Vitamin D-inducible antimicrobial peptide LL-37 binds SARS-CoV-2 Spike and accessory proteins ORF7a and ORF8
et al., Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2025.1671738, Sep 2025
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro study showing that vitamin D-inducible antimicrobial peptide LL-37 binds to multiple SARS-CoV-2 proteins and inhibits viral entry.
29 preclinical studies support the efficacy of vitamin D for COVID-19:
Vitamin D has been identified by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) as having sufficient evidence for a causal relationship between intake and optimal immune system function27-30.
Vitamin D inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro17,24, mitigates lung inflammation, damage, and lethality in mice with an MHV-3 model for β-CoV respiratory infections17,24, reduces SARS-CoV-2 replication in nasal epithelial cells via increased type I interferon expression20, downregulates proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-stimulated cells16, attenuates nucleocapsid protein-induced hyperinflammation by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome through the VDR-BRCC3 signaling pathway21, may be neuroprotective by protecting the blood-brain barrier, reducing neuroinflammation, and via immunomodulatory effects31, may mitigate hyperinflammation and cytokine storm by upregulating TLR10 expression which downregulates proinflammatory cytokines13, downregulates ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in human trophoblasts and minimizes spike protein-induced inflammation19, may minimize cytokine storm by dampening excessive cytokine production2, may suppress viral entry and replication via LL-37 induction11,12, and minimizes platelet aggregation mediated by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein via inhibiting integrin αIIbβ3 outside-in signaling15.
Cholecalciferol and calcifediol directly bind two allosteric pockets on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD, bias the trimer toward a closed state, weaken ACE2 engagement, and reduce viral entry in cell models1.
Calcitriol may destabilize the Spike protein architecture and inhibit IL-17R dimerization, blocking viral entry and mitigating hyperinflammatory cytokine storm32.
Vitamin D improves regulatory immune cell levels and control of proinflammatory cytokines in severe COVID-1933.
Calcifediol inhibits SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease (PLpro), a critical enzyme for viral replication14.
Symptomatic COVID-19 is associated with a lower frequency of natural killer (NK) cells and vitamin D has been shown to improve NK cell activity34,35.
1.
García-Marín et al., Exploring SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Pockets as Targets for Generic Drugs: A Combined Computational, Biophysical, and Biological Approach, ACS Omega, doi:10.1021/acsomega.5c05175.
2.
Alzahrani, A., A new investigation into the molecular mechanism of cholecalciferol towards reducing cytokines storm, Octahedron Drug Research, doi:10.21608/odr.2024.308273.1043.
3.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
4.
Morales-Bayuelo et al., New findings on ligand series used as SARS-CoV-2 virus inhibitors within the frameworks of molecular docking, molecular quantum similarity and chemical reactivity indices, F1000Research, doi:10.12688/f1000research.123550.3.
5.
Chellasamy et al., Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors, Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277.
6.
Pandya et al., Unravelling Vitamin B12 as a potential inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2: A computational approach, Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2022.100951.
7.
Mansouri et al., The impact of calcitriol and estradiol on the SARS-CoV-2 biological activity: a molecular modeling approach, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-04778-y.
8.
Song et al., Vitamin D3 and its hydroxyderivatives as promising drugs against COVID-19: a computational study, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1964601.
9.
Qayyum et al., Vitamin D and lumisterol novel metabolites can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication machinery enzymes, Endocrinology and Metabolism, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00174.2021.
10.
Al-Mazaideh et al., Vitamin D is a New Promising Inhibitor to the Main Protease (Mpro) of COVID-19 by Molecular Docking, Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International, doi:10.9734/jpri/2021/v33i29B31603.
11.
Roth et al., Vitamin D-inducible antimicrobial peptide LL-37 binds SARS-CoV-2 Spike and accessory proteins ORF7a and ORF8, Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2025.1671738.
12.
Vercellino et al., Influence of Sex and 1,25α Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Viral Entry, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens14080765.
13.
Knez et al., TLR10 overexpression modulates immune response in A549 lung epithelial cells challenged with SARS-CoV-2 S and N proteins, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1490478.
14.
Chen et al., In Vitro Characterization of Inhibition Function of Calcifediol to the Protease Activity of SARS-COV-2 PLpro, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.70085.
15.
Wang et al., 1,25‐Dihydroxyvitamin D3 attenuates platelet aggregation potentiated by SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein via inhibiting integrin αIIbβ3 outside‐in signaling, Cell Biochemistry and Function, doi:10.1002/cbf.4039.
16.
Alcalá-Santiago et al., Disentangling the Immunomodulatory Effects of Vitamin D on the SARS-CoV-2 Virus by In Vitro Approaches, The 14th European Nutrition Conference FENS 2023, doi:10.3390/proceedings2023091415.
17.
Campolina-Silva et al., Dietary Vitamin D Mitigates Coronavirus-Induced Lung Inflammation and Damage in Mice, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15122434.
18.
Moatasim et al., Potent Antiviral Activity of Vitamin B12 against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, and Human Coronavirus 229E, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11112777.
19.
Vargas-Castro et al., Calcitriol prevents SARS-CoV spike-induced inflammation in human trophoblasts through downregulating ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2024.106625.
20.
Sposito et al., Age differential CD13 and interferon expression in airway epithelia affect SARS-CoV-2 infection - effects of vitamin D, Mucosal Immunology, doi:10.1016/j.mucimm.2023.08.002.
21.
Chen (B) et al., Vitamin D3 attenuates SARS‐CoV‐2 nucleocapsid protein‐caused hyperinflammation by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome through the VDR‐BRCC3 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo, MedComm, doi:10.1002/mco2.318.
22.
Rybakovsky et al., Calcitriol modifies tight junctions, improves barrier function, and reduces TNF‐α‐induced barrier leak in the human lung‐derived epithelial cell culture model, 16HBE 14o‐, Physiological Reports, doi:10.14814/phy2.15592.
23.
DiGuilio et al., The multiphasic TNF-α-induced compromise of Calu-3 airway epithelial barrier function, Experimental Lung Research, doi:10.1080/01902148.2023.2193637.
24.
Pickard et al., Discovery of re-purposed drugs that slow SARS-CoV-2 replication in human cells, PLOS Pathogens, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009840.
25.
Mok et al., Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, is a promising candidate for COVID-19 prophylaxis, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.21.162396.
26.
Fernandes de Souza et al., Lung Inflammation Induced by Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 in C57BL/6 Female Mice Is Controlled by Intranasal Instillation of Vitamin D, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells12071092.
27.
Galmés et al., Suboptimal Consumption of Relevant Immune System Micronutrients Is Associated with a Worse Impact of COVID-19 in Spanish Populations, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14112254.
28.
Galmés (B) et al., Current State of Evidence: Influence of Nutritional and Nutrigenetic Factors on Immunity in the COVID-19 Pandemic Framework, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092738.
29.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
30.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
31.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
32.
Fadel et al., Targeting asparagine and cysteine in SARS-CoV-2 variants and human pro-inflammatory mediators to alleviate COVID-19 severity; a cross-section and in-silico study, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-19359-y.
33.
Saheb Sharif-Askari et al., Increased blood immune regulatory cells in severe COVID-19 with autoantibodies to type I interferons, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-43675-w.
Roth et al., 23 Sep 2025, Germany, peer-reviewed, 14 authors.
Contact: dzemal.elezagic@uk-koeln.de, manuel.koch@uni-koeln.de.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Vitamin D-inducible antimicrobial peptide LL-37 binds SARS-CoV-2 Spike and accessory proteins ORF7a and ORF8
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2025.1671738
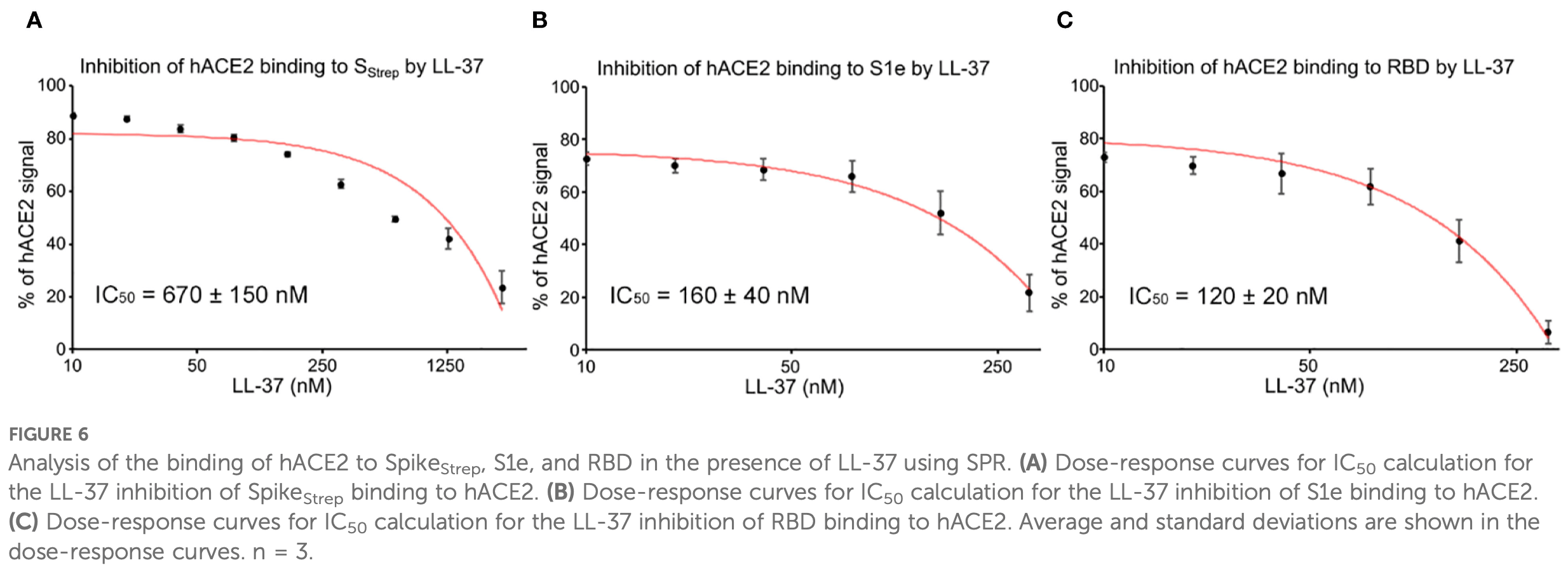
Background: The role of vitamin D in Coronavirus Disease 2019 outcomes remains debated, but emerging evidence suggests it may enhance recovery by strengthening immune responses. Vitamin D upregulates LL-37, an antimicrobial peptide with broad antiviral activity, including potential benefits against SARS-CoV-2. LL-37's interactions with viral proteins, however, remain incompletely understood. Methods: We investigated LL-37's interactions with the SARS-CoV-2 Spike glycoprotein and the accessory proteins ORF7a and ORF8 using surface plasmon resonance and negative-stain electron microscopy. These approaches were employed to assess LL-37's binding capabilities and potential impact on viral infectivity. Results: LL-37 bound multiple domains of the Spike protein and inhibited its interaction with the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2) receptor in vitro. Up to seven LL-37 molecules were observed surrounding Spike, forming a halo-like structure that may block receptor engagement. LL-37 also bound to ORF7a and ORF8, potentially impairing their ability to disrupt host cell processes. Notably, LL-37's interaction with ORF7a may prevent degradation of SNAP29, restoring autophagy and promoting viral clearance.
Funding The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Funding for this study was provided by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) via 384170921 FOR2722/ C2 to GS, FOR2722/B2 to MK, and FOR2722/B1 to MP.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. During the preparation of this work the authors used Chat GPT in order to assist with improving the clarity, structure, and grammar of the manuscript text. After using this tool, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication. Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer,..
References
Accorsi, Britton, Fleming-Dutra, Smith, Shang et al., Association between 3 doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and symptomatic infection caused by the SARS-CoV-2 omicron and delta variants, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.0470
Alcala-Diaz, Limia-Perez, Gomez-Huelgas, Martin-Escalante, Cortes-Rodriguez et al., Calcifediol treatment and hospital mortality due to COVID-19: A cohort study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061760
Aloul, Nielsen, Defensor, Lin, Fortkort et al., Upregulating human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL-37 expression may prevent severe COVID-19 inflammatory responses and reduce microthrombosis, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.880961
Alsafar, Grant, Hijazi, Uddin, Alkaabi et al., COVID-19 disease severity and death in relation to vitamin D status among SARS-CoV-2-positive UAE residents, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13051714
Anzic, Stoiber, Obermeyer, Mertz, Stalder et al., Two-sided effects of neutrophil extracellular traps and changes in the myeloid compartment in acute COVID-19: A histopathological study on autopsy cases from the first and second COVID-19 waves in Switzerland, J. Leukoc. Biol, doi:10.1093/jleuko/qiaf056
Barlow, Svoboda, Mackellar, Nash, York et al., Antiviral activity and increased host defense against influenza infection elicited by the human cathelicidin LL-37, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025333
Bober, Enochsson, Collin, Mörgelin, Collagen VI is a subepithelial adhesive target for human respiratory tract pathogens, J. Innate Immun, doi:10.1159/000232587
Can, Köseoglu, Erkunt Alak, Güvendi, Dösķaya et al., In silico discovery of antigenic proteins and epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 for the development of a vaccine or a diagnostic approach for COVID-19, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-79645-9
Castillo, Entrenas Costa, Vaquero Barrios, Alcaládıáz, Loṕez Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Chen, Wang, Gilby, Wei, Omicron variant (B.1.1.529): infectivity, vaccine breakthrough, and antibody resistance, J. Chem. Inf. Modeling, doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.1c01451
Crane-Godreau, Clem, Payne, Fiering, Vitamin D deficiency and air pollution exacerbate COVID-19 through suppression of antiviral peptide LL37, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2020.00232
Dai, Gao, Viral targets for vaccines against COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-00480-0
Duan, Zhang, Chen, Liu, Zhao et al., Role of LL-37 in thrombotic complications in patients with COVID-19, Cell Mol. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-022-04309-y
Elenius, Palomares, Waris, Turunen, Puhakka et al., The relationship of serum vitamins A, D, E and LL-37 levels with allergic status, tonsillar virus detection and immune response, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0172350
Hachim, Kavian, Cohen, Chin, Chu et al., ORF8 and ORF3b antibodies are accurate serological markers of early and late SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-020-0773-7
Hassan, Aljabali, Panda, Ghosh, Attrish et al., A unique view of SARS-CoV-2 through the lens of ORF8 protein, Comput. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104380
Hou, Wang, Wang, Wang, Yu et al., The ORF7a protein of SARS-CoV-2 initiates autophagy and limits autophagosomelysosome fusion via degradation of SNAP29 to promote virus replication, Autophagy, doi:10.1080/15548627.2022.2084686
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Iuliano, Brunkard, Boehmer, Peterson, Adjei et al., Trends in disease severity and health care utilization during the early omicron variant period compared with previous SARS-coV-2 high transmission periods -United States, december 2020-january 2022, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7104e4
Jaratsittisin, Sornjai, Chailangkarn, Jongkaewwattana, Smith, The vitamin D receptor agonist EB1089 can exert its antiviral activity independently of the vitamin D receptor, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0293010
Kohyama, Suzuki, Nakai, Ono, Matsuoka et al., SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 is a viral cytokine regulating immune responses, Int. Immunol, doi:10.1093/intimm/dxac044
Koo, Seo, Antimicrobial peptides under clinical investigation, Pept. Sci, doi:10.1002/pep2.24122
Kowarz, Löscher, Marschalek, Optimized Sleeping Beauty transposons rapidly generate stable transgenic cell lines, Biotechnol. J, doi:10.1002/biot.201400821
Li, Chen, Shi, Mehmood, Qiu, HD5 and LL-37 inhibit SARS-coV and SARS-CoV-2 binding to human ACE2 by molecular simulation, Interdiscip Sci, doi:10.1007/s12539-021-00462-3
Li, Liao, Wang, Tan, Luo et al., The ORF6, ORF8 and nucleocapsid proteins of SARS-CoV-2 inhibit type I interferon signaling pathway, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198074
Lin, Fu, Yin, Li, Liu et al., ORF8 contributes to cytokine storm during SARS-CoV-2 infection by activating IL-17 pathway, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2021.102293
Luo, Yan, Yang, Ren, Luo et al., Antiviral activity of vitamin D derivatives against severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in vitro and in vivo, Virol. Sin, doi:10.1016/j.virs.2024.08.007
Matsuoka, Imahashi, Ohno, Ode, Nakata et al., SARS-CoV-2 accessory protein ORF8 is secreted extracellularly as a glycoprotein homodimer, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101724
Meinberger, Koch, Roth, Hermes, Stemler et al., Analysis of IgM, IgA, and IgG isotype antibodies Directed against SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and ORF8 in the course of COVID-19, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-88356-8
Mellet, Pepper, A COVID-19 vaccine: big strides come with big challenges, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines9010039
Miller, Gallo, Vitamin D and innate immunity, Dermatologic Ther, doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2009.01287.x
Nogues, Ovejero, Pineda-Moncusı, Bouillon, Arenas et al., Calcifediol treatment and COVID-19-related outcomes, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab405
Oren, Lerman, Gudmundsson, Agerberth, Shai, Structure and organization of the human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 in phospholipid membranes: relevance to the molecular basis for its non-cell-selective activity, Biochem. J, doi:10.1042/bj3410501
Pacha, Sallman, Evans, COVID-19: a case for inhibiting IL-17?, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0328-z
Pahar, Madonna, Das, Albanesi, Girolomoni, Immunomodulatory role of the antimicrobial LL-37 peptide in autoimmune diseases and viral infections, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines8030517
Qiao, Olvera De La Cruz, Enhanced binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to receptor by distal polybasic cleavage sites, ACS nano, doi:10.1021/acsnano.0c04798
Radic, Muller, LL-37, a multi-faceted amphipathic peptide involved in NETosis, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells11152463
Ramakrishnan, Nicolau, Langford, Mahdi, Jeffers et al., Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0
Raucci, Mansour, Casillo, Saviano, Caso et al., Interleukin-17A (IL-17A), a key molecule of innate and adaptive immunity, and its potential involvement in COVID-19-related thrombotic and vascular mechanisms, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102572
Ricci, Pagliuca, D'ascanio, Innammorato, De Vitis et al., Circulating Vitamin D levels status and clinical prognostic indices in COVID-19 patients, Respir. Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-021-01666-3
Sancho-Vaello, Francois, Bonetti, Lilie, Finger et al., Structural remodeling and oligomerization of human cathelicidin on membranes suggest fibril-like structures as active species, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-14206-1
Sancho-Vaello, Gil-Carton, Francois, Bonetti, Kreir et al., The structure of the antimicrobial human cathelicidin LL-37 shows oligomerization and channel formation in the presence of membrane mimics, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-74401-5
Sengle, Charbonneau, Ono, Sasaki, Alvarez et al., Targeting of bone morphogenetic protein growth factor complexes to fibrillin, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M707820200
Sengle, Ono, Lyons, Bächinger, Sakai, A new model for growth factor activation: type II receptors compete with the prodomain for BMP-7, J. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.06.074
Sharun, Tiwari, Dhama, COVID-19 and sunlight: Impact on SARS-CoV-2 transmissibility, morbidity, and mortality, Ann. Med. Surg, doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102419
Svensson, Lagerstedt, Nilsson, Del Giudice, Apolipoprotein A-I attenuates LL-37-induced endothelial cell cytotoxicity, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.09.072
Säll, Carlsson, Gidlöf, Holm, Humleń et al., The antimicrobial peptide LL-37 alters human osteoblast Ca2+ handling and induces Ca2 +-independent apoptosis, J. Innate Immun, doi:10.1159/000346587
Tang, Basavarajappa, Haeggström, P2X7 receptor regulates internalization of antimicrobial peptide LL-37 by human macrophages that promotes intracellular pathogen clearance, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1402845
Tang, Liu, Zhang, Xu, Ji et al., Cytokine storm in COVID-19: the current evidence and treatment strategies, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01708
Tang, Yu, Shen, Qi, Hu, Conjugation with 8-arm PEG and CRM(197) enhances the immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 protein, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108922
Vinjamuri, Li, Bouvier, SARS-CoV-2 ORF8: One protein, seemingly one structure, and many functions, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035559
Walls, Park, Tortorici, Wall, Mcguire et al., Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.032
Wang, Lam, Wong, Yuen, Cai et al., Accurate diagnosis of COVID-19 by a novel immunogenic secreted SARS-coV-2 orf8 protein, mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.02431-20
Wang, Nestel, Bourdeau, Nagai, Wang et al., Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.2909
Wang, Wang, Li, Chen, Han et al., Human cathelicidin inhibits SARS-coV-2 infection: killing two birds with one stone, ACS Infect. Dis, doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00096
Wang, Wang, Wang, Wang, Jiang et al., SARS-coV-2 ORF8 protein induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-like responses and facilitates virus replication by triggering calnexin: an unbiased study, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.00011-23
Wrapp, Wang, Corbett, Goldsmith, Hsieh et al., Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb2507
Xhindoli, Pacor, Guida, Antcheva, Tossi, Native oligomerization determines the mode of action and biological activities of human cathelicidin LL-37, Biochem. J, doi:10.1042/bj20131048
Xiao, Lu, Zhang, Johnson, Mckay et al., A trimeric human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as an anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1038/s41594-020-00549-3
Young, Fong, Chan, Mak, Ang et al., Effects of a major deletion in the SARS-CoV-2 genome on the severity of infection and the inflammatory response: an observational cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31757-8
Zhang, Chen, Li, Huang, Luo et al., The ORF8 protein of SARS-CoV-2 mediates immune evasion through down-regulating MHC-I, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2024202118
Zhang, Ghosh, Basavarajappa, Chen, Shrestha et al., HBD-2 binds SARS-CoV-2 RBD and blocks viral entry: Strategy to combat COVID-19, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2022.103856
Zhao, Zhang, Zhao, Liu, Dong et al., Efficacy and safety of Oral LL-37 against the Omicron BA.5.1.3 variant of SARS-COV-2: A randomized trial, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.29035
Zhou, Huang, Zhou, Huang, Su et al., Structural insight reveals SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a as an immunomodulating factor for human CD14 monocytes, Iscience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2021.102187
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2025.1671738",
"ISSN": [
"2235-2988"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1671738",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>The role of vitamin D in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) outcomes remains debated, but emerging evidence suggests it may enhance recovery by strengthening immune responses. Vitamin D upregulates LL-37, an antimicrobial peptide with broad antiviral activity, including potential benefits against SARS-CoV-2. LL-37’s interactions with viral proteins, however, remain incompletely understood.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>We investigated LL-37’s interactions with the SARS-CoV-2 Spike glycoprotein and the accessory proteins ORF7a and ORF8 using surface plasmon resonance and negative-stain electron microscopy. These approaches were employed to assess LL-37’s binding capabilities and potential impact on viral infectivity.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>LL-37 bound multiple domains of the Spike protein and inhibited its interaction with the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2) receptor <jats:italic>in vitro</jats:italic>. Up to seven LL-37 molecules were observed surrounding Spike, forming a halo-like structure that may block receptor engagement. LL-37 also bound to ORF7a and ORF8, potentially impairing their ability to disrupt host cell processes. Notably, LL-37’s interaction with ORF7a may prevent degradation of SNAP29, restoring autophagy and promoting viral clearance.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>LL-37 disrupts key viral-host interactions by binding to Spike, ORF7a, and ORF8, thereby reducing SARS-CoV-2 infectivity. These findings highlight LL-37’s potential as a therapeutic agent in COVID-19 and provide mechanistic insight into its antiviral actions.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fcimb.2025.1671738"
],
"article-number": "1671738",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roth",
"given": "Annika",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lütke",
"given": "Steffen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mörgelin",
"given": "Matthias",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meinberger",
"given": "Denise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hermes",
"given": "Gabriele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sengle",
"given": "Gerhard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koch",
"given": "Manuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drexelius",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gebauer",
"given": "Jan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neundorf",
"given": "Ines",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elezagic",
"given": "Dzemal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paulsson",
"given": "Mats",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Streichert",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Klatt",
"given": "Andreas R.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-23T05:30:03Z",
"timestamp": 1758605403000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-23T05:30:04Z",
"timestamp": 1758605404000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-24T00:06:51Z",
"timestamp": 1758672411968,
"version": "3.44.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
23
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1758585600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1671738/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.0470",
"article-title": "Association between 3 doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and symptomatic infection caused by the SARS-CoV-2 omicron and delta variants",
"author": "Accorsi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "639",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061760",
"article-title": "Calcifediol treatment and hospital mortality due to COVID-19: A cohort study",
"author": "Alcala-Diaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1760",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.880961",
"article-title": "Upregulating human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL-37 expression may prevent severe COVID-19 inflammatory responses and reduce microthrombosis",
"author": "Aloul",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13051714",
"article-title": "COVID-19 disease severity and death in relation to vitamin D status among SARS-CoV-2-positive UAE residents",
"author": "AlSafar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1714",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jleuko/qiaf056",
"article-title": "Two-sided effects of neutrophil extracellular traps and changes in the myeloid compartment in acute COVID-19: A histopathological study on autopsy cases from the first and second COVID-19 waves in Switzerland",
"author": "Anzic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Leukoc. Biol.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0025333",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity and increased host defense against influenza infection elicited by the human cathelicidin LL-37",
"author": "Barlow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000232587",
"article-title": "Collagen VI is a subepithelial adhesive target for human respiratory tract pathogens",
"author": "Bober",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "160",
"journal-title": "J. Innate Immun.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-79645-9",
"article-title": "In silico discovery of antigenic proteins and epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 for the development of a vaccine or a diagnostic approach for COVID-19",
"author": "Can",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "22387",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.1c01451",
"article-title": "Omicron variant (B.1.1.529): infectivity, vaccine breakthrough, and antibody resistance",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "412",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inf. Modeling",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2020.00232",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and air pollution exacerbate COVID-19 through suppression of antiviral peptide LL37",
"author": "Crane-Godreau",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Public Health",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-00480-0",
"article-title": "Viral targets for vaccines against COVID-19",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-022-04309-y",
"article-title": "Role of LL-37 in thrombotic complications in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Duan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol. Life Sci.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0172350",
"article-title": "The relationship of serum vitamins A, D, E and LL-37 levels with allergic status, tonsillar virus detection and immune response",
"author": "Elenius",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"article-title": "Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study",
"author": "Entrenas Castillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-020-0773-7",
"article-title": "ORF8 and ORF3b antibodies are accurate serological markers of early and late SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Hachim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1293",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104380",
"article-title": "A unique view of SARS-CoV-2 through the lens of ORF8 protein",
"author": "Hassan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Comput. Biol. Med.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2022.2084686",
"article-title": "The ORF7a protein of SARS-CoV-2 initiates autophagy and limits autophagosome-lysosome fusion via degradation of SNAP29 to promote virus replication",
"author": "Hou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "551",
"journal-title": "Autophagy",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7104e4",
"article-title": "Trends in disease severity and health care utilization during the early omicron variant period compared with previous SARS-coV-2 high transmission periods - United States, december 2020-january 2022",
"author": "Iuliano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "146",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0293010",
"article-title": "The vitamin D receptor agonist EB1089 can exert its antiviral activity independently of the vitamin D receptor",
"author": "Jaratsittisin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/intimm/dxac044",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 is a viral cytokine regulating immune responses",
"author": "Kohyama",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunol",
"key": "B21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pep2.24122",
"article-title": "Antimicrobial peptides under clinical investigation",
"author": "Koo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pept. Sci.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/biot.201400821",
"article-title": "Optimized Sleeping Beauty transposons rapidly generate stable transgenic cell lines",
"author": "Kowarz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "647",
"journal-title": "Biotechnol. J.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12539-021-00462-3",
"article-title": "HD5 and LL-37 inhibit SARS-coV and SARS-CoV-2 binding to human ACE2 by molecular simulation",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Interdiscip Sci.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198074",
"article-title": "The ORF6, ORF8 and nucleocapsid proteins of SARS-CoV-2 inhibit type I interferon signaling pathway",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "286",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2021.102293",
"article-title": "ORF8 contributes to cytokine storm during SARS-CoV-2 infection by activating IL-17 pathway",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virs.2024.08.007",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of vitamin D derivatives against severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in vitro and in vivo",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "802",
"journal-title": "Virol. Sin.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101724",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 accessory protein ORF8 is secreted extracellularly as a glycoprotein homodimer",
"author": "Matsuoka",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "298",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-88356-8",
"article-title": "Analysis of IgM, IgA, and IgG isotype antibodies Directed against SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and ORF8 in the course of COVID-19",
"author": "Meinberger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8920",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines9010039",
"article-title": "A COVID-19 vaccine: big strides come with big challenges",
"author": "Mellet",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Vaccines",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1529-8019.2009.01287.x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and innate immunity",
"author": "Miller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Dermatologic Ther.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab405",
"article-title": "Calcifediol treatment and COVID-19–related outcomes",
"author": "Nogues",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e4017",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bj3410501",
"article-title": "Structure and organization of the human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 in phospholipid membranes: relevance to the molecular basis for its non-cell-selective activity",
"author": "Oren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "501",
"journal-title": "Biochem. J.",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "341",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0328-z",
"article-title": "COVID-19: a case for inhibiting\nIL-17",
"author": "Pacha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "345",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines8030517",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory role of the antimicrobial LL-37 peptide in autoimmune diseases and viral infections",
"author": "Pahar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Vaccines",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsnano.0c04798",
"article-title": "Enhanced binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to receptor by distal polybasic cleavage sites",
"author": "Qiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10616",
"journal-title": "ACS nano",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells11152463",
"article-title": "LL-37, a multi-faceted amphipathic peptide involved in NETosis",
"author": "Radic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0",
"article-title": "Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Ramakrishnan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med",
"key": "B38",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102572",
"article-title": "Interleukin-17A (IL-17A), a key molecule of innate and adaptive immunity, and its potential involvement in COVID-19-related thrombotic and vascular mechanisms",
"author": "Raucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102572",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-021-01666-3",
"article-title": "Circulating Vitamin D levels status and clinical prognostic indices in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Ricci",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Respir. Res.",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000346587",
"article-title": "The antimicrobial peptide LL-37 alters human osteoblast Ca2+ handling and induces Ca2+-independent apoptosis",
"author": "Säll",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "290",
"journal-title": "J. Innate Immun.",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-017-14206-1",
"article-title": "Structural remodeling and oligomerization of human cathelicidin on membranes suggest fibril-like structures as active species",
"author": "Sancho-Vaello",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15371",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-74401-5",
"article-title": "The structure of the antimicrobial human cathelicidin LL-37 shows oligomerization and channel formation in the presence of membrane mimics",
"author": "Sancho-Vaello",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "17356",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M707820200",
"article-title": "Targeting of bone morphogenetic protein growth factor complexes to fibrillin",
"author": "Sengle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13874",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "283",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2008.06.074",
"article-title": "A new model for growth factor activation: type II receptors compete with the prodomain for BMP-7",
"author": "Sengle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1025",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "381",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102419",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and sunlight: Impact on SARS-CoV-2 transmissibility, morbidity, and mortality",
"author": "Sharun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Ann. Med. Surg.",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.09.072",
"article-title": "Apolipoprotein A-I attenuates LL-37-induced endothelial cell cytotoxicity",
"author": "Svensson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "493",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1402845",
"article-title": "P2X7 receptor regulates internalization of antimicrobial peptide LL-37 by human macrophages that promotes intracellular pathogen clearance",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1191",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "195",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01708",
"article-title": "Cytokine storm in COVID-19: the current evidence and treatment strategies",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108922",
"article-title": "Conjugation with 8-arm PEG and CRM(197) enhances the immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 protein",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035559",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 ORF8: One protein, seemingly one structure, and many functions",
"author": "Vinjamuri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.032",
"article-title": "Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein",
"author": "Walls",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1735",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.02431-20",
"article-title": "Accurate diagnosis of COVID-19 by a novel immunogenic secreted SARS-coV-2 orf8 protein",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e02431",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.2909",
"article-title": "Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2909",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00096",
"article-title": "Human cathelicidin inhibits SARS-coV-2 infection: killing two birds with one stone",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1545",
"journal-title": "ACS Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.00011-23",
"article-title": "SARS-coV-2 ORF8 protein induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-like responses and facilitates virus replication by triggering calnexin: an unbiased study",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2507",
"article-title": "Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation",
"author": "Wrapp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1260",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bj20131048",
"article-title": "Native oligomerization determines the mode of action and biological activities of human cathelicidin LL-37",
"author": "Xhindoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "263",
"journal-title": "Biochem. J.",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "457",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-020-00549-3",
"article-title": "A trimeric human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as an anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent",
"author": "Xiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "202",
"journal-title": "Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31757-8",
"article-title": "Effects of a major deletion in the SARS-CoV-2 genome on the severity of infection and the inflammatory response: an observational cohort study",
"author": "Young",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "396",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2024202118",
"article-title": "The ORF8 protein of SARS-CoV-2 mediates immune evasion through down-regulating MHC-I",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2022.103856",
"article-title": "HBD-2 binds SARS-CoV-2 RBD and blocks viral entry: Strategy to combat COVID-19",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29035",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of Oral LL-37 against the Omicron BA.5.1.3 variant of SARS-COV-2: A randomized trial",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B63",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2021.102187",
"article-title": "Structural insight reveals SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a as an immunomodulating factor for human CD14 monocytes",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Iscience",
"key": "B64",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 64,
"references-count": 64,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1671738/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D-inducible antimicrobial peptide LL-37 binds SARS-CoV-2 Spike and accessory proteins ORF7a and ORF8",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "15"
}
