Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors
et al., Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277, Aug 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
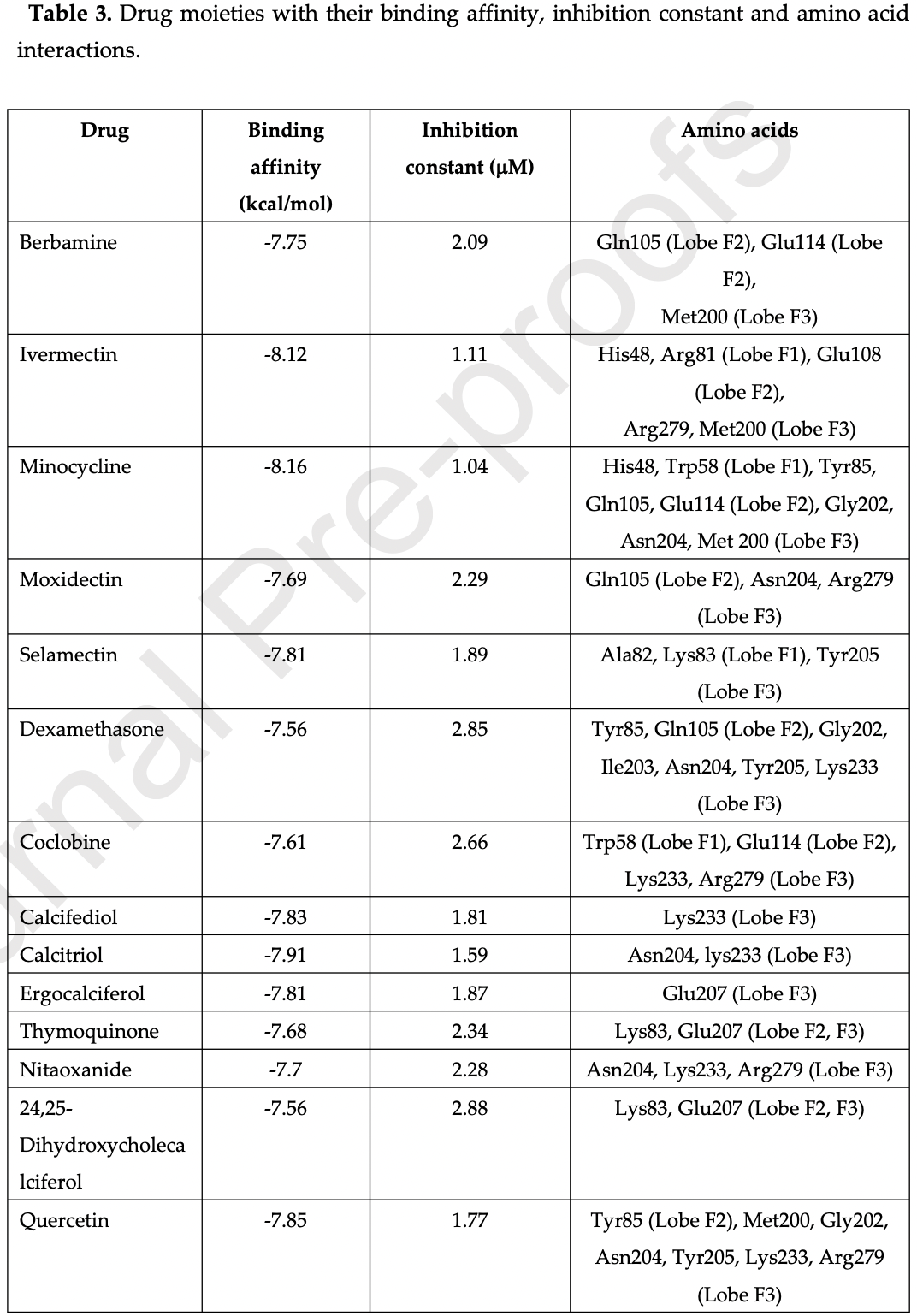
In silico study of SARS-CoV-1&2 endodomains and ezrin docking, identifying ivermectin, quercetin, calcifediol, calcitriol, selamectin, and minocycline as potential therapeutic drugs with strong ezrin binding which may restrict viral endodomain interaction while also stabilizing ezrin, thereby reducing virus fusion and infection.
29 preclinical studies support the efficacy of vitamin D for COVID-19:
Vitamin D has been identified by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) as having sufficient evidence for a causal relationship between intake and optimal immune system function27-30.
Vitamin D inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro17,24, mitigates lung inflammation, damage, and lethality in mice with an MHV-3 model for β-CoV respiratory infections17,24, reduces SARS-CoV-2 replication in nasal epithelial cells via increased type I interferon expression20, downregulates proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-stimulated cells16, attenuates nucleocapsid protein-induced hyperinflammation by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome through the VDR-BRCC3 signaling pathway21, may be neuroprotective by protecting the blood-brain barrier, reducing neuroinflammation, and via immunomodulatory effects31, may mitigate hyperinflammation and cytokine storm by upregulating TLR10 expression which downregulates proinflammatory cytokines13, downregulates ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in human trophoblasts and minimizes spike protein-induced inflammation19, may minimize cytokine storm by dampening excessive cytokine production2, may suppress viral entry and replication via LL-37 induction11,12, and minimizes platelet aggregation mediated by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein via inhibiting integrin αIIbβ3 outside-in signaling15.
Cholecalciferol and calcifediol directly bind two allosteric pockets on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD, bias the trimer toward a closed state, weaken ACE2 engagement, and reduce viral entry in cell models1.
Calcitriol may destabilize the Spike protein architecture and inhibit IL-17R dimerization, blocking viral entry and mitigating hyperinflammatory cytokine storm32.
Vitamin D improves regulatory immune cell levels and control of proinflammatory cytokines in severe COVID-1933.
Calcifediol inhibits SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease (PLpro), a critical enzyme for viral replication14.
Symptomatic COVID-19 is associated with a lower frequency of natural killer (NK) cells and vitamin D has been shown to improve NK cell activity34,35.
Study covers quercetin, vitamin D, and ivermectin.
1.
García-Marín et al., Exploring SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Pockets as Targets for Generic Drugs: A Combined Computational, Biophysical, and Biological Approach, ACS Omega, doi:10.1021/acsomega.5c05175.
2.
Alzahrani, A., A new investigation into the molecular mechanism of cholecalciferol towards reducing cytokines storm, Octahedron Drug Research, doi:10.21608/odr.2024.308273.1043.
3.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
4.
Morales-Bayuelo et al., New findings on ligand series used as SARS-CoV-2 virus inhibitors within the frameworks of molecular docking, molecular quantum similarity and chemical reactivity indices, F1000Research, doi:10.12688/f1000research.123550.3.
5.
Chellasamy et al., Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors, Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277.
6.
Pandya et al., Unravelling Vitamin B12 as a potential inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2: A computational approach, Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2022.100951.
7.
Mansouri et al., The impact of calcitriol and estradiol on the SARS-CoV-2 biological activity: a molecular modeling approach, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-04778-y.
8.
Song et al., Vitamin D3 and its hydroxyderivatives as promising drugs against COVID-19: a computational study, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1964601.
9.
Qayyum et al., Vitamin D and lumisterol novel metabolites can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication machinery enzymes, Endocrinology and Metabolism, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00174.2021.
10.
Al-Mazaideh et al., Vitamin D is a New Promising Inhibitor to the Main Protease (Mpro) of COVID-19 by Molecular Docking, Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International, doi:10.9734/jpri/2021/v33i29B31603.
11.
Roth et al., Vitamin D-inducible antimicrobial peptide LL-37 binds SARS-CoV-2 Spike and accessory proteins ORF7a and ORF8, Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2025.1671738.
12.
Vercellino et al., Influence of Sex and 1,25α Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Viral Entry, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens14080765.
13.
Knez et al., TLR10 overexpression modulates immune response in A549 lung epithelial cells challenged with SARS-CoV-2 S and N proteins, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1490478.
14.
Chen et al., In Vitro Characterization of Inhibition Function of Calcifediol to the Protease Activity of SARS-COV-2 PLpro, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.70085.
15.
Wang et al., 1,25‐Dihydroxyvitamin D3 attenuates platelet aggregation potentiated by SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein via inhibiting integrin αIIbβ3 outside‐in signaling, Cell Biochemistry and Function, doi:10.1002/cbf.4039.
16.
Alcalá-Santiago et al., Disentangling the Immunomodulatory Effects of Vitamin D on the SARS-CoV-2 Virus by In Vitro Approaches, The 14th European Nutrition Conference FENS 2023, doi:10.3390/proceedings2023091415.
17.
Campolina-Silva et al., Dietary Vitamin D Mitigates Coronavirus-Induced Lung Inflammation and Damage in Mice, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15122434.
18.
Moatasim et al., Potent Antiviral Activity of Vitamin B12 against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, and Human Coronavirus 229E, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11112777.
19.
Vargas-Castro et al., Calcitriol prevents SARS-CoV spike-induced inflammation in human trophoblasts through downregulating ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2024.106625.
20.
Sposito et al., Age differential CD13 and interferon expression in airway epithelia affect SARS-CoV-2 infection - effects of vitamin D, Mucosal Immunology, doi:10.1016/j.mucimm.2023.08.002.
21.
Chen (B) et al., Vitamin D3 attenuates SARS‐CoV‐2 nucleocapsid protein‐caused hyperinflammation by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome through the VDR‐BRCC3 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo, MedComm, doi:10.1002/mco2.318.
22.
Rybakovsky et al., Calcitriol modifies tight junctions, improves barrier function, and reduces TNF‐α‐induced barrier leak in the human lung‐derived epithelial cell culture model, 16HBE 14o‐, Physiological Reports, doi:10.14814/phy2.15592.
23.
DiGuilio et al., The multiphasic TNF-α-induced compromise of Calu-3 airway epithelial barrier function, Experimental Lung Research, doi:10.1080/01902148.2023.2193637.
24.
Pickard et al., Discovery of re-purposed drugs that slow SARS-CoV-2 replication in human cells, PLOS Pathogens, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009840.
25.
Mok et al., Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, is a promising candidate for COVID-19 prophylaxis, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.21.162396.
26.
Fernandes de Souza et al., Lung Inflammation Induced by Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 in C57BL/6 Female Mice Is Controlled by Intranasal Instillation of Vitamin D, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells12071092.
27.
Galmés et al., Suboptimal Consumption of Relevant Immune System Micronutrients Is Associated with a Worse Impact of COVID-19 in Spanish Populations, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14112254.
28.
Galmés (B) et al., Current State of Evidence: Influence of Nutritional and Nutrigenetic Factors on Immunity in the COVID-19 Pandemic Framework, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092738.
29.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
30.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
31.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
32.
Fadel et al., Targeting asparagine and cysteine in SARS-CoV-2 variants and human pro-inflammatory mediators to alleviate COVID-19 severity; a cross-section and in-silico study, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-19359-y.
33.
Saheb Sharif-Askari et al., Increased blood immune regulatory cells in severe COVID-19 with autoantibodies to type I interferons, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-43675-w.
Chellasamy et al., 10 Aug 2022, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
Contact: selvaakumar.c@dypatil.edu, eleanorwatson@connect.glos.ac.uk.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors
Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no competing or conflicting interests.
References
Bairoch, Apweiler, The Swiss-Prot protein sequence database: its relevance to human molecular medical research, J. Mol. Med
Berendsen, GROMACS: A message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation, Comp. Phys. Comm
Berman, Westbrook, Feng, Gilliland, Bhat et al., The protein data bank, Nucleic Acids Res
Biovia, Systèmes, None
Bretscher, Edwards, Fehon, ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol
Bulut, Hong, Chen, Beauchamp, Rahim et al., Small molecule inhibitors of ezrin inhibit the invasive phenotype of osteosarcoma cells, Oncogene Jan, doi:10.1038/onc.2011.245
Chen, Sawaya, Phillips, Reisler, Quinlan, Multiple Forms of Spire-Actin Complexes and their Functional Consequences, J. Biol. Chem
Ehsani, COVID-19 and iron dysregulation: distant sequence similarity between hepcidin and the novel coronavirus spike glycoprotein, Biol Direct, doi:10.1186/s13062-020-00275-2
Fehon, Mcclatchey, Bretscher, Organizing the cell cortex: the role of
Fehr, Perlman, Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and 15. pathogenesis, Methods Mol. Biol
Fievet, Louvard, Arpin, ERM proteins in epithelial cell organization and 13. functions, Biochim Biophys Acta
Gautreau, Poullet, Louvard, Arpin, Ezrin, a plasma membrane-microfilament linker, signals cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway
Jorgensen, Chandrasekhar, Madura, Impey, Klein, Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water, J. Chem. Phys
Kim, Thiessen, Bolton, Chen, Fu et al., PubChem Substance and Compound databases, Nucleic Acids Res
Kumar, Kumar, Wei, Comparative docking studies to understand the binding affinity of nicotine with soluble ACE2 (sACE2)-SARS-CoV-2 complex over sACE2, Toxicology Reports
Laskowski, Macarthur, Moss, Thornton, PROCHECK -a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures, J. App. Cryst
Li, Li, Farzan, Harrison, Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor binding domain complexed with receptor, Science
Lu, Hu, Wang, Qi, Gao et al., Molecular basis of binding between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor. CD26, Nature
Lu, Zhao, Li, Genomic characterization and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet
Millet, Kien, Cheung, Siu, Chan et al., Ezrin interacts with the SARS coronavirus spike protein and restrains infection at the entry stage, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049566
Miteva, Guyon, Tufféry, Frog2: Efficient 3D conformation ensemble generator for small compounds, Nucleic Acids Res. Jul
Morris, Huey, Lindstrom, Sanner, Belew et al., Autodock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility, J. Computational Chemistry
Nose, A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods, The Journal of Chemical Physics
Paules, Marston, Fauci, Coronavirus infections-more than just the common cold, JAMA
Petit, Chouljenko, Iyer, Colgrove, Farzan et al., Palmitoylation of the cysteine-rich endodomain of the SARS-coronavirus spike glycoprotein is important for spike-mediated cell fusion, Virology Apr
Phang, Harrop, Duff, Sokolova, Crossett et al., Structural characterization suggests models for monomeric and dimeric forms of full length ezrin, Biochem. J
Ramadan, Mayilsamy, Mcgill, Ghosh, Giulianotti et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Palmitoylation Inhibitors That Results in Release of Attenuated Virus with Reduced Infectivity, Viruses
Schwede, Kopp, Guex, Peitsch, SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modelling server, Nucleic Acids Res. Jul
Shaw Research, Maestro-Desmond Interoperability Tools, version 3.6
Smith, Nassar, Bretscher, Cerione, Andrew et al., Structure of the active N-terminal domain of Ezrin. Conformational and mobility changes identify keystone interactions, J. Biol. Chem. Feb, doi:10.1074/jbc.M210601200
Turunen, Wahlström, Vaheri, Ezrin has a COOH-terminal actin-binding site that is conserved in the ezrin protein family, J. Cell Biol
Van Zundert, Melquiond, Bonvin, Integrative Modeling of Biomolecular Complexes: HADDOCKing with Cryo-Electron Microscopy Data, Structure
Wiederstein, Sippl, ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins, Nucleic Acids Research
Xia, Domains and Functions of Spike Protein in Sars-Cov-2 in the Context of Vaccine Design, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v1301010
Xue, Rodrigues, Kastritis, Bonvin, Vangone, PRODIGY: a web server for predicting the binding affinity of protein-protein complexes, Bioinformatics
Zhang, Holmes, A genomic perspective on the origin and emergence of SARS-CoV 2, Cell
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277",
"ISSN": [
"1018-3647"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277",
"alternative-id": [
"S101836472200458X"
],
"article-number": "102277",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of King Saud University - Science"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chellasamy",
"given": "Selvaa Kumar",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "Eleanor",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of King Saud University - Science",
"container-title-short": "Journal of King Saud University - Science",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-10T22:02:31Z",
"timestamp": 1660168951000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-10T22:03:10Z",
"timestamp": 1660168990000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-10T22:42:29Z",
"timestamp": 1660171349293
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1659312000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 7,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1659916800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S101836472200458X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S101836472200458X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "102277",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "The Swiss-Prot protein sequence database: its relevance to human molecular medical research",
"author": "Bairoch",
"first-page": "312",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0005",
"volume": "75",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0010-4655(95)00042-E",
"article-title": "GROMACS: A message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation",
"author": "Berendsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43",
"issue": "1-3",
"journal-title": "Comp. Phys. Comm.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0010",
"volume": "91",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/28.1.235",
"article-title": "The protein data bank",
"author": "Berman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "235",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0015",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"article-title": "Discovery Studio",
"author": "BIOVIA,",
"journal-title": "San Diego: Dassault Systèmes",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0020",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrm882",
"article-title": "ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex",
"author": "Bretscher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "586",
"issue": "2002",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0025",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/onc.2011.245",
"article-title": "Small molecule inhibitors of ezrin inhibit the invasive phenotype of osteosarcoma cells",
"author": "Bulut",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Oncogene",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0030",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M111.317792",
"article-title": "Multiple Forms of Spire-Actin Complexes and their Functional Consequences",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10684",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0035",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0040",
"unstructured": "D. E. Shaw Research 2013.Desmond Molecular Dynamics System, version 3.6. New York, NY,2013. Maestro-Desmond Interoperability Tools, version 3.6, Schrodinger, New York, NY,2013."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13062-020-00275-2",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and iron dysregulation: distant sequence similarity between hepcidin and the novel coronavirus spike glycoprotein",
"author": "Ehsani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "19",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biol Direct",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0045",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrm2866",
"article-title": "Organizing the cell cortex: the role of ERM proteins",
"author": "Fehon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0050",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.06.013",
"article-title": "ERM proteins in epithelial cell organization and functions",
"author": "Fiévet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "653",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0055",
"volume": "1773",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis",
"author": "Fehr",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "2015",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0060",
"volume": "1282",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.96.13.7300",
"article-title": "Ezrin, a plasma membrane-microfilament linker, signals cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway",
"author": "Gautreau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7300",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0065",
"volume": "96",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparative docking studies to understand the binding affinity of nicotine with soluble ACE2 (sACE2)-SARS-CoV-2 complex over sACE2",
"author": "Kumar",
"first-page": "1366",
"issue": "2020",
"journal-title": "Toxicology Reports",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0070",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/1.445869",
"article-title": "Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water",
"author": "Jorgensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "926",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Phys",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0075",
"volume": "79",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0021889892009944",
"article-title": "PROCHECK - a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures",
"author": "Laskowski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "283",
"journal-title": "J. App. Cryst.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0080",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1116480",
"article-title": "Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor binding domain complexed with receptor",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1864",
"issue": "5742",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0085",
"volume": "309",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8",
"article-title": "Genomic characterization and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0090",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature12328",
"article-title": "Molecular basis of binding between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor. CD26",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"issue": "7461",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0095",
"volume": "500",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkv951",
"article-title": "PubChem Substance and Compound databases",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "D1202",
"issue": "Database issue",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0100",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0049566",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0105",
"unstructured": "J.K. Millet F. Kien C.-Y. Cheung Y.-L. Siu W.-L. Chan H. Li H.-L. Leung M. Jaume R. Bruzzone J.S. Malik Peiris R.M. Altmeyer B. Nal S. Pöhlmann Ezrin Interacts with the SARS Coronavirus Spike Protein and Restrains Infection at the Entry Stage PLoS One 7 11 e49566"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkq325",
"article-title": "Frog2: Efficient 3D conformation ensemble generator for small compounds",
"author": "Miteva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W622",
"issue": "Web Server",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Research",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0110",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.21256",
"article-title": "Autodock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility",
"author": "Morris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2785",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "J. Computational Chemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0115",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/1.447334",
"article-title": "A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods",
"author": "Nosé",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "511",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "The Journal of Chemical Physics",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0120",
"volume": "81",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.0757",
"article-title": "Coronavirus infections-more than just the common cold",
"author": "Paules",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "707",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0125",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2006.10.034",
"article-title": "Palmitoylation of the cysteine-rich endodomain of the SARS-coronavirus spike glycoprotein is important for spike-mediated cell fusion",
"author": "Petit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "264",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Virology Apr 10",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0130",
"volume": "360",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BCJ20160541",
"article-title": "Structural characterization suggests models for monomeric and dimeric forms of full length ezrin",
"author": "Phang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2763",
"journal-title": "Biochem. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0135",
"volume": "473",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14030531",
"article-title": "Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Palmitoylation Inhibitors That Results in Release of Attenuated Virus with Reduced Infectivity",
"author": "Ramadan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "531",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0140",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkg520",
"article-title": "SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modelling server",
"author": "Schwede",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3381",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res. Jul 1",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0145",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M210601200",
"article-title": "Structure of the Active N-terminal Domain of Ezrin",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4949",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Journal of Biological Chemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0150",
"volume": "278",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.126.6.1445",
"article-title": "Ezrin has a COOH-terminal actin-binding site that is conserved in the ezrin protein family",
"author": "Turunen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1445",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0155",
"volume": "126",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkm290",
"article-title": "ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins",
"author": "Wiederstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W407",
"issue": "2007",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Research",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0160",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0165",
"unstructured": "WHO Dashboard https://covid19.who.int"
},
{
"author": "Xia",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "Domains and Functions of Spike Protein in Sars-Cov-2 in the Context of Vaccine Design.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0170",
"volume": "Viruses,13(1)",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "PRODIGY: a web server for predicting the binding affinity of protein-protein complexes",
"author": "Xue",
"first-page": "3676",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics (Oxford, England)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0175",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.035",
"article-title": "A genomic perspective on the origin and emergence of SARS-CoV 2",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0180",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.str.2015.03.014",
"article-title": "Integrative Modeling of Biomolecular Complexes: HADDOCKing with Cryo-Electron Microscopy Data",
"author": "van Zundert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "949",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Structure",
"key": "10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277_b0185",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S101836472200458X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
chellasamy
