Development of nanoparticles incorporated with quercetin and ACE2-membrane as a novel therapy for COVID-19
et al., Journal of Nanobiotechnology, doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02435-2, Apr 2024
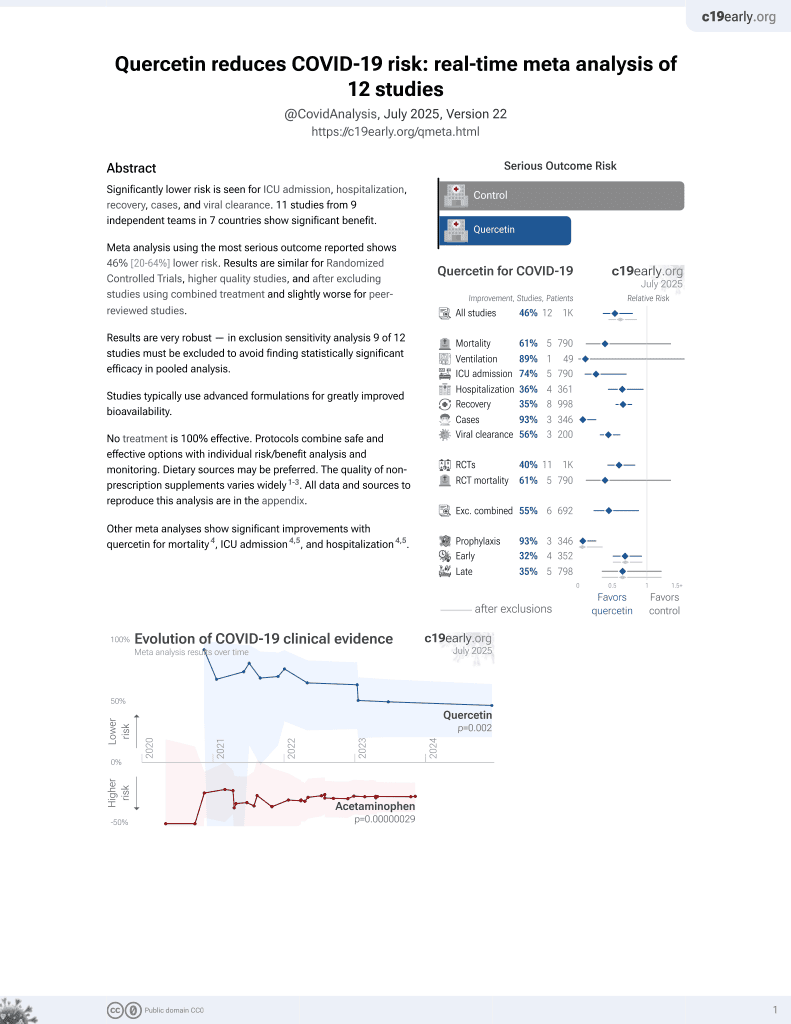
Quercetin for COVID-19
27th treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2021, now with p = 0.002 from 12 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
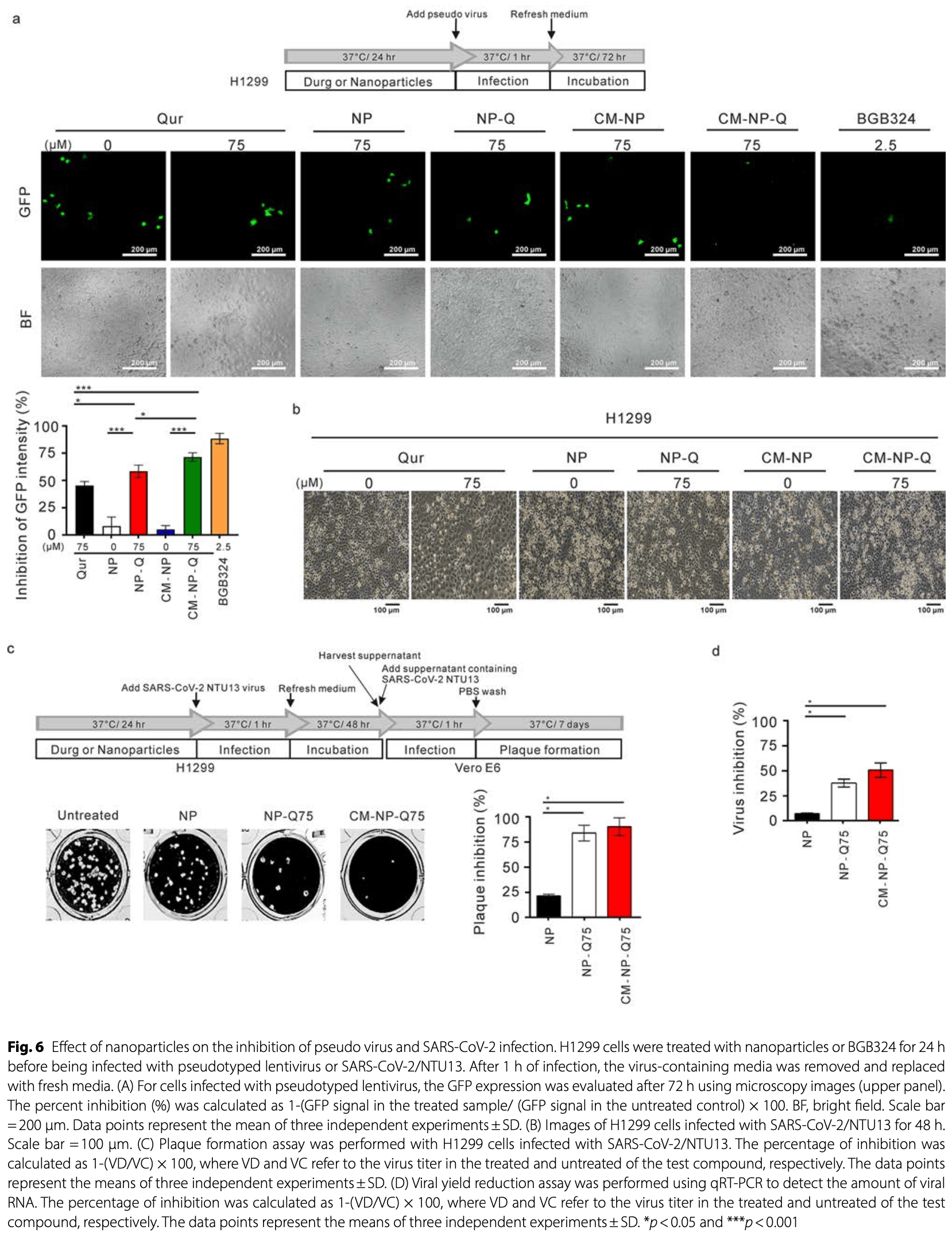
In vitro study showing that nanoparticles coated with both ACE2-containing cell membranes and quercetin (CM-NP-Q) inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lung cells. Authors developed nanoparticles incorporated with quercetin (NP-Q), ACE2-containing cell membranes (CM-NP), or both (CM-NP-Q). CM-NP-Q showed the strongest antiviral activity by neutralizing extracellular pseudo-SARS-CoV-2 virus in ACE2-expressing H1975, 293T, and BEAS-2B cells, and inhibiting infection of H1299 lung cancer cells by both pseudo-SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-2/NTU13 virus. NP-Q and free quercetin also inhibited viral infection, but CM-NP-Q was most effective. The enhanced activity of CM-NP-Q is attributed to its ability to both neutralize extracellular virus through its ACE2-containing membrane and inhibit viral entry through quercetin's suppression of the AXL receptor. CM-NP-Q showed no significant cytotoxicity or in vivo toxicity in mice. The results suggest CM-NP-Q has potential as an inhaled therapy to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Bioavailability. Quercetin has low bioavailability and studies typically use advanced formulations to improve bioavailability which may be required to reach therapeutic concentrations.
Fang et al., 12 Apr 2024, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Contact: pcyang@ntu.edu.tw, cychen@mail.cgust.edu.tw.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Development of nanoparticles incorporated with quercetin and ACE2-membrane as a novel therapy for COVID-19
Journal of Nanobiotechnology, doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02435-2
Introduction Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and AXL tyrosine kinase receptor are known to be involved in the SARS-CoV-2 entry of the host cell. Therefore, targeting ACE2 and AXL should be an effective strategy to inhibit virus entry into cells. However, developing agents that can simultaneously target ACE2 and AXL remains a formidable task. The natural compound quercetin has been shown to inhibit AXL expression.
Materials and methods In this study, we employed PLGA nanoparticles to prepare nanoparticles encapsulated with quercetin, coated with ACE2-containing cell membranes, or encapsulated with quercetin and then coated with ACE-2-containing cell membranes. These nanoparticles were tested for their abilities to neutralize or inhibit viral infection.
Results Our data showed that nanoparticles encapsulated with quercetin and then coated with ACE2-containing cell membrane inhibited the expression of AXL without causing cytotoxic activity. Nanoparticles incorporated with both quercetin and ACE2-containing cell membrane were found to be able to neutralize pseudo virus infection and were more effective than free quercetin and nanoparticles encapsulated with quercetin at inhibition of pseudo virus and SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Conclusions We have shown that the biomimetic nanoparticles incorporated with both ACE-2 membrane and quercetin showed the most antiviral activity and may be further explored for clinical application.
Data availability All data generated for this study are included in the article.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate The study involving SARS-CoV-2 was approved by the National Taiwan University Hospital Research Ethics Committee (202002002RIND). All of the mouse experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Chang Gung University (IACUC approval no.: CGU110-015) and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (IACUC approval no.: 2020121704).
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Abian, Ortega-Alarcon, Jimenez-Alesanco, Ceballos-Laita, Vega et al., Structural stability of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro and identification of quercetin as an inhibitor by experimental screening, Int J Biol Macromol
Anwer, Al-Mansoor, Jamil, Al-Shdefat, Ansari et al., Development and evaluation of PLGA Polymer based nanoparticles of quercetin, Int J Biol Macromol
Bhowmik, Nandi, Prakash, Kumar, Evaluation of flavonoids as 2019-nCoV cell entry inhibitor through molecular docking and pharmacological analysis, Heliyon
Bohan, Van Ert, Ruggio, Rogers, Badreddine et al., Phosphatidylserine receptors enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection, PLoS Pathog
Boots, Haenen, Bast, Health effects of quercetin: from antioxidant to nutraceutical, Eur J Pharmacol
Bouhaddou, Memon, Meyer, White, Rezelj et al., The Global Phosphorylation Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Cell
Cantuti-Castelvetri, Ojha, Pedro, Djannatian, Franz et al., Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity, Science
Chen, Huang, Law, Chu, Chen et al., Biodegradable polymers for gene-delivery applications, Int J Nanomed
Chen, Jan, Lo, Yang, Chang et al., Tid1-L inhibits EGFR signaling in lung adenocarcinoma by enhancing EGFR Ubiquitinylation and degradation, Cancer Res
Clausen, Sandoval, Spliid, Pihl, Perrett et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection depends on Cellular Heparan Sulfate and ACE2, Cell
Han, Wang, Cai, Liu, Zhang et al., Quercetin nanoparticles with enhanced bioavailability as multifunctional agents toward amyloid induced neurotoxicity, J Mater Chem B
Holland, Pan, Franci, Hu, Chang et al., R428, a selective small molecule inhibitor of Axl kinase, blocks tumor spread and prolongs survival in models of metastatic breast cancer, Cancer Res
Holzer, Vogel, Mantele, Schwartz, Haase et al., Physico-chemical characterisation of PLGA nanoparticles after freeze-drying and storage, Eur J Pharm Biopharm
Hoshyar, Gray, Han, Bao, The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction, Nanomed (Lond)
Huang, Lin, Kuo, Chen, Lin et al., Humanized COVID-19 decoy antibody effectively blocks viral entry and prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection, EMBO Mol Med
Huang, Wang, Chen, Leu, Li et al., Growth suppression in Lung Cancer cells harboring EGFR-C797S mutation by Quercetin, Biomolecules
Kamel, Helmy, Abdelfattah, Khattab, Ragab et al., Inhalable dual-targeted hybrid lipid nanocore-protein Shell composites for Combined Delivery of Genistein and All-Trans Retinoic Acid to Lung Cancer cells, ACS Biomater Sci Eng
Lee, Song, Oh, Lee, Kim et al., ERK1/2 activation in quercetin-treated BEAS-2B cell plays a role in Nrf2-driven HO-1 expression, Mol Cell Toxicol
Lee, Yoo, Simultaneous inactivation of GSK-3beta suppresses quercetin-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the JNK pathway, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol
Leu, Wang, Wu, Huang, Jiang et al., Hydroxygenkwanin suppresses Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Progression by enhancing EGFR Degradation, Molecules
Liu, Yu, Lin, Elzoghby, Hwang et al., Use of cilomilastloaded phosphatiosomes to suppress neutrophilic inflammation for attenuating acute lung injury: the effect of nanovesicular surface charge, J Nanobiotechnol
Mitchell, Billingsley, Haley, Wechsler, Peppas et al., Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery, Nat Rev Drug Discov
Mukherjee, Khuda-Bukhsh, Quercetin Down-regulates IL-6/STAT-3 signals to induce mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in a nonsmall-cell lungcancer cell line, A549, J Pharmacopunct
Oh, Ambigaipalan, Shahidi, Preparation of Quercetin Esters and their antioxidant activity, J Agric Food Chem
Pierro, Derosa, Maffioli, Bertuccioli, Togni et al., Possible therapeutic effects of Adjuvant Quercetin Supplementation against early-stage COVID-19 infection: a prospective, randomized, controlled, and open-label study, Int J Gen Med
Pool, Quintanar, Figueroa, Mano, Bechara et al., Antioxidant effects of Quercetin and Catechin Encapsulated into PLGA nanoparticles, J Nanomaterials
Prutskij, Deriabina, Melendez, Castro, Trejo et al., Concentration-dependent fluorescence Emission of Quercetin, Chemosensors
Rai, Tiwari, Singh, Singh, Mishra et al., Exploring the Paradox of COVID-19 in Neurological Complications with Emphasis on Parkinson's and Alzheimer's Disease, Oxid Med Cell Longev
Rayson, Lupichuk, Potvin, Dent, Shenkier et al., Canadian Cancer trials Group IND197: a phase II study of foretinib in patients with estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative recurrent or metastatic breast cancer, Breast Cancer Res Treat
Rockx, Kuiken, Herfst, Bestebroer, Lamers et al., Comparative pathogenesis of COVID-19, MERS, and SARS in a nonhuman primate model, Science
Rosita, Ambarwati, Erawati, Hariyadi, Characterization and in vitro release of inhalation quercetin solid lipid microparticles: Effect of lipid, J Adv Pharm Technol Res
Sadarangani, Marchant, Kollmann, Immunological mechanisms of vaccine-induced protection against COVID-19 in humans, Nat Rev Immunol
Scalia, Haghi, Losi, Trotta, Young et al., Quercetin solid lipid microparticles: a flavonoid for inhalation lung delivery, Eur J Pharm Sci
Sheridan, First Axl inhibitor enters clinical trials, Nat Biotechnol
Singh, Bhushan, Maurya, Mishra, Singh et al., Novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and neurodegenerative disorders, Dermatol Ther
Singh, Maurya, Mishra, Awasthi, Dua et al., Nanovaccine: a hope to Triumph the Battle Against Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Recent Pat Nanotechnol
Singh, Mishra, Maurya, Kulkarni, Awasthi, Biofabrication: an interesting tool to create in vitro model for COVID-19 drug targets, Med Hypotheses
Singh, Singh, Rathore, Singh, Mishra et al., Lipid-coated MCM-41 mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with Berberine Improved Inhibition of Acetylcholine Esterase and amyloid formation, ACS Biomater Sci Eng
Takashima, Matsushima, Hashimoto, Nose, Sato et al., Protective effects of intratracheally administered quercetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury, Respir Res
Taniguchi, Yamada, Wang, Tanimura, Adachi et al., AXL confers intrinsic resistance to osimertinib and advances the emergence of tolerant cells, Nat Commun
Tsai, Lin, Trousil, Sung, Lee et al., Proteinase K/ Retinoic acid-loaded Cationic liposomes as multifunctional anti-acne therapy to Disorganize Biofilm and regulate keratinocyte proliferation, Int J Nanomed
V'kovski, Kratzel, Steiner, Stalder, Thiel, Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2, Nat Rev Microbiol
Wang, Qiu, Hou, Deng, Xu et al., AXL is a candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 that promotes infection of pulmonary and bronchial epithelial cells, Cell Res
Wang, Wu, Huang, Chuang, Hsueh et al., Profiling of subcellular EGFR interactome reveals hnRNP A3 modulates nuclear EGFR localization, Oncogenesis
Yau, Lencioni, Sukeepaisarnjaroen, Chao, Yen et al., A phase I/II Multicenter Study of single-Agent Foretinib as First-Line therapy in patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Clin Cancer Res
Zhang, Honko, Zhou, Gong, Downs et al., Cellular Nanosponges inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infectivity, Nano Lett
Zhang, Xiang, Huo, Zhou, Jiang et al., Molecular mechanism of interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and host cells and interventional therapy, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Zhao, Chen, Wu, Wang, Du et al., Highly efficient photothermal nanoagent achieved by harvesting energy via excited-state intramolecular motion within nanoparticles, Nat Commun
Zhao, Yuan, Meng, Qiu, Wang, Quercetin-loaded mixed micelles exhibit enhanced cytotoxic efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer in vitro, Exp Ther Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12951-024-02435-2",
"ISSN": [
"1477-3155"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12951-024-02435-2",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Introduction</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and AXL tyrosine kinase receptor are known to be involved in the SARS-CoV-2 entry of the host cell. Therefore, targeting ACE2 and AXL should be an effective strategy to inhibit virus entry into cells. However, developing agents that can simultaneously target ACE2 and AXL remains a formidable task. The natural compound quercetin has been shown to inhibit AXL expression.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Materials and methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this study, we employed PLGA nanoparticles to prepare nanoparticles encapsulated with quercetin, coated with ACE2-containing cell membranes, or encapsulated with quercetin and then coated with ACE-2-containing cell membranes. These nanoparticles were tested for their abilities to neutralize or inhibit viral infection.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Our data showed that nanoparticles encapsulated with quercetin and then coated with ACE2-containing cell membrane inhibited the expression of AXL without causing cytotoxic activity. Nanoparticles incorporated with both quercetin and ACE2-containing cell membrane were found to be able to neutralize pseudo virus infection and were more effective than free quercetin and nanoparticles encapsulated with quercetin at inhibition of pseudo virus and SARS-CoV-2 infection.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We have shown that the biomimetic nanoparticles incorporated with both ACE-2 membrane and quercetin showed the most antiviral activity and may be further explored for clinical application.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"2435"
],
"article-number": "169",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "15 October 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "22 March 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "12 April 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The study involving SARS-CoV-2 was approved by the National Taiwan University Hospital Research Ethics Committee (202002002RIND)."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "All of the mouse experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Chang Gung University (IACUC approval no.: CGU110-015) and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (IACUC approval no.: 2020121704)."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 5,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fang",
"given": "Jia-You",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Kuo-Yen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Tong-Hong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Zih-Chan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Chin-Chuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Sui-Yuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "En-Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chao",
"given": "Tai-Ling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Shuenn-Chen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Pan-Chyr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Chi-Yuan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Nanobiotechnology",
"container-title-short": "J Nanobiotechnol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-12T13:01:53Z",
"timestamp": 1712926913000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-12T13:06:13Z",
"timestamp": 1712927173000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"NSTC 111-2124-M-002 -010"
],
"name": "National Science and Technology Council"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100012553",
"award": [
"CMRPF1L0052"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "Chang Gung Memorial Hospital"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004663",
"award": [
"MOST 111-2320-B-255-003"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan"
},
{
"award": [
"ZRRPF3M0091"
],
"name": "Chang Gung University of Science and Technology"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-12T13:41:27Z",
"timestamp": 1712929287125
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1712880000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1712880000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12951-024-02435-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12951-024-02435-2/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12951-024-02435-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"author": "AK Singh",
"first-page": "e13591",
"journal-title": "Dermatol Ther",
"key": "2435_CR1",
"unstructured": "Singh AK, Bhushan B, Maurya A, Mishra G, Singh SK, Awasthi R. Novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and neurodegenerative disorders. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13591.",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/3012778",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2435_CR2",
"unstructured": "Rai SN, Tiwari N, Singh P, Singh AK, Mishra D, Imran M, Singh S, Hooshmandi E, Vamanu E, Singh SK, Singh MP. Exploring the Paradox of COVID-19 in Neurological Complications with Emphasis on Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022:3012778."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6",
"author": "P V’Kovski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "2435_CR3",
"unstructured": "V’Kovski P, Kratzel A, Steiner S, Stalder H, Thiel V. Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19:155–70.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00578-z",
"author": "M Sadarangani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "475",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "2435_CR4",
"unstructured": "Sadarangani M, Marchant A, Kollmann TR. Immunological mechanisms of vaccine-induced protection against COVID-19 in humans. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21:475–84.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "AK Singh",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Recent Pat Nanotechnol",
"key": "2435_CR5",
"unstructured": "Singh AK, Maurya A, Mishra G, Awasthi R, Dua K, Kulkarni GT. Nanovaccine: a hope to Triumph the Battle Against Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2023;17:15–7.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-00460-y",
"author": "S Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "126",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "2435_CR6",
"unstructured": "Wang S, Qiu Z, Hou Y, Deng X, Xu W, Zheng T, Wu P, Xie S, Bian W, Zhang C, et al. AXL is a candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 that promotes infection of pulmonary and bronchial epithelial cells. Cell Res. 2021;31:126–40.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd2985",
"author": "L Cantuti-Castelvetri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "856",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2435_CR7",
"unstructured": "Cantuti-Castelvetri L, Ojha R, Pedro LD, Djannatian M, Franz J, Kuivanen S, van der Meer F, Kallio K, Kaya T, Anastasina M, et al. Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity. Science. 2020;370:856–60.",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.033",
"author": "TM Clausen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1043",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2435_CR8",
"unstructured": "Clausen TM, Sandoval DR, Spliid CB, Pihl J, Perrett HR, Painter CD, Narayanan A, Majowicz SA, Kwong EM, McVicar RN, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection depends on Cellular Heparan Sulfate and ACE2. Cell. 2020;183:1043–e10571015.",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009743",
"author": "D Bohan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1009743",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "2435_CR9",
"unstructured": "Bohan D, Van Ert H, Ruggio N, Rogers KJ, Badreddine M, Aguilar Briseno JA, Elliff JM, Rojas Chavez RA, Gao B, Stokowy T, et al. Phosphatidylserine receptors enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2021;17:e1009743.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.034",
"author": "M Bouhaddou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "685",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2435_CR10",
"unstructured": "Bouhaddou M, Memon D, Meyer B, White KM, Rezelj VV, Correa Marrero M, Polacco BJ, Melnyk JE, Ulferts S, Kaake RM, et al. The Global Phosphorylation Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell. 2020;182:685–e712619.",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2997",
"author": "SJ Holland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1544",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res",
"key": "2435_CR11",
"unstructured": "Holland SJ, Pan A, Franci C, Hu Y, Chang B, Li W, Duan M, Torneros A, Yu J, Heckrodt TJ, et al. R428, a selective small molecule inhibitor of Axl kinase, blocks tumor spread and prolongs survival in models of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1544–54.",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nbt0913-775a",
"author": "C Sheridan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "775",
"journal-title": "Nat Biotechnol",
"key": "2435_CR12",
"unstructured": "Sheridan C. First Axl inhibitor enters clinical trials. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31:775–6.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10549-016-3812-1",
"author": "D Rayson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "Breast Cancer Res Treat",
"key": "2435_CR13",
"unstructured": "Rayson D, Lupichuk S, Potvin K, Dent S, Shenkier T, Dhesy-Thind S, Ellard SL, Prady C, Salim M, Farmer P, et al. Canadian Cancer trials Group IND197: a phase II study of foretinib in patients with estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative recurrent or metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016;157:109–16.",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1789",
"author": "TCC Yau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2405",
"journal-title": "Clin Cancer Res",
"key": "2435_CR14",
"unstructured": "Yau TCC, Lencioni R, Sukeepaisarnjaroen W, Chao Y, Yen CJ, Lausoontornsiri W, Chen PJ, Sanpajit T, Camp A, Cox DS, et al. A phase I/II Multicenter Study of single-Agent Foretinib as First-Line therapy in patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:2405–13.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.03.008",
"author": "AW Boots",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "325",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharmacol",
"key": "2435_CR15",
"unstructured": "Boots AW, Haenen GR, Bast A. Health effects of quercetin: from antioxidant to nutraceutical. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;585:325–37.",
"volume": "585",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom11091271",
"author": "K-Y Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1271",
"journal-title": "Biomolecules",
"key": "2435_CR16",
"unstructured": "Huang K-Y, Wang T-H, Chen C-C, Leu Y-L, Li H-J, Jhong C-L, Chen C-Y. Growth suppression in Lung Cancer cells harboring EGFR-C797S mutation by Quercetin. Biomolecules. 2021;11:1271.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3831/KPI.2015.18.002",
"author": "A Mukherjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "J Pharmacopunct",
"key": "2435_CR17",
"unstructured": "Mukherjee A, Khuda-Bukhsh AR. Quercetin Down-regulates IL-6/STAT-3 signals to induce mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in a nonsmall- cell lung-cancer cell line, A549. J Pharmacopunct. 2015;18:19–26.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.235",
"author": "O Abian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1693",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Macromol",
"key": "2435_CR18",
"unstructured": "Abian O, Ortega-Alarcon D, Jimenez-Alesanco A, Ceballos-Laita L, Vega S, Reyburn HT, Rizzuti B, Velazquez-Campoy A. Structural stability of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro and identification of quercetin as an inhibitor by experimental screening. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;164:1693–703.",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06515",
"author": "D Bhowmik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e06515",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "2435_CR19",
"unstructured": "Bhowmik D, Nandi R, Prakash A, Kumar D. Evaluation of flavonoids as 2019-nCoV cell entry inhibitor through molecular docking and pharmacological analysis. Heliyon. 2021;7:e06515.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S318720",
"author": "F Di Pierro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2359",
"journal-title": "Int J Gen Med",
"key": "2435_CR20",
"unstructured": "Di Pierro F, Derosa G, Maffioli P, Bertuccioli A, Togni S, Riva A, Allegrini P, Khan A, Khan S, Khan BA, et al. Possible therapeutic effects of Adjuvant Quercetin Supplementation against early-stage COVID-19 infection: a prospective, randomized, controlled, and open-label study. Int J Gen Med. 2021;14:2359–66.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C7TB03053C",
"author": "Q Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1387",
"journal-title": "J Mater Chem B",
"key": "2435_CR21",
"unstructured": "Han Q, Wang X, Cai S, Liu X, Zhang Y, Yang L, Wang C, Yang R. Quercetin nanoparticles with enhanced bioavailability as multifunctional agents toward amyloid induced neurotoxicity. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6:1387–93.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"author": "MH Zhao",
"first-page": "5503",
"journal-title": "Exp Ther Med",
"key": "2435_CR22",
"unstructured": "Zhao MH, Yuan L, Meng LY, Qiu JL, Wang CB. Quercetin-loaded mixed micelles exhibit enhanced cytotoxic efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer in vitro. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14:5503–8.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00348.2012",
"author": "KH Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "L782",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol",
"key": "2435_CR23",
"unstructured": "Lee KH, Yoo CG. Simultaneous inactivation of GSK-3beta suppresses quercetin-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the JNK pathway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013;304:L782–789.",
"volume": "304",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13273-011-0044-7",
"author": "Y-J Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "347",
"journal-title": "Mol Cell Toxicol",
"key": "2435_CR24",
"unstructured": "Lee Y-J, Song J-H, Oh M-H, Lee Y-J, Kim Y-B, Im J-H, Lee S-H. ERK1/2 activation in quercetin-treated BEAS-2B cell plays a role in Nrf2-driven HO-1 expression. Mol Cell Toxicol. 2011;7:347–55.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00653-w",
"author": "Q Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "233",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "2435_CR25",
"unstructured": "Zhang Q, Xiang R, Huo S, Zhou Y, Jiang S, Wang Q, Yu F. Molecular mechanism of interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and host cells and interventional therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:233.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8",
"author": "MJ Mitchell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Drug Discov",
"key": "2435_CR26",
"unstructured": "Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM, Wechsler ME, Peppas NA, Langer R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20:101–24.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJN.S222419",
"author": "CK Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2131",
"journal-title": "Int J Nanomed",
"key": "2435_CR27",
"unstructured": "Chen CK, Huang PK, Law WC, Chu CH, Chen NT, Lo LW. Biodegradable polymers for gene-delivery applications. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:2131–50.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c00514",
"author": "AK Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3737",
"journal-title": "ACS Biomater Sci Eng",
"key": "2435_CR28",
"unstructured": "Singh AK, Singh SS, Rathore AS, Singh SP, Mishra G, Awasthi R, Mishra SK, Gautam V, Singh SK. Lipid-coated MCM-41 mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with Berberine Improved Inhibition of Acetylcholine Esterase and amyloid formation. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7:3737–53.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/nnm.16.5",
"author": "N Hoshyar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "673",
"journal-title": "Nanomed (Lond)",
"key": "2435_CR29",
"unstructured": "Hoshyar N, Gray S, Han H, Bao G. The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction. Nanomed (Lond). 2016;11:673–92.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-019-08722-z",
"author": "Z Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "768",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2435_CR30",
"unstructured": "Zhao Z, Chen C, Wu W, Wang F, Du L, Zhang X, Xiong Y, He X, Cai Y, Kwok RTK, et al. Highly efficient photothermal nanoagent achieved by harvesting energy via excited-state intramolecular motion within nanoparticles. Nat Commun. 2019;10:768.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/chemosensors9110315",
"author": "T Prutskij",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "315",
"journal-title": "Chemosensors",
"key": "2435_CR31",
"unstructured": "Prutskij T, Deriabina A, Melendez FJ, Castro ME, Castillo Trejo L, Vazquez Leon GD, Gonzalez E, Perova TS. Concentration-dependent fluorescence Emission of Quercetin. Chemosensors. 2021;9:315.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejpb.2009.02.002",
"author": "M Holzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "428",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharm Biopharm",
"key": "2435_CR32",
"unstructured": "Holzer M, Vogel V, Mantele W, Schwartz D, Haase W, Langer K. Physico-chemical characterisation of PLGA nanoparticles after freeze-drying and storage. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;72:428–37.",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejps.2013.03.009",
"author": "S Scalia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "278",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharm Sci",
"key": "2435_CR33",
"unstructured": "Scalia S, Haghi M, Losi V, Trotta V, Young PM, Traini D. Quercetin solid lipid microparticles: a flavonoid for inhalation lung delivery. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013;49:278–85.",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-018-08074-0",
"author": "H Taniguchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "259",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2435_CR34",
"unstructured": "Taniguchi H, Yamada T, Wang R, Tanimura K, Adachi Y, Nishiyama A, Tanimoto A, Takeuchi S, Araujo LH, Boroni M, et al. AXL confers intrinsic resistance to osimertinib and advances the emergence of tolerant cells. Nat Commun. 2019;10:259.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb7314",
"author": "B Rockx",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1012",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2435_CR35",
"unstructured": "Rockx B, Kuiken T, Herfst S, Bestebroer T, Lamers MM, Oude Munnink BB, de Meulder D, van Amerongen G, van den Brand J, Okba NMA, et al. Comparative pathogenesis of COVID-19, MERS, and SARS in a nonhuman primate model. Science. 2020;368:1012–5.",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04154",
"author": "WY Oh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10653",
"journal-title": "J Agric Food Chem",
"key": "2435_CR36",
"unstructured": "Oh WY, Ambigaipalan P, Shahidi F. Preparation of Quercetin Esters and their antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67:10653–9.",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"author": "N Rosita",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "J Adv Pharm Technol Res",
"key": "2435_CR37",
"unstructured": "Rosita N, Ambarwati N, Erawati T, Hariyadi DM. Characterization and in vitro release of inhalation quercetin solid lipid microparticles: Effect of lipid. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2022;13:11–7.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.002",
"author": "MK Anwer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "213",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Macromol",
"key": "2435_CR38",
"unstructured": "Anwer MK, Al-Mansoor MA, Jamil S, Al-Shdefat R, Ansari MN, Shakeel F. Development and evaluation of PLGA Polymer based nanoparticles of quercetin. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;92:213–9.",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2012/145380",
"author": "H Pool",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145380",
"journal-title": "J Nanomaterials",
"key": "2435_CR39",
"unstructured": "Pool H, Quintanar D, Figueroa JD, Marinho Mano C, Bechara JEH, Godínez LA, Mendoza S. Antioxidant effects of Quercetin and Catechin Encapsulated into PLGA nanoparticles. J Nanomaterials. 2012;2012:145380.",
"volume": "2012",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110059",
"author": "AK Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110059",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "2435_CR40",
"unstructured": "Singh AK, Mishra G, Maurya A, Kulkarni GT, Awasthi R. Biofabrication: an interesting tool to create in vitro model for COVID-19 drug targets. Med Hypotheses. 2020;144:110059.",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/emmm.202012828",
"author": "KY Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e12828",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol Med",
"key": "2435_CR41",
"unstructured": "Huang KY, Lin MS, Kuo TC, Chen CL, Lin CC, Chou YC, Chao TL, Pang YH, Kao HC, Huang RS, et al. Humanized COVID-19 decoy antibody effectively blocks viral entry and prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection. EMBO Mol Med. 2021;13:e12828.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c02278",
"author": "Q Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5570",
"journal-title": "Nano Lett",
"key": "2435_CR42",
"unstructured": "Zhang Q, Honko A, Zhou J, Gong H, Downs SN, Vasquez JH, Fang RH, Gao W, Griffiths A, Zhang L. Cellular Nanosponges inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infectivity. Nano Lett. 2020;20:5570–4.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b01374",
"author": "NM Kamel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "ACS Biomater Sci Eng",
"key": "2435_CR43",
"unstructured": "Kamel NM, Helmy MW, Abdelfattah EZ, Khattab SN, Ragab D, Samaha MW, Fang JY, Elzoghby AO. Inhalable dual-targeted hybrid lipid nanocore-protein Shell composites for Combined Delivery of Genistein and All-Trans Retinoic Acid to Lung Cancer cells. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6:71–87.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJN.S416966",
"author": "MJ Tsai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3879",
"journal-title": "Int J Nanomed",
"key": "2435_CR44",
"unstructured": "Tsai MJ, Lin CY, Trousil J, Sung CT, Lee MH, Fang JY, Yang SC. Proteinase K/Retinoic acid-loaded Cationic liposomes as multifunctional anti-acne therapy to Disorganize Biofilm and regulate keratinocyte proliferation. Int J Nanomed. 2023;18:3879–96.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12951-018-0364-z",
"author": "FC Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "J Nanobiotechnol",
"key": "2435_CR45",
"unstructured": "Liu FC, Yu HP, Lin CY, Elzoghby AO, Hwang TL, Fang JY. Use of cilomilast-loaded phosphatiosomes to suppress neutrophilic inflammation for attenuating acute lung injury: the effect of nanovesicular surface charge. J Nanobiotechnol. 2018;16:35.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41389-020-0225-0",
"author": "TH Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "40",
"journal-title": "Oncogenesis",
"key": "2435_CR46",
"unstructured": "Wang TH, Wu CC, Huang KY, Chuang WY, Hsueh C, Li HJ, Chen CY. Profiling of subcellular EGFR interactome reveals hnRNP A3 modulates nuclear EGFR localization. Oncogenesis. 2020;9:40.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25040941",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2435_CR47",
"unstructured": "Leu YL, Wang TH, Wu CC, Huang KY, Jiang YW, Hsu YC, Chen CY. Hydroxygenkwanin suppresses Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Progression by enhancing EGFR Degradation. Molecules 2020, 25."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4066",
"author": "CY Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4009",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res",
"key": "2435_CR48",
"unstructured": "Chen CY, Jan CI, Lo JF, Yang SC, Chang YL, Pan SH, Wang WL, Hong TM, Yang PC. Tid1-L inhibits EGFR signaling in lung adenocarcinoma by enhancing EGFR Ubiquitinylation and degradation. Cancer Res. 2013;73:4009–19.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-014-0150-x",
"author": "K Takashima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "150",
"journal-title": "Respir Res",
"key": "2435_CR49",
"unstructured": "Takashima K, Matsushima M, Hashimoto K, Nose H, Sato M, Hashimoto N, Hasegawa Y, Kawabe T. Protective effects of intratracheally administered quercetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Respir Res. 2014;15:150.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 49,
"references-count": 49,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jnanobiotechnology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12951-024-02435-2"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmaceutical Science",
"Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology",
"Biomedical Engineering",
"Molecular Medicine",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)",
"Bioengineering"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Development of nanoparticles incorporated with quercetin and ACE2-membrane as a novel therapy for COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "22"
}