Efficacy and Safety of Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 in Frontline Healthcare Workers. A Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003, Apr 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 321 healthcare workers in Mexico, showing significantly lower SARS-CoV-2 infection with vitamin D prophylaxis. 4,000IU daily for 30 days.
In comparison to Jolliffe et al., this study used a higher dose, the participants had much higher exposure to SARS-CoV-2 patients, and the study was prior to vaccination. In Jolliffe et al., 89% of participants had received a vaccine dose by the end of the study period, and the period overlapped with increasing solar UVB.
For more discussion see twitter.com.
This is the 16th of 40 COVID-19 RCTs for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
This is the 79th of 136 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of hospitalization, 66.5% lower, RR 0.33, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 150 (0.0%), control 1 of 152 (0.7%), NNT 152, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), ITT.
|
|
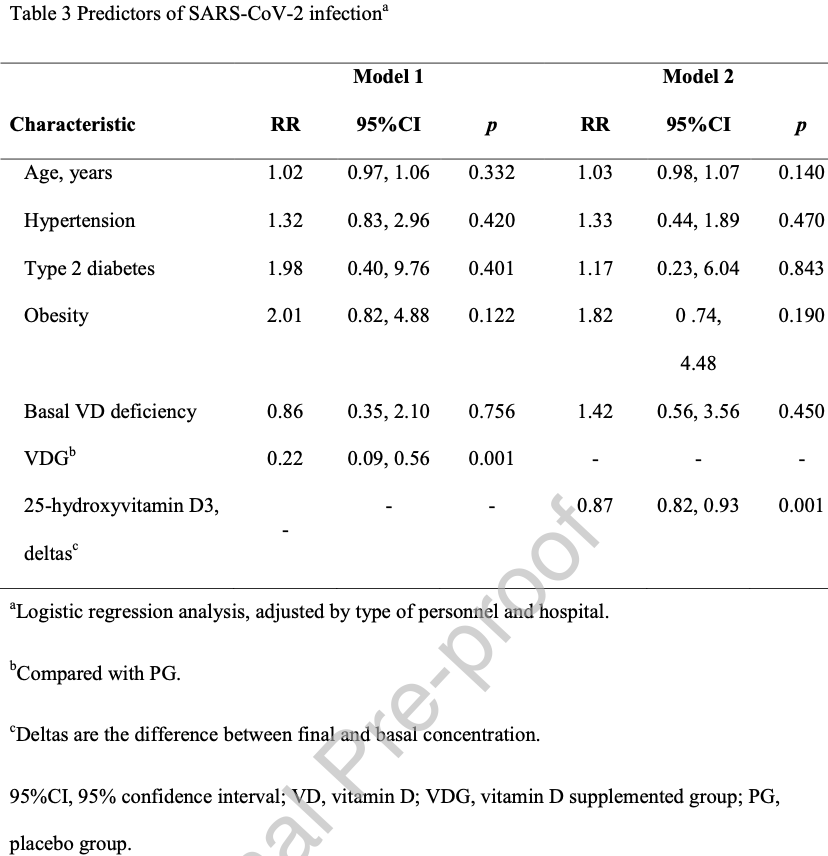
risk of case, 78.0% lower, RR 0.22, p = 0.001, treatment 7 of 150 (4.7%), control 26 of 152 (17.1%), NNT 8.0, adjusted per study, multivariable, Table 3.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Villasis-Keever et al., 18 Apr 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Mexico, peer-reviewed, 16 authors, study period 15 July, 2020 - 30 December, 2020, dosage 4,000IU daily.
Efficacy and Safety of Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 in Frontline Healthcare Workers. A Randomized Clinical Trial
Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conflict of Interest Mardia G López-Alarcón, is the Editor-in-Chief of Archives of Medical Research. All other authors do not have any Conflict of Interest. Arch Med Res 22-00242
References
Abbott, ARCHITECT SARS-CoV-2 IgG instructions for use
Alguwaihes, Sabico, Hasanato, Severe vitamin D deficiency is not related to SARS-CoV-2 infection but may increase mortality risk in hospitalized adults: a retrospective case-Arch Med Res 22-00242 15 control study in an Arab Gulf country, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-021-01831-0
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J Infect Public Health
Amer, Alotaibi, Vitamin D status of Arab Gulf residents screened for SARS-CoV-2 and its association with COVID-19 infection: a multi-centre case-control study, J Transl Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-021-02838-x
Campi, Gennari, Merlotti, Vitamin D and COVID-19 severity and related mortality: a prospective study in Italy, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06281-7
Cashman, Dowling, Škrabáková, D deficiency in Europe: pandemic?, Am J Clin Nutr
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J Arch Med Res
Chapa-Koloffon, Jean-Tron, Ávila-Hernández, Frequency of acute stress disorder in health care workers of a tertiary level pediatric hospital during the National Safe Distance Strategy for COVID-19 prevention, Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex
Chiodini, Gatti, Soranna, Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.736665
Corman, Landt, Kaiser, Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR, Euro Surveill, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045
Crafa, Cannarella, Condorelli, Influence of 25-hydroxy-cholecalciferol levels on SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis, E Clinical Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100967
Ferder, Giménez, Inserra, Vitamin D supplementation as a rational pharmacological approach in the COVID-19 pandemic, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00186.2020
Ghasemian, Shamshirian, Heydari, The role of vitamin D in the age of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Int J Clin Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14675
Gutiérrez, Rivera-Dommarco, Shamah-Levy, Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición 2012. Resultados Nacionales
Herrick, Storandt, Afful, Vitamin D status in the United States, 2011-2014, Am J Clin Nutr
Jolliffe, Camargo, Jr, Sluyter, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239252
Liu, Sun, Wang, Low vitamin D status is associated with coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis
Ma, Nguyen, Yue, Associations between predicted vitamin D status, vitamin D intake, and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and Coronavirus Disease 2019 severity, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab389
Malek, A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2119
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Nogues, Ovejero, Pineda-Moncusí, Calcifediol treatment and COVID-19-related outcomes, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab405
Pal, Banerjee, Bhadada, Vitamin D supplementation and clinical outcomes in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Endocrinol Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01614-4
Petrelli, Luciani, Perego, Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883
Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: a randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study), Postgrad Med J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065
Ross, Manson, Abrams, The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: what clinicians need to know, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Roth, Abrams, Aloia, Global prevalence and disease burden of vitamin D deficiency: a roadmap for action in low-and middle-income countries, Ann N Y Acad Sci
Sabico, Enani, Sheshah, Effects of a 2-Week 5000 IU versus 1000 IU Vitamin D3 supplementation on recovery of symptoms in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072170
Van Den Ouweland, Beijers, Demacker, Van Daal, Measurement of 25-OHvitamin D in human serum using liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry with comparison to radioimmunoassay and automated immunoassay, J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Life Sci
Vanherwegen, Gysemans, Mathieu, Regulation of Immune Function by Vitamin D and Its Use in Diseases of Immunity, Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am
Vanherwegen, Gysemans, Mathieu, Regulation of immune function by vitamin D and its use in diseases of immunity, Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003",
"ISSN": [
"0188-4409"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003",
"alternative-id": [
"S0188440922000455"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Villasis-Keever",
"given": "Miguel A",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "López-Alarcón",
"given": "Mardia G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3262-2608",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Miranda-Novales",
"given": "Guadalupe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zurita-Cruz",
"given": "Jessie N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0016-2267",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Barrada-Vázquez",
"given": "Aly S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "González-Ibarra",
"given": "Joaquín",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martínez-Reyes",
"given": "Monserrat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grajales-Muñiz",
"given": "Concepción",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santacruz-Tinoco",
"given": "Clara E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martínez-Miguel",
"given": "Bernardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maldonado-Hernández",
"given": "Jorge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cifuentes-González",
"given": "Yazmín",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Klünder-Klünder",
"given": "Miguel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garduño-Espinosa",
"given": "Juan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "López-Martínez",
"given": "Briseida",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7195-1749",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Parra-Ortega",
"given": "Israel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Archives of Medical Research"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-18T04:40:25Z",
"timestamp": 1650256825000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-18T04:40:47Z",
"timestamp": 1650256847000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-18T05:11:31Z",
"timestamp": 1650258691029
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0188-4409"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1648771200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0188440922000455?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0188440922000455?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0001",
"unstructured": "The World Health Organization (WHO). https://covid19.who.int/. (Access February 4, 2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nyas.13968",
"article-title": "Global prevalence and disease burden of vitamin D deficiency: a roadmap for action in low- and middle-income countries",
"author": "Roth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "Ann N Y Acad Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0002",
"volume": "1430",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.115.120873",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in Europe: pandemic?",
"author": "Cashman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0003",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqz037",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in the United States, 2011–2014",
"author": "Herrick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "150",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0004",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"author": "Gutiérrez",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0005",
"series-title": "Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición 2012. Resultados Nacionales",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.010",
"article-title": "Regulation of immune function by vitamin D and its use in diseases of immunity",
"author": "Vanherwegen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0006",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels",
"author": "Kaufman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0007",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in preventing COVID-19 infection, progression and severity",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1373",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0008",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-021-01831-0",
"article-title": "Severe vitamin D deficiency is not related to SARS-CoV-2 infection but may increase mortality risk in hospitalized adults: a retrospective case-control study in an Arab Gulf country",
"author": "Alguwaihes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1415",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0009",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-021-02838-x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status of Arab Gulf residents screened for SARS-CoV-2 and its association with COVID-19 infection: a multi-centre case-control study",
"author": "Al-Daghri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "166",
"journal-title": "J Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0010",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06281-7",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID-19 severity and related mortality: a prospective study in Italy",
"author": "Campi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "566",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0011",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.736665",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes",
"author": "Chiodini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0012",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883",
"article-title": "Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies",
"author": "Petrelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0013",
"volume": "211",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.077",
"article-title": "Low vitamin D status is associated with coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0014",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the age of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Ghasemian",
"first-page": "e14675",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0015",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"article-title": "Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Murai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1053",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0016",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"article-title": "Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study",
"author": "Entrenas Castillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0017",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab405",
"article-title": "Calcifediol treatment and COVID-19-related outcomes",
"author": "Nogues",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e4017",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0018",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: a randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study)",
"author": "Rastogi",
"first-page": "87",
"journal-title": "Postgrad Med J",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0019",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045",
"article-title": "Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR",
"author": "Corman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Euro Surveill",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0020",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0021",
"unstructured": "Abbott. ARCHITECT SARS-CoV-2 IgG instructions for use. H14806R03. Available at: https://www.corelaboratory.abbott/int/en/offerings/segments/infectious-disease/sars-cov-2- (Accessed March 20, 2022)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jchromb.2010.03.035",
"article-title": "Measurement of 25-OH-vitamin D in human serum using liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry with comparison to radioimmunoassay and automated immunoassay",
"author": "Van den Ouweland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1163",
"journal-title": "J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Life Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0022",
"volume": "878",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2010-2704",
"article-title": "The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: what clinicians need to know",
"author": "Ross",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "53",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0023",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.010",
"article-title": "Regulation of Immune Function by Vitamin D and Its Use in Diseases of Immunity",
"author": "Vanherwegen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0024",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "Malek",
"first-page": "e2119",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0025",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00186.2020",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation as a rational pharmacological approach in the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Ferder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "L941",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0026",
"volume": "319",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0027",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqab389",
"article-title": "Associations between predicted vitamin D status, vitamin D intake, and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and Coronavirus Disease 2019 severity",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1123",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0028",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Influence of 25-hydroxy-cholecalciferol levels on SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Crafa",
"journal-title": "E Clinical Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0029",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072170",
"article-title": "Effects of a 2-Week 5000 IU versus 1000 IU Vitamin D3 supplementation on recovery of symptoms in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Sabico",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2170",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0030",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-021-01614-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation and clinical outcomes in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "53",
"journal-title": "J Endocrinol Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0031",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Frequency of acute stress disorder in health care workers of a tertiary level pediatric hospital during the National Safe Distance Strategy for COVID-19 prevention",
"author": "Chapa-Koloffon",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003_bib0032",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0188440922000455"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Archives of Medical Research"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Efficacy and Safety of Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 in Frontline Healthcare Workers. A Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}
