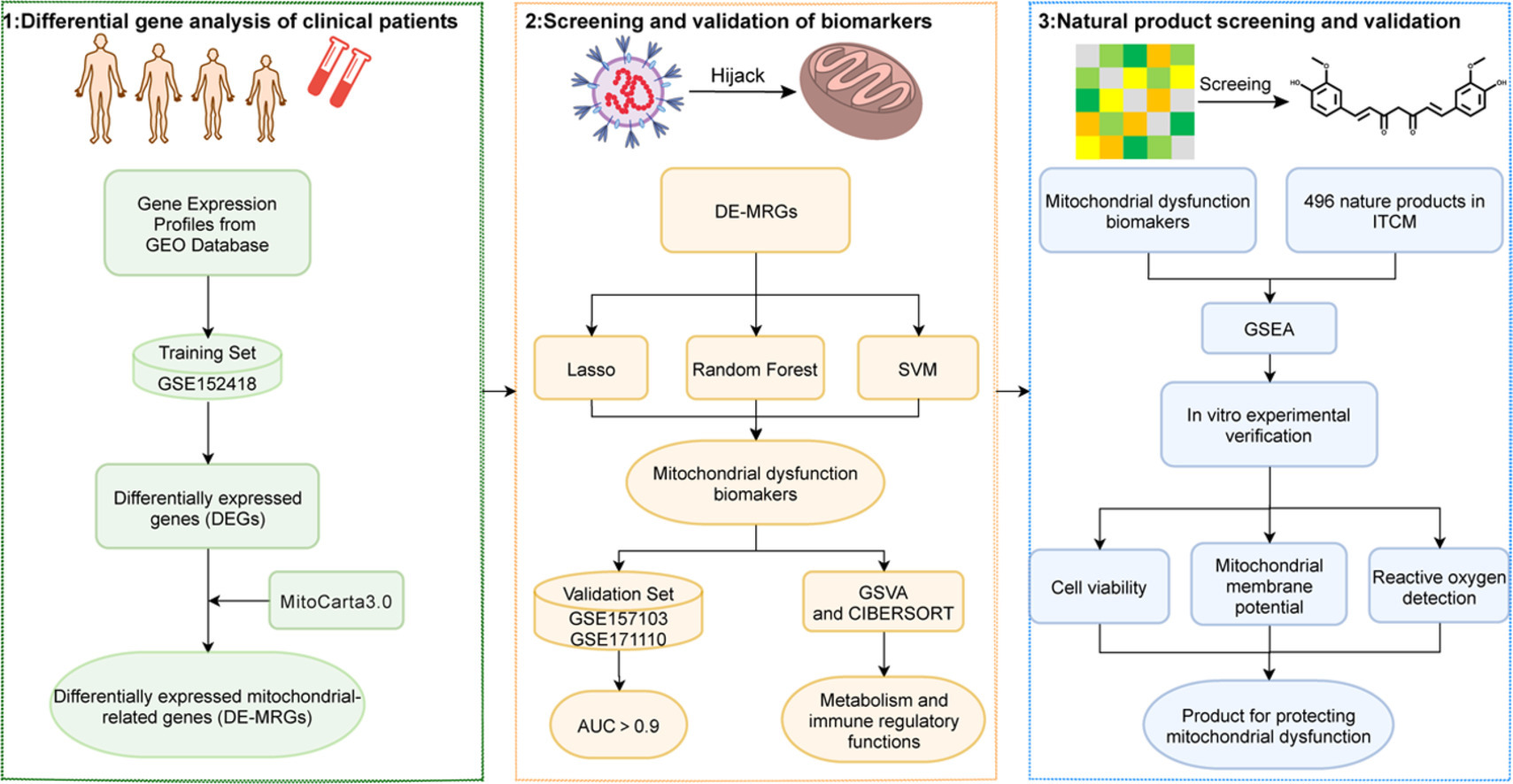
Computational Discovery of Mitochondrial Dysfunction Biomarkers in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Facilitating Pytomedicine Screening
et al., Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784, May 2024
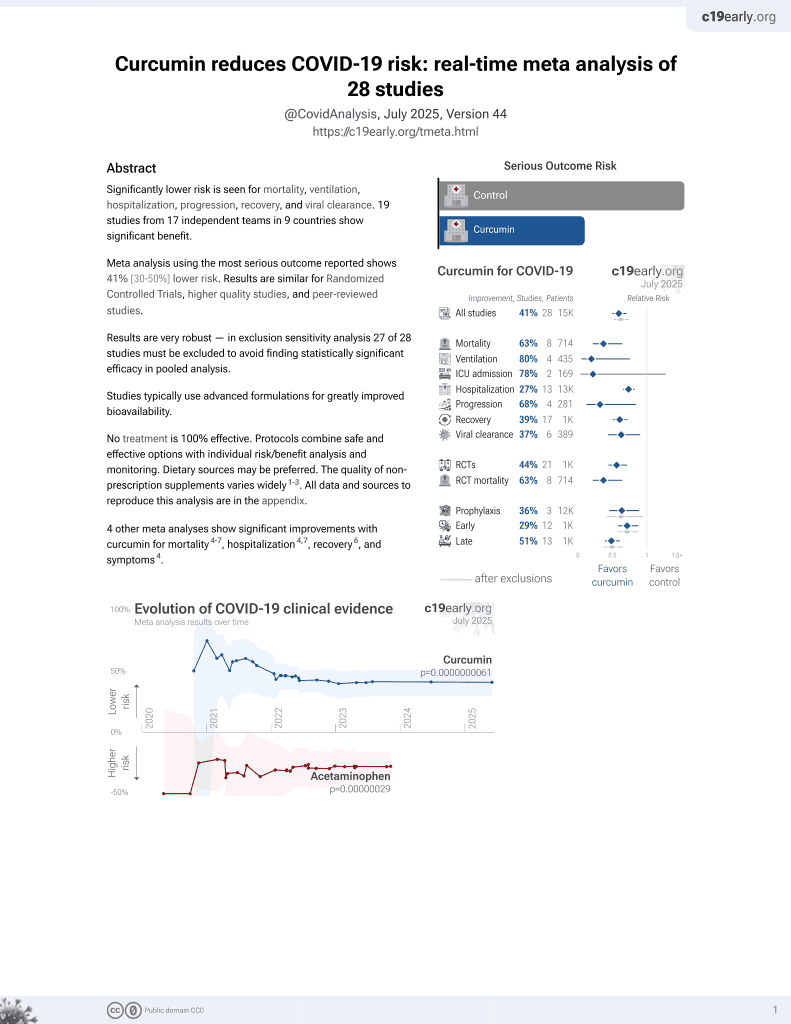
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In silico and in vitro study showing potential benefits of curcumin for severe COVID-19 by protecting mitochondrial function and reducing dysregulated metabolism and immune response. Authors identified five mitochondrial dysfunction biomarkers (RECQL4, PYCR1, PIF1, POLQ, GLDC) that distinguish severe COVID-19 patients and regulate abnormal metabolism and immunity. In silico screening of 496 natural compounds found curcumin had the highest potential to modulate these biomarkers. In vitro, pre-treatment with curcumin for 8 hours alleviated SARS-CoV-2 S1 protein-induced mitochondrial membrane potential damage and reduced elevated reactive oxygen species levels in cells.
62 preclinical studies support the efficacy of curcumin for COVID-19:
In silico studies predict inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 with curcumin or metabolites via binding to the spikeA,1,5,6,11,16,18,24,27 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,2,4,14,17,20 ), MproC,4-6,11,13,15-17,19,20,22,25,27,28,30,48 , RNA-dependent RNA polymeraseD,4-6,17,26 , PLproE,6, ACE2F,2,18,19,21 , nucleocapsidG,12,29 , nsp10H,29, and helicaseI,36 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3.
In vitro studies demonstrate inhibition of the spikeA,41 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,51), MproC,23,41,48,50 , ACE2F,51, and TMPRSS2K,51 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3,34 .
In vitro studies demonstrate efficacy in Calu-3L,49, A549M,41, A549-ATN,31, 293TO,7, HEK293-hACE2P,23,39 , 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2Q,40, Vero E6R,1,13,17,27,39,41,43,45,47,49 , and SH-SY5YS,38 cells.
Curcumin decreases pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by SARS-CoV-2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells47, alleviates SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-induced mitochondrial membrane damage and oxidative stress7, may limit COVID-19 induced cardiac damage by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway which mediates the profibrotic effects of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein on cardiac fibroblasts35, is predicted to inhibit the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain and the human ACE2 receptor for the delta and omicron variants14, lowers ACE2 and STAT3, curbing lung inflammation and ARDS in preclinical COVID-19 models32, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a ion channel activity, which contributes to viral pathogenicity and cytotoxicity42, has direct virucidal action by disrupting viral envelope integrity44, may inhibit viral replication and modulate inflammatory pathways like NF-κB via SIRT1 activation52, and can function as a photosensitizer in photodynamic therapy to generate reactive oxygen species that damage the virus44.
1.
Marzouk et al., Computational and Experimental Insights into the Antiviral Mechanism of Turmeric (Curcuma longa) against SARS-CoV-2 D614G, BIO Web of Conferences, doi:10.1051/bioconf/202519804002.
2.
Wu et al., Utilizing natural compounds as ligands to disrupt the binding of SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, impeding viral infection, Phytochemistry Letters, doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2025.102999.
3.
Najimi et al., Phytochemical Inhibitors of SARS‐CoV‐2 Entry: Targeting the ACE2‐RBD Interaction with l‐Tartaric Acid, l‐Ascorbic Acid, and Curcuma longa Extract, ChemistrySelect, doi:10.1002/slct.202406035.
4.
Rajamanickam et al., Exploring the Potential of Siddha Formulation MilagaiKudineer-Derived Phytotherapeutics Against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Investigation for Antiviral Intervention, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, doi:10.26502/fjppr.0105.
5.
Al balawi et al., Assessing multi-target antiviral and antioxidant activities of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2: an integrated in vitro and in silico study, Bioresources and Bioprocessing, doi:10.1186/s40643-024-00822-z.
6.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
7.
Zhang et al., Computational Discovery of Mitochondrial Dysfunction Biomarkers in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Facilitating Pytomedicine Screening, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784.
8.
Öztürkkan et al., In Silico investigation of the effects of curcuminoids on the spike protein of the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, Baku State University Journal of Chemistry and Material Sciences, 1:2, bsuj.bsu.edu.az/uploads/pdf/ec4204d62f7802de54e6092bf7860029.pdf.
9.
Yunze et al., Therapeutic effect and potential mechanism of curcumin, an active ingredient in Tongnao Decoction, on COVID-19 combined with stroke: a network pharmacology study and GEO database mining, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4329762/v1.
10.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
11.
Boseila et al., Throat spray formulated with virucidal Pharmaceutical excipients as an effective early prophylactic or treatment strategy against pharyngitis post-exposure to SARS CoV-2, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2024.114279.
12.
Hidayah et al., Bioinformatics study of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin and cyclocurcumin compounds in Curcuma longa as an antiviral agent via nucleocapsid on SARS-CoV-2 inhibition, International Conference on Organic and Applied Chemistry, doi:10.1063/5.0197724.
13.
Singh et al., Unlocking the potential of phytochemicals in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 M Pro protein - An in-silico and cell-based approach, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3888947/v1.
14.
Kant et al., Structure-based drug discovery to identify SARS-CoV2 spike protein–ACE2 interaction inhibitors, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2023.2300060.
15.
Naderi Beni et al., In silico studies of anti-oxidative and hot temperament-based phytochemicals as natural inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0295014.
16.
Moschovou et al., Exploring the Binding Effects of Natural Products and Antihypertensive Drugs on SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Investigation of Main Protease and Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242115894.
17.
Eleraky et al., Curcumin Transferosome-Loaded Thermosensitive Intranasal in situ Gel as Prospective Antiviral Therapy for SARS-Cov-2, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S423251.
18.
Singh (B) et al., Computational studies to analyze effect of curcumin inhibition on coronavirus D614G mutated spike protein, The Seybold Report, doi:10.17605/OSF.IO/TKEXJ.
19.
Thapa et al., In-silico Approach for Predicting the Inhibitory Effect of Home Remedies on Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2, Makara Journal of Science, doi:10.7454/mss.v27i3.1609.
20.
Srivastava et al., Paradigm of Well-Orchestrated Pharmacokinetic Properties of Curcuminoids Relative to Conventional Drugs for the Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 Receptors: An In Silico Approach, Stresses, doi:10.3390/stresses3030043.
21.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
22.
Winih Kinasih et al., Analisis in silico interaksi senyawa kurkuminoid terhadap enzim main protease 6LU7 dari SARS-CoV-2, Duta Pharma Journal, doi:10.47701/djp.v3i1.2904.
23.
Wu (B) et al., Potential Mechanism of Curcumin and Resveratrol against SARS-CoV-2, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2780614/v1.
24.
Nag et al., Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552.
25.
Rampogu et al., Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations Discover Curcumin Analogue as a Plausible Dual Inhibitor for SARS-CoV-2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23031771.
26.
Singh (C) et al., Potential of turmeric-derived compounds against RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2: An in-silico approach, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104965.
27.
Kandeil et al., Bioactive Polyphenolic Compounds Showing Strong Antiviral Activities against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10060758.
28.
Rajagopal et al., Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach, Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x.
29.
Suravajhala et al., Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin with COVID-19 Proteins, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v3.
30.
Sekiou et al., In-Silico Identification of Potent Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) from Natural Products: Quercetin, Hispidulin, and Cirsimaritin Exhibited Better Potential Inhibition than Hydroxy-Chloroquine Against COVID-19 Main Protease Active Site and ACE2, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12181404.v1.
31.
Grüneberg et al., Dose-dependent antiviral effects of glycyrrhizin, curcumin, and harmaline against clinical SARS-CoV-2 isolates, including D614G, Omicron BA.5, and Omicron XBB.1, BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, doi:10.1186/s12906-026-05253-1.
32.
Aktay et al., Oral Administration of Water-Soluble Curcumin Complex Prevents ARDS With the Potential for COVID-19 Treatment, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.70046.
33.
Olubiyi et al., Novel dietary herbal preparations with inhibitory activities against multiple SARS-CoV-2 targets: A multidisciplinary investigation into antiviral activities, Food Chemistry Advances, doi:10.1016/j.focha.2025.100969.
34.
Emam et al., Establishment of in-house assay for screening of anti-SARS-CoV-2 protein inhibitors, AMB Express, doi:10.1186/s13568-024-01739-8.
35.
Van Tin et al., Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Activates Cardiac Fibrogenesis through NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161331.
36.
Li et al., Thermal shift assay (TSA)-based drug screening strategy for rapid discovery of inhibitors against the Nsp13 helicase of SARS-CoV-2, Animals and Zoonoses, doi:10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001.
37.
Kamble et al., Nanoparticulate curcumin spray imparts prophylactic and therapeutic properties against SARS-CoV-2, Emergent Materials, doi:10.1007/s42247-024-00754-6.
38.
Nicoliche et al., Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin and curcuminoids in SH-SY5Y cells infected by SARS-CoV-2, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7.
39.
Nittayananta et al., A novel film spray containing curcumin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus infection and enhances mucosal immunity, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02282-x.
40.
Septisetyani et al., Curcumin and turmeric extract inhibited SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus cell entry and Spike mediated cell fusion, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.09.28.560070.
41.
Mohd Abd Razak et al., In Vitro Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activities of Curcumin and Selected Phenolic Compounds, Natural Product Communications, doi:10.1177/1934578X231188861.
42.
Fam et al., Channel activity of SARS-CoV-2 viroporin ORF3a inhibited by adamantanes and phenolic plant metabolites, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31764-9.
43.
Teshima et al., Antiviral activity of curcumin and its analogs selected by an artificial intelligence-supported activity prediction system in SARS-CoV-2-infected VeroE6 cells, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2023.2194647.
44.
Zupin et al., Optimization of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Treatments Based on Curcumin, Used Alone or Employed as a Photosensitizer, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14102132.
45.
Leka et al., In vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 of common herbal medicinal extracts and their bioactive compounds, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7463.
46.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
47.
Marín-Palma et al., Curcumin Inhibits In Vitro SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vero E6 Cells through Multiple Antiviral Mechanisms, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26226900.
48.
Bahun et al., Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro main protease by plant polyphenols, Food Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131594.
49.
Bormann et al., Turmeric Root and Its Bioactive Ingredient Curcumin Effectively Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13101914.
50.
Guijarro-Real et al., Potential In Vitro Inhibition of Selected Plant Extracts against SARS-CoV-2 Chymotripsin-Like Protease (3CLPro) Activity, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods10071503.
a.
The trimeric spike (S) protein is a glycoprotein that mediates viral entry by binding to the host ACE2 receptor, is critical for SARS-CoV-2's ability to infect host cells, and is a target of neutralizing antibodies. Inhibition of the spike protein prevents viral attachment, halting infection at the earliest stage.
b.
The receptor binding domain is a specific region of the spike protein that binds ACE2 and is a major target of neutralizing antibodies. Focusing on the precise binding site allows highly specific disruption of viral attachment with reduced potential for off-target effects.
c.
The main protease or Mpro, also known as 3CLpro or nsp5, is a cysteine protease that cleaves viral polyproteins into functional units needed for replication. Inhibiting Mpro disrupts the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle within the host cell, preventing the creation of new copies.
d.
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called nsp12, is the core enzyme of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex that copies the positive-sense viral RNA genome into negative-sense templates for progeny RNA synthesis. Inhibiting RdRp blocks viral genome replication and transcription.
e.
The papain-like protease (PLpro) has multiple functions including cleaving viral polyproteins and suppressing the host immune response by deubiquitination and deISGylation of host proteins. Inhibiting PLpro may block viral replication and help restore normal immune responses.
f.
The angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) protein is a host cell transmembrane protein that serves as the cellular receptor for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. ACE2 is expressed on many cell types, including epithelial cells in the lungs, and allows the virus to enter and infect host cells. Inhibition may affect ACE2's physiological function in blood pressure control.
g.
The nucleocapsid (N) protein binds and encapsulates the viral genome by coating the viral RNA. N enables formation and release of infectious virions and plays additional roles in viral replication and pathogenesis. N is also an immunodominant antigen used in diagnostic assays.
h.
Non-structural protein 10 (nsp10) serves as an RNA chaperone and stabilizes conformations of nsp12 and nsp14 in the replicase-transcriptase complex, which synthesizes new viral RNAs. Nsp10 disruption may destabilize replicase-transcriptase complex activity.
i.
The helicase, or nsp13, protein unwinds the double-stranded viral RNA, a crucial step in replication and transcription. Inhibition may prevent viral genome replication and the creation of new virus components.
j.
The interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the human ACE2 receptor is a primary method of viral entry, inhibiting this interaction can prevent the virus from attaching to and entering host cells, halting infection at an early stage.
k.
Transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) is a host cell protease that primes the spike protein, facilitating cellular entry. TMPRSS2 activity helps enable cleavage of the spike protein required for membrane fusion and virus entry. Inhibition may especially protect respiratory epithelial cells, buy may have physiological effects.
l.
Calu-3 is a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line with moderate ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. It provides a model of the human respiratory epithelium, but many not be ideal for modeling early stages of infection due to the moderate expression levels of ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
m.
A549 is a human lung carcinoma cell line with low ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Viral entry/replication can be studied but the cells may not replicate all aspects of lung infection.
n.
A549-AT is a human lung carcinoma cell line stably transfected with ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors. Unlike the parental line, this overexpression ensures stable infection and enhanced viral entry, allowing for the evaluation of antiviral efficacy against various SARS-CoV-2 variants.
o.
293T is a human embryonic kidney cell line that can be engineered for high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. 293T cells are easily transfected and support high protein expression.
p.
HEK293-hACE2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line with high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Cells have been transfected with a plasmid to express the human ACE2 (hACE2) protein.
q.
293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line engineered for high ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression, which mimics key aspects of human infection. 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 cells are very susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
r.
Vero E6 is an African green monkey kidney cell line with low/no ACE2 expression and high SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. The cell line is easy to maintain and supports robust viral replication, however the monkey origin may not accurately represent human responses.
s.
SH-SY5Y is a human neuroblastoma cell line that exhibits neuronal phenotypes. It is commonly used as an in vitro model for studying neurotoxicity, neurodegenerative diseases, and neuronal differentiation.
Zhang et al., 31 May 2024, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784",
"ISSN": [
"0944-7113"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784",
"alternative-id": [
"S0944711324004422"
],
"article-number": "155784",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Computational Discovery of Mitochondrial Dysfunction Biomarkers in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Facilitating Pytomedicine Screening"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Phytomedicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 Published by Elsevier GmbH."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Lihui",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Yuehan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Wanting",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Shengqiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tang",
"given": "Yiran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Ning",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xiao",
"given": "Zhiyong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Han",
"given": "Lu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Wenxia",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Phytomedicine",
"container-title-short": "Phytomedicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-28T20:30:06Z",
"timestamp": 1716928206000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-28T20:30:57Z",
"timestamp": 1716928257000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82141218"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012166",
"award": [
"2022YFC3500304"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Key Research and Development Program of China"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-29T00:28:06Z",
"timestamp": 1716942486584
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714521600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714521600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714521600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714521600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714521600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714521600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714521600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0944711324004422?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0944711324004422?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "155784",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13321-022-00644-1",
"article-title": "Random-forest model for drug-target interaction prediction via Kullbeck-Leibler divergence",
"author": "Ahn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "67",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Cheminformatics.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0001",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.109976",
"article-title": "Mitochondria and immunity in chronic fatigue syndrome",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0002",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc6261",
"article-title": "Systems biological assessment of immunity to mild versus severe COVID-19 infection in humans",
"author": "Arunachalam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1210",
"issue": "6508",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0003",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-15-293",
"article-title": "jvenn: an interactive Venn diagram viewer",
"author": "Bardou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "293",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Bioinform",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0004",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets–update",
"author": "Barrett",
"first-page": "D991",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0005",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00726-021-02999-5",
"article-title": "Structure, biochemistry, and gene expression patterns of the proline biosynthetic enzyme pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase (PYCR), an emerging cancer therapy target",
"author": "Bogner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1817",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Amino acids",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0006",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13101914",
"article-title": "Turmeric Root and Its Bioactive Ingredient Curcumin Effectively Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro",
"author": "Bormann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1914",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0007",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2023.07.019",
"article-title": "Epigenetic memory of coronavirus infection in innate immune cells and their progenitors",
"author": "Cheong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0008",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biocel.2012.07.016",
"article-title": "RecQL4 cytoplasmic localization: implications in mitochondrial DNA oxidative damage repair",
"author": "Chi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1942",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0009",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/liv.13441",
"article-title": "The transformation in biomarker detection and management of drug-induced liver injury",
"author": "Church",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1582",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Liver Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0010",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.07.007",
"article-title": "Elevated Glucose Levels Favor SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Monocyte Response through a HIF-1α/Glycolysis-Dependent Axis",
"author": "Codo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0011",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2023.107283",
"article-title": "Failing categorization of severe COVID-19 ARDS into ventilatory subphenotypes studied via the clinical-histopathologic relationship",
"author": "Colombo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "RESP MED",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0012",
"volume": "215",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43044-021-00234-w",
"article-title": "Bilirubin levels as an independent predictor of myocarditis in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Cosgun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Egypt Heart J",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0013",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00803.x",
"article-title": "RECQL4 localizes to mitochondria and preserves mitochondrial DNA integrity",
"author": "Croteau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "456",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Aging cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0014",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/gb-2003-4-5-p3",
"article-title": "DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery",
"author": "Dennis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "P3",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Genome Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0015",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2021.01.016",
"article-title": "Diabetes, obesity, metabolism, and SARS-CoV-2 infection: the end of the beginning",
"author": "Drucker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "479",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0016",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.946731",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Achieves Immune Escape by Destroying Mitochondrial Quality: Comprehensive Analysis of the Cellular Landscapes of Lung and Blood Specimens From Patients With COVID-19",
"author": "Duan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0017",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13148-019-0730-1",
"article-title": "Statistical predictions with glmnet",
"author": "Engebretsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "123",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin Epigenetics",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0018",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/728751",
"article-title": "Curcumin inhibits mitochondrial injury and apoptosis from the early stage in EAE mice",
"author": "Feng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0019",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/emmm.202013001",
"article-title": "Altered bioenergetics and mitochondrial dysfunction of monocytes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Gibellini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13001",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0020",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-15668-8",
"article-title": "Differential chromatin accessibility in peripheral blood mononuclear cells underlies COVID-19 disease severity prior to seroconversion",
"author": "Giroux",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11714",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0021",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27068",
"article-title": "Cytokine storm in severe COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Gürsoy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5474",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0022",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abq1533",
"article-title": "Core mitochondrial genes are down-regulated during SARS-CoV-2 infection of rodent and human hosts",
"author": "Guarnieri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabq1533",
"issue": "708",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0023",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-14-7",
"article-title": "GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data",
"author": "Hänzelmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "BMC Bioinf",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0024",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Applications of Support Vector Machine (SVM) Learning in Cancer Genomics",
"author": "Huang",
"first-page": "41",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cancer Genomics Proteomics",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0025",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26232",
"article-title": "The cytokine storm and COVID-19",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "250",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0026",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000925",
"article-title": "Drug-induced regulation of target expression",
"author": "Iskar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "PLOS COMPUT BIOL",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0027",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04702-4",
"article-title": "FcγR-mediated SARS-CoV-2 infection of monocytes activates inflammation",
"author": "Junqueira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "576",
"issue": "7914",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0028",
"volume": "606",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/28.1.27",
"article-title": "KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes",
"author": "Kanehisa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0029",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"article-title": "Mitochondrial functions of RECQL4 are required for the prevention of aerobic glycolysis-dependent cell invasion",
"author": "Kumari",
"first-page": "1312",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0030",
"volume": "129",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08034.x",
"article-title": "PIF1: a DNA helicase in yeast mitochondria",
"author": "Lahaye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "997",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "EMBO J",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0031",
"volume": "10",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318902",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Impairs Endothelial Function via Downregulation of ACE 2",
"author": "Lei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1323",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "CIRC RES",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0032",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2021.102711",
"article-title": "CD177, a specific marker of neutrophil activation, is associated with coronavirus disease 2019 severity and death",
"author": "Lévy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0033",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.12.019",
"article-title": "Design and characterization of α-lipoic acyl shikonin ester twin drugs as tubulin and PDK1 dual inhibitors",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0034",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00726-021-03047-y",
"article-title": "PYCR, a key enzyme in proline metabolism, functions in tumorigenesis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1841",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Amino acids",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0035",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-37567-w",
"article-title": "Neutrophil metabolomics in severe COVID-19 reveal GAPDH as a suppressor of neutrophil extracellular trap formation",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2610",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0036",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jgv.0.001466",
"article-title": "Antiviral and virucidal effects of curcumin on transmissible gastroenteritis virus in vitro",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1079",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J. Gen. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0037",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26226900",
"article-title": "Curcumin Inhibits In Vitro SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vero E6 Cells through Multiple Antiviral Mechanisms",
"author": "Marín-Palma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6900",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0038",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI59755",
"article-title": "The mechanism underlying acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in humans and mice involves mitochondrial damage and nuclear DNA fragmentation",
"author": "McGill",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1574",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0039",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-021-00407-6",
"article-title": "Acute and long-term disruption of glycometabolic control after SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Montefusco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "774",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nat. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0040",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.3337",
"article-title": "Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles",
"author": "Newman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "453",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat. Methods.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0041",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Large-Scale Multi-omic Analysis of COVID-19 Severity",
"author": "Overmyer",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Syst",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0042",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkaa1011",
"article-title": "MitoCarta3.0: an updated mitochondrial proteome now with sub-organelle localization and pathway annotations",
"author": "Rath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "D1541",
"issue": "D1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0043",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jim-2016-000240",
"article-title": "Protective effects of a natural product, curcumin, against amyloid β induced mitochondrial and synaptic toxicities in Alzheimer's disease",
"author": "Reddy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1220",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J INVEST MED",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0044",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.053",
"article-title": "COVID-19 immune features revealed by a large-scale single-cell transcriptome atlas",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0045",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkv007",
"article-title": "limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies",
"author": "Ritchie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e47",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0046",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-12-77",
"article-title": "pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves",
"author": "Robin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "BMC Bioinf",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0047",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom12101405",
"article-title": "The Credible Role of Curcumin in Oxidative Stress-Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Mammals",
"author": "Sathyabhama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1405",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Biomolecules",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0048",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/gr.1239303",
"article-title": "Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks",
"author": "Shannon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2498",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Genome Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0049",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41556-018-0124-1",
"article-title": "The multifaceted contributions of mitochondria to cellular metabolism",
"author": "Spinelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "745",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nat. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0050",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0506580102",
"article-title": "Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles",
"author": "Subramanian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15545",
"issue": "43",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0051",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkac1000",
"article-title": "The STRING database in 2023: protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest",
"author": "Szklarczyk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "D638",
"issue": "D1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0052",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmc.2012.05.055",
"article-title": "Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling of novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives based on Vanillic acid as potential immunosuppressive agents",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4226",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "BIOORGAN MED CHEM",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0053",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bib/bbad027",
"article-title": "Exploring pharmacological active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine by pharmacotranscriptomic map in ITCM",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Brief. Bioinformatics.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0054",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00474.2020",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2: influence of phosphate and magnesium, moderated by vitamin D, on energy (ATP) metabolism and on severity of COVID-19",
"author": "van Kempen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E2",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0055",
"volume": "320",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12944-020-01382-9",
"article-title": "Low high-density lipoprotein level is correlated with the severity of COVID-19 patients: an observational study",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "204",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Lipids Health Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0056",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110320",
"article-title": "Proline synthesis through PYCR1 is required to support cancer cell proliferation and survival in oxygen-limiting conditions",
"author": "Westbrook",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0057",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.003",
"article-title": "DNA polymerase θ (POLQ), double-strand break repair, and cancer",
"author": "Wood",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "22",
"journal-title": "DNA Repair (Amst.)",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0058",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2018030117",
"article-title": "Transcriptional and proteomic insights into the host response in fatal COVID-19 cases",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28336",
"issue": "45",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0059",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.snb.2018.08.138",
"article-title": "A selective fluorescence probe for H2S from biothiols with a significant regioselective turn-on response and its application for H2S detection in living cells and in living Caenorhabditis elegans",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "456",
"journal-title": "Sens. Actuators B Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0060",
"volume": "276",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-022-00928-x",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein causes the mitochondrial apoptosis and pulmonary edema via targeting BOK",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1395",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0061",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmc.2016.05.012",
"article-title": "Design, biological evaluation and 3D QSAR studies of novel dioxin-containing triaryl pyrazoline derivatives as potential B-Raf inhibitors",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3052",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "BIOORGAN MED CHEM",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0062",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection alters mitochondrial and cytoskeletal function in human respiratory epithelial cells mediated by expression of spike protein",
"author": "Yeung-Luk",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0063",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/omi.2011.0118",
"article-title": "clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "284",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "OMICS",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0064",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3377",
"article-title": "Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19)",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e3377",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784_bib0065",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 65,
"references-count": 65,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0944711324004422"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Computational Discovery of Mitochondrial Dysfunction Biomarkers in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Facilitating Pytomedicine Screening",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}