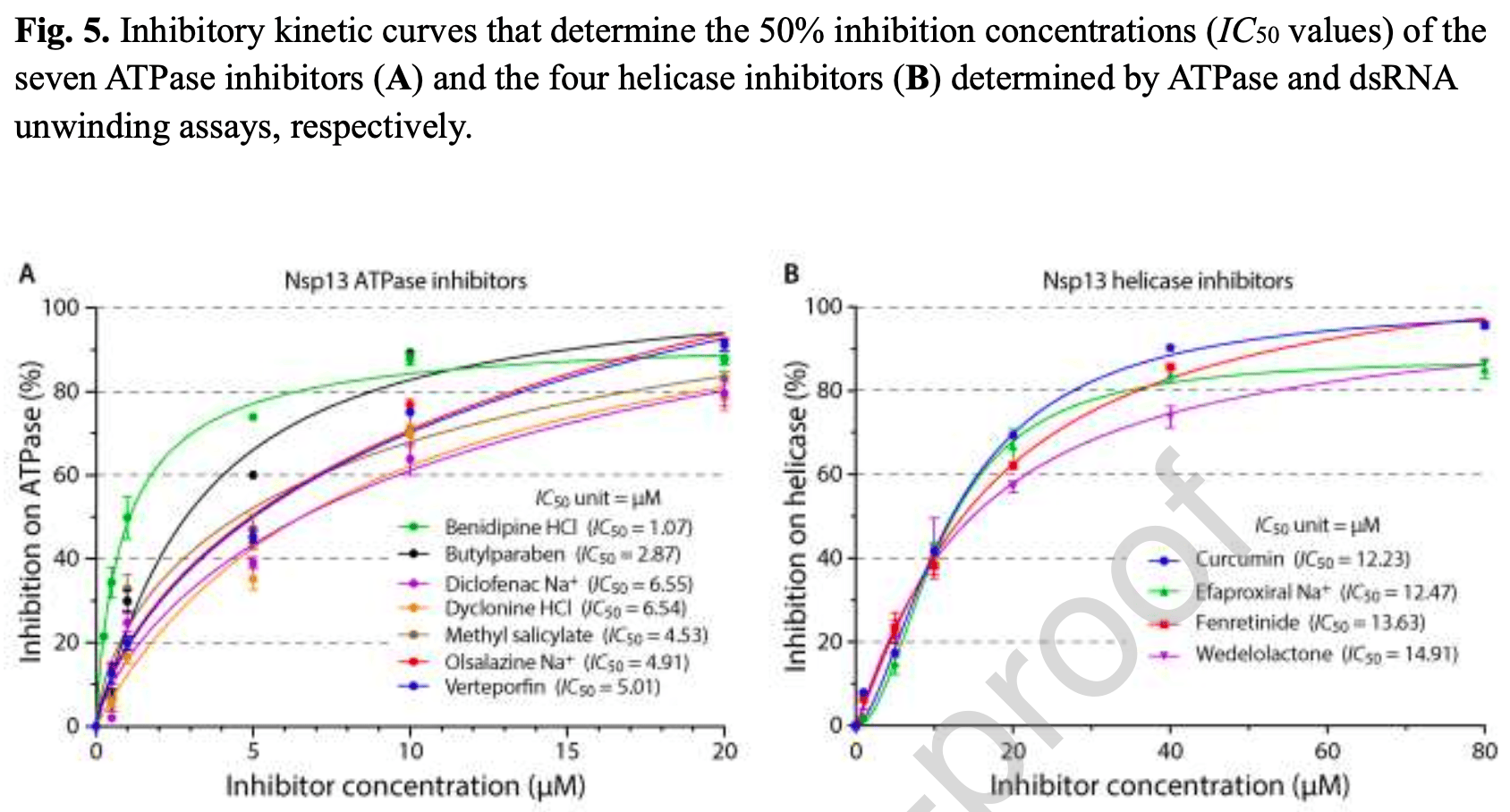
Thermal shift assay (TSA)-based drug screening strategy for rapid discovery of inhibitors against the Nsp13 helicase of SARS-CoV-2
et al., Animals and Zoonoses, doi:10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001, Jul 2024
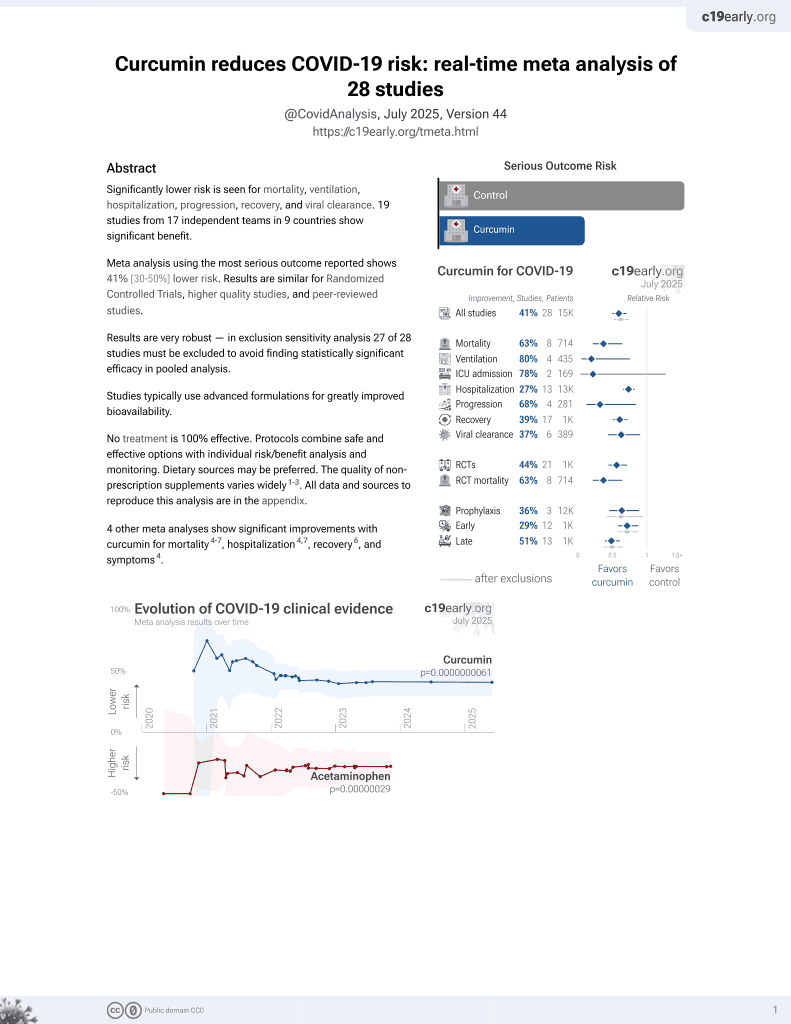
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro study showing that 11 compounds inhibited the SARS-CoV-2 helicase Nsp13, with 7 compounds inhibiting ATPase activity and 4 inhibiting RNA unwinding activity at micromolar concentrations. Authors screened 1,970 FDA-approved drugs using a thermal shift assay, identifying 26 top binders to Nsp13. Biochemical assays confirmed 7 ATPase inhibitors (verteporfin, olsalazine sodium, diclofenac, benidipine, dyclonine, methyl salicylate, butylparaben; IC50 1.07-6.55 μM) and 4 RNA unwinding inhibitors (efaproxiral, fenretinide, curcumin, wedelolactone; IC50 12.23-14.91 μM). The inhibitors were reversible and docking predicted binding to Nsp13's ATPase or RNA binding domains. Curcumin was the most promising helicase inhibitor identified.
62 preclinical studies support the efficacy of curcumin for COVID-19:
In silico studies predict inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 with curcumin or metabolites via binding to the spikeA,1,5,6,11,16,18,24,27 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,2,4,14,17,20 ), MproC,4-6,11,13,15-17,19,20,22,25,27,28,30,48 , RNA-dependent RNA polymeraseD,4-6,17,26 , PLproE,6, ACE2F,2,18,19,21 , nucleocapsidG,12,29 , nsp10H,29, and helicaseI,36 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3.
In vitro studies demonstrate inhibition of the spikeA,41 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,51), MproC,23,41,48,50 , ACE2F,51, and TMPRSS2K,51 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3,34 .
In vitro studies demonstrate efficacy in Calu-3L,49, A549M,41, A549-ATN,31, 293TO,7, HEK293-hACE2P,23,39 , 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2Q,40, Vero E6R,1,13,17,27,39,41,43,45,47,49 , and SH-SY5YS,38 cells.
Curcumin decreases pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by SARS-CoV-2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells47, alleviates SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-induced mitochondrial membrane damage and oxidative stress7, may limit COVID-19 induced cardiac damage by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway which mediates the profibrotic effects of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein on cardiac fibroblasts35, is predicted to inhibit the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain and the human ACE2 receptor for the delta and omicron variants14, lowers ACE2 and STAT3, curbing lung inflammation and ARDS in preclinical COVID-19 models32, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a ion channel activity, which contributes to viral pathogenicity and cytotoxicity42, has direct virucidal action by disrupting viral envelope integrity44, may inhibit viral replication and modulate inflammatory pathways like NF-κB via SIRT1 activation52, and can function as a photosensitizer in photodynamic therapy to generate reactive oxygen species that damage the virus44.
1.
Marzouk et al., Computational and Experimental Insights into the Antiviral Mechanism of Turmeric (Curcuma longa) against SARS-CoV-2 D614G, BIO Web of Conferences, doi:10.1051/bioconf/202519804002.
2.
Wu et al., Utilizing natural compounds as ligands to disrupt the binding of SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, impeding viral infection, Phytochemistry Letters, doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2025.102999.
3.
Najimi et al., Phytochemical Inhibitors of SARS‐CoV‐2 Entry: Targeting the ACE2‐RBD Interaction with l‐Tartaric Acid, l‐Ascorbic Acid, and Curcuma longa Extract, ChemistrySelect, doi:10.1002/slct.202406035.
4.
Rajamanickam et al., Exploring the Potential of Siddha Formulation MilagaiKudineer-Derived Phytotherapeutics Against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Investigation for Antiviral Intervention, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, doi:10.26502/fjppr.0105.
5.
Al balawi et al., Assessing multi-target antiviral and antioxidant activities of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2: an integrated in vitro and in silico study, Bioresources and Bioprocessing, doi:10.1186/s40643-024-00822-z.
6.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
7.
Zhang et al., Computational Discovery of Mitochondrial Dysfunction Biomarkers in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Facilitating Pytomedicine Screening, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784.
8.
Öztürkkan et al., In Silico investigation of the effects of curcuminoids on the spike protein of the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, Baku State University Journal of Chemistry and Material Sciences, 1:2, bsuj.bsu.edu.az/uploads/pdf/ec4204d62f7802de54e6092bf7860029.pdf.
9.
Yunze et al., Therapeutic effect and potential mechanism of curcumin, an active ingredient in Tongnao Decoction, on COVID-19 combined with stroke: a network pharmacology study and GEO database mining, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4329762/v1.
10.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
11.
Boseila et al., Throat spray formulated with virucidal Pharmaceutical excipients as an effective early prophylactic or treatment strategy against pharyngitis post-exposure to SARS CoV-2, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2024.114279.
12.
Hidayah et al., Bioinformatics study of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin and cyclocurcumin compounds in Curcuma longa as an antiviral agent via nucleocapsid on SARS-CoV-2 inhibition, International Conference on Organic and Applied Chemistry, doi:10.1063/5.0197724.
13.
Singh et al., Unlocking the potential of phytochemicals in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 M Pro protein - An in-silico and cell-based approach, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3888947/v1.
14.
Kant et al., Structure-based drug discovery to identify SARS-CoV2 spike protein–ACE2 interaction inhibitors, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2023.2300060.
15.
Naderi Beni et al., In silico studies of anti-oxidative and hot temperament-based phytochemicals as natural inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0295014.
16.
Moschovou et al., Exploring the Binding Effects of Natural Products and Antihypertensive Drugs on SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Investigation of Main Protease and Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242115894.
17.
Eleraky et al., Curcumin Transferosome-Loaded Thermosensitive Intranasal in situ Gel as Prospective Antiviral Therapy for SARS-Cov-2, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S423251.
18.
Singh (B) et al., Computational studies to analyze effect of curcumin inhibition on coronavirus D614G mutated spike protein, The Seybold Report, doi:10.17605/OSF.IO/TKEXJ.
19.
Thapa et al., In-silico Approach for Predicting the Inhibitory Effect of Home Remedies on Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2, Makara Journal of Science, doi:10.7454/mss.v27i3.1609.
20.
Srivastava et al., Paradigm of Well-Orchestrated Pharmacokinetic Properties of Curcuminoids Relative to Conventional Drugs for the Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 Receptors: An In Silico Approach, Stresses, doi:10.3390/stresses3030043.
21.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
22.
Winih Kinasih et al., Analisis in silico interaksi senyawa kurkuminoid terhadap enzim main protease 6LU7 dari SARS-CoV-2, Duta Pharma Journal, doi:10.47701/djp.v3i1.2904.
23.
Wu (B) et al., Potential Mechanism of Curcumin and Resveratrol against SARS-CoV-2, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2780614/v1.
24.
Nag et al., Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552.
25.
Rampogu et al., Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations Discover Curcumin Analogue as a Plausible Dual Inhibitor for SARS-CoV-2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23031771.
26.
Singh (C) et al., Potential of turmeric-derived compounds against RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2: An in-silico approach, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104965.
27.
Kandeil et al., Bioactive Polyphenolic Compounds Showing Strong Antiviral Activities against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10060758.
28.
Rajagopal et al., Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach, Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x.
29.
Suravajhala et al., Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin with COVID-19 Proteins, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v3.
30.
Sekiou et al., In-Silico Identification of Potent Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) from Natural Products: Quercetin, Hispidulin, and Cirsimaritin Exhibited Better Potential Inhibition than Hydroxy-Chloroquine Against COVID-19 Main Protease Active Site and ACE2, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12181404.v1.
31.
Grüneberg et al., Dose-dependent antiviral effects of glycyrrhizin, curcumin, and harmaline against clinical SARS-CoV-2 isolates, including D614G, Omicron BA.5, and Omicron XBB.1, BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, doi:10.1186/s12906-026-05253-1.
32.
Aktay et al., Oral Administration of Water-Soluble Curcumin Complex Prevents ARDS With the Potential for COVID-19 Treatment, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.70046.
33.
Olubiyi et al., Novel dietary herbal preparations with inhibitory activities against multiple SARS-CoV-2 targets: A multidisciplinary investigation into antiviral activities, Food Chemistry Advances, doi:10.1016/j.focha.2025.100969.
34.
Emam et al., Establishment of in-house assay for screening of anti-SARS-CoV-2 protein inhibitors, AMB Express, doi:10.1186/s13568-024-01739-8.
35.
Van Tin et al., Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Activates Cardiac Fibrogenesis through NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161331.
36.
Li et al., Thermal shift assay (TSA)-based drug screening strategy for rapid discovery of inhibitors against the Nsp13 helicase of SARS-CoV-2, Animals and Zoonoses, doi:10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001.
37.
Kamble et al., Nanoparticulate curcumin spray imparts prophylactic and therapeutic properties against SARS-CoV-2, Emergent Materials, doi:10.1007/s42247-024-00754-6.
38.
Nicoliche et al., Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin and curcuminoids in SH-SY5Y cells infected by SARS-CoV-2, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7.
39.
Nittayananta et al., A novel film spray containing curcumin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus infection and enhances mucosal immunity, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02282-x.
40.
Septisetyani et al., Curcumin and turmeric extract inhibited SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus cell entry and Spike mediated cell fusion, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.09.28.560070.
41.
Mohd Abd Razak et al., In Vitro Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activities of Curcumin and Selected Phenolic Compounds, Natural Product Communications, doi:10.1177/1934578X231188861.
42.
Fam et al., Channel activity of SARS-CoV-2 viroporin ORF3a inhibited by adamantanes and phenolic plant metabolites, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31764-9.
43.
Teshima et al., Antiviral activity of curcumin and its analogs selected by an artificial intelligence-supported activity prediction system in SARS-CoV-2-infected VeroE6 cells, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2023.2194647.
44.
Zupin et al., Optimization of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Treatments Based on Curcumin, Used Alone or Employed as a Photosensitizer, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14102132.
45.
Leka et al., In vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 of common herbal medicinal extracts and their bioactive compounds, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7463.
46.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
47.
Marín-Palma et al., Curcumin Inhibits In Vitro SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vero E6 Cells through Multiple Antiviral Mechanisms, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26226900.
48.
Bahun et al., Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro main protease by plant polyphenols, Food Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131594.
49.
Bormann et al., Turmeric Root and Its Bioactive Ingredient Curcumin Effectively Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13101914.
50.
Guijarro-Real et al., Potential In Vitro Inhibition of Selected Plant Extracts against SARS-CoV-2 Chymotripsin-Like Protease (3CLPro) Activity, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods10071503.
a.
The trimeric spike (S) protein is a glycoprotein that mediates viral entry by binding to the host ACE2 receptor, is critical for SARS-CoV-2's ability to infect host cells, and is a target of neutralizing antibodies. Inhibition of the spike protein prevents viral attachment, halting infection at the earliest stage.
b.
The receptor binding domain is a specific region of the spike protein that binds ACE2 and is a major target of neutralizing antibodies. Focusing on the precise binding site allows highly specific disruption of viral attachment with reduced potential for off-target effects.
c.
The main protease or Mpro, also known as 3CLpro or nsp5, is a cysteine protease that cleaves viral polyproteins into functional units needed for replication. Inhibiting Mpro disrupts the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle within the host cell, preventing the creation of new copies.
d.
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called nsp12, is the core enzyme of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex that copies the positive-sense viral RNA genome into negative-sense templates for progeny RNA synthesis. Inhibiting RdRp blocks viral genome replication and transcription.
e.
The papain-like protease (PLpro) has multiple functions including cleaving viral polyproteins and suppressing the host immune response by deubiquitination and deISGylation of host proteins. Inhibiting PLpro may block viral replication and help restore normal immune responses.
f.
The angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) protein is a host cell transmembrane protein that serves as the cellular receptor for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. ACE2 is expressed on many cell types, including epithelial cells in the lungs, and allows the virus to enter and infect host cells. Inhibition may affect ACE2's physiological function in blood pressure control.
g.
The nucleocapsid (N) protein binds and encapsulates the viral genome by coating the viral RNA. N enables formation and release of infectious virions and plays additional roles in viral replication and pathogenesis. N is also an immunodominant antigen used in diagnostic assays.
h.
Non-structural protein 10 (nsp10) serves as an RNA chaperone and stabilizes conformations of nsp12 and nsp14 in the replicase-transcriptase complex, which synthesizes new viral RNAs. Nsp10 disruption may destabilize replicase-transcriptase complex activity.
i.
The helicase, or nsp13, protein unwinds the double-stranded viral RNA, a crucial step in replication and transcription. Inhibition may prevent viral genome replication and the creation of new virus components.
j.
The interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the human ACE2 receptor is a primary method of viral entry, inhibiting this interaction can prevent the virus from attaching to and entering host cells, halting infection at an early stage.
k.
Transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) is a host cell protease that primes the spike protein, facilitating cellular entry. TMPRSS2 activity helps enable cleavage of the spike protein required for membrane fusion and virus entry. Inhibition may especially protect respiratory epithelial cells, buy may have physiological effects.
l.
Calu-3 is a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line with moderate ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. It provides a model of the human respiratory epithelium, but many not be ideal for modeling early stages of infection due to the moderate expression levels of ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
m.
A549 is a human lung carcinoma cell line with low ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Viral entry/replication can be studied but the cells may not replicate all aspects of lung infection.
n.
A549-AT is a human lung carcinoma cell line stably transfected with ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors. Unlike the parental line, this overexpression ensures stable infection and enhanced viral entry, allowing for the evaluation of antiviral efficacy against various SARS-CoV-2 variants.
o.
293T is a human embryonic kidney cell line that can be engineered for high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. 293T cells are easily transfected and support high protein expression.
p.
HEK293-hACE2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line with high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Cells have been transfected with a plasmid to express the human ACE2 (hACE2) protein.
q.
293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line engineered for high ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression, which mimics key aspects of human infection. 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 cells are very susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
r.
Vero E6 is an African green monkey kidney cell line with low/no ACE2 expression and high SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. The cell line is easy to maintain and supports robust viral replication, however the monkey origin may not accurately represent human responses.
s.
SH-SY5Y is a human neuroblastoma cell line that exhibits neuronal phenotypes. It is commonly used as an in vitro model for studying neurotoxicity, neurodegenerative diseases, and neuronal differentiation.
Li et al., 1 Jul 2024, China, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: cryptosporida@gmail.com (corresponding author).
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Thermal shift assay (TSA)-based drug screening strategy for rapid discovery of inhibitors against the Nsp13 helicase of SARS-CoV-2
Animals and Zoonoses, doi:10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001
Thermal shift assay (TSA)-based drug screening strategy for rapid discovery of inhibitors against the Nsp13 helicase of SARS
CRediT authorship contribution statement Meng Li played a key role in the experimental setup and data collection, and were responsible for ensuring the quality and integrity of the data obtained. In addition, Meng Li contributed to the analysis J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The author Guan Zhu and Chang Li are Editorial Board Member for Animals and Zoonoses and were not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article.
Declaration of interests ☐ The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
References
Bormann, Alt, Schipper, Van De Sand, Vtk et al., Turmeric Root and Its Bioactive Ingredient Curcumin Effectively Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13101914
Chen, Malone, Llewellyn, Grasso, Shelton et al., Structural Basis for Helicase-Polymerase Coupling in the SARS-CoV-2 Replication-Transcription Complex, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.033
Dart, Machleidt, Jost, Schwinn, Robers et al., Homogeneous Assay for Target Engagement Utilizing Bioluminescent Thermal Shift, ACS Med Chem Lett, doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00081
De Groot, Baker, Baric, Brown, Drosten et al., Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): announcement of the Coronavirus Study Group, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01244-13
Donnelly, Liu, Rockwell, Efaproxiral (RSR13) plus oxygen breathing increases the therapeutic ratio of carboplatin in EMT6 mouse mammary tumors, Exp Biol Med (Maywood), doi:10.1177/153537020623100312
Fehr, Perlman, Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis, Methods Mol Biol, doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1
Ferner, Aronson, Remdesivir in covid-19, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1610
Ghosh, Hazra, Pal, Nelson, Pal, Prostate cancer: Therapeutic prospect with herbal medicine, Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100034.Journ
Gordon, Tchesnokov, Woolner, Perry, Feng et al., Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.RA120.013679
Guilbault, Sanctis, Wojewodka, Saeed, Lachance et al., Fenretinide corrects newly found ceramide deficiency in cystic fibrosis, Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, doi:10.1165/rcmb.2007-0036OC
Gupta, Patchva, Aggarwal, Therapeutic roles of curcumin: lessons learned from clinical trials, AAPS J, doi:10.1208/s12248-012-9432-8
Gupta, Song, Lee, Lee, Park et al., Malachite Green Assay for the Discovery of Heat-Shock Protein 90 Inhibitors, J Vis Exp, doi:10.3791/64693
Ha, Hop, Son, Wedelolactone: A molecule of interests, Fitoterapia, doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2022.105355
Hao, Wojdyla, Zhao, Han, Das et al., Crystal structure of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus helicase, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006474
Hou, Khan, Grinberg, Yu, Grinberg et al., The effects of Efaproxyn (efaproxiral) on subcutaneous RIF-1 tumor oxygenation and enhancement of radiotherapy-mediated inhibition of tumor growth in mice, Radiat Res, doi:10.1667/RR0962
Hui, Memish, Zumla, Severe acute respiratory syndrome vs. the Middle East respiratory J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f syndrome, Curr Opin Pulm Med, doi:10.1097/MCP.0000000000000046
Huynh, Partch, Analysis of protein stability and ligand interactions by thermal shift assay, Curr Protoc Protein Sci, doi:10.1002/0471140864.ps2809s79
Iversen, Beck, Chen, Dere, Devanarayan et al., HTS Assay Validation
J O U R N A L P R E, None
Jia, Yan, Ren, Wu, Wang et al., Delicate structural coordination of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus Nsp13 upon ATP hydrolysis, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkz409
Kabinger, Stiller, Schmitzova, Dienemann, Kokic et al., Mechanism of molnupiravir-induced SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis, Nat Struct Mol Biol, doi:10.1038/s41594-021-00651-0
Klein, Barthels, Johe, Wagner, Tenzer et al., Naphthoquinones as Covalent Reversible Inhibitors of Cysteine Proteases-Studies on Inhibition Mechanism and Kinetics, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules25092064
Langer, Bartoschik, Cehlar, Duhr, Baaske et al., A New Spectral Shift-Based Method to Characterize Molecular Interactions, Assay Drug Dev Technol, doi:10.1089/adt.2021.133
Lo, Aulabaugh, Jin, Cowling, Bard et al., Evaluation of fluorescence-based thermal shift assays for hit identification in drug discovery, Anal Biochem, doi:10.1016/j.ab.2004.04.031
Lu, Peng, Yao, Wang, Li et al., Punicalagin as an allosteric NSP13 helicase inhibitor potently suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105389
Malone, Chen, Wang, Llewellyn, Choi et al., Structural basis for backtracking by the SARS-CoV-2 replication-transcription complex, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2102516118
Murail, De Vries, Rey, Moroy, Tuffery, SeamDock: An Interactive and Collaborative Online Docking Resource to Assist Small Compound Molecular Docking, Front Mol Biosci, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.716466
Nelson, Dahlin, Bisson, Graham, Pauli et al., Curcumin May (Not) Defy Science, ACS Med Chem Lett, doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00139
Nelson, Dahlin, Bisson, Graham, Pauli et al., The Essential Medicinal Chemistry of Curcumin, J Med Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00975
Newman, Douangamath, Yadzani, Yosaatmadja, Aimon et al., Structure, mechanism and crystallographic fragment screening of the SARS-CoV-2 NSP13 helicase, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25166-6
Orienti, Gentilomi, Farruggia, Pulmonary Delivery of Fenretinide: A Possible Adjuvant Treatment In COVID-19, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms21113812
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, Aschenbrenner, Avery et al., An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abl4784
Sarveswaran, Gautam, Ghosh, Wedelolactone, a medicinal plant-derived coumestan, induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells via downregulation of PKCepsilon without inhibiting Akt, Int J Oncol, doi:10.3892/ijo.2012.1664
Sheahan, Sims, Zhou, Graham, Pruijssers et al., An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abb5883
Van De Leemput, Han, Understanding Individual SARS-CoV-2 Proteins for Targeted Drug Development against COVID-19, Mol Cell Biol, doi:10.1128/MCB.00185-21
Vivoli, Novak, Littlechild, Harmer, Determination of protein-ligand interactions using differential scanning fluorimetry, J Vis Exp, doi:10.3791/51809:51809
Von Delft, Hall, Kwong, Purcell, Saikatendu et al., Accelerating antiviral drug discovery: lessons from COVID-19, Nat Rev Drug Discov, doi:10.1038/s41573-023-00692-8
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Yang, Liu et al., Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0
White, Cheng, Discovery of COVID-19 Inhibitors Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Nsp13 Helicase, J Phys Chem Lett, doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c02421
Wu, Dipietrantonio, Hsieh, Mechanism of fenretinide (4-HPR)-induced cell death, Apoptosis, doi:10.1023/a:1011342220621
Xiong, Su, Zhao, Xie, Shao et al., What coronavirus 3C-like protease tells us: From structure, substrate selectivity, to inhibitor design, Med Res Rev, doi:10.1002/med.21783
Yan, Zhang, Ge, Zheng, Gao et al., Architecture of a SARS-CoV-2 mini replication and transcription complex, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19770-1
Yazdi, Pakarian, Perveen, Hajian, Santhakumar et al., Kinetic Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nsp13 ATPase Activity and Discovery of Small-Molecule Inhibitors, ACS Infect Dis, doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.2c00165
Zeng, Weissmann, Bertolin, Posse, Canal et al., Identifying SARS-CoV-2 antiviral compounds by screening for small molecule inhibitors of nsp13 helicase, Biochem J, doi:10.1042/BCJ20210201
Zhang, Zhu, Quantitative RT-PCR assay for high-throughput screening (HTS) of drugs against the growth of Cryptosporidium parvum in vitro, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00991
Zhu, Chen, Monophyletic relationship between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and group 2 coronaviruses, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1086/382892
Zhu, Deuremidevir and Simnotrelvir-Ritonavir for the Treatment of COVID-19, ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci, doi:10.1021/acsptsci.3c00134
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001",
"ISSN": [
"2950-2489"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001",
"alternative-id": [
"S295024892400004X"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Thermal shift assay (TSA)-based drug screening strategy for rapid discovery of inhibitors against the Nsp13 helicase of SARS-CoV-2"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Animals and Zoonoses"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co. Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Meng",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yin",
"given": "Jigang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Chang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3888-0659",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Guan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Animals and Zoonoses",
"container-title-short": "Animals and Zoonoses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-01T18:02:04Z",
"timestamp": 1719856924000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-08T04:51:24Z",
"timestamp": 1720414284000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-09T00:17:55Z",
"timestamp": 1720484275332
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1719792000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1719792000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1719446400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S295024892400004X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S295024892400004X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib1",
"unstructured": "United States Food & Drug Administration. 2023. Coronavirus (COVID-19) | Drugs. Last update on 05/25/2023. 〈https://www.fda.gov/drugs/emergency-preparedness-drugs/coronavirus-covid-19-drugs〉. Accessed 12/1/2023."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib2",
"unstructured": "Drugs.com. 2023. Veklury FDA Approval History. Last update on 07/18/2023. 〈https://www.drugs.com/history/veklury.html〉. Accessed 12/1/2023."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib3",
"unstructured": "Drug.com. 2022. Lagevrio FDA Approval Status. Last update on 4/4/2023. 〈https://www.drugs.com/history/lagevrio.html〉. Accessed 12/1/2023."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib4",
"unstructured": "Drugs.com. 2023. Paxlovid FDA Approval History. Last update on 11/5/2023. 〈https://www.drugs.com/history/paxlovid.html〉. Accessed 12/1/2023."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1610",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in covid-19",
"author": "Ferner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1610",
"journal-title": "BMJ 369",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abb5883",
"article-title": "An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice",
"author": "Sheahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib6",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"article-title": "An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1586",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib7",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.RA120.013679",
"article-title": "Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6785",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib8",
"volume": "295",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-021-00651-0",
"article-title": "Mechanism of molnupiravir-induced SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis",
"author": "Kabinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "740",
"journal-title": "Nat Struct Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib9",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/med.21783",
"article-title": "What coronavirus 3C-like protease tells us: From structure, substrate selectivity, to inhibitor design",
"author": "Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1965",
"journal-title": "Med Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib10",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsptsci.3c00134",
"article-title": "Deuremidevir and Simnotrelvir-Ritonavir for the Treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1306",
"journal-title": "ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib11",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib12",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-25166-6",
"article-title": "Structure, mechanism and crystallographic fragment screening of the SARS-CoV-2 NSP13 helicase",
"author": "Newman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4848",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib13",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2102516118",
"article-title": "Structural basis for backtracking by the SARS-CoV-2 replication-transcription complex",
"author": "Malone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib14",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19770-1",
"article-title": "Architecture of a SARS-CoV-2 mini replication and transcription complex",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5874",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib15",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.033",
"article-title": "Structural Basis for Helicase-Polymerase Coupling in the SARS-CoV-2 Replication-Transcription Complex",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1560",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib16",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01244-13",
"article-title": "Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): announcement of the Coronavirus Study Group",
"author": "de Groot",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7790",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib17",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis",
"author": "Fehr",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol Biol 1282",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib18",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCP.0000000000000046",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome vs. the Middle East respiratory syndrome",
"author": "Hui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "233",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Pulm Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib19",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/382892",
"article-title": "Monophyletic relationship between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and group 2 coronaviruses",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1676",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib20",
"volume": "189",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00081",
"article-title": "Homogeneous Assay for Target Engagement Utilizing Bioluminescent Thermal Shift",
"author": "Dart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "546",
"journal-title": "ACS Med Chem Lett",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib21",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ab.2004.04.031",
"article-title": "Evaluation of fluorescence-based thermal shift assays for hit identification in drug discovery",
"author": "Lo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Anal Biochem",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib22",
"volume": "332",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3791/64693",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib23",
"unstructured": "Gupta S.D., Song D.G., Lee S., Lee J.W., Park J.S., Prodromou C., Pan C.H. 2023. Malachite Green Assay for the Discovery of Heat-Shock Protein 90 Inhibitors. J Vis Exp doi:10.3791/64693. doi:10.3791/64693."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1006474",
"article-title": "Crystal structure of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus helicase",
"author": "Hao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib24",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkz409",
"article-title": "Delicate structural coordination of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus Nsp13 upon ATP hydrolysis",
"author": "Jia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6538",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib25",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "HTS Assay Validation",
"author": "Iversen",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib26",
"series-title": "Assay Guidance Manual",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2015.00991",
"article-title": "Quantitative RT-PCR assay for high-throughput screening (HTS) of drugs against the growth of Cryptosporidium parvum in vitro",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "991",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib27",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3791/51809-v",
"article-title": "Determination of protein-ligand interactions using differential scanning fluorimetry",
"author": "Vivoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Vis Exp",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib28",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/adt.2021.133",
"article-title": "A New Spectral Shift-Based Method to Characterize Molecular Interactions",
"author": "Langer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "83",
"journal-title": "Assay Drug Dev Technol",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib29",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25092064",
"article-title": "Naphthoquinones as Covalent Reversible Inhibitors of Cysteine Proteases-Studies on Inhibition Mechanism and Kinetics",
"author": "Klein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib30",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmolb.2021.716466",
"article-title": "SeamDock: An Interactive and Collaborative Online Docking Resource to Assist Small Compound Molecular Docking",
"author": "Murail",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Mol Biosci",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib31",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Analysis of protein stability and ligand interactions by thermal shift assay",
"author": "Huynh",
"journal-title": "Curr Protoc Protein Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib32",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41573-023-00692-8",
"article-title": "Accelerating antiviral drug discovery: lessons from COVID-19",
"author": "von Delft",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "585",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Drug Discov",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib33",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/MCB.00185-21",
"article-title": "Understanding Individual SARS-CoV-2 Proteins for Targeted Drug Development against COVID-19",
"author": "van de Leemput",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Mol Cell Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib34",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.2c00165",
"article-title": "Kinetic Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nsp13 ATPase Activity and Discovery of Small-Molecule Inhibitors",
"author": "Yazdi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1533",
"journal-title": "ACS Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib35",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BCJ20210201",
"article-title": "Identifying SARS-CoV-2 antiviral compounds by screening for small molecule inhibitors of nsp13 helicase",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2405",
"journal-title": "Biochem J",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib36",
"volume": "478",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c02421",
"article-title": "Discovery of COVID-19 Inhibitors Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Nsp13 Helicase",
"author": "White",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9144",
"journal-title": "J Phys Chem Lett",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib37",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105389",
"article-title": "Punicalagin as an allosteric NSP13 helicase inhibitor potently suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib38",
"volume": "206",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1208/s12248-012-9432-8",
"article-title": "Therapeutic roles of curcumin: lessons learned from clinical trials",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "195",
"journal-title": "AAPS J",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib39",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13101914",
"article-title": "Turmeric Root and Its Bioactive Ingredient Curcumin Effectively Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro",
"author": "Bormann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib40",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00139",
"article-title": "Curcumin May (Not) Defy Science",
"author": "Nelson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "467",
"journal-title": "ACS Med Chem Lett",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib41",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00975",
"article-title": "The Essential Medicinal Chemistry of Curcumin",
"author": "Nelson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1620",
"journal-title": "J Med Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib42",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21113812",
"article-title": "Pulmonary Delivery of Fenretinide: A Possible Adjuvant Treatment In COVID-19",
"author": "Orienti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib43",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1165/rcmb.2007-0036OC",
"article-title": "Fenretinide corrects newly found ceramide deficiency in cystic fibrosis",
"author": "Guilbault",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "47",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib44",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1011342220621",
"article-title": "Mechanism of fenretinide (4-HPR)-induced cell death",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "Apoptosis",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib45",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/153537020623100312",
"article-title": "Efaproxiral (RSR13) plus oxygen breathing increases the therapeutic ratio of carboplatin in EMT6 mouse mammary tumors",
"author": "Donnelly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "317",
"journal-title": "Exp Biol Med (Maywood)",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib46",
"volume": "231",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1667/RR0962.1",
"article-title": "The effects of Efaproxyn (efaproxiral) on subcutaneous RIF-1 tumor oxygenation and enhancement of radiotherapy-mediated inhibition of tumor growth in mice",
"author": "Hou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "218",
"journal-title": "Radiat Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib47",
"volume": "168",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijo.2012.1664",
"article-title": "Wedelolactone, a medicinal plant-derived coumestan, induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells via downregulation of PKCepsilon without inhibiting Akt.",
"author": "Sarveswaran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2191",
"journal-title": "Int J Oncol",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib48",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fitote.2022.105355",
"article-title": "Wedelolactone: A molecule of interests",
"author": "Ha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Fitoterapia",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib49",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100034",
"article-title": "Prostate cancer: Therapeutic prospect with herbal medicine",
"author": "Ghosh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov",
"key": "10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001_bib50",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 50,
"references-count": 50,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S295024892400004X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Thermal shift assay (TSA)-based drug screening strategy for rapid discovery of inhibitors against the Nsp13 helicase of SARS-CoV-2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}