Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors
et al., Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277, Aug 2022
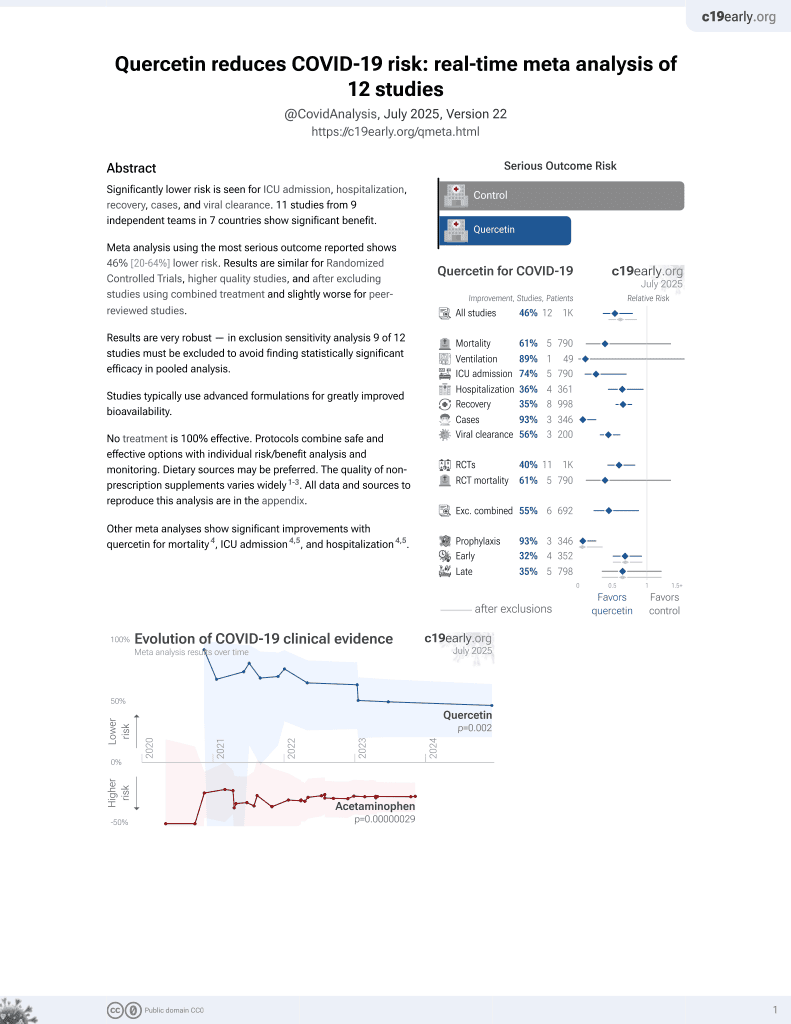
Quercetin for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2022, now with p = 0.0018 from 9 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
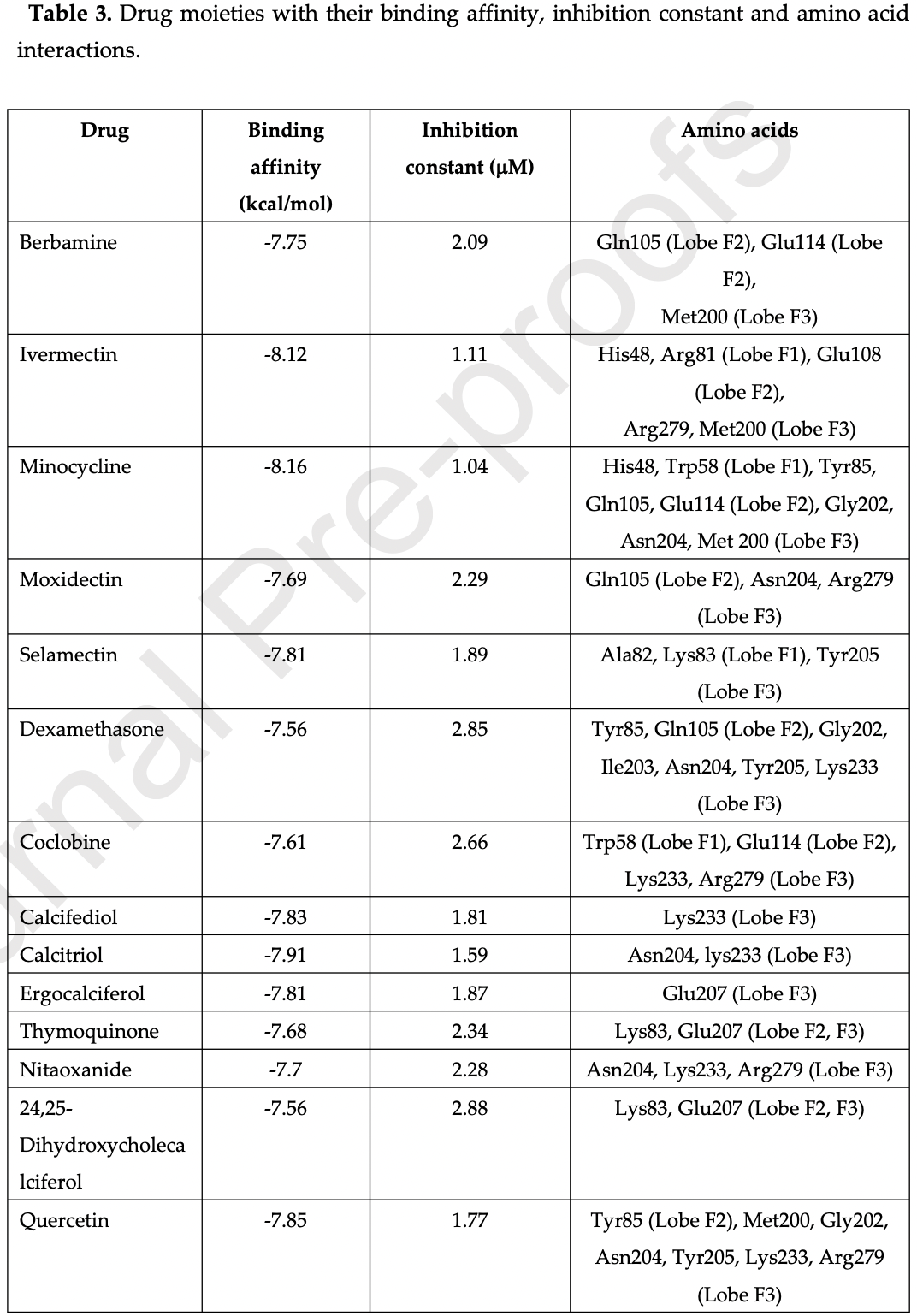
In silico study of SARS-CoV-1&2 endodomains and ezrin docking, identifying ivermectin, quercetin, calcifediol, calcitriol, selamectin, and minocycline as potential therapeutic drugs with strong ezrin binding which may restrict viral endodomain interaction while also stabilizing ezrin, thereby reducing virus fusion and infection.
91 preclinical studies support the efficacy of quercetin for COVID-19:
In silico studies predict inhibition of SARS-CoV-2, or minimization of side effects, with quercetin or metabolites via binding to the spikeA,11,12,18,19,32,34,35,37,40,48,49,51,52,75 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,8), MproC,7,8,11,12,16,18,20,22,24,26,28,30,33,34,37,40,44,46-48,52-55,72 , RNA-dependent RNA polymeraseD,8,10-12,18,42 , PLproE,12,47,55 , ACE2F,27,32,33,37,38,47,51 , TMPRSS2G,32, nucleocapsidH,12, helicaseI,12,39,44 , endoribonucleaseJ,49, NSP16/10K,15, cathepsin LL,36, Wnt-3M,32, FZDN,32, LRP6O,32, ezrinP,50, ADRPQ,48, NRP1R,51, EP300S,25, PTGS2T,33, HSP90AA1U,25,33 , matrix metalloproteinase 9V,41, IL-6W,31,45 , IL-10X,31, VEGFAY,45, and RELAZ,45 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionAA,9.
In vitro studies demonstrate inhibition of the MproC,24,58,63,71 protein, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionAA,59.
In vitro studies demonstrate efficacy in Calu-3AB,62, A549AC,31, HEK293-ACE2+AD,70, Huh-7AE,35, Caco-2AF,61, Vero E6AG,29,52,61 , mTECAH,64, RAW264.7AI,64, and HLMECAJ,9 cells.
Animal studies demonstrate efficacy in K18-hACE2 miceAK,67, db/db miceAL,64,74 , BALB/c miceAM,73, and rats29.
Quercetin reduced proinflammatory cytokines and protected lung and kidney tissue against LPS-induced damage in mice73, inhibits LPS-induced cytokine storm by modulating key inflammatory and antioxidant pathways in macrophages14, may block ACE2-spike interaction and NLRP3 inflammasome, limiting viral entry and inflammation5, upregulates the SIRT1/AMPK axis to inhibit oxidative injury and accelerate viral clearance76, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a ion channel activity, which contributes to viral pathogenicity and cytotoxicity66, may alleviate COVID-19 ARDS via inhibition of EGFR and JAK2 inflammatory targets1, may destabilize the Spike protein, IL-6R, and integrins via conserved residues, blocking viral entry, hyperinflammation, and platelet aggregation77, and may reduce COVID-19 neuroinflammation and cognitive dysfunction through anti-inflammatory mechanisms and neuroprotective effects78.
Study covers quercetin, vitamin D, and ivermectin.
1.
Gupta et al., Harnessing phytoconstituents to treat COVID-19 triggered acute respiratory distress syndrome: Insights from network pharmacology, and molecular modeling, Phytochemistry Letters, doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2025.104105.
2.
Sun et al., Feasibility of the inhibitor development for SARS-CoV-2: a systematic approach for drug design, Journal of Molecular Modeling, doi:10.1007/s00894-025-06541-2.
3.
Torabfam et al., Improving quercetin solubility via structural modification enhances dual-target coronavirus entry: an integrated in-vitro and in-silico study, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-27374-2.
4.
Abdelhameed et al., Phytochemical and antiviral investigation of Cynanchum acutum L. extract and derived semi-synthetic analogs targeting SARS-CoV-2 main protease, Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1186/s43094-025-00907-2.
5.
Manikyam et al., INP-Guided Network Pharmacology Discloses Multi-Target Therapeutic Strategy Against Cytokine and IgE Storms in the SARS-CoV-2 NB.1.8.1 Variant, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-6819274/v1.
6.
Makoana et al., Integration of metabolomics and chemometrics with in-silico and in-vitro approaches to unravel SARS-Cov-2 inhibitors from South African plants, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0320415.
7.
Bano et al., Biochemical Screening of Phytochemicals and Identification of Scopoletin as a Potential Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, Revealing Its Biophysical Impact on Structural Stability, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17030402.
8.
Rajamanickam et al., Exploring the Potential of Siddha Formulation MilagaiKudineer-Derived Phytotherapeutics Against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Investigation for Antiviral Intervention, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, doi:10.26502/fjppr.0105.
9.
Moharram et al., Secondary metabolites of Alternaria alternate appraisal of their SARS-CoV-2 inhibitory and anti-inflammatory potentials, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0313616.
10.
Metwaly et al., Integrated study of Quercetin as a potent SARS-CoV-2 RdRp inhibitor: Binding interactions, MD simulations, and In vitro assays, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0312866.
11.
Al balawi et al., Assessing multi-target antiviral and antioxidant activities of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2: an integrated in vitro and in silico study, Bioresources and Bioprocessing, doi:10.1186/s40643-024-00822-z.
12.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
13.
Pan et al., Decoding the mechanism of Qingjie formula in the prevention of COVID-19 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39167.
14.
Xu et al., Quercetin inhibited LPS-induced cytokine storm by interacting with the AKT1-FoxO1 and Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway in macrophages, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-71569-y.
15.
Tamil Selvan et al., Computational Investigations to Identify Potent Natural Flavonoid Inhibitors of the Nonstructural Protein (NSP) 16/10 Complex Against Coronavirus, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.68098.
16.
Sunita et al., Characterization of Phytochemical Inhibitors of the COVID-19 Primary Protease Using Molecular Modelling Approach, Asian Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, doi:10.56557/ajmab/2024/v9i28800.
17.
Wu et al., Biomarkers Prediction and Immune Landscape in Covid-19 and “Brain Fog”, Elsevier BV, doi:10.2139/ssrn.4897774.
18.
Raman et al., Phytoconstituents of Citrus limon (Lemon) as Potential Inhibitors Against Multi Targets of SARS‐CoV‐2 by Use of Molecular Modelling and In Vitro Determination Approaches, ChemistryOpen, doi:10.1002/open.202300198.
19.
Asad et al., Exploring the antiviral activity of Adhatoda beddomei bioactive compounds in interaction with coronavirus spike protein, Archives of Medical Reports, 1:1, archmedrep.com/index.php/amr/article/view/3.
20.
Irfan et al., Phytoconstituents of Artemisia Annua as potential inhibitors of SARS CoV2 main protease: an in silico study, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-024-09387-w.
21.
Yuan et al., Network pharmacology and molecular docking reveal the mechanisms of action of Panax notoginseng against post-COVID-19 thromboembolism, Review of Clinical Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics - International Edition, doi:10.61873/DTFA3974.
22.
Nalban et al., Targeting COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) main protease through phytochemicals of Albizia lebbeck: molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation, MM–PBSA free energy calculations, and DFT analysis, Journal of Proteins and Proteomics, doi:10.1007/s42485-024-00136-w.
23.
Zhou et al., Bioinformatics and system biology approaches to determine the connection of SARS-CoV-2 infection and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0300441.
24.
Waqas et al., Discovery of Novel Natural Inhibitors Against SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: A Rational Approach to Antiviral Therapeutics, Current Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.2174/0109298673292839240329081008.
25.
Hasanah et al., Decoding the therapeutic potential of empon-empon: a bioinformatics expedition unraveling mechanisms against COVID-19 and atherosclerosis, International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics, doi:10.22159/ijap.2024v16i2.50128.
26.
Shaik et al., Computational identification of selected bioactive compounds from Cedrus deodara as inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 main protease: a pharmacoinformatics study, Indian Drugs, doi:10.53879/id.61.02.13859.
27.
Wang et al., Investigating the Mechanism of Qu Du Qiang Fei 1 Hao Fang Formula against Coronavirus Disease 2019 Based on Network Pharmacology Method, World Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, doi:10.4103/2311-8571.395061.
28.
Singh et al., Unlocking the potential of phytochemicals in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 M Pro protein - An in-silico and cell-based approach, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3888947/v1.
29.
El-Megharbel et al., Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of (Artemisinin/Quercetin/ Zinc) novel mixed ligand complex with assessment of its potent high antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and antioxidant capacity against toxicity induced by acrylamide in male rats, PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.15638.
30.
Akinwumi et al., Evaluation of therapeutic potentials of some bioactive compounds in selected African plants targeting main protease (Mpro) in SARS-CoV-2: a molecular docking study, Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics, doi:10.1186/s43042-023-00456-4.
31.
Yang et al., Active ingredient and mechanistic analysis of traditional Chinese medicine formulas for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: Insights from bioinformatics and in vitro experiments, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000036238.
32.
Chandran et al., Molecular docking analysis of quercetin with known CoVid-19 targets, Bioinformation, doi:10.6026/973206300191081.
33.
Qin et al., Exploring the bioactive compounds of Feiduqing formula for the prevention and management of COVID-19 through network pharmacology and molecular docking, Medical Data Mining, doi:10.53388/MDM202407003.
34.
Moschovou et al., Exploring the Binding Effects of Natural Products and Antihypertensive Drugs on SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Investigation of Main Protease and Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242115894.
35.
Pan (B) et al., Quercetin: A promising drug candidate against the potential SARS-CoV-2-Spike mutants with high viral infectivity, Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2023.10.029.
36.
Ahmed et al., Evaluation of the Effect of Zinc, Quercetin, Bromelain and Vitamin C on COVID-19 Patients, International Journal of Diabetes Management, doi:10.61797/ijdm.v2i2.259.
37.
Thapa et al., In-silico Approach for Predicting the Inhibitory Effect of Home Remedies on Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2, Makara Journal of Science, doi:10.7454/mss.v27i3.1609.
38.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
39.
Singh (B) et al., Flavonoids as Potent Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp13 Helicase: Grid Based Docking Approach, Middle East Research Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.36348/merjps.2023.v03i04.001.
40.
Mandal et al., In silico anti-viral assessment of phytoconstituents in a traditional (Siddha Medicine) polyherbal formulation – Targeting Mpro and pan-coronavirus post-fusion Spike protein, Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.07.004.
41.
Sai Ramesh et al., Computational analysis of the phytocompounds of Mimusops elengi against spike protein of SARS CoV2 – An Insilico model, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125553.
42.
Corbo et al., Inhibitory potential of phytochemicals on five SARS-CoV-2 proteins: in silico evaluation of endemic plants of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, doi:10.1080/13102818.2023.2222196.
43.
Azmi et al., Utilization of quercetin flavonoid compounds in onion (Allium cepa L.) as an inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein against ACE2 receptors, 11th International Seminar on New Paradigm and Innovation on Natural Sciences and its Application, doi:10.1063/5.0140285.
44.
Alanzi et al., Structure-based virtual identification of natural inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 and its Delta and Omicron variant proteins, Future Virology, doi:10.2217/fvl-2022-0184.
45.
Yang (B) et al., In silico evidence implicating novel mechanisms of Prunella vulgaris L. as a potential botanical drug against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1188086.
46.
Wang (B) et al., Computational Analysis of Lianhua Qingwen as an Adjuvant Treatment in Patients with COVID-19, Society of Toxicology Conference, 2023, www.researchgate.net/publication/370491709_Y_Wang_A_E_Tan_O_Chew_A_Hsueh_and_D_E_Johnson_2023_Computational_Analysis_of_Lianhua_Qingwen_as_an_Adjuvant_Treatment_in_Patients_with_COVID-19_Toxicologist_1921_507.
47.
Ibeh et al., Computational studies of potential antiviral compounds from some selected Nigerian medicinal plants against SARS-CoV-2 proteins, Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2023.101230.
48.
Nguyen et al., The Potential of Ameliorating COVID-19 and Sequelae From Andrographis paniculata via Bioinformatics, Bioinformatics and Biology Insights, doi:10.1177/11779322221149622.
49.
Alavi et al., Interaction of Epigallocatechin Gallate and Quercetin with Spike Glycoprotein (S-Glycoprotein) of SARS-CoV-2: In Silico Study, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10123074.
50.
Chellasamy et al., Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors, Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277.
51.
Şimşek et al., In silico identification of SARS-CoV-2 cell entry inhibitors from selected natural antivirals, Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, doi:10.1016/j.jmgm.2021.108038.
52.
Kandeil et al., Bioactive Polyphenolic Compounds Showing Strong Antiviral Activities against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10060758.
53.
Rehman et al., Natural Compounds as Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (3CLpro): A Molecular Docking and Simulation Approach to Combat COVID-19, Current Pharmaceutical Design, doi:10.2174/1381612826999201116195851.
54.
Sekiou et al., In-Silico Identification of Potent Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) from Natural Products: Quercetin, Hispidulin, and Cirsimaritin Exhibited Better Potential Inhibition than Hydroxy-Chloroquine Against COVID-19 Main Protease Active Site and ACE2, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12181404.v1.
55.
Zhang et al., In silico screening of Chinese herbal medicines with the potential to directly inhibit 2019 novel coronavirus, Journal of Integrative Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.joim.2020.02.005.
56.
Sisti et al., Evaluation of respiratory virus transmissibility and resilience from fomites: the case of 11 SARS-CoV-2 clinical isolates, Applied and Environmental Microbiology, doi:10.1128/aem.00774-25.
57.
Spinelli et al., Amphibian‐Derived Peptides as Natural Inhibitors of SARS‐CoV‐2 Main Protease (Mpro): A Combined In Vitro and In Silico Approach, Chemistry & Biodiversity, doi:10.1002/cbdv.202403202.
58.
Aguilera-Rodriguez et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro by chemically modified tyrosinase from Agaricus bisporus, RSC Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.1039/D4MD00289J.
59.
Emam et al., Establishment of in-house assay for screening of anti-SARS-CoV-2 protein inhibitors, AMB Express, doi:10.1186/s13568-024-01739-8.
60.
Fang et al., Development of nanoparticles incorporated with quercetin and ACE2-membrane as a novel therapy for COVID-19, Journal of Nanobiotechnology, doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02435-2.
61.
Roy et al., Quercetin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection and prevents syncytium formation by cells co-expressing the viral spike protein and human ACE2, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-024-02299-w.
62.
DiGuilio et al., Quercetin improves and protects Calu-3 airway epithelial barrier function, Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, doi:10.3389/fcell.2023.1271201.
63.
Zhang (B) et al., Discovery of the covalent SARS‐CoV‐2 Mpro inhibitors from antiviral herbs via integrating target‐based high‐throughput screening and chemoproteomic approaches, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29208.
64.
Wu (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 N protein induced acute kidney injury in diabetic db/db mice is associated with a Mincle-dependent M1 macrophage activation, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1264447.
65.
Xu (B) et al., Bioactive compounds from Huashi Baidu decoction possess both antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects against COVID-19, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, doi:10.1073/pnas.2301775120.
66.
Fam et al., Channel activity of SARS-CoV-2 viroporin ORF3a inhibited by adamantanes and phenolic plant metabolites, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31764-9.
67.
Aguado et al., Senolytic therapy alleviates physiological human brain aging and COVID-19 neuropathology, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.01.17.524329.
68.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
69.
Munafò et al., Quercetin and Luteolin Are Single-digit Micromolar Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1149846/v1.
70.
Singh (C) et al., The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 virus induces heme oxygenase-1: Pathophysiologic implications, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166322.
71.
Bahun et al., Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro main protease by plant polyphenols, Food Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131594.
72.
Abian et al., Structural stability of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro and identification of quercetin as an inhibitor by experimental screening, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.235.
73.
Shaker et al., Anti-cytokine Storm Activity of Fraxin, Quercetin, and their Combination on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cytokine Storm in Mice: Implications in COVID-19, Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.30476/ijms.2023.98947.3102.
74.
Wu (C) et al., Treatment with Quercetin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 N protein-induced acute kidney injury by blocking Smad3-dependent G1 cell cycle arrest, Molecular Therapy, doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.12.002.
75.
Azmi (B) et al., The role of vitamin D receptor and IL‐6 in COVID‐19, Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine, doi:10.1002/mgg3.2172.
76.
Shokri-Afra et al., Targeting SIRT1: A Potential Strategy for Combating Severe COVID‐19, BioMed Research International, doi:10.1155/bmri/9507417.
a.
The trimeric spike (S) protein is a glycoprotein that mediates viral entry by binding to the host ACE2 receptor, is critical for SARS-CoV-2's ability to infect host cells, and is a target of neutralizing antibodies. Inhibition of the spike protein prevents viral attachment, halting infection at the earliest stage.
b.
The receptor binding domain is a specific region of the spike protein that binds ACE2 and is a major target of neutralizing antibodies. Focusing on the precise binding site allows highly specific disruption of viral attachment with reduced potential for off-target effects.
c.
The main protease or Mpro, also known as 3CLpro or nsp5, is a cysteine protease that cleaves viral polyproteins into functional units needed for replication. Inhibiting Mpro disrupts the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle within the host cell, preventing the creation of new copies.
d.
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called nsp12, is the core enzyme of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex that copies the positive-sense viral RNA genome into negative-sense templates for progeny RNA synthesis. Inhibiting RdRp blocks viral genome replication and transcription.
e.
The papain-like protease (PLpro) has multiple functions including cleaving viral polyproteins and suppressing the host immune response by deubiquitination and deISGylation of host proteins. Inhibiting PLpro may block viral replication and help restore normal immune responses.
f.
The angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) protein is a host cell transmembrane protein that serves as the cellular receptor for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. ACE2 is expressed on many cell types, including epithelial cells in the lungs, and allows the virus to enter and infect host cells. Inhibition may affect ACE2's physiological function in blood pressure control.
g.
Transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) is a host cell protease that primes the spike protein, facilitating cellular entry. TMPRSS2 activity helps enable cleavage of the spike protein required for membrane fusion and virus entry. Inhibition may especially protect respiratory epithelial cells, buy may have physiological effects.
h.
The nucleocapsid (N) protein binds and encapsulates the viral genome by coating the viral RNA. N enables formation and release of infectious virions and plays additional roles in viral replication and pathogenesis. N is also an immunodominant antigen used in diagnostic assays.
i.
The helicase, or nsp13, protein unwinds the double-stranded viral RNA, a crucial step in replication and transcription. Inhibition may prevent viral genome replication and the creation of new virus components.
j.
The endoribonuclease, also known as NendoU or nsp15, cleaves specific sequences in viral RNA which may help the virus evade detection by the host immune system. Inhibition may hinder the virus's ability to mask itself from the immune system, facilitating a stronger immune response.
k.
The NSP16/10 complex consists of non-structural proteins 16 and 10, forming a 2'-O-methyltransferase that modifies the viral RNA cap structure. This modification helps the virus evade host immune detection by mimicking host mRNA, making NSP16/10 a promising antiviral target.
l.
Cathepsin L is a host lysosomal cysteine protease that can prime the spike protein through an alternative pathway when TMPRSS2 is unavailable. Dual targeting of cathepsin L and TMPRSS2 may maximize disruption of alternative pathways for virus entry.
m.
Wingless-related integration site (Wnt) ligand 3 is a host signaling molecule that activates the Wnt signaling pathway, which is important in development, cell growth, and tissue repair. Some studies suggest that SARS-CoV-2 infection may interfere with the Wnt signaling pathway, and that Wnt3a is involved in SARS-CoV-2 entry.
n.
The frizzled (FZD) receptor is a host transmembrane receptor that binds Wnt ligands, initiating the Wnt signaling cascade. FZD serves as a co-receptor, along with ACE2, in some proposed mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. The virus may take advantage of this pathway as an alternative entry route.
o.
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 is a cell surface co-receptor essential for Wnt signaling. LRP6 acts in tandem with FZD for signal transduction and has been discussed as a potential co-receptor for SARS-CoV-2 entry.
p.
The ezrin protein links the cell membrane to the cytoskeleton (the cell's internal support structure) and plays a role in cell shape, movement, adhesion, and signaling. Drugs that occupy the same spot on ezrin where the viral spike protein would bind may hindering viral attachment, and drug binding could further stabilize ezrin, strengthening its potential natural capacity to impede viral fusion and entry.
q.
The Adipocyte Differentiation-Related Protein (ADRP, also known as Perilipin 2 or PLIN2) is a lipid droplet protein regulating the storage and breakdown of fats in cells. SARS-CoV-2 may hijack the lipid handling machinery of host cells and ADRP may play a role in this process. Disrupting ADRP's interaction with the virus may hinder the virus's ability to use lipids for replication and assembly.
r.
Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) is a cell surface receptor with roles in blood vessel development, nerve cell guidance, and immune responses. NRP1 may function as a co-receptor for SARS-CoV-2, facilitating viral entry into cells. Blocking NRP1 may disrupt an alternative route of viral entry.
s.
EP300 (E1A Binding Protein P300) is a transcriptional coactivator involved in several cellular processes, including growth, differentiation, and apoptosis, through its acetyltransferase activity that modifies histones and non-histone proteins. EP300 facilitates viral entry into cells and upregulates inflammatory cytokine production.
t.
Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 (PTGS2, also known as COX-2) is an enzyme crucial for the production of inflammatory molecules called prostaglandins. PTGS2 plays a role in the inflammatory response that can become severe in COVID-19 and inhibitors (like some NSAIDs) may have benefits in dampening harmful inflammation, but note that prostaglandins have diverse physiological functions.
u.
Heat Shock Protein 90 Alpha Family Class A Member 1 (HSP90AA1) is a chaperone protein that helps other proteins fold correctly and maintains their stability. HSP90AA1 plays roles in cell signaling, survival, and immune responses. HSP90AA1 may interact with numerous viral proteins, but note that it has diverse physiological functions.
v.
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), also called gelatinase B, is a zinc-dependent enzyme that breaks down collagen and other components of the extracellular matrix. MMP9 levels increase in severe COVID-19. Overactive MMP9 can damage lung tissue and worsen inflammation. Inhibition of MMP9 may prevent excessive tissue damage and help regulate the inflammatory response.
w.
The interleukin-6 (IL-6) pro-inflammatory cytokine (signaling molecule) has a complex role in the immune response and may trigger and perpetuate inflammation. Elevated IL-6 levels are associated with severe COVID-19 cases and cytokine storm. Anti-IL-6 therapies may be beneficial in reducing excessive inflammation in severe COVID-19 cases.
x.
The interleukin-10 (IL-10) anti-inflammatory cytokine helps regulate and dampen immune responses, preventing excessive inflammation. IL-10 levels can also be elevated in severe COVID-19. IL-10 could either help control harmful inflammation or potentially contribute to immune suppression.
y.
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGFA) promotes the growth of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) and has roles in inflammation and immune responses. VEGFA may contribute to blood vessel leakiness and excessive inflammation associated with severe COVID-19.
z.
RELA is a transcription factor subunit of NF-kB and is a key regulator of inflammation, driving pro-inflammatory gene expression. SARS-CoV-2 may hijack and modulate NF-kB pathways.
aa.
The interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the human ACE2 receptor is a primary method of viral entry, inhibiting this interaction can prevent the virus from attaching to and entering host cells, halting infection at an early stage.
ab.
Calu-3 is a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line with moderate ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. It provides a model of the human respiratory epithelium, but many not be ideal for modeling early stages of infection due to the moderate expression levels of ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
ac.
A549 is a human lung carcinoma cell line with low ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Viral entry/replication can be studied but the cells may not replicate all aspects of lung infection.
ad.
HEK293-ACE2+ is a human embryonic kidney cell line engineered for high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility.
ae.
Huh-7 cells were derived from a liver tumor (hepatoma).
af.
Caco-2 cells come from a colorectal adenocarcinoma (cancer). They are valued for their ability to form a polarized cell layer with properties similar to the intestinal lining.
ag.
Vero E6 is an African green monkey kidney cell line with low/no ACE2 expression and high SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. The cell line is easy to maintain and supports robust viral replication, however the monkey origin may not accurately represent human responses.
ah.
mTEC is a mouse tubular epithelial cell line.
ai.
RAW264.7 is a mouse macrophage cell line.
aj.
HLMEC (Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells) are primary endothelial cells derived from the lung microvasculature. They are used to study endothelial function, inflammation, and viral interactions, particularly in the context of lung infections such as SARS-CoV-2. HLMEC express ACE2 and are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection, making them a relevant model for studying viral entry and endothelial responses in the lung.
ak.
A mouse model expressing the human ACE2 receptor under the control of the K18 promoter.
al.
A mouse model of obesity and severe insulin resistance leading to type 2 diabetes due to a mutation in the leptin receptor gene that impairs satiety signaling.
am.
A mouse model commonly used in infectious disease and cancer research due to higher immune response and susceptibility to infection.
Chellasamy et al., 10 Aug 2022, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
Contact: selvaakumar.c@dypatil.edu, eleanorwatson@connect.glos.ac.uk.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors
Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no competing or conflicting interests.
References
Bairoch, Apweiler, The Swiss-Prot protein sequence database: its relevance to human molecular medical research, J. Mol. Med
Berendsen, GROMACS: A message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation, Comp. Phys. Comm
Berman, Westbrook, Feng, Gilliland, Bhat et al., The protein data bank, Nucleic Acids Res
Biovia, Systèmes, None
Bretscher, Edwards, Fehon, ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol
Bulut, Hong, Chen, Beauchamp, Rahim et al., Small molecule inhibitors of ezrin inhibit the invasive phenotype of osteosarcoma cells, Oncogene Jan, doi:10.1038/onc.2011.245
Chen, Sawaya, Phillips, Reisler, Quinlan, Multiple Forms of Spire-Actin Complexes and their Functional Consequences, J. Biol. Chem
Ehsani, COVID-19 and iron dysregulation: distant sequence similarity between hepcidin and the novel coronavirus spike glycoprotein, Biol Direct, doi:10.1186/s13062-020-00275-2
Fehon, Mcclatchey, Bretscher, Organizing the cell cortex: the role of
Fehr, Perlman, Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and 15. pathogenesis, Methods Mol. Biol
Fievet, Louvard, Arpin, ERM proteins in epithelial cell organization and 13. functions, Biochim Biophys Acta
Gautreau, Poullet, Louvard, Arpin, Ezrin, a plasma membrane-microfilament linker, signals cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway
Jorgensen, Chandrasekhar, Madura, Impey, Klein, Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water, J. Chem. Phys
Kim, Thiessen, Bolton, Chen, Fu et al., PubChem Substance and Compound databases, Nucleic Acids Res
Kumar, Kumar, Wei, Comparative docking studies to understand the binding affinity of nicotine with soluble ACE2 (sACE2)-SARS-CoV-2 complex over sACE2, Toxicology Reports
Laskowski, Macarthur, Moss, Thornton, PROCHECK -a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures, J. App. Cryst
Li, Li, Farzan, Harrison, Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor binding domain complexed with receptor, Science
Lu, Hu, Wang, Qi, Gao et al., Molecular basis of binding between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor. CD26, Nature
Lu, Zhao, Li, Genomic characterization and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet
Millet, Kien, Cheung, Siu, Chan et al., Ezrin interacts with the SARS coronavirus spike protein and restrains infection at the entry stage, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049566
Miteva, Guyon, Tufféry, Frog2: Efficient 3D conformation ensemble generator for small compounds, Nucleic Acids Res. Jul
Morris, Huey, Lindstrom, Sanner, Belew et al., Autodock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility, J. Computational Chemistry
Nose, A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods, The Journal of Chemical Physics
Paules, Marston, Fauci, Coronavirus infections-more than just the common cold, JAMA
Petit, Chouljenko, Iyer, Colgrove, Farzan et al., Palmitoylation of the cysteine-rich endodomain of the SARS-coronavirus spike glycoprotein is important for spike-mediated cell fusion, Virology Apr
Phang, Harrop, Duff, Sokolova, Crossett et al., Structural characterization suggests models for monomeric and dimeric forms of full length ezrin, Biochem. J
Ramadan, Mayilsamy, Mcgill, Ghosh, Giulianotti et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Palmitoylation Inhibitors That Results in Release of Attenuated Virus with Reduced Infectivity, Viruses
Schwede, Kopp, Guex, Peitsch, SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modelling server, Nucleic Acids Res. Jul
Shaw Research, Maestro-Desmond Interoperability Tools, version 3.6
Smith, Nassar, Bretscher, Cerione, Andrew et al., Structure of the active N-terminal domain of Ezrin. Conformational and mobility changes identify keystone interactions, J. Biol. Chem. Feb, doi:10.1074/jbc.M210601200
Turunen, Wahlström, Vaheri, Ezrin has a COOH-terminal actin-binding site that is conserved in the ezrin protein family, J. Cell Biol
Van Zundert, Melquiond, Bonvin, Integrative Modeling of Biomolecular Complexes: HADDOCKing with Cryo-Electron Microscopy Data, Structure
Wiederstein, Sippl, ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins, Nucleic Acids Research
Xia, Domains and Functions of Spike Protein in Sars-Cov-2 in the Context of Vaccine Design, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v1301010
Xue, Rodrigues, Kastritis, Bonvin, Vangone, PRODIGY: a web server for predicting the binding affinity of protein-protein complexes, Bioinformatics
Zhang, Holmes, A genomic perspective on the origin and emergence of SARS-CoV 2, Cell
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277",
"ISSN": [
"1018-3647"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277",
"alternative-id": [
"S101836472200458X"
],
"article-number": "102277",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of King Saud University - Science"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chellasamy",
"given": "Selvaa Kumar",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "Eleanor",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of King Saud University - Science",
"container-title-short": "Journal of King Saud University - Science",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-10T22:02:31Z",
"timestamp": 1660168951000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-10T22:03:10Z",
"timestamp": 1660168990000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-10T22:42:29Z",
"timestamp": 1660171349293
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1659312000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 7,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1659916800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S101836472200458X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S101836472200458X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "102277",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "The Swiss-Prot protein sequence database: its relevance to human molecular medical research",
"author": "Bairoch",
"first-page": "312",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0005",
"volume": "75",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0010-4655(95)00042-E",
"article-title": "GROMACS: A message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation",
"author": "Berendsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43",
"issue": "1-3",
"journal-title": "Comp. Phys. Comm.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0010",
"volume": "91",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/28.1.235",
"article-title": "The protein data bank",
"author": "Berman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "235",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0015",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"article-title": "Discovery Studio",
"author": "BIOVIA,",
"journal-title": "San Diego: Dassault Systèmes",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0020",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrm882",
"article-title": "ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex",
"author": "Bretscher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "586",
"issue": "2002",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0025",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/onc.2011.245",
"article-title": "Small molecule inhibitors of ezrin inhibit the invasive phenotype of osteosarcoma cells",
"author": "Bulut",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Oncogene",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0030",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M111.317792",
"article-title": "Multiple Forms of Spire-Actin Complexes and their Functional Consequences",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10684",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0035",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0040",
"unstructured": "D. E. Shaw Research 2013.Desmond Molecular Dynamics System, version 3.6. New York, NY,2013. Maestro-Desmond Interoperability Tools, version 3.6, Schrodinger, New York, NY,2013."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13062-020-00275-2",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and iron dysregulation: distant sequence similarity between hepcidin and the novel coronavirus spike glycoprotein",
"author": "Ehsani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "19",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biol Direct",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0045",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrm2866",
"article-title": "Organizing the cell cortex: the role of ERM proteins",
"author": "Fehon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0050",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.06.013",
"article-title": "ERM proteins in epithelial cell organization and functions",
"author": "Fiévet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "653",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0055",
"volume": "1773",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis",
"author": "Fehr",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "2015",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0060",
"volume": "1282",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.96.13.7300",
"article-title": "Ezrin, a plasma membrane-microfilament linker, signals cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway",
"author": "Gautreau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7300",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0065",
"volume": "96",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparative docking studies to understand the binding affinity of nicotine with soluble ACE2 (sACE2)-SARS-CoV-2 complex over sACE2",
"author": "Kumar",
"first-page": "1366",
"issue": "2020",
"journal-title": "Toxicology Reports",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0070",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/1.445869",
"article-title": "Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water",
"author": "Jorgensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "926",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Phys",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0075",
"volume": "79",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0021889892009944",
"article-title": "PROCHECK - a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures",
"author": "Laskowski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "283",
"journal-title": "J. App. Cryst.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0080",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1116480",
"article-title": "Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor binding domain complexed with receptor",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1864",
"issue": "5742",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0085",
"volume": "309",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8",
"article-title": "Genomic characterization and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0090",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature12328",
"article-title": "Molecular basis of binding between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor. CD26",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"issue": "7461",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0095",
"volume": "500",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkv951",
"article-title": "PubChem Substance and Compound databases",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "D1202",
"issue": "Database issue",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0100",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0049566",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0105",
"unstructured": "J.K. Millet F. Kien C.-Y. Cheung Y.-L. Siu W.-L. Chan H. Li H.-L. Leung M. Jaume R. Bruzzone J.S. Malik Peiris R.M. Altmeyer B. Nal S. Pöhlmann Ezrin Interacts with the SARS Coronavirus Spike Protein and Restrains Infection at the Entry Stage PLoS One 7 11 e49566"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkq325",
"article-title": "Frog2: Efficient 3D conformation ensemble generator for small compounds",
"author": "Miteva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W622",
"issue": "Web Server",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Research",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0110",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.21256",
"article-title": "Autodock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility",
"author": "Morris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2785",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "J. Computational Chemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0115",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/1.447334",
"article-title": "A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods",
"author": "Nosé",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "511",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "The Journal of Chemical Physics",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0120",
"volume": "81",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.0757",
"article-title": "Coronavirus infections-more than just the common cold",
"author": "Paules",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "707",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0125",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2006.10.034",
"article-title": "Palmitoylation of the cysteine-rich endodomain of the SARS-coronavirus spike glycoprotein is important for spike-mediated cell fusion",
"author": "Petit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "264",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Virology Apr 10",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0130",
"volume": "360",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BCJ20160541",
"article-title": "Structural characterization suggests models for monomeric and dimeric forms of full length ezrin",
"author": "Phang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2763",
"journal-title": "Biochem. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0135",
"volume": "473",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14030531",
"article-title": "Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Palmitoylation Inhibitors That Results in Release of Attenuated Virus with Reduced Infectivity",
"author": "Ramadan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "531",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0140",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkg520",
"article-title": "SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modelling server",
"author": "Schwede",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3381",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res. Jul 1",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0145",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M210601200",
"article-title": "Structure of the Active N-terminal Domain of Ezrin",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4949",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Journal of Biological Chemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0150",
"volume": "278",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.126.6.1445",
"article-title": "Ezrin has a COOH-terminal actin-binding site that is conserved in the ezrin protein family",
"author": "Turunen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1445",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0155",
"volume": "126",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkm290",
"article-title": "ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins",
"author": "Wiederstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W407",
"issue": "2007",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Research",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0160",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0165",
"unstructured": "WHO Dashboard https://covid19.who.int"
},
{
"author": "Xia",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "Domains and Functions of Spike Protein in Sars-Cov-2 in the Context of Vaccine Design.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0170",
"volume": "Viruses,13(1)",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "PRODIGY: a web server for predicting the binding affinity of protein-protein complexes",
"author": "Xue",
"first-page": "3676",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics (Oxford, England)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0175",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.035",
"article-title": "A genomic perspective on the origin and emergence of SARS-CoV 2",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0180",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.str.2015.03.014",
"article-title": "Integrative Modeling of Biomolecular Complexes: HADDOCKing with Cryo-Electron Microscopy Data",
"author": "van Zundert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "949",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Structure",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0185",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S101836472200458X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
chellasamy