Vitamin D, acute respiratory infections, and Covid-19: the curse of small-size randomised trials. A critical review with meta-analysis of randomised trials
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.04.26.24306354, Apr 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
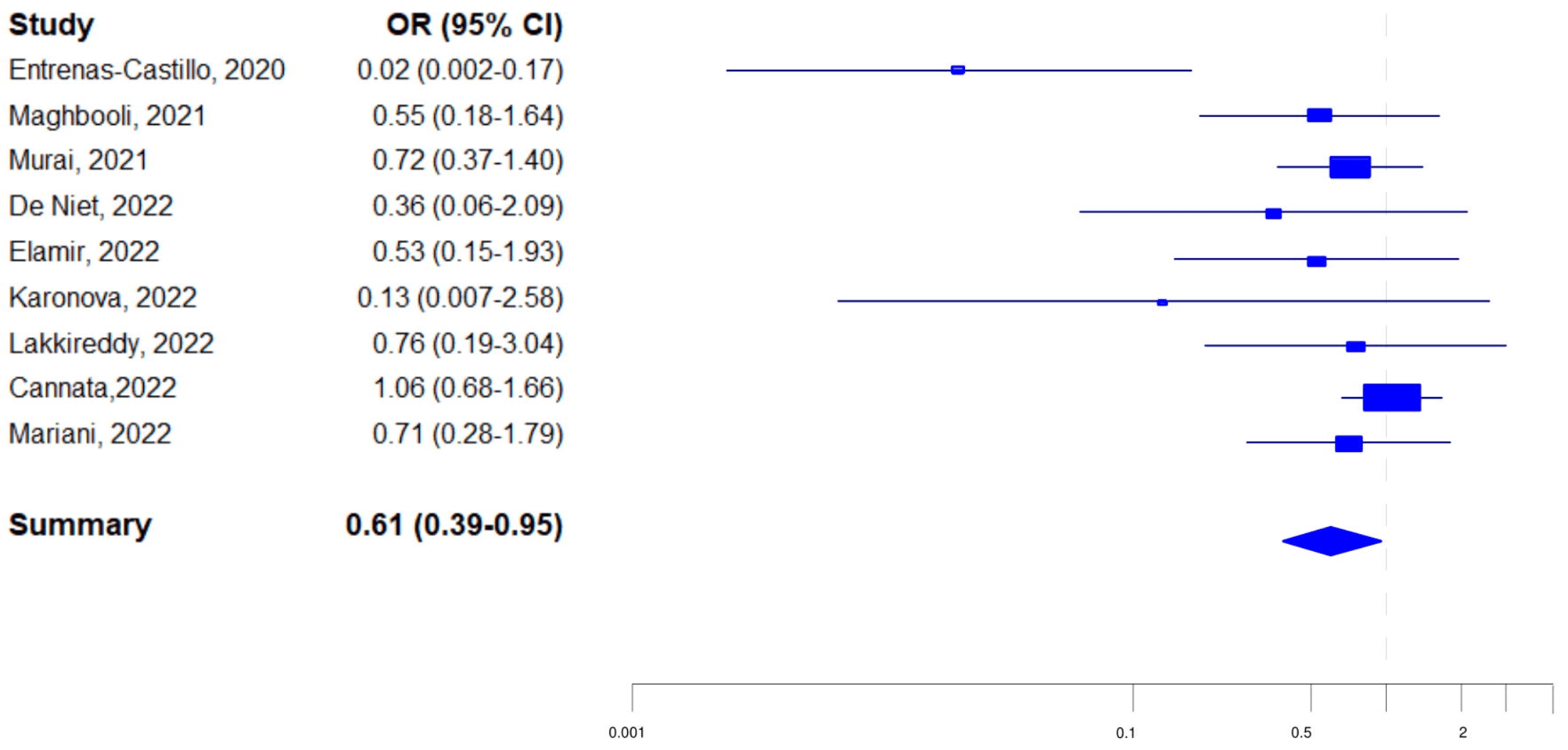
Unregistered meta analysis cherry-picking the ICU outcome and including 9 late treatment RCTs with ICU outcomes for vitamin D. It's unclear why ICU risk would be used when there are more studies reporting mortality which is also less subject to bias.
8 of the 9 report lower risk with treatment and one reports higher risk. The one study with a higher risk is also the study with the largest number of patients1. Authors suggest this trial is more trustworthy than the many more positive studies, however Cannata-Andía et al. has very high negative bias, containing a trifecta of poor design, which is a more logical reason for the observed results.
Studies show that earlier treatment is more effective than later treatment2, ongoing treatment with multiple doses is more effective than single bolus doses3, and late stage treatment with calcitriol/calcifediol and analogs is more effective than cholecalciferol4. Cannata-Andía et al. uses very late stage treatment (>80% pulmonary involvement at baseline), uses a single bolus dose, and uses cholecalciferol rather than calcitriol/calcifediol and analogs.
Note that all of the authors' exclusions and trim and fill in Table 2 still result in a lower risk with treatment, just no longer reaching statistical significance. Also note that the funnel plot conclusions are not valid5 - asymmetry may result from many factors, including poor design in a subset of trials, as seen in Cannata-Andía et al.
20 meta-analyses show significant improvements with vitamin D treatment for mortality6-19,
mechanical ventilation6,10,11,16,20-22 ,
ICU admission6,8,10,11,14,16,18,20-24 ,
hospitalization16,
severity7,9,10,15,25 , and
cases12,24,25 .
Currently there are 136 vitamin D treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 39% lower mortality [31‑45%], 17% lower ventilation [-5‑35%], 45% lower ICU admission [28‑57%], 22% lower hospitalization [13‑30%], and 17% fewer cases [9‑25%].
1.
Cannata-Andía et al., A single-oral bolus of 100,000 IU of cholecalciferol at hospital admission did not improve outcomes in the COVID-19 disease: the COVID-VIT-D — a randomised multicentre international clinical trial, BMC Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12916-022-02290-8.
6.
Shah et al., Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? - a systematic review, QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040.
7.
Nikniaz et al., The impact of vitamin D supplementation on mortality rate and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.34172/PS.2021.13.
8.
Hosseini et al., Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19 Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134.
9.
D’Ecclesiis et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396.
10.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
11.
Hariyanto et al., Vitamin D supplementation and Covid‐19 outcomes: A systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2269.
12.
Begum et al., The Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Survival and Prevention: A Meta-analysis, Sudan Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.18502/sjms.v19i1.15776.
13.
Jamilian et al., The role of vitamin D in outcomes of critical care in COVID-19 patients: Evidence from an umbrella meta-analysis of interventional and observational studies, Public Health Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S1368980024000934.
14.
Sobczak et al., Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Severe COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16101402.
15.
Petrelli et al., Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883.
16.
Asla et al., Vitamin D on COVID-19 Patients During the Pandemic, 2022. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science Journal, doi:10.12944/CRNFSJ.11.1.3.
17.
Kow et al., The impact of vitamin D administration on mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01564-2.
18.
Zhang et al., The impact of supplementing vitamin D through different methods on the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1441847.
19.
Doustmohammadian et al., Impact of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme, doi:10.1016/j.nupar.2025.12.001.
20.
Meng et al., The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.09.008.
21.
Yang et al., Therapeutic effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 aggravation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1367686.
22.
Szarpak et al., Vitamin D supplementation to treat SARS-CoV-2 positive patients. Evidence from meta-analysis, Cardiology Journal, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2021.0122.
23.
Tentolouris et al., The effect of vitamin D supplementation on mortality and intensive care unit admission of COVID-19 patients. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3517.
Autier et al., 27 Apr 2024, preprint, 6 authors.
Contact: philippe.autier@i-pri.org.
Vitamin D, acute respiratory infections, and Covid-19: the curse of small-size randomised trials. A critical review with meta-analysis of randomised trials
doi:10.1101/2024.04.26.24306354
Background: Randomised trials conducted before 2021 indicated that vitamin D supplementation (VDS) was able to prevent severe COVID-19 and acute respiratory infections (ARI). However, these health benefits were not confirmed by larger randomised trials published after 2021. Objective: To examine the characteristics of randomised trials on VDS to COVID-19 patients and admission to intensive care unit (ICU), and on VDS for the prevention of ARI. Method: A systematic search retrieved randomised trials on VDS to COVID-19 patients and admission to ICU. Data on VDS and ARI were extracted from the meta-analysis of Jolliffe et al., 2021. The associations between VDS vs no VDS, and admission to ICU were evaluated using random effect models. Meta-analyses were done for all trials and by groups trial size. Publication bias was assessed using the LFK index (no bias if index between -1 and +1) and the Trim and Fill method. Results: Nine trials on VDS for preventing admission to ICU were identified. The summary odds ratio (SOR) was 0.61 (95%CI: 0.39-0.95) for all trials, 0.34 (0.13-0.93) for trials including 50 to <106 patients and 0.88 (0.62-1.24) for trials including 106 to 548 patients (effect modification: p=0.04). The LFK index was -3.79, and after Trim and Fill, the SOR was 0.80 (0.40-1.61). The SOR for the 37 trials on VDS for ARI prevention was 0.92 (0.86-0.99) for all trials, 0.69 (0.57-0.83) for trials including 25 to <248 patients and 0.98 (0.94-1.03) for trials including 248 to 16,000 patients (effect modification p=0.0001). The LFK index was -3.11, and after Trim and Fill, the SOR was 0.96 (0.88-1.05). Conclusion: Strong publication bias affected randomised trials on VDS for the prevention of severe COVID-19 and of ARI. Systematic reviews should beware of smallsize randomised trials that generally exaggerate health benefits.
References
Abroug, Maatouk, Bennasrallah, Dhouib, Fredj et al., Effect of vitamin D supplementation versus placebo on recovery delay among COVID-19 Tunisian patients: a randomizedcontrolled clinical trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-023-07114-5
Amin, Drenos, No evidence that vitamin D is able to prevent or affect the severity of COVID-19 in individuals with European ancestry: a Mendelian randomisation study of open data, BMJ Nutr Prev Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000151
Amrein, Schnedl, Holl, Riedl, Christopher et al., Effect of high-dose vitamin D3on hospital length of stay in critically ill patients with vitamin D deficiency: The VITdAL-ICU randomized clinical trial, JAMA -Journal of the American Medical Association, doi:10.1001/jama.2014.13204
Annweiler, Beaudenon, Gautier, Gonsard, Boucher et al., High-dose versus standard-dose vitamin D supplementation in older adults with COVID-19 (COVIT-TRIAL): A multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled superiority trial, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003999
Antonelli, Kushner, Low Serum Levels of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Accompany Severe COVID-19 Because it is a Negative Acute Phase Reactant, Am J Med Sci, doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2021.06.005
Autier, Boniol, Pizot, Mullie, Vitamin D status and ill health: a systematic review, The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(13)70165-7
Autier, Mullie, Macacu, Dragomir, Boniol et al., Effect of vitamin D supplementation on non-skeletal disorders: a systematic review of meta-analyses and randomised trials, The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(17)30357-1
Bergman, The link between vitamin D and COVID-19: distinguishing facts from fiction, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13158
Binkley, Coursin, Krueger, Iglar, Heiner et al., Surgery alters parameters of vitamin D status and other laboratory results, Osteoporos Int, doi:10.1007/s00198-016-3819-9
Bishop, Ashfaq, Melnick, Vazquez-Escarpanter, Fialkow et al., REsCue trial: Randomized controlled clinical trial with extended-release calcifediol in symptomatic COVID-19 outpatients, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2022.111899
Borenstein, Common mistakes in meta-analysis
Brunvoll, Nygaard, Ellingjord-Dale, Holland, Istre et al., Prevention of covid-19 and other acute respiratory infections with cod liver oil supplementation, a low dose vitamin D supplement: quadruple blinded, randomised placebo controlled trial, Bmj, doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-071245
Butler-Laporte, Nakanishi, Mooser, Morrison, Abdullah et al., Vitamin D and COVID-19 susceptibility and severity in the COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative: A Mendelian randomization study, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003605
Cannata-Andia, Diaz-Sottolano, Fernandez, Palomo-Antequera, Herrero-Puente et al., A single-oral bolus of 100,000 IU of cholecalciferol at hospital admission did not improve outcomes in the COVID-19 disease: the COVID-VIT-D-a randomised multicentre international clinical trial, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-022-02290-8
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Díaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Cervero, López-Wolf, Casado, Mena, Ryan-Murua et al., Beneficial Effect of Short-Term Supplementation of High Dose of Vitamin D(3) in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Multicenter, Single-Blinded, Prospective Randomized Pilot Clinical Trial, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.863587
Chakhtoura, Napoli, Hajj Fuleihan, Commentary: Myths and facts on vitamin D amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154276
Chauss, Freiwald, Mcgregor, Yan, Wang et al., Autocrine vitamin D signaling switches off pro-inflammatory programs of T(H)1 cells, Nat Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-021-01080-3
Cornell, Mulrow, Localio, Stack, Meibohm et al., Random-effects metaanalysis of inconsistent effects: a time for change, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M13-2886
Cui, Tian, Using genetic variants to evaluate the causal effect of serum vitamin D concentration on COVID-19 susceptibility, severity and hospitalization traits: a Mendelian randomization study, J Transl Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-021-02973-5
D'ecclesiis, Gavioli, Martinoli, Raimondi, Chiocca et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396
Dissanayake, Silva, Sumanatilleke, De Silva, Gamage et al., Prognostic and Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab892
Duval, Tweedie, Trim and Fill: A Simple Funnel-Plot-Based Method of Testing and Adjusting for Publication Bias in Meta-Analysi, Biometrics, doi:10.1111/j.0006-341x.2000.00455.x
Elamir, Amir, Lim, Rana, Lopez et al., A randomized pilot study using calcitriol in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Bone, doi:10.1016/j.bone.2021.116175
Else, How a torrent of COVID science changed research publishing -in seven charts, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-020-03564-y
Furuya-Kanamori, Barendregt, Doi, A new improved graphical and quantitative method for detecting bias in meta-analysis, Int J Evid Based Healthc, doi:10.1097/XEB.0000000000000141
Ginde, Brower, Caterino, Finck, Banner-Goodspeed et al., Early High-Dose Vitamin D(3) for Critically Ill, Vitamin D-Deficient Patients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1911124
Hopefl, Ben-Eltriki, Association Between Vitamin D Levels and Inflammatory Markers in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies, J Pharm Pharm Sci, doi:10.18433/jpps32518
Ioannidis, Greenland, Hlatky, Khoury, Macleod et al., Increasing value and reducing waste in research design, conduct, and analysis, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(13)62227-8
Jevalikar, Mithal, Singh, Sharma, Farooqui et al., Lack of association of baseline 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with disease severity and mortality in Indian patients hospitalized for COVID-19, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-85809-y
Jolliffe, Camargo, Sluyter, Aglipay, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6
Jolliffe, Holt, Greenig, Talaei, Perdek et al., Effect of a test-and-treat approach to vitamin D supplementation on risk of all cause acute respiratory tract infection and covid-19: phase 3 randomised controlled trial (CORONAVIT), Bmj, doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-071230
Karonova, Golovatyuk, Kudryavtsev, Chernikova, Mikhaylova et al., Effect of Cholecalciferol Supplementation on the Clinical Features and Inflammatory Markers in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Open-Label, Single-Center Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132602
Kjaergard, Villumsen, Gluud, Reported methodologic quality and discrepancies between large and small randomized trials in meta-analyses, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-135-11-200112040-00010
Kummel, Krumbein, Fragkou, Hunerbein, Reiter et al., Vitamin D supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1023903
Lakkireddy, Gadiga, Malathi, Karra, Raju et al., Effect of Short Term High Dose Oral Vitamin D Therapy on the Inflammatory Markers in Patients with COVID 19 Disease, Archives of Clinical and Biomedical Research, doi:10.26502/acbr.50170273
Langan, Higgins, Jackson, Bowden, Veroniki et al., A comparison of heterogeneity variance estimators in simulated random-effects meta-analyses, Res Synth Methods, doi:10.1002/jrsm.1316
Lau, Ioannidis, Terrin, Schmid, Olkin, The case of the misleading funnel plot, Bmj, doi:10.1136/bmj.333.7568.597
Li, Van Geffen, Van Weele, Zhang, He et al., An observational and Mendelian randomisation study on vitamin D and COVID-19 risk in UK Biobank, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-97679-5
Li-Ng, Aloia, Pollack, Cunha, Mikhail et al., A randomized controlled trial of vitamin D3 supplementation for the prevention of symptomatic upper respiratory tract infections, Epidemiol Infect, doi:10.1017/S0950268809002404
Liu, Stenger, Li, Wenzel, Tan et al., Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1123933
Looker, Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of major osteoporotic fractures in older U.S. adults, J Bone Miner Res, doi:10.1002/jbmr.1828
Lopez, Fah, Woetmann, Ødum, Bonefeld et al., Macrophages Control the Bioavailability of Vitamin D and Vitamin D-Regulated T Cell Responses, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.722806
Ma, Zhou, Heianza, Qi, Habitual use of vitamin D supplements and risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: a prospective study in UK Biobank, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa381
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Jamalimoghadamsiahkali, Asadi, Zarei et al., Treatment With 25-Hydroxyvitamin D(3) (Calcifediol) Is Associated With a Reduction in the Blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Marker of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Pilot Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial, Endocr Pract, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016
Mariani, Antonietti, Tajer, Ferder, Inserra et al., High-dose vitamin D versus placebo to prevent complications in COVID-19 patients: Multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0267918
Martineau, Forouhi, Vitamin D for COVID-19: a case to answer?, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30268-0
Martineau, Vitamin D in the prevention or treatment of COVID-19, Proc Nutr Soc
Murai, Fernandes, Antonangelo, Gualano, Pereira, Effect of a Single High-Dose Vitamin D3 on the Length of Hospital Stay of Severely 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-Deficient Patients with COVID-19, Clinics, doi:10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549
Niet, Trémège, Coffiner, Rousseau, Calmes et al., Positive Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14153048
Nogues, Ovejero, Pineda-Moncusí, Bouillon, Arenas et al., Calcifediol Treatment and COVID-19-Related Outcomes, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab405
Patchen, Clark, Gaddis, Hancock, Cassano, Genetically predicted serum vitamin D and COVID-19: a Mendelian randomisation study, BMJ Nutr Prev Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000255
Pham, Rahman, Majidi, Waterhouse, Neale, Acute Respiratory Tract Infection and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph16173020
Pittas, Hughes, Sheehan, Ware, Knowler et al., Vitamin D Supplementation and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1900906
Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Suri, Yaddanapudi et al., Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: a randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study), Postgrad Med J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065
Sabico, Enani, Sheshah, Aljohani, Aldisi et al., Effects of a 2-Week 5000 IU versus 1000 IU Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Recovery of Symptoms in Patients with Mild to Moderate Covid-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072170
Sanchez-Zuno, Gonzalez-Estevez, Matuz-Flores, Macedo-Ojeda, Hernandez-Bello et al., Vitamin D Levels in COVID-19 Outpatients from Western Mexico: Clinical Correlation and Effect of Its Supplementation, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10112378
Schwab, Kreiliger, Held, Assessing treatment effects and publication bias across different specialties in medicine: a meta-epidemiological study, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-045942
Scragg, Stewart, Waayer, Lawes, Toop et al., Effect of Monthly High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation on Cardiovascular Disease in the Vitamin D Assessment Study : A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Cardiol, doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2017.0175
Silva, Furlanetto, Does serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D decrease during acute-phase response? A systematic review, Nutr Res, doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2014.12.008
Sjoding, Luo, Miller, Iwashyna, When do confounding by indication and inadequate risk adjustment bias critical care studies? A simulation study, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-015-0923-8
Smaha, Kužma, Jackuliak, Nachtmann, Max et al., Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Significantly Decreases in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia during the First 48 Hours after Hospital Admission, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14122362
Soliman, Abdelaziz, Fathy, Impact of Vitamin D Therapy on the Progress COVID-19: Six Weeks Follow-Up Study of Vitamin D Deficient Elderly Diabetes Patients, Proceedings of Singapore Healthcare, doi:10.1177/20101058211041405
Sterne, Sutton, Ioannidis, Terrin, Jones et al., Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.d4002
Subramanian, Griffin, Hewison, Hopkin, Kenny et al., Vitamin D and COVID-19-Revisited, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13536
Veroniki, Jackson, Viechtbauer, Bender, Bowden et al., Methods to estimate the between-study variance and its uncertainty in meta-analysis, Res Synth Methods, doi:10.1002/jrsm.1164
Villasis-Keever, López-Alarcón, Miranda-Novales, Zurita-Cruz, Barrada-Vázquez et al., Efficacy and Safety of Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 in Frontline Healthcare Workers. A Randomized Clinical Trial, Arch Med Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003
Yao, Bennett, Mafham, Lin, Chen et al., Vitamin D and Calcium for the Prevention of Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.17789
Zhang, Xu, Ni, Small studies may overestimate the effect sizes in critical care metaanalyses: a meta-epidemiological study, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/cc11919
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2024.04.26.24306354",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2024.04.26.24306354",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Randomised trials conducted before 2021 indicated that vitamin D supplementation (VDS) was able to prevent severe COVID-19 and acute respiratory infections (ARI). However, these health benefits were not confirmed by larger randomised trials published after 2021.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To examine the characteristics of randomised trials on VDS to COVID-19 patients and admission to intensive care unit (ICU), and on VDS for the prevention of ARI.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Method</jats:title><jats:p>A systematic search retrieved randomised trials on VDS to COVID-19 patients and admission to ICU. Data on VDS and ARI were extracted from the meta-analysis of Jolliffe et al., 2021. The associations between VDS vs no VDS, and admission to ICU were evaluated using random effect models. Meta-analyses were done for all trials and by groups trial size. Publication bias was assessed using the LFK index (no bias if index between -1 and +1) and the Trim and Fill method.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Nine trials on VDS for preventing admission to ICU were identified. The summary odds ratio (SOR) was 0.61 (95%CI: 0.39-0.95) for all trials, 0.34 (0.13-0.93) for trials including 50 to <106 patients and 0.88 (0.62-1.24) for trials including 106 to 548 patients (effect modification: p=0.04). The LFK index was -3.79, and after Trim and Fill, the SOR was 0.80 (0.40-1.61). The SOR for the 37 trials on VDS for ARI prevention was 0.92 (0.86-0.99) for all trials, 0.69 (0.57-0.83) for trials including 25 to <248 patients and 0.98 (0.94-1.03) for trials including 248 to 16,000 patients (effect modification p=0.0001). The LFK index was -3.11, and after Trim and Fill, the SOR was 0.96 (0.88-1.05).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Strong publication bias affected randomised trials on VDS for the prevention of severe COVID-19 and of ARI. Systematic reviews should beware of small-size randomised trials that generally exaggerate health benefits.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
27
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1538-5321",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Autier",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doi",
"given": "Giulia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mullie",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1047-9732",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vankrunkelsven",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "D’Ecclesiis",
"given": "Oriana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1348-4548",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gandini",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-27T22:15:16Z",
"timestamp": 1714256116000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-30T10:40:16Z",
"timestamp": 1714473616000
},
"group-title": "Public and Global Health",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T00:31:02Z",
"timestamp": 1714523462538
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
27
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2024.04.26.24306354",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
27
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154276",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13158",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30268-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1123933",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-015-0923-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.722806",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-021-01080-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268809002404",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph16173020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab892",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0268396",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.1023903",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj-2022-071230",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj-2022-071245",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-022-02290-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqaa381",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003605",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000255",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-021-02973-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-97679-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000151",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M13-2886",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jrsm.1316",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jrsm.1164",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/XEB.0000000000000141",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00455.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26502/acbr.50170273",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/20101058211041405",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10112378",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14153048",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bone.2021.116175",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14132602",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0267918",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003999",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072170",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.863587",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14122362",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-023-07114-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2022.111899",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-85809-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab405",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2014.13204",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1911124",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-020-03564-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.d4002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.51"
},
{
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.52",
"unstructured": "Borenstein M. Common mistakes in meta-analysis. New Jersey: Biostat, Inc.; 2019."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.333.7568.597",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.53"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-045942",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.54"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(13)62227-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.55"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-135-11-200112040-00010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.56"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/cc11919",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.57"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18433/jpps32518",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.58"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjms.2021.06.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.59"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-016-3819-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.60"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutres.2014.12.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.61"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-8587(13)70165-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.62"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jbmr.1828",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.63"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamacardio.2017.0175",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.64"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1900906",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.65"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.17789",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.66"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-8587(17)30357-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.67"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13536",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.68"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/s0029665122002798",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024043003400700000_2024.04.26.24306354v1.69"
}
],
"reference-count": 69,
"references-count": 69,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2024.04.26.24306354"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Vitamin D, acute respiratory infections, and Covid-19: the curse of small-size randomised trials. A critical review with meta-analysis of randomised trials",
"type": "posted-content"
}
