Influence of Sex and 1,25α Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Viral Entry
et al., Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens14080765, Aug 2025
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
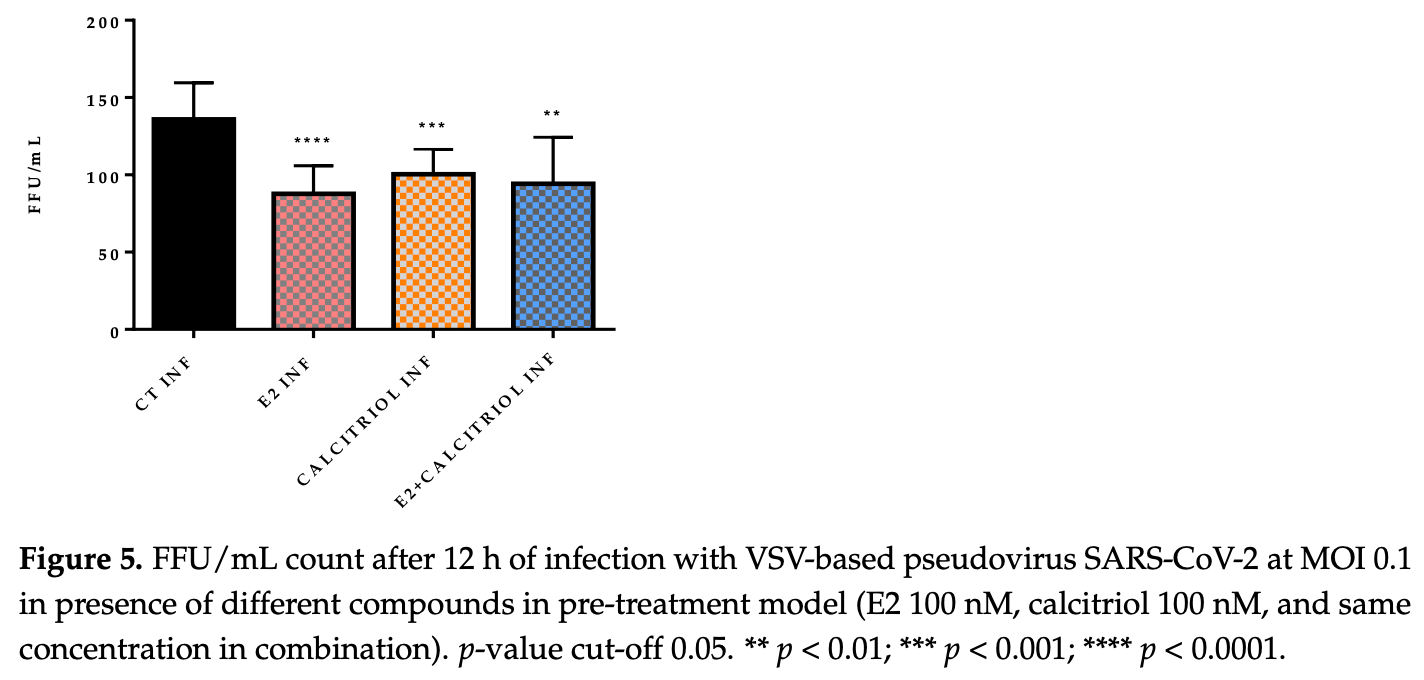
In vitro study showing that calcitriol and 17β-estradiol (E2) inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in Vero E6 cells. Authors treated cells with 100 nM of E2 and calcitriol for 15 days before infection with VSV-based pseudovirus SARS-CoV-2 and wild-type D614G variant. Both compounds significantly reduced focus-forming units (FFU) when used individually in the pre-treatment model. However, when E2 and calcitriol were combined, viral production slightly increased with SARS-CoV-2. Authors found no changes in ACE2 or vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene expression after treatment, suggesting the antiviral mechanism operates independently of receptor modulation.
29 preclinical studies support the efficacy of vitamin D for COVID-19:
Vitamin D has been identified by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) as having sufficient evidence for a causal relationship between intake and optimal immune system function27-30.
Vitamin D inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro17,24, mitigates lung inflammation, damage, and lethality in mice with an MHV-3 model for β-CoV respiratory infections17,24, reduces SARS-CoV-2 replication in nasal epithelial cells via increased type I interferon expression20, downregulates proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-stimulated cells16, attenuates nucleocapsid protein-induced hyperinflammation by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome through the VDR-BRCC3 signaling pathway21, may be neuroprotective by protecting the blood-brain barrier, reducing neuroinflammation, and via immunomodulatory effects31, may mitigate hyperinflammation and cytokine storm by upregulating TLR10 expression which downregulates proinflammatory cytokines13, downregulates ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in human trophoblasts and minimizes spike protein-induced inflammation19, may minimize cytokine storm by dampening excessive cytokine production2, may suppress viral entry and replication via LL-37 induction11,12, and minimizes platelet aggregation mediated by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein via inhibiting integrin αIIbβ3 outside-in signaling15.
Cholecalciferol and calcifediol directly bind two allosteric pockets on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD, bias the trimer toward a closed state, weaken ACE2 engagement, and reduce viral entry in cell models1.
Calcitriol may destabilize the Spike protein architecture and inhibit IL-17R dimerization, blocking viral entry and mitigating hyperinflammatory cytokine storm32.
Vitamin D improves regulatory immune cell levels and control of proinflammatory cytokines in severe COVID-1933.
Calcifediol inhibits SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease (PLpro), a critical enzyme for viral replication14.
Symptomatic COVID-19 is associated with a lower frequency of natural killer (NK) cells and vitamin D has been shown to improve NK cell activity34,35.
1.
García-Marín et al., Exploring SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Pockets as Targets for Generic Drugs: A Combined Computational, Biophysical, and Biological Approach, ACS Omega, doi:10.1021/acsomega.5c05175.
2.
Alzahrani, A., A new investigation into the molecular mechanism of cholecalciferol towards reducing cytokines storm, Octahedron Drug Research, doi:10.21608/odr.2024.308273.1043.
3.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
4.
Morales-Bayuelo et al., New findings on ligand series used as SARS-CoV-2 virus inhibitors within the frameworks of molecular docking, molecular quantum similarity and chemical reactivity indices, F1000Research, doi:10.12688/f1000research.123550.3.
5.
Chellasamy et al., Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors, Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277.
6.
Pandya et al., Unravelling Vitamin B12 as a potential inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2: A computational approach, Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2022.100951.
7.
Mansouri et al., The impact of calcitriol and estradiol on the SARS-CoV-2 biological activity: a molecular modeling approach, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-04778-y.
8.
Song et al., Vitamin D3 and its hydroxyderivatives as promising drugs against COVID-19: a computational study, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1964601.
9.
Qayyum et al., Vitamin D and lumisterol novel metabolites can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication machinery enzymes, Endocrinology and Metabolism, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00174.2021.
10.
Al-Mazaideh et al., Vitamin D is a New Promising Inhibitor to the Main Protease (Mpro) of COVID-19 by Molecular Docking, Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International, doi:10.9734/jpri/2021/v33i29B31603.
11.
Roth et al., Vitamin D-inducible antimicrobial peptide LL-37 binds SARS-CoV-2 Spike and accessory proteins ORF7a and ORF8, Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2025.1671738.
12.
Vercellino et al., Influence of Sex and 1,25α Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Viral Entry, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens14080765.
13.
Knez et al., TLR10 overexpression modulates immune response in A549 lung epithelial cells challenged with SARS-CoV-2 S and N proteins, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1490478.
14.
Chen et al., In Vitro Characterization of Inhibition Function of Calcifediol to the Protease Activity of SARS-COV-2 PLpro, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.70085.
15.
Wang et al., 1,25‐Dihydroxyvitamin D3 attenuates platelet aggregation potentiated by SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein via inhibiting integrin αIIbβ3 outside‐in signaling, Cell Biochemistry and Function, doi:10.1002/cbf.4039.
16.
Alcalá-Santiago et al., Disentangling the Immunomodulatory Effects of Vitamin D on the SARS-CoV-2 Virus by In Vitro Approaches, The 14th European Nutrition Conference FENS 2023, doi:10.3390/proceedings2023091415.
17.
Campolina-Silva et al., Dietary Vitamin D Mitigates Coronavirus-Induced Lung Inflammation and Damage in Mice, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15122434.
18.
Moatasim et al., Potent Antiviral Activity of Vitamin B12 against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, and Human Coronavirus 229E, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11112777.
19.
Vargas-Castro et al., Calcitriol prevents SARS-CoV spike-induced inflammation in human trophoblasts through downregulating ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2024.106625.
20.
Sposito et al., Age differential CD13 and interferon expression in airway epithelia affect SARS-CoV-2 infection - effects of vitamin D, Mucosal Immunology, doi:10.1016/j.mucimm.2023.08.002.
21.
Chen (B) et al., Vitamin D3 attenuates SARS‐CoV‐2 nucleocapsid protein‐caused hyperinflammation by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome through the VDR‐BRCC3 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo, MedComm, doi:10.1002/mco2.318.
22.
Rybakovsky et al., Calcitriol modifies tight junctions, improves barrier function, and reduces TNF‐α‐induced barrier leak in the human lung‐derived epithelial cell culture model, 16HBE 14o‐, Physiological Reports, doi:10.14814/phy2.15592.
23.
DiGuilio et al., The multiphasic TNF-α-induced compromise of Calu-3 airway epithelial barrier function, Experimental Lung Research, doi:10.1080/01902148.2023.2193637.
24.
Pickard et al., Discovery of re-purposed drugs that slow SARS-CoV-2 replication in human cells, PLOS Pathogens, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009840.
25.
Mok et al., Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, is a promising candidate for COVID-19 prophylaxis, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.21.162396.
26.
Fernandes de Souza et al., Lung Inflammation Induced by Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 in C57BL/6 Female Mice Is Controlled by Intranasal Instillation of Vitamin D, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells12071092.
27.
Galmés et al., Suboptimal Consumption of Relevant Immune System Micronutrients Is Associated with a Worse Impact of COVID-19 in Spanish Populations, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14112254.
28.
Galmés (B) et al., Current State of Evidence: Influence of Nutritional and Nutrigenetic Factors on Immunity in the COVID-19 Pandemic Framework, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092738.
29.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
30.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
31.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
32.
Fadel et al., Targeting asparagine and cysteine in SARS-CoV-2 variants and human pro-inflammatory mediators to alleviate COVID-19 severity; a cross-section and in-silico study, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-19359-y.
33.
Saheb Sharif-Askari et al., Increased blood immune regulatory cells in severe COVID-19 with autoantibodies to type I interferons, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-43675-w.
Vercellino et al., 2 Aug 2025, Italy, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: d.lilleri@smatteo.pv.it (corresponding author), nicole.vercellino@uniupo.it, mattia.bellan@med.uniupo.it, rosalba.minisini@med.uniupo.it, alessandro.ferrari04@universitadipavia.it, e.iskandar@smatteo.pv.it, jose.sammartino@iusspavia.it.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Influence of Sex and 1,25α Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Viral Entry
Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens14080765
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the etiologic agent that causes the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) identified in Wuhan, in 2019. Men are more prone to developing severe manifestations than women, suggesting a possible crucial role of sex hormones. 17,β-Estradiol (E2) and 1,25 α dihydroxyvitamin D 3 (calcitriol) act upon gene pathways as immunomodulators in several infectious respiratory diseases. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the influence of E2 and calcitriol on the VSV-based pseudovirus SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. We infected Vero E6 cells with the recombinant VSV-based pseudovirus SARS-CoV-2 and the SARS-CoV-2 viruses according to the pre-treatment and pre-post-treatment models. The Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) and Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) gene expression did not change under different treatments. The VSV-based pseudovirus SARS-CoV-2 infection showed a significant decrease in the focus-forming unit count in the presence of E2 and calcitriol (either alone or in combination) in the pre-treatment model, while in the pre-post-treatment model, the infection was inhibited only in the presence of E2. Th SARS-CoV-2 infection highlighted a decrease in viral titres in the presence of E2 and calcitriol only in the pre-post-treatment model. 17,β-Estradiol and calcitriol can exert an inhibitory effect on SARS-CoV-2 infections, demonstrating their protective role against viral infections.
Informed Consent Statement: Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
References
Adil, Rahman, Whitelaw, Jain, Al-Taan et al., SARS-CoV-2 and the Pandemic of COVID-19, Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138386
Apaydin, Polat, Dincer Yazan, Ilgin, Elbasan et al., Effects of Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphisms on the Prognosis of COVID-19, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/cen.14664
Beserra, Alberca, Branco, De Mendonça Oliveira, De Souza Andrade et al., Upregulation of PD-1 Expression and High SPD-L1 Levels Associated with COVID-19 Severity, J. Immunol. Res, doi:10.1155/2022/9764002
Bonam, Hu, Bayry, Role of the PD-1 and PD-L1 Axis in COVID-19, Future Microbiol, doi:10.2217/fmb-2022-0103
Borborema, Lucena, Silva, Vitamin D and Estrogen Steroid Hormones and Their Immunogenetic Roles in Infectious Respiratory (TB and COVID-19) Diseases, Genet. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1590/1415-4757-gmb-2022-0158
Briceno Noriega, Savelkoul, Vitamin, A Potential Mitigation Tool for the Endemic Stage of the COVID-19 Pandemic? Front, Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.888168
Chen, Li, Ou-Yang, Role of Estrogen Receptors in Health and Disease, Front. Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.839005
Condor Capcha, Lambert, Dykxhoorn, Salerno, Hare et al., Generation of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Pseudotyped Virus for Viral Entry and Neutralization Assays: A 1-Week Protocol, Front. Cardiovasc. Med, doi:10.3389/fcvm.2020.618651
Dupuis, Pagano, Pierdominici, Ortona, The Role of Vitamin D in Autoimmune Diseases: Could Sex Make the Difference?, Biol. Sex Differ, doi:10.1186/s13293-021-00358-3
Garg, Agrawal, Gautam, Pursnani, Agarwal et al., Covid-19 Outcomes in Postmenopausal and Perimenopausal Females: Is Estrogen Hormone Attributing to Gender Differences?, J. Midlife Health, doi:10.4103/jmh.JMH_287_20
Geerling, Pinski, Stone, Dipaolo, Zulu et al., Roles of Antiviral Sensing and Type I Interferon Signaling in the Restriction of SARS-CoV-2 Replication, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2021.103553
Gupta, Jayakumar, Saleh, Kannan, Halwani et al., SARS-CoV-2 Infection-Induced Growth Factors Play Differential Roles in COVID-19 Pathogenesis, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120703
Gusev, Sarapultsev, Solomatina, Chereshnev, Sars-Cov-2-Specific Immune Response and the Pathogenesis of COVID-19, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23031716
Hafezi, Saheb Sharif-Askari, Saheb Sharif-Askari, Ali Hussain Alsayed, Alsafar et al., Vitamin D Enhances Type I IFN Signaling in COVID-19 Patients, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-22307-9
Hartenian, Nandakumar, Lari, Ly, Tucker et al., The Molecular Virology of Coronaviruses, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.REV120.013930
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Entry into Cells, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x
Lampropoulou, Bala, Zerva, Pliakou, Filippou et al., The Potential Role of the Combined PARP-1 and VEGF Inhibition in Severe SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Infection, J. Infect. Dev. Ctries, doi:10.3855/jidc.15386
Lemes, Costa, Bartolomeo, Bassani, Nishino et al., 17β-Estradiol Reduces SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Vitro, Physiol. Rep, doi:10.14814/phy2.14707
Liu, Zhang, Liu, Xia, Zou et al., A Live-Attenuated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Candidate with Accessory Protein Deletions, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-31930-z
Madeleine, Altfeld, Implications of Sex Differences in Immunity for SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis and Design of Therapeutic Interventions, Immunity
Manik, Singh, Role of Toll-like Receptors in Modulation of Cytokine Storm Signaling in SARS-CoV-2-Induced COVID-19, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27405
Mohan, Cherian, Sharma, Exploring Links between Vitamin D Deficiency and Covid-19, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1008874
Mok, Ng, Ahidjo, Aw, Chen et al., Evaluation of In Vitro and In Vivo Antiviral Activities of Vitamin D for SARS-CoV-2 and Variants, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15030925
Montazersaheb, Hosseiniyan Khatibi, Hejazi, Tarhriz, Farjami et al., COVID-19 Infection: An Overview on Cytokine Storm and Related Interventions, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/s12985-022-01814-1
Mura, Dos Santos, Stewart, Liu, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Related Molecules in Acute Lung Injury, J. Appl. Physiol, doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00202.2004
Ogando, Dalebout, Zevenhoven-Dobbe, Limpens, Van Der Meer et al., SARS-Coronavirus-2 Replication in Vero E6 Cells: Replication Kinetics, Rapid Adaptation and Cytopathology, J. Gen. Virol
Pagano, Peruzzu, Ruggieri, Ortona, Gagliardi, Vitamin D and Sex Differences in COVID-19, Front. Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.567824
Peruzzu, Pagano, Pierdominici, Ruggieri, Antinori et al., Synergy Between Vitamin D and Sex Hormones in Respiratory Functionality of Patients Affected by COVID-19, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.683529
Qaderi, Hosseinirad, Kalhor, Zangeneh, Pournaghi et al., The Relationship between Sex Steroids (E2, Progesterone, and AMH) Levels and Severity and Fatality of COVID-19: A Systematic Review, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14218
Reed, Muench, A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints, AJE, doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a118408
Sabbatino, Conti, Franci, Sellitto, Manzo et al., PD-L1 Dysregulation in COVID-19 Patients, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.695242
Samavati, Uhal, ACE2, Much More Than Just a Receptor for SARS-COV-2, Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2020.00317
Schwartz, Verma, Bivens, Schwartz, Boyan, Rapid Steroid Hormone Actions via Membrane Receptors, Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res, doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.06.004
Smither, Lear-Rooney, Biggins, Pettitt, Lever et al., Comparison of the Plaque Assay and 50% Tissue Culture Infectious Dose Assay as Methods for Measuring Filovirus Infectivity, J. Virol. Methods, doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2013.05.015
Tingskov, Mutsaers, Nørregaard, Estrogen Regulates Aquaporin-2 Expression in the Kidney
Wang, Hua, Jiu, Ge, Bai, Biofunctional Roles of Estrogen in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Beyond a Steroid Hormone, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1003469
Zhang, Xiang, Huo, Zhou, Jiang et al., Molecular Mechanism of Interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and Host Cells and Interventional Therapy, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00653-w
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens14080765",
"ISSN": [
"2076-0817"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080765",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the etiologic agent that causes the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) identified in Wuhan, in 2019. Men are more prone to developing severe manifestations than women, suggesting a possible crucial role of sex hormones. 17,β-Estradiol (E2) and 1,25 α dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) act upon gene pathways as immunomodulators in several infectious respiratory diseases. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the influence of E2 and calcitriol on the VSV-based pseudovirus SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. We infected Vero E6 cells with the recombinant VSV-based pseudovirus SARS-CoV-2 and the SARS-CoV-2 viruses according to the pre-treatment and pre–post-treatment models. The Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) and Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) gene expression did not change under different treatments. The VSV-based pseudovirus SARS-CoV-2 infection showed a significant decrease in the focus-forming unit count in the presence of E2 and calcitriol (either alone or in combination) in the pre-treatment model, while in the pre–post-treatment model, the infection was inhibited only in the presence of E2. Th SARS-CoV-2 infection highlighted a decrease in viral titres in the presence of E2 and calcitriol only in the pre–post-treatment model. 17,β-Estradiol and calcitriol can exert an inhibitory effect on SARS-CoV-2 infections, demonstrating their protective role against viral infections.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"pathogens14080765"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0005-7453-2151",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Translational Medicine, Università del Piemonte Orientale, 28100 Novara, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vercellino",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2397-7079",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiology and Virology Unit, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
},
{
"name": "National PhD Programme in One Health Approaches to Infectious Diseases and Life Science Research, Department of Public Health, Experimental and Forensic Medicine, University of Pavia, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ferrari",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3707-3118",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical-Surgical, Diagnostic and Pediatric Sciences, Università degli Studi di Pavia, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sammartino",
"given": "José Camilla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1488-8736",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Translational Medicine, Università del Piemonte Orientale, 28100 Novara, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Center for Autoimmune and Allergic Disease (CAAD), Università del Piemonte Orientale, 28100 Novara, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine and Rheumatology Unit, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria, Maggiore della Carità, 28100 Novara, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria, Maggiore della Carità, 28100 Novara, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bellan",
"given": "Mattia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiology and Virology Unit, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
},
{
"name": "National PhD Programme in One Health Approaches to Infectious Diseases and Life Science Research, Department of Public Health, Experimental and Forensic Medicine, University of Pavia, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Iskandar",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7747-7622",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiology and Virology Unit, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lilleri",
"given": "Daniele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7548-9731",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Translational Medicine, Università del Piemonte Orientale, 28100 Novara, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Minisini",
"given": "Rosalba",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pathogens",
"container-title-short": "Pathogens",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-06T07:45:11Z",
"timestamp": 1754466311000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-06T08:34:10Z",
"timestamp": 1754469250000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003196",
"award": [
"VISION 08069621"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100003196",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Ministero della Salute, Ricerca Corrente 5 × 1000 progetto"
},
{
"award": [
"PE00000007",
"CUP F13C22001220007"
],
"name": "EU funding within the NextGeneration EU-MUR -PNRR Extended Partnership initiative on Emerging Infectious Diseases INF-ACT"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-07T00:06:53Z",
"timestamp": 1754525213528,
"version": "3.41.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1754092800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/14/8/765/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "765",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138386",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 and the Pandemic of COVID-19",
"author": "Adil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23031716",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "Gusev, E., Sarapultsev, A., Solomatina, L., and Chereshnev, V. (2022). Sars-Cov-2-Specific Immune Response and the Pathogenesis of COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.REV120.013930",
"article-title": "The Molecular Virology of Coronaviruses",
"author": "Hartenian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1910",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "295",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2020.00317",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "Samavati, L., and Uhal, B.D. (2020). ACE2, Much More Than Just a Receptor for SARS-COV-2. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00653-w",
"article-title": "Molecular Mechanism of Interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and Host Cells and Interventional Therapy",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "233",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-022-01814-1",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Infection: An Overview on Cytokine Storm and Related Interventions",
"author": "Montazersaheb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "92",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27405",
"article-title": "Role of Toll-like Receptors in Modulation of Cytokine Storm Signaling in SARS-CoV-2-Induced COVID-19",
"author": "Manik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "869",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/9764002",
"article-title": "Upregulation of PD-1 Expression and High SPD-L1 Levels Associated with COVID-19 Severity",
"author": "Beserra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9764002",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol. Res.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.695242",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_9",
"unstructured": "Sabbatino, F., Conti, V., Franci, G., Sellitto, C., Manzo, V., Pagliano, P., De Bellis, E., Masullo, A., Salzano, F.A., and Caputo, A. (2021). PD-L1 Dysregulation in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fmb-2022-0103",
"article-title": "Role of the PD-1 and PD-L1 Axis in COVID-19",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "985",
"journal-title": "Future Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Implications of Sex Differences in Immunity for SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis and Design of Therapeutic Interventions",
"author": "Madeleine",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.683529",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Peruzzu, D., Pagano, M.T., Pierdominici, M., Ruggieri, A., Antinori, A., D’Offizi, G., Petrosillo, N., Palmieri, F., Piselli, P., and Boumis, E. (2021). Synergy Between Vitamin D and Sex Hormones in Respiratory Functionality of Patients Affected by COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.14814/phy2.14707",
"article-title": "17β-Estradiol Reduces SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Vitro",
"author": "Lemes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e14707",
"journal-title": "Physiol. Rep.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.1003469",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_14",
"unstructured": "Wang, Z.P., Hua, M., Jiu, T., Ge, R.L., and Bai, Z. (2022). Biofunctional Roles of Estrogen in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Beyond a Steroid Hormone. Front. Pharmacol., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.vh.2019.08.016",
"article-title": "Estrogen Regulates Aquaporin-2 Expression in the Kidney",
"author": "Tingskov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "243",
"journal-title": "Vitamins and Hormones",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "Volume 112",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/1415-4757-gmb-2022-0158",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Borborema, M.E.A., Lucena, T.M.C., and Silva, J.A. (2023). Vitamin D and Estrogen Steroid Hormones and Their Immunogenetic Roles in Infectious Respiratory (TB and COVID-19) Diseases. Genet. Mol. Biol., 1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2022.839005",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Chen, P., Li, B., and Ou-Yang, L. (2022). Role of Estrogen Receptors in Health and Disease. Front. Endocrinol., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.888168",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Briceno Noriega, D., and Savelkoul, H.F.J. (2022). Vitamin D: A Potential Mitigation Tool for the Endemic Stage of the COVID-19 Pandemic?. Front. Public Health, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.14664",
"article-title": "Effects of Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphisms on the Prognosis of COVID-19",
"author": "Apaydin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "819",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1008874",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_20",
"unstructured": "Mohan, M., Cherian, J.J., and Sharma, A. (2020). Exploring Links between Vitamin D Deficiency and Covid-19. PLoS Pathog., 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13293-021-00358-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "Dupuis, M.L., Pagano, M.T., Pierdominici, M., and Ortona, E. (2021). The Role of Vitamin D in Autoimmune Diseases: Could Sex Make the Difference?. Biol. Sex Differ., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2020.618651",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_22",
"unstructured": "Condor Capcha, J.M., Lambert, G., Dykxhoorn, D.M., Salerno, A.G., Hare, J.M., Whitt, M.A., Pahwa, S., Jayaweera, D.T., and Shehadeh, L.A. (2021). Generation of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Pseudotyped Virus for Viral Entry and Neutralization Assays: A 1-Week Protocol. Front. Cardiovasc. Med., 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jviromet.2013.05.015",
"article-title": "Comparison of the Plaque Assay and 50% Tissue Culture Infectious Dose Assay as Methods for Measuring Filovirus Infectivity",
"author": "Smither",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "J. Virol. Methods",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "193",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a118408",
"article-title": "A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints",
"author": "Reed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "493",
"journal-title": "AJE",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "27",
"year": "1938"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14218",
"article-title": "The Relationship between Sex Steroids (E2, Progesterone, and AMH) Levels and Severity and Fatality of COVID-19: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Qaderi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e14218",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Covid-19 Outcomes in Postmenopausal and Perimenopausal Females: Is Estrogen Hormone Attributing to Gender Differences?",
"author": "Garg",
"first-page": "250",
"journal-title": "J. Midlife Health",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics15030925",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Mok, C.-K., Ng, Y.L., Ahidjo, B.A., Aw, Z.Q., Chen, H., Wong, Y.H., Lee, R.C.H., Loe, M.W.C., Liu, J., and Tan, K.S. (2023). Evaluation of In Vitro and In Vivo Antiviral Activities of Vitamin D for SARS-CoV-2 and Variants. Pharmaceutics, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.567824",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_28",
"unstructured": "Pagano, M.T., Peruzzu, D., Ruggieri, A., Ortona, E., and Gagliardi, M.C. (2020). Vitamin D and Sex Differences in COVID-19. Front. Endocrinol., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Entry into Cells",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-22307-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_30",
"unstructured": "Hafezi, S., Saheb Sharif-Askari, F., Saheb Sharif-Askari, N., Ali Hussain Alsayed, H., Alsafar, H., Al Anouti, F., Hamid, Q., and Halwani, R. (2022). Vitamin D Enhances Type I IFN Signaling in COVID-19 Patients. Sci. Rep., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.06.004",
"article-title": "Rapid Steroid Hormone Actions via Membrane Receptors",
"author": "Schwartz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2289",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "1863",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2021.103553",
"article-title": "Roles of Antiviral Sensing and Type I Interferon Signaling in the Restriction of SARS-CoV-2 Replication",
"author": "Geerling",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103553",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-31930-z",
"article-title": "A Live-Attenuated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Candidate with Accessory Protein Deletions",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4337",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120703",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Infection- Induced Growth Factors Play Differential Roles in COVID-19 Pathogenesis",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "120703",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "304",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3855/jidc.15386",
"article-title": "The Potential Role of the Combined PARP-1 and VEGF Inhibition in Severe SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Infection",
"author": "Lampropoulou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dev. Ctries.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/japplphysiol.00202.2004",
"article-title": "Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Related Molecules in Acute Lung Injury",
"author": "Mura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1605",
"journal-title": "J. Appl. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jgv.0.001453",
"article-title": "SARS-Coronavirus-2 Replication in Vero E6 Cells: Replication Kinetics, Rapid Adaptation and Cytopathology",
"author": "Ogando",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "925",
"journal-title": "J. Gen. Virol.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/14/8/765"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Influence of Sex and 1,25α Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Viral Entry",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}
