REsCue Trial: Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial with Extended-Release Calcifediol in Symptomatic COVID-19 Outpatients
et al., Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2022.111899, REsCue, NCT04551911, Feb 2022 (preprint)
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Small RCT with low-risk patients in the USA showing no significant differences in overall recovery. Minimal details on outcomes are provided in the preprint. Authors note significantly faster resolution of respiratory symptoms when treatment increased vitamin D levels. Baseline vitamin D was relatively high, mean 37±1 ng/mL, 95% >20ng/mL, leaving little room for improvement. Treatment delay is not specified but is likely relatively late based on the symptoms at baseline, PCR testing delay, and exclusion with FLU-PRO scores <1.5. ER/urgent care data from clinicaltrials.gov.
Meta-analysis shows that late stage treatment with calcitriol / calcifediol (or
paricalcitol, alfacalcidol, etc.) is more effective than cholecalciferol: 66% [47‑78%] lower risk vs. 45% [34‑54%] lower risk.
Cholecalciferol requires two hydroxylation steps to become activated - first
in the liver to calcifediol, then in the kidney to calcitriol. Calcitriol,
paricalcitol, and alfacalcidol are active vitamin D analogs that do not
require conversion. This allows them to have more rapid onset of action
compared to cholecalciferol. The time delay for cholecalciferol to increase
serum calcifediol levels can be 2-3 days, and the delay for converting
calcifediol to active calcitriol can be up to 7 days.
This is the 12th of 40 COVID-19 RCTs for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
This is the 70th of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
ER/urgent care visits, 85.4% lower, RR 0.15, p = 0.25, treatment 0 of 65 (0.0%), control 3 of 69 (4.3%), NNT 23, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
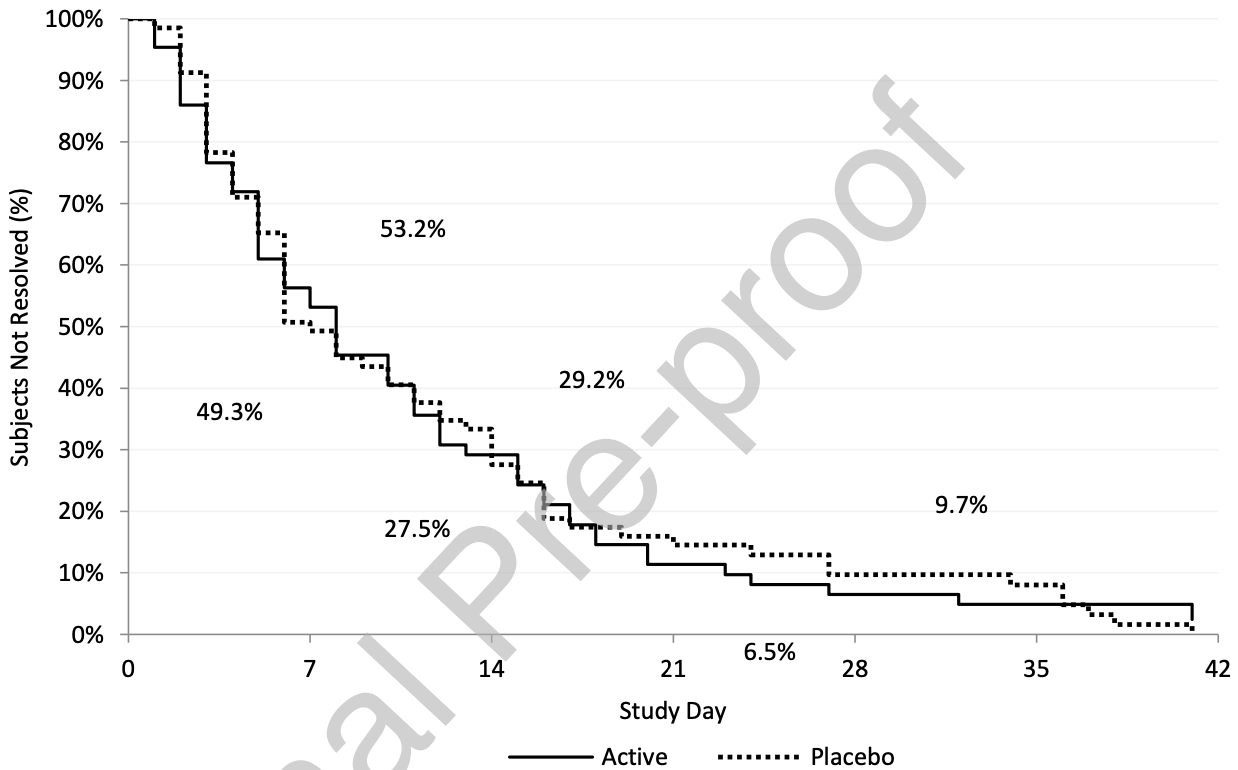
risk of no recovery, 33.7% lower, RR 0.66, p = 0.56, treatment 5 of 65 (7.7%), control 8 of 69 (11.6%), NNT 26, day 21, mid-trial.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 73.5% lower, RR 0.27, p = 0.37, treatment 1 of 65 (1.5%), control 4 of 69 (5.8%), NNT 23, day 35.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 57.5% lower, RR 0.42, p = 0.44, treatment 2 of 65 (3.1%), control 5 of 69 (7.2%), NNT 24, day 28.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 6.2% higher, RR 1.06, p = 0.85, treatment 17 of 65 (26.2%), control 17 of 69 (24.6%), day 14.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 3.0% higher, RR 1.03, p = 1.00, treatment 33 of 65 (50.8%), control 34 of 69 (49.3%), day 7.
|
|
resolution of 5 aggregated symptoms, 9.3% lower, relative time 0.91, p = 0.52, treatment mean 9.8 (±8.15) n=65, control mean 10.8 (±9.54) n=69.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Bishop et al., 5 Feb 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, survey, 11 authors, study period 2 November, 2020 - 8 October, 2021, dosage calcifediol 300μg days 1-3, 60μg days 4-27, trial NCT04551911 (history) (REsCue).
Contact: sstrugnell@opko.com.
REsCue trial: Randomized controlled clinical trial with extended-release calcifediol in symptomatic COVID-19 outpatients
Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2022.111899
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, ERC was effective in increasing serum total 25D to levels of at least 50 ng/mL in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19 and may have accelerated resolution of respiratory symptoms, suggesting mitigation of COVID-19 pneumonia risk. The positive findings from this RCT warrant confirmation in additional larger studies. Data Availability: Restrictions apply to the availability of some or all data generated or analyzed during this study to preserve patient confidentiality or because they were used under license. The corresponding author will on request detail the restrictions and any conditions under which access to some data may be provided.
References
Armas, Hollis, Heaney, Vitamin D 2 is much less effective than vitamin D 3 in humans, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Bilezikian, Bikle, Hewison, Mechanisms in endocrinology:vitamin D and COVID-19, Eur J Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-20-0665
Bishop, Strugnell, Csomor, Extended-release calcifediol effectively raises serum total 25-hydroyxvitamin D even in overweight non-dialysis CKD patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism, Am J Nephrol
Borsche, Glauner, Mendel, COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D 3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D 3 : results of a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13103596
Cannata-Andia, Diaz-Sottolano, Fernandez, A single-oral bolus of 100,000 IU of cholecalciferol at hospital admission did not improve outcomes in the COVID-19 disease: the COVID-VIT-D -a randomized multicenter international clinical trial, BMC Medicine
Chiu, Tsai, Wu, Putative role of vitamin D for COVID-19 vaccination, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22168988
Didriksen, Build, Jakobsen, Vitamin D 3 increase in abdominal subcutaneous fat tissue after supplementation with vitamin D 3, Eur J Endocrinol
Didriksen, Grimnes, Hutchinson, The serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D response to vitamin D supplementation is related to genetic factors, BMI, and baseline levels, Eu J Endocrinol
Ekwaru, Zwicker, Holick, The importance of body weight for the dose response relationship of oral vitamin D supplementation and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in healthy volunteers, Plos One
Ghelani, Alesi, Mousa, Vitamin D and COVID-19: an overview of recent evidence, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms221910559
Gombart, Saito, Koeffler, Exaptation of an ancient Alu short interspersed element provides a highly conserved vitamin D-mediated innate immune response in humans and primates, BMC Genomics, doi:10.1186/1471-2164-10-321
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of Influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Grant, Vitamin D's role in reducing risk of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 incidence, severity, and death, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14010183
Griffin, Hewison, Hopkin, Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: implications for COVID-19, Clin Med
Hengist, Perkin, Gonzelez, Mobilizing vitamin D from adipose tissue: the potential impact of exercise, Nutr Bull
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Jude, Ling, Allcock, Vitamin D deficiency is associated with higher hospitalization risk from COVID-19: a retrospective case-control study, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab439
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, Plos One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239252
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Jamalimoghadamsiahkali, Treatment with 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcifediol) is associated with a reduction in the blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio marker of disease severity in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a pilot multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded clinical trial, Endocr Pract
Martens, Gysemans, Verstuyf, Vitamin D's effect on immune function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12051248
Mazess, Bischoff-Ferrari, Hughes, Vitamin D: Bolus is bogus -a narrative review, JBMR Plus
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D 3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.3390/nu13103596
Nogues, Ovejero, Pineda-Moncusi, Calcifediol treatment and COVID-19-related outcomes, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Powers, Guerrero, Leidy, Development of the Flu-PRO: a patient-reported outcome (PRO) instrument to evaluate symptoms of influenza, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-015-1330-0
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, Clin Infect Dis
Roizen, Long, Casella, Obesity decreases hepatic 25-hydroxylase activity causing low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, J Bone Miner Res
Sprague, Crawford, Melnick, Use of extended-release calcifediol to treat secondary hyperparathyroidism in stages 3 and 4 chronic kidney disease, Am J Nephrol
Wang, Joshi, Leopold, Association of vitamin D deficiency with COVID-19 infection severity: systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Encrinol, doi:10.1111/cen.14540
White, Emerging roles of vitamin D-induced antimicrobial peptides in antiviral innate immunity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14020284
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2022.111899",
"ISSN": [
"0899-9007"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2022.111899",
"alternative-id": [
"S0899900722003100"
],
"article-number": "111899",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "REsCue Trial: Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial with Extended-Release Calcifediol in Symptomatic COVID-19 Outpatients"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Nutrition"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2022.111899"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 OPKO Health. Published by Elsevier Inc."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7877-6795",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bishop",
"given": "Charles W.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashfaq",
"given": "Akhtar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Melnick",
"given": "Joel Z.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vazquez-Escarpanter",
"given": "Enrique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fialkow",
"given": "Jonathan A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Strugnell",
"given": "Stephen A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Choe",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalantar-Zadeh",
"given": "Kamyar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Federman",
"given": "Noah C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9607-5020",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Adams",
"given": "John S.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Nutrition",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-07T17:15:49Z",
"timestamp": 1667841349000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-07T17:15:51Z",
"timestamp": 1667841351000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-08T05:45:46Z",
"timestamp": 1667886346908
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667260800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667260800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900722003100?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900722003100?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "111899",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0899900722003100"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "REsCue Trial: Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial with Extended-Release Calcifediol in Symptomatic COVID-19 Outpatients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
