptoms in Patients with Mild to Moderate Covid-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072170
Seal, Bertenthal, Carey, Grunfeld, Bikle et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and COVID-19-Related Hospitalization and Mortality, J. Gen. Intern. Med, doi:10.1007/s11606-021-07170-0
Shafqat, Shafqat, Salameh, Kashir, Alkattan et al., Mechanistic Insights Into the Immune Pathophysiology of COVID-19
Shah, Varna, Sharma, Mavalankar, Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity?: A systematic review, QJM Int. J. Med, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040
Shuwa, Shaw, Knight, Wemyss, Mcclure et al., Alterations in T and B cell function persist in convalescent COVID-19 patients, Med, doi:10.1016/j.medj.2021.03.013
Soliman, Abdelaziz, Fathy, Impact of Vitamin D Therapy on the Progress COVID-19: Six Weeks Follow-Up Study of Vitamin D Deficient Elderly Diabetes Patients, Proc. Singap. Healthc, doi:10.1177/20101058211041405
Taefehshokr, Taefehshokr, Heit, Mechanisms of Dysregulated Humoral and Cellular Immunity by SARS-CoV-2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens9121027
Terrier, Derian, Schoindre, Chaara, Geri et al., Restoration of regulatory and effector T cell balance and B cell homeostasis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients through vitamin D supplementation, Arthritis Res. Ther, doi:10.1186/ar4060
Todosenko, Vulf, Yurova, Khaziakhmatova, Mikhailova et al., Causal Links between Hypovitaminosis D and Dysregulation of the T Cell Connection of Immunity Associated with Obesity and Concomitant Pathologies, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines9121750
Torres, Casado, Vigón, Rodríguez-Mora, Mateos et al., Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D, Biomed. Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965
Xu, Yang, Chen, Luo, Zhang et al., Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system, Mol. Med. Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.7546
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14132602",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu14132602",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Recent studies showed that a low 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) level was associated with a higher risk of morbidity and severe course of COVID-19. Our study aimed to evaluate the effects of cholecalciferol supplementation on the clinical features and inflammatory markers in patients with COVID-19. A serum 25(OH)D level was determined in 311 COVID-19 patients. Among them, 129 patients were then randomized into two groups with similar concomitant medication. Group I (n = 56) received a bolus of cholecalciferol at a dose of 50,000 IU on the first and the eighth days of hospitalization. Patients from Group II (n = 54) did not receive the supplementation. We found significant differences between groups with the preferential increase in serum 25(OH)D level and Δ 25(OH)D in Group I on the ninth day of hospitalization (p < 0.001). The serum 25(OH)D level on the ninth day was negatively associated with the number of bed days (r = −0.23, p = 0.006); we did not observe other clinical benefits in patients receiving an oral bolus of cholecalciferol. Moreover, in Group I, neutrophil and lymphocyte counts were significantly higher (p = 0.04; p = 0.02), while the C-reactive protein level was significantly lower on the ninth day of hospitalization (p = 0.02). Patients with supplementation of 100,000 IU of cholecalciferol, compared to those without supplementation, showed a decrease in the frequencies of CD38++CD27 transitional and CD27−CD38+ mature naive B cells (p = 0.006 and p = 0.02) and an increase in the level of CD27−CD38− DN B cells (p = 0.02). Thus, the rise in serum 25(OH)D level caused by vitamin D supplementation in vitamin D insufficient and deficient patients may positively affect immune status and hence the course of COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu14132602"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karonova",
"given": "Tatiana L.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0651-7110",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Golovatyuk",
"given": "Ksenia A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kudryavtsev",
"given": "Igor V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4878-6909",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chernikova",
"given": "Alena T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mikhaylova",
"given": "Arina A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aquino",
"given": "Arthur D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lagutina",
"given": "Daria I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0584-2330",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zaikova",
"given": "Ekaterina K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1916-5705",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kalinina",
"given": "Olga V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7577-628X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Golovkin",
"given": "Alexey S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1439-3285",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Grant",
"given": "William B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shlyakhto",
"given": "Evgeny V.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-24T02:43:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656038580000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-24T03:08:07Z",
"timestamp": 1656040087000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012190",
"award": [
"075-15-2022-301"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-24T03:41:11Z",
"timestamp": 1656042071794
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "13",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
23
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "13",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1655942400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/13/2602/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2602",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmab012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114511001991",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113361",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/9276380",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.steroids.2018.11.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/er.2018-00126",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2017.7546",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13093021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph15030305",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab892",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"article-title": "Prevention, diagnosis and treatment of new coronavirus infection (COVID-19)",
"key": "ref13",
"series-title": "Temporary Guidelines",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.01.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13101966",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2017.09.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4178/epih.e2021074",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14030639",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11606-021-07170-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph19010447",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcac040",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12123799",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13114047",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061760",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-021-01639-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/20101058211041405",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000486078",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13050767",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14657",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.01-0433rev",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom11111624",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2015.00100",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines9121750",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.03.078",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.179.3.1634",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.200838216",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nyas.12440",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102350",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-97181-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072170",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bone.2021.116175",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens9121027",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines9101342",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23031716",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.835104",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14051082",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/ar4060",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref53"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2016.00697",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref54"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medj.2021.03.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref55"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cimb44010014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref56"
}
],
"reference-count": 56,
"references-count": 56,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/13/2602"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of Cholecalciferol Supplementation on the Clinical Features and Inflammatory Markers in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Open-Label, Single-Center Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}
