Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases
et al., ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1, Apr 2024
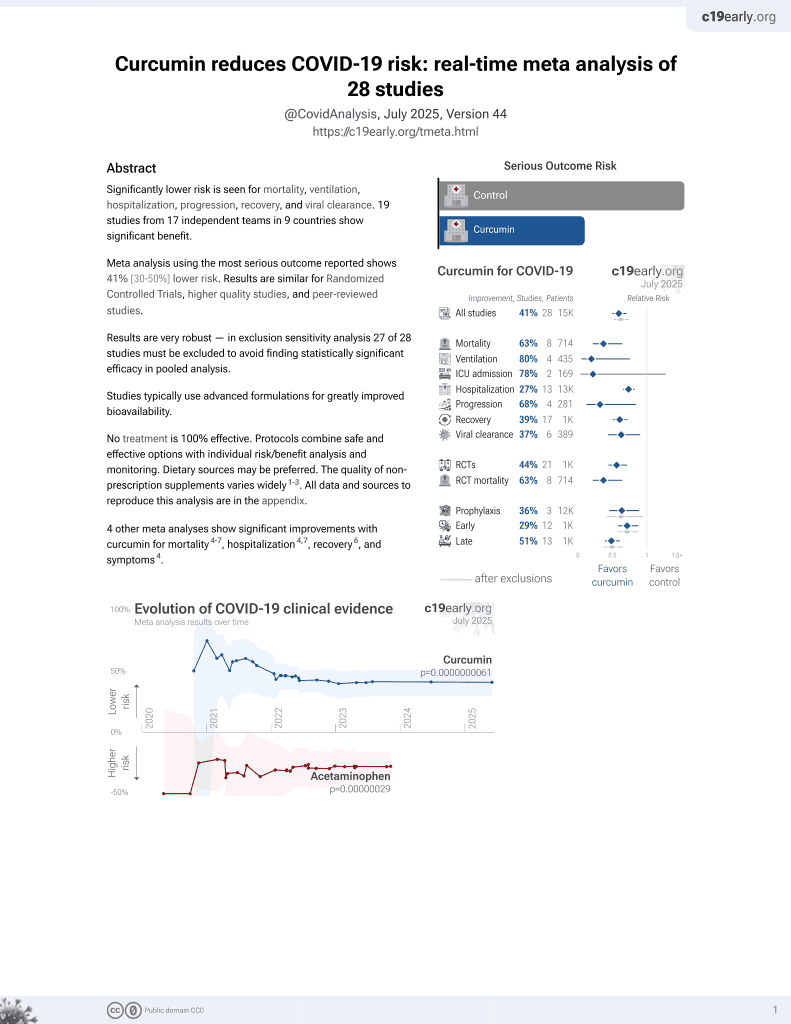
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In silico study identifying potential drugs beneficial for COVID-19 by integrating transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, lipidomics, and drug data. Authors explore interactions between drugs, molecular features, and disease severity. Hypothesis-driven analysis, using IL-6 and IL-6R as seeds, highlighted immunosuppressants, corticosteroids, and IL-6 inhibitors as promising candidates, while data-driven analysis, using STAT1, SOD2, and lipid/metabolite markers as seeds, identified antioxidants, kinase inhibitors, and protein synthesis inhibitors. Network analysis revealed key hubs like CCL2, CCL4, NFKB1, and HGF that interact with drug candidates and influence disease progression. Treatments identified in the top 20 lists include ivermectin, zinc, azithromycin, indomethacin, curcumin, vitamin C, metformin, mebendazole, and acetylcysteine.
62 preclinical studies support the efficacy of curcumin for COVID-19:
In silico studies predict inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 with curcumin or metabolites via binding to the spikeA,1,5,6,11,16,18,24,27 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,2,4,14,17,20 ), MproC,4-6,11,13,15-17,19,20,22,25,27,28,30,48 , RNA-dependent RNA polymeraseD,4-6,17,26 , PLproE,6, ACE2F,2,18,19,21 , nucleocapsidG,12,29 , nsp10H,29, and helicaseI,36 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3.
In vitro studies demonstrate inhibition of the spikeA,41 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,51), MproC,23,41,48,50 , ACE2F,51, and TMPRSS2K,51 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3,34 .
In vitro studies demonstrate efficacy in Calu-3L,49, A549M,41, A549-ATN,31, 293TO,7, HEK293-hACE2P,23,39 , 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2Q,40, Vero E6R,1,13,17,27,39,41,43,45,47,49 , and SH-SY5YS,38 cells.
Curcumin decreases pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by SARS-CoV-2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells47, alleviates SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-induced mitochondrial membrane damage and oxidative stress7, may limit COVID-19 induced cardiac damage by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway which mediates the profibrotic effects of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein on cardiac fibroblasts35, is predicted to inhibit the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain and the human ACE2 receptor for the delta and omicron variants14, lowers ACE2 and STAT3, curbing lung inflammation and ARDS in preclinical COVID-19 models32, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a ion channel activity, which contributes to viral pathogenicity and cytotoxicity42, has direct virucidal action by disrupting viral envelope integrity44, may inhibit viral replication and modulate inflammatory pathways like NF-κB via SIRT1 activation52, and can function as a photosensitizer in photodynamic therapy to generate reactive oxygen species that damage the virus44.
Study covers ivermectin, zinc, indomethacin, curcumin, vitamin C, metformin, N-acetylcysteine, and mebendazole.
1.
Marzouk et al., Computational and Experimental Insights into the Antiviral Mechanism of Turmeric (Curcuma longa) against SARS-CoV-2 D614G, BIO Web of Conferences, doi:10.1051/bioconf/202519804002.
2.
Wu et al., Utilizing natural compounds as ligands to disrupt the binding of SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, impeding viral infection, Phytochemistry Letters, doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2025.102999.
3.
Najimi et al., Phytochemical Inhibitors of SARS‐CoV‐2 Entry: Targeting the ACE2‐RBD Interaction with l‐Tartaric Acid, l‐Ascorbic Acid, and Curcuma longa Extract, ChemistrySelect, doi:10.1002/slct.202406035.
4.
Rajamanickam et al., Exploring the Potential of Siddha Formulation MilagaiKudineer-Derived Phytotherapeutics Against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Investigation for Antiviral Intervention, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, doi:10.26502/fjppr.0105.
5.
Al balawi et al., Assessing multi-target antiviral and antioxidant activities of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2: an integrated in vitro and in silico study, Bioresources and Bioprocessing, doi:10.1186/s40643-024-00822-z.
6.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
7.
Zhang et al., Computational Discovery of Mitochondrial Dysfunction Biomarkers in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Facilitating Pytomedicine Screening, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784.
8.
Öztürkkan et al., In Silico investigation of the effects of curcuminoids on the spike protein of the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, Baku State University Journal of Chemistry and Material Sciences, 1:2, bsuj.bsu.edu.az/uploads/pdf/ec4204d62f7802de54e6092bf7860029.pdf.
9.
Yunze et al., Therapeutic effect and potential mechanism of curcumin, an active ingredient in Tongnao Decoction, on COVID-19 combined with stroke: a network pharmacology study and GEO database mining, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4329762/v1.
10.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
11.
Boseila et al., Throat spray formulated with virucidal Pharmaceutical excipients as an effective early prophylactic or treatment strategy against pharyngitis post-exposure to SARS CoV-2, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2024.114279.
12.
Hidayah et al., Bioinformatics study of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin and cyclocurcumin compounds in Curcuma longa as an antiviral agent via nucleocapsid on SARS-CoV-2 inhibition, International Conference on Organic and Applied Chemistry, doi:10.1063/5.0197724.
13.
Singh et al., Unlocking the potential of phytochemicals in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 M Pro protein - An in-silico and cell-based approach, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3888947/v1.
14.
Kant et al., Structure-based drug discovery to identify SARS-CoV2 spike protein–ACE2 interaction inhibitors, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2023.2300060.
15.
Naderi Beni et al., In silico studies of anti-oxidative and hot temperament-based phytochemicals as natural inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0295014.
16.
Moschovou et al., Exploring the Binding Effects of Natural Products and Antihypertensive Drugs on SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Investigation of Main Protease and Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242115894.
17.
Eleraky et al., Curcumin Transferosome-Loaded Thermosensitive Intranasal in situ Gel as Prospective Antiviral Therapy for SARS-Cov-2, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S423251.
18.
Singh (B) et al., Computational studies to analyze effect of curcumin inhibition on coronavirus D614G mutated spike protein, The Seybold Report, doi:10.17605/OSF.IO/TKEXJ.
19.
Thapa et al., In-silico Approach for Predicting the Inhibitory Effect of Home Remedies on Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2, Makara Journal of Science, doi:10.7454/mss.v27i3.1609.
20.
Srivastava et al., Paradigm of Well-Orchestrated Pharmacokinetic Properties of Curcuminoids Relative to Conventional Drugs for the Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 Receptors: An In Silico Approach, Stresses, doi:10.3390/stresses3030043.
21.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
22.
Winih Kinasih et al., Analisis in silico interaksi senyawa kurkuminoid terhadap enzim main protease 6LU7 dari SARS-CoV-2, Duta Pharma Journal, doi:10.47701/djp.v3i1.2904.
23.
Wu (B) et al., Potential Mechanism of Curcumin and Resveratrol against SARS-CoV-2, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2780614/v1.
24.
Nag et al., Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552.
25.
Rampogu et al., Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations Discover Curcumin Analogue as a Plausible Dual Inhibitor for SARS-CoV-2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23031771.
26.
Singh (C) et al., Potential of turmeric-derived compounds against RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2: An in-silico approach, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104965.
27.
Kandeil et al., Bioactive Polyphenolic Compounds Showing Strong Antiviral Activities against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10060758.
28.
Rajagopal et al., Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach, Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x.
29.
Suravajhala et al., Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin with COVID-19 Proteins, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v3.
30.
Sekiou et al., In-Silico Identification of Potent Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) from Natural Products: Quercetin, Hispidulin, and Cirsimaritin Exhibited Better Potential Inhibition than Hydroxy-Chloroquine Against COVID-19 Main Protease Active Site and ACE2, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12181404.v1.
31.
Grüneberg et al., Dose-dependent antiviral effects of glycyrrhizin, curcumin, and harmaline against clinical SARS-CoV-2 isolates, including D614G, Omicron BA.5, and Omicron XBB.1, BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, doi:10.1186/s12906-026-05253-1.
32.
Aktay et al., Oral Administration of Water-Soluble Curcumin Complex Prevents ARDS With the Potential for COVID-19 Treatment, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.70046.
33.
Olubiyi et al., Novel dietary herbal preparations with inhibitory activities against multiple SARS-CoV-2 targets: A multidisciplinary investigation into antiviral activities, Food Chemistry Advances, doi:10.1016/j.focha.2025.100969.
34.
Emam et al., Establishment of in-house assay for screening of anti-SARS-CoV-2 protein inhibitors, AMB Express, doi:10.1186/s13568-024-01739-8.
35.
Van Tin et al., Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Activates Cardiac Fibrogenesis through NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161331.
36.
Li et al., Thermal shift assay (TSA)-based drug screening strategy for rapid discovery of inhibitors against the Nsp13 helicase of SARS-CoV-2, Animals and Zoonoses, doi:10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001.
37.
Kamble et al., Nanoparticulate curcumin spray imparts prophylactic and therapeutic properties against SARS-CoV-2, Emergent Materials, doi:10.1007/s42247-024-00754-6.
38.
Nicoliche et al., Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin and curcuminoids in SH-SY5Y cells infected by SARS-CoV-2, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7.
39.
Nittayananta et al., A novel film spray containing curcumin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus infection and enhances mucosal immunity, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02282-x.
40.
Septisetyani et al., Curcumin and turmeric extract inhibited SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus cell entry and Spike mediated cell fusion, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.09.28.560070.
41.
Mohd Abd Razak et al., In Vitro Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activities of Curcumin and Selected Phenolic Compounds, Natural Product Communications, doi:10.1177/1934578X231188861.
42.
Fam et al., Channel activity of SARS-CoV-2 viroporin ORF3a inhibited by adamantanes and phenolic plant metabolites, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31764-9.
43.
Teshima et al., Antiviral activity of curcumin and its analogs selected by an artificial intelligence-supported activity prediction system in SARS-CoV-2-infected VeroE6 cells, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2023.2194647.
44.
Zupin et al., Optimization of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Treatments Based on Curcumin, Used Alone or Employed as a Photosensitizer, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14102132.
45.
Leka et al., In vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 of common herbal medicinal extracts and their bioactive compounds, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7463.
46.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
47.
Marín-Palma et al., Curcumin Inhibits In Vitro SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vero E6 Cells through Multiple Antiviral Mechanisms, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26226900.
48.
Bahun et al., Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro main protease by plant polyphenols, Food Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131594.
49.
Bormann et al., Turmeric Root and Its Bioactive Ingredient Curcumin Effectively Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13101914.
50.
Guijarro-Real et al., Potential In Vitro Inhibition of Selected Plant Extracts against SARS-CoV-2 Chymotripsin-Like Protease (3CLPro) Activity, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods10071503.
a.
The trimeric spike (S) protein is a glycoprotein that mediates viral entry by binding to the host ACE2 receptor, is critical for SARS-CoV-2's ability to infect host cells, and is a target of neutralizing antibodies. Inhibition of the spike protein prevents viral attachment, halting infection at the earliest stage.
b.
The receptor binding domain is a specific region of the spike protein that binds ACE2 and is a major target of neutralizing antibodies. Focusing on the precise binding site allows highly specific disruption of viral attachment with reduced potential for off-target effects.
c.
The main protease or Mpro, also known as 3CLpro or nsp5, is a cysteine protease that cleaves viral polyproteins into functional units needed for replication. Inhibiting Mpro disrupts the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle within the host cell, preventing the creation of new copies.
d.
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called nsp12, is the core enzyme of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex that copies the positive-sense viral RNA genome into negative-sense templates for progeny RNA synthesis. Inhibiting RdRp blocks viral genome replication and transcription.
e.
The papain-like protease (PLpro) has multiple functions including cleaving viral polyproteins and suppressing the host immune response by deubiquitination and deISGylation of host proteins. Inhibiting PLpro may block viral replication and help restore normal immune responses.
f.
The angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) protein is a host cell transmembrane protein that serves as the cellular receptor for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. ACE2 is expressed on many cell types, including epithelial cells in the lungs, and allows the virus to enter and infect host cells. Inhibition may affect ACE2's physiological function in blood pressure control.
g.
The nucleocapsid (N) protein binds and encapsulates the viral genome by coating the viral RNA. N enables formation and release of infectious virions and plays additional roles in viral replication and pathogenesis. N is also an immunodominant antigen used in diagnostic assays.
h.
Non-structural protein 10 (nsp10) serves as an RNA chaperone and stabilizes conformations of nsp12 and nsp14 in the replicase-transcriptase complex, which synthesizes new viral RNAs. Nsp10 disruption may destabilize replicase-transcriptase complex activity.
i.
The helicase, or nsp13, protein unwinds the double-stranded viral RNA, a crucial step in replication and transcription. Inhibition may prevent viral genome replication and the creation of new virus components.
j.
The interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the human ACE2 receptor is a primary method of viral entry, inhibiting this interaction can prevent the virus from attaching to and entering host cells, halting infection at an early stage.
k.
Transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) is a host cell protease that primes the spike protein, facilitating cellular entry. TMPRSS2 activity helps enable cleavage of the spike protein required for membrane fusion and virus entry. Inhibition may especially protect respiratory epithelial cells, buy may have physiological effects.
l.
Calu-3 is a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line with moderate ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. It provides a model of the human respiratory epithelium, but many not be ideal for modeling early stages of infection due to the moderate expression levels of ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
m.
A549 is a human lung carcinoma cell line with low ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Viral entry/replication can be studied but the cells may not replicate all aspects of lung infection.
n.
A549-AT is a human lung carcinoma cell line stably transfected with ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors. Unlike the parental line, this overexpression ensures stable infection and enhanced viral entry, allowing for the evaluation of antiviral efficacy against various SARS-CoV-2 variants.
o.
293T is a human embryonic kidney cell line that can be engineered for high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. 293T cells are easily transfected and support high protein expression.
p.
HEK293-hACE2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line with high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Cells have been transfected with a plasmid to express the human ACE2 (hACE2) protein.
q.
293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line engineered for high ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression, which mimics key aspects of human infection. 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 cells are very susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
r.
Vero E6 is an African green monkey kidney cell line with low/no ACE2 expression and high SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. The cell line is easy to maintain and supports robust viral replication, however the monkey origin may not accurately represent human responses.
s.
SH-SY5Y is a human neuroblastoma cell line that exhibits neuronal phenotypes. It is commonly used as an in vitro model for studying neurotoxicity, neurodegenerative diseases, and neuronal differentiation.
Agamah et al., 16 Apr 2024, preprint, 6 authors.
Contact: francisagamahh@gmail.com, peter-bram.thoen@radboudumc.nl, emile.chimusa@northumbria.ac.uk.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for
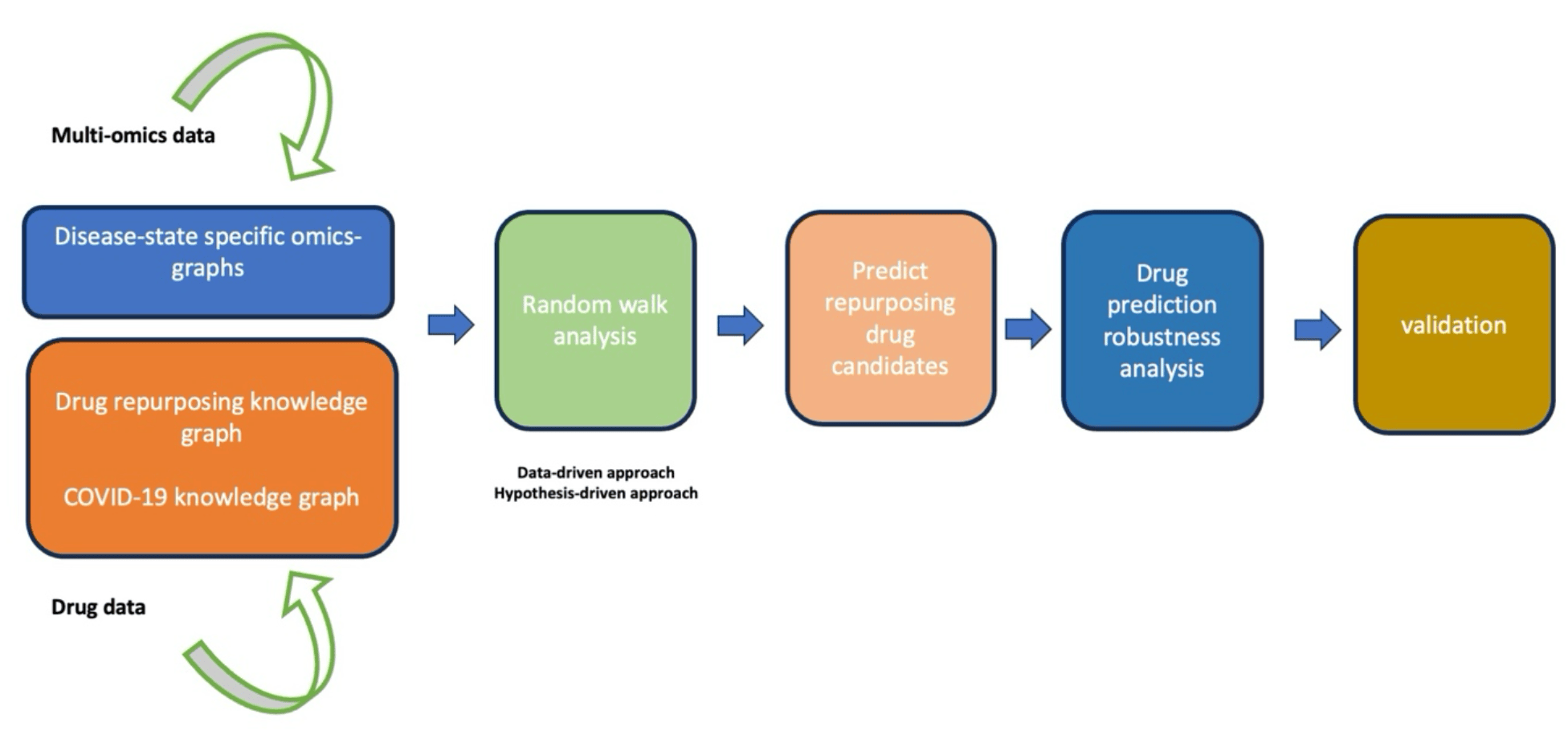
Background: The development and roll-out of vaccines, and the use of various drugs have contributed to controlling the COVID-19 pandemic. Nevertheless, challenges such as the inequitable distribution of vaccines, the influence of emerging viral lineages and immune evasive variants on vaccine efficacy, and the inadequate immune defense in subgroups of the population continue to motivate the development of new drugs to combat the disease. Aim: In this study, we sought to identify, prioritize, and characterize drug repurposing candidates appropriate for treating mild, moderate, or severe COVID-19 using a network-based integrative approach that systematically integrates drug-related data and multi-omics datasets.
Methods: We leveraged drug data, and multi-omics data, and used a random walk restart algorithm to explore an integrated knowledge graph comprised of three subgraphs: (i) a COVID-19 knowledge graph, (ii) a drug repurposing knowledge graph, and (iii) a COVID-19 disease-state specific omics graph.
Results: We prioritized twenty FDA-approved agents as potential candidate drugs for mild, moderate, and severe COVID-19 disease phases. Specifically, drugs that could stimulate immune cell recruitment and activation including histamine, curcumin, and paclitaxel have potential utility in mild disease states to mitigate disease progression. Drugs like omacetaxine, crizotinib, and vorinostat that exhibit antiviral properties and have the potential to inhibit viral replication can be considered for mild to moderate COVID-19 disease states. Also, given the association between antioxidant deficiency and high inflammatory factors that trigger cytokine storms, antioxidants like glutathione can be considered for moderate disease states. Drugs that exhibit potent antiinflammatory effects like (i) anti-inflammatory drugs (sarilumab and tocilizumab), (ii) corticosteroids (dexamethasone and hydrocortisone), and (iii) immunosuppressives (sirolimus and cyclosporine) are potential candidates for moderate to severe disease states that trigger a hyperinflammatory cascade of COVID-19.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that the multi-omics data-driven integrative analysis within the drug data enables prioritizing drug candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, offering a comprehensive basis for therapeutic strategies that can be brought to market quickly given their established safety profiles. Importantly, the multi-omics data-driven integrative analysis within the drug data approach implemented here can be used to prioritize drug repurposing candidates appropriate for other diseases.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication The authors have consented for the work to be published.
Supplementary Files
Supplementary data Supplementary file 1 Supplementary file 2 Supplementary file 3 Supplementary file 4 Supplementary file 5 Next, we prioritized and characterized candidate drugs followed by drug prediction robustness analysis. Finally, we concluded the analysis by validating the predicted drug candidates. Figure legends
References
Agamah, Computational approaches for network-based integrative multiomics analysis, Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences
Agamah, Network-based integrative multi-omics approach reveals biosignatures specific to COVID-19 disease phases, bioRxiv
Al-Kuraishy, Anti-histamines and Covid-19: hype or hope, JPMA J Pak Med Assoc
Alam, Czajkowsky, SARS-CoV-2 infection and oxidative stress: Pathophysiological insight into thrombosis and therapeutic opportunities, Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews
Aoyagi, Case Report: Successful Treatment of Five Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients Using Combination Therapy With Etoposide and Corticosteroids, Frontiers in Medicine
Arazi, Human systems immunology: hypothesis-based modeling and unbiased data-driven approaches
Archin, Administration of vorinostat disrupts HIV-1 latency in patients on antiretroviral therapy, Nature
Attademo, Bernardini, Are dopamine and serotonin involved in COVID-19 pathophysiology?, The European journal of psychiatry
Bailly, Etoposide: A rider on the cytokine storm, Cytokine
Baptista, Brière, Baudot, Random Walk with Restart on multilayer networks: from node prioritisation to supervised link prediction and beyond, BMC bioinformatics
Baptista, Gonzalez, Baudot, Universal multilayer network exploration by random walk with restart, Communications Physics
Battaglia, Rapamycin and interleukin-10 treatment induces T regulatory type 1 cells that mediate antigen-specific transplantation tolerance, Diabetes
Beigel, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine
Belli, Protective role of tacrolimus, deleterious role of age and comorbidities in liver transplant recipients with Covid-19: results from the ELITA/ELTR multi-center European study, Gastroenterology
Ben Abdallah, Twice-daily oral zinc in the treatment of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a randomized double-blind controlled trial, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Bengtson, An open label trial to assess safety of losartan for treating worsening respiratory illness in COVID-19, Frontiers in medicine
Benucci, COVID-19 pneumonia treated with Sarilumab: A clinical series of eight patients
Benucci, COVID-19 pneumonia treated with sarilumab: a clinical series of eight patients, Journal of medical virology
Bharadwaj, SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors: identification of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Mpro compounds from FDA approved drugs, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics
Bhimraj, Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clinical Infectious Diseases
Boor, Rapamycin has suppressive and stimulatory effects on human plasmacytoid dendritic cell functions, Clinical & Experimental Immunology
Bramante, Outpatient treatment of COVID-19 and incidence of post-COVID-19 condition over 10 months (COVID-OUT): a multicentre, randomised, quadruple-blind, parallel-group, phase 3 trial, The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Bramante, Outpatient treatment of COVID-19 and incidence of post-COVID-19 condition over 10 months (COVID-OUT): a multicentre, randomised, quadruple-blind, parallel-group, phase 3 trial, The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Bustamante, Tryptophan Metabolism 'Hub'Gene Expression Associates with Increased Inflammation and Severe Disease Outcomes in COVID-19 Infection and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Carlos, Histamine modulates mast cell degranulation through an indirect mechanism in a model IgE-mediated reaction, European journal of immunology
Cecchini, Cecchini ; Pono, COVID-19 infection and oxidative stress: an under-explored approach for prevention and treatment? The Pan African Medical Journal, Archives of medical research
Cengiz, Effect of oral l-Glutamine supplementation on Covid-19 treatment, Clinical nutrition experimental
Chen, Confronting the controversy: interleukin-6 and the COVID-19 cytokine storm syndrome, Eur Respiratory Soc
Chen, Immunomodulatory and antiviral activity of metformin and its potential implications in treating coronavirus disease 2019 and lung injury, Frontiers in Immunology
Chow, Association of early aspirin use with in-hospital mortality in patients with moderate COVID-19, JAMA network open
Chowdhury, Pathak, Neuroprotective immunity by essential nutrient "Choline" for the prevention of SARS CoV2 infections: An in silico study by molecular dynamics approach, Chemical physics letters
Consortium, Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19-interim WHO solidarity trial results, New England journal of medicine
Coomes, Haghbayan, Interleukin-6 in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Reviews in medical virology
Davies, Adlimoghaddam, Albensi, The effect of COVID-19 on NF-κB and neurological manifestations of disease, Molecular Neurobiology
Davis, Comparative toxicogenomics database (CTD): update 2021, Nucleic acids research
De Flora, Balansky, La Maestra, Antioxidants and COVID-19, Journal of preventive medicine and hygiene
Del Toro, The IntAct database: efficient access to fine-grained molecular interaction data, Nucleic acids research
Diaz, Remdesivir and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Dong, Du, Gardner, An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time, The Lancet infectious diseases
Dryden-Peterson, Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir for early COVID-19 in a large US health system: a population-based cohort study, Annals of internal medicine
Durante, Glutamine Deficiency Promotes Immune and Endothelial Cell Dysfunction in COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences
El Bairi, Repurposing anticancer drugs for the management of COVID-19, European Journal of Cancer
El-Tanani, Phase II, Double-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial Investigating the Efficacy of Mebendazole in the Management of Symptomatic COVID-19 Patients, Pharmaceuticals
Ennis, Tiligada, Histamine receptors and COVID-19, Inflammation Research
Eriksson, Combining hypothesis-and data-driven neuroscience modeling in FAIR workflows, Elife
Ferdinands, Waning of vaccine effectiveness against moderate and severe covid-19 among adults in the US from the VISION network: test negative, casecontrol study
Freshour, Integration of the Drug-Gene Interaction Database (DGIdb 4.0) with open crowdsource efforts, Nucleic acids research
Gajjela, Zhou, Calming the cytokine storm of COVID-19 through inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling, Drug discovery today
Giamarellos-Bourboulis, Complex immune dysregulation in COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory failure, Cell host & microbe
Gordon, A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature
Group, Aspirin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet
Group, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine
Group, Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet
Gupta, Association between early treatment with tocilizumab and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19
Gupta, Association between early treatment with tocilizumab and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19, JAMA internal medicine
Guy, Rapid repurposing of drugs for COVID-19, Science
Halpin, A prospective, single-center, randomized phase 2 trial of etoposide in severe COVID-19
Hamizi, Aouidane, Belaaloui, Etoposide-based therapy for severe forms of COVID-19, Medical Hypotheses
Hammond, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine
Han, Discovery of podofilox as a potent cGAMP-STING signaling enhancer with antitumor activity, Cancer Immunology Research
Heskin, Caution required with use of ritonavir-boosted PF-07321332 in COVID-19 management, The Lancet
Himmelstein, Systematic integration of biomedical knowledge prioritizes drugs for repurposing, Elife
Hinkson, COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines
Horby, Effect of dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19preliminary report, MedRxiv
Hsieh, Drug repurposing for COVID-19 using graph neural network and harmonizing multiple evidence, Scientific reports
Hudzik, Nowak, Zubelewicz-Szkodzinska, Consideration of immunomodulatory actions of morphine in COVID-19-Short report, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Ioannidis, Drkg-drug repurposing knowledge graph for covid-19
Izquierdo-Alonso, N-acetylcysteine for prevention and treatment of COVID-19: Current state of evidence and future directions, Journal of infection and public health
Jamal, Alharbi, Ahmad, Identification of doxorubicin as a potential therapeutic against SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) protease: a molecular docking and dynamics simulation studies, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics
Jennings, Parks, Curcumin as an antiviral agent, Viruses
Johnson, Etoposide selectively ablates activated T cells to control the immunoregulatory disorder hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, The Journal of Immunology
Jones, Hunter, Is IL-6 a key cytokine target for therapy in COVID-19?, Nature Reviews Immunology
Jung, Random walk with restart on large graphs using block elimination, ACM Transactions on Database Systems (TODS)
Jørgensen, Sirolimus interferes with the innate response to bacterial products in human whole blood by attenuation of IL-10 production, Scandinavian journal of immunology
Karsulovic, mTORC inhibitor Sirolimus deprograms monocytes in "cytokine storm" in SARS-CoV2 secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-like syndrome, Clinical Immunology
Khaledi, COVID-19 and the potential of Janus family kinase (JAK) pathway inhibition: A novel treatment strategy, Frontiers in medicine
Khalili, Novel coronavirus treatment with ribavirin: groundwork for an evaluation concerning COVID-19, Journal of medical virology
Kim, Serious Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Related to Acetaminophen or NSAIDs from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
Kim, The architecture of SARS-CoV-2 transcriptome, Cell
Kocks, A potential harmful effect of dexamethasone in non-severe COVID-19: results from the COPPER-pilot study, ERJ Open Research
Laforge, Tissue damage from neutrophil-induced oxidative stress in COVID-19, Nature Reviews Immunology
Laing, A dynamic COVID-19 immune signature includes associations with poor prognosis, Nature medicine
Lau, Real-world COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness against the Omicron BA. 2 variant in a SARS-CoV-2 infection-naive population, Nature medicine
Li, Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes in men with HIV, Aids
Liew, SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody bebtelovimab-a systematic scoping review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Immunology
Liu, DrugCombDB: a comprehensive database of drug combinations toward the discovery of combinatorial therapy, Nucleic acids research
Lucas, Longitudinal analyses reveal immunological misfiring in severe COVID-19, Nature
Lv, Efficient processing node proximity via random walk with restart
Ma, Does aspirin have an effect on risk of death in patients with COVID-19? A meta-analysis, European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology
Ma, Homo-harringtonine, highly effective against coronaviruses, is safe in treating COVID-19 by nebulization, Science China Life Sciences
Mahdian, Ebrahim-Habibi, Zarrabi, Drug repurposing using computational methods to identify therapeutic options for COVID-19, Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders
Malone, COVID-19: famotidine, histamine, mast cells, and mechanisms, Frontiers in Pharmacology
Manjani, Effects of acetaminophen on outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Chest
Mashauri, Covid-19 Histamine theory: Why antihistamines should be incorporated as the basic component in Covid-19 management?, Health Science Reports
Menni, COVID-19 vaccine waning and effectiveness and side-effects of boosters: a prospective community study from the ZOE COVID Study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Mirjalili, Does Losartan reduce the severity of COVID-19 in hypertensive patients?, BMC Cardiovascular Disorders
Mushtaq, Tocilizumab in critically ill COVID-19 patients: An observational study, International Immunopharmacology
Nair, Sharma, Tiwary, Glutathione deficiency in COVID19 illnessdoes supplementation help?, Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia
Nevalainen, Effect of remdesivir post hospitalization for COVID-19 infection from the randomized SOLIDARITY Finland trial, Nature Communications
Nguyen, Cannabidiol inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication through induction of the host ER stress and innate immune responses, Science Advances
Organization, The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in patients with COVID-19
Overmyer, Large-scale multi-omic analysis of COVID-19 severity, Cell systems
Panda, Computational Approaches for Novel Therapeutic and Diagnostic Designing to Mitigate SARS-CoV2 Infection
Pashmforosh, Possible Benefits of Paclitaxel Therapy for COVID-19, Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Research
Patel, Azithromycin for mild-to-moderate COVID-19, The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Pathania, Fenizia, Cyclosporine a inhibits viral infection and release as well as cytokine production in lung cells by three SARS-CoV-2 variants, Microbiology Spectrum
Patocka, Rapamycin: drug repurposing in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Pharmaceuticals
Pektaş, Gürsoy, Demirbilek, The use of pregabalin in Intensive Care Unit in the treatment of Covid-19-related pain and cough
Perreau, The cytokines HGF and CXCL13 predict the severity and the mortality in COVID-19 patients, Nature Communications
Puskarich, Efficacy of losartan in hospitalized patients with COVID-19induced lung injury: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA Network Open
Páez-Franco, Metabolomics analysis reveals a modified amino acid metabolism that correlates with altered oxygen homeostasis in COVID-19 patients, Scientific reports
Ravichandran, An open label randomized clinical trial of Indomethacin for mild and moderate hospitalised Covid-19 patients, Scientific reports
Ravid, Leiva, Chitalia, Janus kinase signaling pathway and its role in COVID-19 inflammatory, vascular, and thrombotic manifestations, Cells
Rheingold, Zinc Supplementation Associated With a Decrease in Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis, Cureus
Rincon-Arevalo, Altered increase in STAT1 expression and phosphorylation in severe COVID-19, European Journal of Immunology
Ripamonti, HDAC inhibition as potential therapeutic strategy to restore the deregulated immune response in severe COVID-19, Frontiers in immunology
Sajgure, Safety and efficacy of mycophenolate in COVID-19: A nonrandomised prospective study in western India, The Lancet Regional Health-Southeast Asia
Salerni, Vinblastine induces acute, cell cycle phase-independent apoptosis in some leukemias and lymphomas and can induce acute apoptosis in others when Mcl-1 is suppressed, Molecular cancer therapeutics
Salt, Palmer, Exploiting the anti-inflammatory effects of AMP-activated protein kinase activation, Expert opinion on investigational drugs
Samaee, Tocilizumab for treatment patients with COVID-19: recommended medication for novel disease, International immunopharmacology
Samuel, Varghese, Büsselberg, Therapeutic potential of metformin in COVID-19: reasoning for its protective role, Trends in microbiology
Schoot, Immunosuppressive drugs and COVID-19: a review, Frontiers in pharmacology
Schwartz, Does ivermectin have a place in the treatment of mild Covid-19? New microbes and new infections
Singh, A comparative study of 5-fluorouracil, doxorubicin, methotrexate, paclitaxel for their inhibition ability for Mpro of nCoV: Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations, Journal of the Indian Chemical Society
Sivapalasingam, Efficacy and safety of sarilumab in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a randomized clinical trial, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Sosa, A literature-based knowledge graph embedding method for identifying drug repurposing opportunities in rare diseases
Sperry, Target-agnostic drug prediction integrated with medical record analysis uncovers differential associations of statins with increased survival in COVID-19 patients, PLOS Computational Biology
Sterne, Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, Jama
Su, Multi-omics resolves a sharp disease-state shift between mild and moderate COVID-19, Cell
Suresh, Therapeutic potential of curcumin in ARDS and COVID-19, Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
Suriawinata, Mehta, Iron and iron-related proteins in COVID-19, Clinical and Experimental Medicine
Szklarczyk, The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets, Nucleic acids research
Takimoto, Anticancer drug development at the US National Cancer Institute, Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology
Tanaka, Narazaki, Kishimoto, Interleukin (IL-6) immunotherapy, Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology
Teixeira, Simvastatin downregulates the SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammatory response and impairs viral infection through disruption of lipid rafts, Frontiers in Immunology
Telenti, After the pandemic: perspectives on the future trajectory of COVID-19, Nature
Thangam, The role of histamine and histamine receptors in mast cellmediated allergy and inflammation: the hunt for new therapeutic targets, Frontiers in immunology
Tomazou, Multi-omics data integration and network-based analysis drives a multiplex drug repurposing approach to a shortlist of candidate drugs against COVID-19, Briefings in bioinformatics
Vahedian-Azimi, Effectiveness of curcumin on outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A systematic review of clinical trials, Nutrients
Valle, An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival, Nature medicine
Vitiello, Porta, Ferrara, Correlation between the use of statins and COVID-19: what do we know?, BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine
Wang, Fast identification of possible drug treatment of coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) through computational drug repurposing study, Journal of chemical information and modeling
Wang, Vinblastine resets tumor-associated macrophages toward M1 phenotype and promotes antitumor immune response, Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer
Weisberg, Repurposing of kinase inhibitors for treatment of COVID-19, Pharmaceutical research
Wishart, DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018, Nucleic acids research
Wróblewska, The Role of Glutathione in Selected Viral Diseases, Antioxidants
Wu, The SARS-CoV-2 induced targeted amino acid profiling in patients at hospitalized and convalescent stage, Bioscience Reports
Xiu, Fludarabine inhibits type I interferon-induced expression of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, Cellular & Molecular Immunology
Xu, Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, The Lancet respiratory medicine
Xu, Ribavirin treatment for critically ill COVID-19 patients: An observational study, Infection and Drug Resistance
Zarkovic, Post-mortem findings of inflammatory cells and the association of 4-hydroxynonenal with systemic vascular and oxidative stress in lethal COVID-19, Cells
Zhang, Immune evasive effects of SARS-CoV-2 variants to COVID-19 emergency used vaccines, Frontiers in Immunology
Zhou, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, The lancet
Zhou, Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2, Cell discovery
Zhou, Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action, The Journal of clinical investigation
Zhou, The role of SARS-CoV-2-mediated NF-κB activation in COVID-19 patients, Hypertension Research
Žarković, The impact of severe COVID-19 on plasma antioxidants, Molecules
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.58647/drugarxiv.pr000010.v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1",
"abstract": "<jats:p> \n <jats:bold>Background:</jats:bold>The development and roll-out of vaccines, and the use of various drugs have contributed to controlling the COVID-19 pandemic. Nevertheless, challenges such as the inequitable distribution of vaccines, the influence of emerging viral lineages and immune evasive variants on vaccine efficacy, and the inadequate immune defense in subgroups of the population continue to motivate the development of new drugs to combat the disease.</jats:p>\n <jats:p> \n <jats:bold>Aim:</jats:bold>In this study, we sought to identify, prioritize, and characterize drug repurposing candidates appropriate for treating mild, moderate, or severe COVID-19 using a network-based integrative approach that systematically integrates drug-related data and multi-omics datasets.</jats:p>\n <jats:p> \n <jats:bold>Methods</jats:bold>: We leveraged drug data, and multi-omics data, and used a random walk restart algorithm to explore an integrated knowledge graph comprised of three sub-graphs: (i) a COVID-19 knowledge graph, (ii) a drug repurposing knowledge graph, and (iii) a COVID-19 disease-state specific omics graph.</jats:p>\n <jats:p> \n <jats:bold>Results:</jats:bold>We prioritized twenty FDA-approved agents as potential candidate drugs for mild, moderate, and severe COVID-19 disease phases. Specifically, drugs that could stimulate immune cell recruitment and activation including histamine, curcumin, and paclitaxel have potential utility in mild disease states to mitigate disease progression. Drugs like omacetaxine, crizotinib, and vorinostat that exhibit antiviral properties and have the potential to inhibit viral replication can be considered for mild to moderate COVID-19 disease states. Also, given the association between antioxidant deficiency and high inflammatory factors that trigger cytokine storms, antioxidants like glutathione can be considered for moderate disease states. Drugs that exhibit potent anti-inflammatory effects like (i) anti-inflammatory drugs (sarilumab and tocilizumab), (ii) corticosteroids (dexamethasone and hydrocortisone), and (iii) immunosuppressives (sirolimus and cyclosporine) are potential candidates for moderate to severe disease states that trigger a hyperinflammatory cascade of COVID-19.</jats:p>\n <jats:p> \n <jats:bold>Conclusion:</jats:bold>Our study demonstrates that the multi-omics data-driven integrative analysis within the drug data enables prioritizing drug candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, offering a comprehensive basis for therapeutic strategies that can be brought to market quickly given their established safety profiles. Importantly, the multi-omics data-driven integrative analysis within the drug data approach implemented here can be used to prioritize drug repurposing candidates appropriate for other diseases.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2980-1392",
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/03p74gp79",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Computational Biology Division, Department of Integrative Biomedical Sciences, Institute of Infectious Disease and Molecular Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Agamah",
"given": "Francis Edem",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/05wg1m734",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Medical BioSciences, Radboud University Medical Center Nijmegen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "Ederveen",
"given": "Thomas H.A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/03p74gp79",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Computational Biology Division, Department of Integrative Biomedical Sciences, Institute of Infectious Disease and Molecular Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa"
}
],
"family": "Skelton",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/03p74gp79",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Computational Biology Division, Department of Integrative Biomedical Sciences, Institute of Infectious Disease and Molecular Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa"
}
],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Darren P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/049e6bc10",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Applied Science, Faculty of Health and Life Sciences, Northumbria University, Newcastle, Tyne and Wear, NE1 8ST, UK"
}
],
"family": "Chimusa",
"given": "Emile R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/05wg1m734",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Medical BioSciences, Radboud University Medical Center Nijmegen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "'t Hoen",
"given": "Peter A.C. 't Hoen",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-17T13:50:17Z",
"timestamp": 1713361817000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-17T13:50:18Z",
"timestamp": 1713361818000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"184.034.019"
],
"name": "Dutch Organization of Scientific Research"
},
{
"award": [
"871096"
],
"name": "European Union to the EATRIS-Plus infrastructure project"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-18T02:13:26Z",
"timestamp": 1713406406464
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "ScienceOpen"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
16
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1713225600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://drugrepocentral.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "5403",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
16
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.58647",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "ScienceOpen",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://drugrepocentral.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases",
"type": "posted-content"
}
agamah