Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin and curcuminoids in SH-SY5Y cells infected by SARS-CoV-2
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7, May 2024
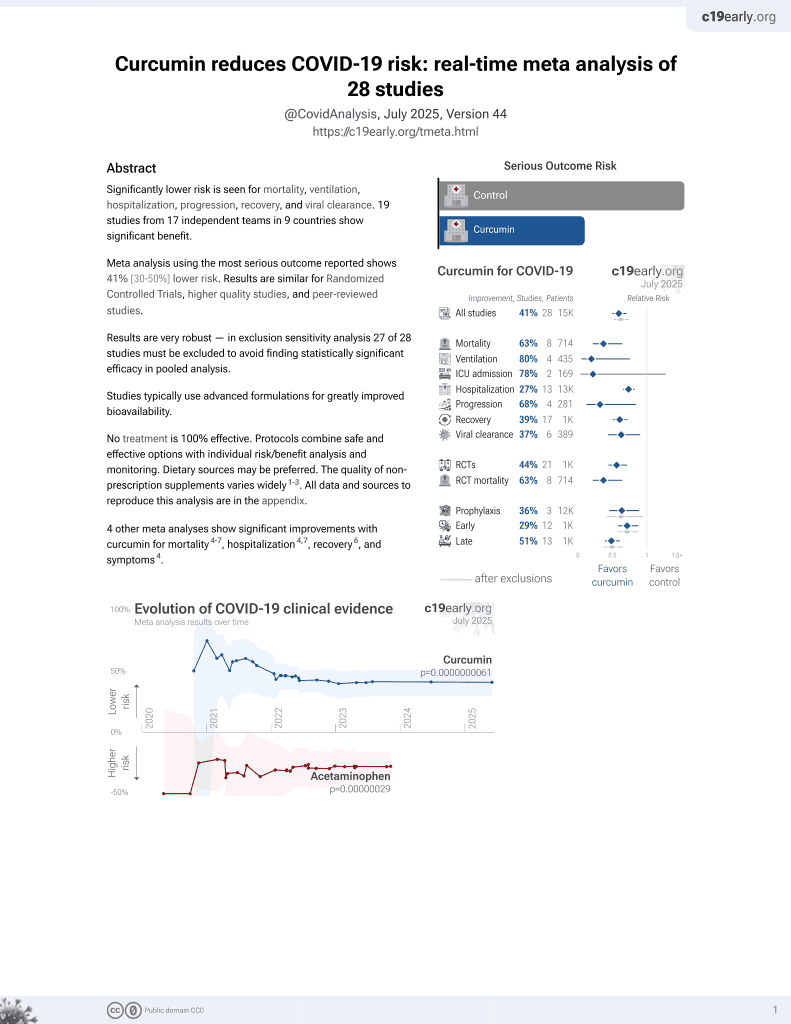
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro study showing antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects of curcumin and curcuminoids in SARS-CoV-2 infected SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Authors found that the curcuminoid Me23 significantly decreased expression of the SARS-CoV-2 entry factors TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS11D, mitigated elevated ROS levels induced by infection, increased expression of the antioxidant response regulator NRF2, and restored activity of the NRF2 target NQO1. Both Me08 and Me23 curcuminoids effectively reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication in SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing the ACE2 receptor. All tested compounds (curcumin, turmeric extract, Me08, Me23) decreased levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-17, while Me08 specifically reduced INF-γ.
62 preclinical studies support the efficacy of curcumin for COVID-19:
In silico studies predict inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 with curcumin or metabolites via binding to the spikeA,1,5,6,11,16,18,24,27 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,2,4,14,17,20 ), MproC,4-6,11,13,15-17,19,20,22,25,27,28,30,48 , RNA-dependent RNA polymeraseD,4-6,17,26 , PLproE,6, ACE2F,2,18,19,21 , nucleocapsidG,12,29 , nsp10H,29, and helicaseI,36 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3.
In vitro studies demonstrate inhibition of the spikeA,41 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,51), MproC,23,41,48,50 , ACE2F,51, and TMPRSS2K,51 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3,34 .
In vitro studies demonstrate efficacy in Calu-3L,49, A549M,41, A549-ATN,31, 293TO,7, HEK293-hACE2P,23,39 , 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2Q,40, Vero E6R,1,13,17,27,39,41,43,45,47,49 , and SH-SY5YS,38 cells.
Curcumin decreases pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by SARS-CoV-2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells47, alleviates SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-induced mitochondrial membrane damage and oxidative stress7, may limit COVID-19 induced cardiac damage by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway which mediates the profibrotic effects of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein on cardiac fibroblasts35, is predicted to inhibit the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain and the human ACE2 receptor for the delta and omicron variants14, lowers ACE2 and STAT3, curbing lung inflammation and ARDS in preclinical COVID-19 models32, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a ion channel activity, which contributes to viral pathogenicity and cytotoxicity42, has direct virucidal action by disrupting viral envelope integrity44, may inhibit viral replication and modulate inflammatory pathways like NF-κB via SIRT1 activation52, and can function as a photosensitizer in photodynamic therapy to generate reactive oxygen species that damage the virus44.
1.
Marzouk et al., Computational and Experimental Insights into the Antiviral Mechanism of Turmeric (Curcuma longa) against SARS-CoV-2 D614G, BIO Web of Conferences, doi:10.1051/bioconf/202519804002.
2.
Wu et al., Utilizing natural compounds as ligands to disrupt the binding of SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, impeding viral infection, Phytochemistry Letters, doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2025.102999.
3.
Najimi et al., Phytochemical Inhibitors of SARS‐CoV‐2 Entry: Targeting the ACE2‐RBD Interaction with l‐Tartaric Acid, l‐Ascorbic Acid, and Curcuma longa Extract, ChemistrySelect, doi:10.1002/slct.202406035.
4.
Rajamanickam et al., Exploring the Potential of Siddha Formulation MilagaiKudineer-Derived Phytotherapeutics Against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Investigation for Antiviral Intervention, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, doi:10.26502/fjppr.0105.
5.
Al balawi et al., Assessing multi-target antiviral and antioxidant activities of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2: an integrated in vitro and in silico study, Bioresources and Bioprocessing, doi:10.1186/s40643-024-00822-z.
6.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
7.
Zhang et al., Computational Discovery of Mitochondrial Dysfunction Biomarkers in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Facilitating Pytomedicine Screening, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784.
8.
Öztürkkan et al., In Silico investigation of the effects of curcuminoids on the spike protein of the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, Baku State University Journal of Chemistry and Material Sciences, 1:2, bsuj.bsu.edu.az/uploads/pdf/ec4204d62f7802de54e6092bf7860029.pdf.
9.
Yunze et al., Therapeutic effect and potential mechanism of curcumin, an active ingredient in Tongnao Decoction, on COVID-19 combined with stroke: a network pharmacology study and GEO database mining, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4329762/v1.
10.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
11.
Boseila et al., Throat spray formulated with virucidal Pharmaceutical excipients as an effective early prophylactic or treatment strategy against pharyngitis post-exposure to SARS CoV-2, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2024.114279.
12.
Hidayah et al., Bioinformatics study of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin and cyclocurcumin compounds in Curcuma longa as an antiviral agent via nucleocapsid on SARS-CoV-2 inhibition, International Conference on Organic and Applied Chemistry, doi:10.1063/5.0197724.
13.
Singh et al., Unlocking the potential of phytochemicals in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 M Pro protein - An in-silico and cell-based approach, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3888947/v1.
14.
Kant et al., Structure-based drug discovery to identify SARS-CoV2 spike protein–ACE2 interaction inhibitors, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2023.2300060.
15.
Naderi Beni et al., In silico studies of anti-oxidative and hot temperament-based phytochemicals as natural inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0295014.
16.
Moschovou et al., Exploring the Binding Effects of Natural Products and Antihypertensive Drugs on SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Investigation of Main Protease and Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242115894.
17.
Eleraky et al., Curcumin Transferosome-Loaded Thermosensitive Intranasal in situ Gel as Prospective Antiviral Therapy for SARS-Cov-2, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S423251.
18.
Singh (B) et al., Computational studies to analyze effect of curcumin inhibition on coronavirus D614G mutated spike protein, The Seybold Report, doi:10.17605/OSF.IO/TKEXJ.
19.
Thapa et al., In-silico Approach for Predicting the Inhibitory Effect of Home Remedies on Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2, Makara Journal of Science, doi:10.7454/mss.v27i3.1609.
20.
Srivastava et al., Paradigm of Well-Orchestrated Pharmacokinetic Properties of Curcuminoids Relative to Conventional Drugs for the Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 Receptors: An In Silico Approach, Stresses, doi:10.3390/stresses3030043.
21.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
22.
Winih Kinasih et al., Analisis in silico interaksi senyawa kurkuminoid terhadap enzim main protease 6LU7 dari SARS-CoV-2, Duta Pharma Journal, doi:10.47701/djp.v3i1.2904.
23.
Wu (B) et al., Potential Mechanism of Curcumin and Resveratrol against SARS-CoV-2, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2780614/v1.
24.
Nag et al., Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552.
25.
Rampogu et al., Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations Discover Curcumin Analogue as a Plausible Dual Inhibitor for SARS-CoV-2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23031771.
26.
Singh (C) et al., Potential of turmeric-derived compounds against RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2: An in-silico approach, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104965.
27.
Kandeil et al., Bioactive Polyphenolic Compounds Showing Strong Antiviral Activities against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10060758.
28.
Rajagopal et al., Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach, Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x.
29.
Suravajhala et al., Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin with COVID-19 Proteins, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v3.
30.
Sekiou et al., In-Silico Identification of Potent Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) from Natural Products: Quercetin, Hispidulin, and Cirsimaritin Exhibited Better Potential Inhibition than Hydroxy-Chloroquine Against COVID-19 Main Protease Active Site and ACE2, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12181404.v1.
31.
Grüneberg et al., Dose-dependent antiviral effects of glycyrrhizin, curcumin, and harmaline against clinical SARS-CoV-2 isolates, including D614G, Omicron BA.5, and Omicron XBB.1, BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, doi:10.1186/s12906-026-05253-1.
32.
Aktay et al., Oral Administration of Water-Soluble Curcumin Complex Prevents ARDS With the Potential for COVID-19 Treatment, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.70046.
33.
Olubiyi et al., Novel dietary herbal preparations with inhibitory activities against multiple SARS-CoV-2 targets: A multidisciplinary investigation into antiviral activities, Food Chemistry Advances, doi:10.1016/j.focha.2025.100969.
34.
Emam et al., Establishment of in-house assay for screening of anti-SARS-CoV-2 protein inhibitors, AMB Express, doi:10.1186/s13568-024-01739-8.
35.
Van Tin et al., Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Activates Cardiac Fibrogenesis through NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161331.
36.
Li et al., Thermal shift assay (TSA)-based drug screening strategy for rapid discovery of inhibitors against the Nsp13 helicase of SARS-CoV-2, Animals and Zoonoses, doi:10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001.
37.
Kamble et al., Nanoparticulate curcumin spray imparts prophylactic and therapeutic properties against SARS-CoV-2, Emergent Materials, doi:10.1007/s42247-024-00754-6.
38.
Nicoliche et al., Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin and curcuminoids in SH-SY5Y cells infected by SARS-CoV-2, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7.
39.
Nittayananta et al., A novel film spray containing curcumin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus infection and enhances mucosal immunity, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02282-x.
40.
Septisetyani et al., Curcumin and turmeric extract inhibited SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus cell entry and Spike mediated cell fusion, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.09.28.560070.
41.
Mohd Abd Razak et al., In Vitro Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activities of Curcumin and Selected Phenolic Compounds, Natural Product Communications, doi:10.1177/1934578X231188861.
42.
Fam et al., Channel activity of SARS-CoV-2 viroporin ORF3a inhibited by adamantanes and phenolic plant metabolites, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31764-9.
43.
Teshima et al., Antiviral activity of curcumin and its analogs selected by an artificial intelligence-supported activity prediction system in SARS-CoV-2-infected VeroE6 cells, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2023.2194647.
44.
Zupin et al., Optimization of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Treatments Based on Curcumin, Used Alone or Employed as a Photosensitizer, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14102132.
45.
Leka et al., In vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 of common herbal medicinal extracts and their bioactive compounds, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7463.
46.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
47.
Marín-Palma et al., Curcumin Inhibits In Vitro SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vero E6 Cells through Multiple Antiviral Mechanisms, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26226900.
48.
Bahun et al., Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro main protease by plant polyphenols, Food Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131594.
49.
Bormann et al., Turmeric Root and Its Bioactive Ingredient Curcumin Effectively Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13101914.
50.
Guijarro-Real et al., Potential In Vitro Inhibition of Selected Plant Extracts against SARS-CoV-2 Chymotripsin-Like Protease (3CLPro) Activity, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods10071503.
a.
The trimeric spike (S) protein is a glycoprotein that mediates viral entry by binding to the host ACE2 receptor, is critical for SARS-CoV-2's ability to infect host cells, and is a target of neutralizing antibodies. Inhibition of the spike protein prevents viral attachment, halting infection at the earliest stage.
b.
The receptor binding domain is a specific region of the spike protein that binds ACE2 and is a major target of neutralizing antibodies. Focusing on the precise binding site allows highly specific disruption of viral attachment with reduced potential for off-target effects.
c.
The main protease or Mpro, also known as 3CLpro or nsp5, is a cysteine protease that cleaves viral polyproteins into functional units needed for replication. Inhibiting Mpro disrupts the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle within the host cell, preventing the creation of new copies.
d.
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called nsp12, is the core enzyme of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex that copies the positive-sense viral RNA genome into negative-sense templates for progeny RNA synthesis. Inhibiting RdRp blocks viral genome replication and transcription.
e.
The papain-like protease (PLpro) has multiple functions including cleaving viral polyproteins and suppressing the host immune response by deubiquitination and deISGylation of host proteins. Inhibiting PLpro may block viral replication and help restore normal immune responses.
f.
The angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) protein is a host cell transmembrane protein that serves as the cellular receptor for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. ACE2 is expressed on many cell types, including epithelial cells in the lungs, and allows the virus to enter and infect host cells. Inhibition may affect ACE2's physiological function in blood pressure control.
g.
The nucleocapsid (N) protein binds and encapsulates the viral genome by coating the viral RNA. N enables formation and release of infectious virions and plays additional roles in viral replication and pathogenesis. N is also an immunodominant antigen used in diagnostic assays.
h.
Non-structural protein 10 (nsp10) serves as an RNA chaperone and stabilizes conformations of nsp12 and nsp14 in the replicase-transcriptase complex, which synthesizes new viral RNAs. Nsp10 disruption may destabilize replicase-transcriptase complex activity.
i.
The helicase, or nsp13, protein unwinds the double-stranded viral RNA, a crucial step in replication and transcription. Inhibition may prevent viral genome replication and the creation of new virus components.
j.
The interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the human ACE2 receptor is a primary method of viral entry, inhibiting this interaction can prevent the virus from attaching to and entering host cells, halting infection at an early stage.
k.
Transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) is a host cell protease that primes the spike protein, facilitating cellular entry. TMPRSS2 activity helps enable cleavage of the spike protein required for membrane fusion and virus entry. Inhibition may especially protect respiratory epithelial cells, buy may have physiological effects.
l.
Calu-3 is a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line with moderate ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. It provides a model of the human respiratory epithelium, but many not be ideal for modeling early stages of infection due to the moderate expression levels of ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
m.
A549 is a human lung carcinoma cell line with low ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Viral entry/replication can be studied but the cells may not replicate all aspects of lung infection.
n.
A549-AT is a human lung carcinoma cell line stably transfected with ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors. Unlike the parental line, this overexpression ensures stable infection and enhanced viral entry, allowing for the evaluation of antiviral efficacy against various SARS-CoV-2 variants.
o.
293T is a human embryonic kidney cell line that can be engineered for high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. 293T cells are easily transfected and support high protein expression.
p.
HEK293-hACE2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line with high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Cells have been transfected with a plasmid to express the human ACE2 (hACE2) protein.
q.
293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line engineered for high ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression, which mimics key aspects of human infection. 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 cells are very susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
r.
Vero E6 is an African green monkey kidney cell line with low/no ACE2 expression and high SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. The cell line is easy to maintain and supports robust viral replication, however the monkey origin may not accurately represent human responses.
s.
SH-SY5Y is a human neuroblastoma cell line that exhibits neuronal phenotypes. It is commonly used as an in vitro model for studying neurotoxicity, neurodegenerative diseases, and neuronal differentiation.
Nicoliche et al., 10 May 2024, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 16 authors.
Contact: roberta.yamaguchi@fcmsantacasasp.edu.br.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin and curcuminoids in SH-SY5Y cells infected by SARS-CoV-2
Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7
COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2, affects neuronal cells, causing several symptoms such as memory loss, anosmia and brain inflammation. Curcuminoids (Me08 e Me23) and curcumin (CUR) are derived from Curcuma Longa extract (EXT). Many therapeutic actions have been linked to these compounds, including antiviral action. Given the severe implications of COVID-19, especially within the central nervous system, our study aims to shed light on the therapeutic potential of curcuminoids against SARS-CoV-2 infection, particularly in neuronal cells. Here, we investigated the effects of CUR, EXT, Me08 and Me23 in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y. We observed that Me23 significantly decreased the expression of plasma membrane-associated transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) and TMPRSS11D, consequently mitigating the elevated ROS levels induced by SARS-CoV-2. Furthermore, Me23 exhibited antioxidative properties by increasing NRF2 gene expression and restoring NQO1 activity following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Both Me08 and Me23 effectively reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication in SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing ACE2 (SH-ACE2). Additionally, all of these compounds demonstrated the ability to decrease proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-17, while Me08 specifically reduced INF-γ levels. Our findings suggest that curcuminoid Me23 could serve as a potential agent for mitigating the impact of COVID-19, particularly within the context of central nervous system involvement.
Author contributions T
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1038/ s41598-024-61662-7. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to R.S.S. Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints. Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Abd-Alkhalek, Eldahshan, Managements of COVID-19 by Curcumin, Acta Sci. Pharm. Sci
Asadi-Pooya, Simani, Central nervous system manifestations of COVID-19: A systematic review, J. Neurol. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jns.2020.116832
Atia, Abdullah, NQO1 Enzyme and its Role in Cellular Protection; an Insight, Iberoamerican J. Med
Badoco, EF24, a schistosomicidal curcumin analog: Insights from its synthesis and phenotypic, biochemical and cytotoxic activities, Chem. Biol. Interact
Bartolomeo, SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication kinetics in different human cell types: The role of autophagy, cellular metabolism and ACE2 expression, Life Sci
Battino, Nrf2 as regulator of innate immunity: A molecular Swiss army knife!, Biotechnol. Adv, doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.12.012
Bormann, Turmeric root and its bioactive ingredient curcumin effectively neutralize sars-cov-2 in vitro, Viruses
Cao, Curcumin ameliorates oxidative stress-induced intestinal barrier injury and mitochondrial damage by promoting Parkin dependent mitophagy through AMPK-TFEB signal pathway, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Chen, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study, The Lancet
Cho, Neurological manifestations of COVID-19 in adults and children, Brain
Cui, Carvacrol protects neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against Fe2+-induced apoptosis by suppressing activation of MAPK/JNK-NF-κB signaling pathway, Acta Pharmacol Sin
Da Silva, Post-Covid condition and clinic characteristics associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a 2-year follow-up to Brazilian cases, Sci Rep
Dai, Curcumin provides neuroprotection in model of traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway, Brain Res. Bull
Ding, Zhao, Long-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on human brain and memory, Cell Death Discov, doi:10.1038/s41420-023-01512-z
Franke, Berlit, Prüss, Neurological manifestations of post-COVID-19 syndrome S1-guideline of the German society of neurology, Neurol Res Pract
Gain, Song, Angtuaco, Satta, Kelesidis, The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of infections with coronaviruses, Front. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.1111930
Garrigues, Post-discharge persistent symptoms and health-related quality of life after hospitalization for COVID-19, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.08.029
Germano, Fetal Brain Damage during Maternal COVID-19: Emerging Hypothesis, Mechanism, and Possible Mitigation through Maternal-Targeted Nutritional Supplementation, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14163303
Ghandadi, Sahebkar, Curcumin: An Effective Inhibitor of Interleukin-6, Curr. Pharm. Des
Giacobone, Leoni, Brambilla, Caccia, Giuseppe, Metabolomic changes in COVID-19 patients, Biochim. Clin
Goel, Kunnumakkara, Aggarwal, Curcumin as 'Curecumin': From kitchen to clinic, Biochem. Pharmacol
Gümüş, Erat, Öztürk, Demir, Koyuncu, Oxidative stress and decreased Nrf2 level in pediatric patients with COVID-19, J. Med. Virol
Hadzi-Petrushev, Comparative study of the antioxidant properties of monocarbonyl curcumin analogues C66 and B2BrBC in isoproteranol induced cardiac damage, Life Sci
Halpin, Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: A cross-sectional evaluation, J. Med. Virol
Hamad, SARS-CoV-2 infection and dysregulation of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway, Cell Stress Chaperon, doi:10.1007/s12192-023-01379-0
Hoffmann, Camostat mesylate inhibits SARS-CoV-2 activation by TMPRSS2-related proteases and its metabolite GBPA exerts antiviral activity, EBioMedicine
Hoffmann, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hosp, Cognitive impairment and altered cerebral glucose metabolism in the subacute stage of COVID-19, Brain
Kelloff, Progress in clinical chemoprevention, Semin. Oncol
Kim, B κ NF-of toll-like Receptor 4-dependent activation involvement of reactive oxygen species in involvement of reactive oxygen species in toll-like Receptor 4-dependent activation of NF-, B1, J. Immunol. Ref
Kishimoto, Tmprss11d and tmprss13 activate the sars-cov-2 spike protein, Viruses
Lemes, 17β-estradiol reduces SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, Physiol. Rep
Lin, Acute necrotizing encephalopathy in children with COVID-19: A retrospective study of 12 cases, Front. Neurol
Liu, Zhang, Joo, Sun, NF-κB signaling in inflammation, Signal Transduct. Target. Therapy, doi:10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
Llano, Gómez, Londoño, Restrepo, Antioxidant activity of curcuminoids, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys
Manik, Singh, Role of toll-like receptors in modulation of cytokine storm signaling in SARS-CoV-2-induced COVID-19, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27405
Mao, Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China, JAMA Neurol
Marín-Palma, Curcumin inhibits in vitro sars-cov-2 infection in vero e6 cells through multiple antiviral mechanisms, Molecules
Marín-Palma, Curcumin inhibits in vitro sars-cov-2 infection in vero e6 cells through multiple antiviral mechanisms, Molecules
Mingoti, COVID-19, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation in the depression route, J. Mol. Neurosci, doi:10.1007/s12031-022-02004-y
Mracsko, Veltkamp, Neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage, Front. Cell Neurosci
Nguyen, Zhang, Pandolfi, Virus against virus: a potential treatment for 2019-nCov (SARS-CoV-2) and other RNA viruses, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0290-0
Pall, Levine, Nrf2, a master regulator of detoxification and also antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and other cytoprotective mechanisms, is raised by health promoting factors, Sheng Li Xue Bao
Pawar, Oral curcumin with piperine as adjuvant therapy for the treatment of COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, Front Pharmacol
Rahimi, Curcumin: A dietary phytochemical for targeting the phenotype and function of dendritic cells, Curr. Med. Chem
Rattis, Ramos, Celes, Curcumin as a Potential Treatment for COVID-19, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.675287
Ruscica, Impact of nutraceuticals on markers of systemic inflammation: Potential relevance to cardiovascular diseases-A position paper from the International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP), Progress Cardiovasc. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2021.06.010
Ryan, Nrf2 activation reprograms macrophage intermediary metabolism and suppresses the type I interferon response, iScience
Saber-Moghaddam, Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in management of mild to moderate hospitalized coronavirus disease-19 patients: An open label nonrandomized clinical trial, Phytother. Res
Seixas, Disruptive 3D in vitro models for respiratory disease investigation: A state-of-the-art approach focused on SARS-CoV-2 infection, Biomater. Biosyst
Shanmugarajan, Kumar, Suresh, Curcumin to inhibit binding of spike glycoprotein to ACE2 receptors: Computational modelling, simulations, and ADMET studies to explore curcuminoids against novel SARS-CoV-2 targets, RSC Adv
Silvestro, Sindona, Bramanti, Mazzon, A state of the art of antioxidant properties of curcuminoids in neurodegenerative diseases, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22063168
Soung, COVID-19 induces CNS cytokine expression and loss of hippocampal neurogenesis, Brain
Tschoe, Bushnell, Duncan, Alexander-Miller, Wolfe, Neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage and potential therapeutic targets, J. Stroke, doi:10.5853/jos.2019.02236
Vahedian-Azimi, Effectiveness of curcumin on outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A systematic review of clinical trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14020256
Valizadeh, Nano-curcumin therapy, a promising method in modulating inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 patients, Int. Immunopharmacol
Vigato, Monoketonic curcuminoid-lidocaine co-deliver using thermosensitive organogels: From drug synthesis to epidermis structural studies, Pharmaceutics
Vomund, Schäfer, Parnham, Brüne, Von Knethen, Nrf2, the master regulator of anti-oxidative responses, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms18122772
Wang, Dan, Xue, Chen, Chen, Curcumin assists anti-EV71 activity of IFN-α by inhibiting IFNAR1 reduction in SH-SY5Y cells, Gut. Pathog
Wang, Role of reactive oxygen species in LPS-induced production of prostaglandin E2 in microglia, J. Neurochem
Woo, Frequent neurocognitive deficits after recovery from mild COVID-19, Brain Commun
Xiang, Curcumin ameliorates copper-induced neurotoxicity through inhibiting oxidative stress and mitochondrial apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells, Neurochem. Res
Xue, Deficiency of optineurin enhances osteoclast differentiation by attenuating the NRF2-mediated antioxidant response, Exp. Mol. Med
Yuandani, Rohani, Sumantri, Immunomodulatory effects and mechanisms of curcuma species and their bioactive compounds: A review, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.643119
Zahedipour, Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID-19 infection, Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.6738
Zhang, Curcumin downregulates homeobox gene NKX3.1 in prostate cancer cell LNCaP, Acta Pharmacol Sin
Zhou, Wang, Wang, Stetler, Yang, Inflammation in intracerebral hemorrhage: From mechanisms to clinical translation, Progress Neurobiol, doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.11.003
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7",
"ISSN": [
"2045-2322"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2, affects neuronal cells, causing several symptoms such as memory loss, anosmia and brain inflammation. Curcuminoids (Me08 e Me23) and curcumin (CUR) are derived from <jats:italic>Curcuma Longa extract</jats:italic> (EXT). Many therapeutic actions have been linked to these compounds, including antiviral action. Given the severe implications of COVID-19, especially within the central nervous system, our study aims to shed light on the therapeutic potential of curcuminoids against SARS-CoV-2 infection, particularly in neuronal cells. Here, we investigated the effects of CUR, EXT, Me08 and Me23 in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y. We observed that Me23 significantly decreased the expression of plasma membrane-associated transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) and TMPRSS11D, consequently mitigating the elevated ROS levels induced by SARS-CoV-2. Furthermore, Me23 exhibited antioxidative properties by increasing <jats:italic>NRF2</jats:italic> gene expression and restoring NQO1 activity following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Both Me08 and Me23 effectively reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication in SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing ACE2 (SH-ACE2). Additionally, all of these compounds demonstrated the ability to decrease proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-17, while Me08 specifically reduced INF-γ levels. Our findings suggest that curcuminoid Me23 could serve as a potential agent for mitigating the impact of COVID-19, particularly within the context of central nervous system involvement.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"61662"
],
"article-number": "10696",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "16 October 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "8 May 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "10 May 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicoliche",
"given": "Tiago",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bartolomeo",
"given": "Cynthia Silva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lemes",
"given": "Robertha Mariana Rodrigues",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pereira",
"given": "Gabriela Cruz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nunes",
"given": "Tamires Alves",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliveira",
"given": "Rafaela Brito",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicastro",
"given": "Arthur Luiz Miranda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soares",
"given": "Érica Novaes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "da Cunha Lima",
"given": "Brenno Fernandes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodrigues",
"given": "Beatriz Moreira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maricato",
"given": "Juliana Terzi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Okuda",
"given": "Liria Hiromi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Sairre",
"given": "Mirela Inês",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prado",
"given": "Carla Máximo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ureshino",
"given": "Rodrigo Portes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stilhano",
"given": "Roberta Sessa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Scientific Reports",
"container-title-short": "Sci Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-10T04:01:48Z",
"timestamp": 1715313708000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-10T04:02:17Z",
"timestamp": 1715313737000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"2021/2023",
"2021/2023"
],
"name": "Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas da Santa Casa de São Paulo"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001807",
"award": [
"2020/13480-4",
"2016/20796-2",
"2019/10922-9"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-11T00:23:32Z",
"timestamp": 1715387012805
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1715299200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1715299200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-61662-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-61662-7",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-61662-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41420-023-01512-z",
"author": "Q Ding",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Discov.",
"key": "61662_CR1",
"unstructured": "Ding, Q. & Zhao, H. J. Long-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on human brain and memory. Cell Death Discov. 9, 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-023-01512-z (2023).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/brain/awab009",
"author": "JA Hosp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1263",
"journal-title": "Brain",
"key": "61662_CR2",
"unstructured": "Hosp, J. A. et al. Cognitive impairment and altered cerebral glucose metabolism in the subacute stage of COVID-19. Brain 144, 1263 (2021).",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26368",
"author": "SJ Halpin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1013",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "61662_CR3",
"unstructured": "Halpin, S. J. et al. Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: A cross-sectional evaluation. J. Med. Virol. 93, 1013 (2021).",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.08.029",
"author": "E Garrigues",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "61662_CR4",
"unstructured": "Garrigues, E. et al. Post-discharge persistent symptoms and health-related quality of life after hospitalization for COVID-19. J. Infect. 81, 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2020.08.029 (2020).",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/braincomms/fcaa205",
"author": "MS Woo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Brain Commun.",
"key": "61662_CR5",
"unstructured": "Woo, M. S. et al. Frequent neurocognitive deficits after recovery from mild COVID-19. Brain Commun. 2, 1 (2020).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s42466-022-00191-y",
"author": "C Franke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Neurol Res Pract",
"key": "61662_CR6",
"unstructured": "Franke, C., Berlit, P. & Prüss, H. Neurological manifestations of post-COVID-19 syndrome S1-guideline of the German society of neurology. Neurol Res Pract 4, 28 (2022).",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-40586-8",
"author": "NS da Silva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "61662_CR7",
"unstructured": "da Silva, N. S. et al. Post-Covid condition and clinic characteristics associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a 2-year follow-up to Brazilian cases. Sci Rep 13, 1 (2023).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fneur.2023.1184864",
"author": "X Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1184864",
"journal-title": "Front. Neurol.",
"key": "61662_CR8",
"unstructured": "Lin, X. et al. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy in children with COVID-19: A retrospective study of 12 cases. Front. Neurol. 14, 1184864 (2023).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"author": "N Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "The Lancet",
"key": "61662_CR9",
"unstructured": "Chen, N. et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. The Lancet 395, 507 (2020).",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/brain/awac332",
"author": "SM Cho",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Brain",
"key": "61662_CR10",
"unstructured": "Cho, S. M. et al. Neurological manifestations of COVID-19 in adults and children. Brain 146, 1 (2023).",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127",
"author": "L Mao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "JAMA Neurol.",
"key": "61662_CR11",
"unstructured": "Mao, L. et al. Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 77, 1 (2020).",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2020.116832",
"author": "AA Asadi-Pooya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Neurol. Sci.",
"key": "61662_CR12",
"unstructured": "Asadi-Pooya, A. A. & Simani, L. Central nervous system manifestations of COVID-19: A systematic review. J. Neurol. Sci. 413, 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2020.116832 (2020).",
"volume": "413",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "ML Seixas",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Biomater. Biosyst.",
"key": "61662_CR13",
"unstructured": "Seixas, M. L. et al. Disruptive 3D in vitro models for respiratory disease investigation: A state-of-the-art approach focused on SARS-CoV-2 infection. Biomater. Biosyst. 11, 1 (2023).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120930",
"author": "CS Bartolomeo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "61662_CR14",
"unstructured": "Bartolomeo, C. S. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication kinetics in different human cell types: The role of autophagy, cellular metabolism and ACE2 expression. Life Sci. 308, 1 (2022).",
"volume": "308",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103255",
"author": "M Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "61662_CR15",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann, M. et al. Camostat mesylate inhibits SARS-CoV-2 activation by TMPRSS2-related proteases and its metabolite GBPA exerts antiviral activity. EBioMedicine 65, 1 (2021).",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"author": "M Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "61662_CR16",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann, M. et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052 (2020).",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13030384",
"author": "M Kishimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "384",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "61662_CR17",
"unstructured": "Kishimoto, M. et al. Tmprss11d and tmprss13 activate the sars-cov-2 spike protein. Viruses 13, 384 (2021).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12031-022-02004-y",
"author": "MED Mingoti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Neurosci.",
"key": "61662_CR18",
"unstructured": "Mingoti, M. E. D. et al. COVID-19, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation in the depression route. J. Mol. Neurosci. 72, 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02004-y (2022).",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2022.1111930",
"author": "C Gain",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Front. Microbiol.",
"key": "61662_CR19",
"unstructured": "Gain, C., Song, S., Angtuaco, T., Satta, S. & Kelesidis, T. The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of infections with coronaviruses. Front. Microbiol. 13, 1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1111930 (2023).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02242.x",
"author": "T Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Neurochem.",
"key": "61662_CR20",
"unstructured": "Wang, T. et al. Role of reactive oxygen species in LPS-induced production of prostaglandin E2 in microglia. J. Neurochem. 88, 1 (2004).",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"author": "Y Kim",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol. Ref.",
"key": "61662_CR21",
"unstructured": "Kim, Y. et al. B κ NF- of toll-like Receptor 4-dependent activation involvement of reactive oxygen species in involvement of reactive oxygen species in toll-like Receptor 4-dependent activation of NF-, B1. J. Immunol. Ref. 172, 1 (2016).",
"volume": "172",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23",
"author": "T Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Therapy",
"key": "61662_CR22",
"unstructured": "Liu, T., Zhang, L., Joo, D. & Sun, S. C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Therapy 2, 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23 (2017).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fncel.2014.00388",
"author": "E Mracsko",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "388",
"journal-title": "Front. Cell Neurosci.",
"key": "61662_CR23",
"unstructured": "Mracsko, E. & Veltkamp, R. Neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. Front. Cell Neurosci. 8, 388 (2014).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5853/jos.2019.02236",
"author": "C Tschoe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Stroke",
"key": "61662_CR24",
"unstructured": "Tschoe, C., Bushnell, C. D., Duncan, P. W., Alexander-Miller, M. A. & Wolfe, S. Q. Neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage and potential therapeutic targets. J. Stroke 22, 1. https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2019.02236 (2020).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.11.003",
"author": "Y Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Progress Neurobiol.",
"key": "61662_CR25",
"unstructured": "Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Anne Stetler, R. & Yang, Q. W. Inflammation in intracerebral hemorrhage: From mechanisms to clinical translation. Progress Neurobiol. 115, 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.11.003 (2014).",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.675287",
"author": "BAC Rattis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "61662_CR26",
"unstructured": "Rattis, B. A. C., Ramos, S. G. & Celes, M. R. N. Curcumin as a Potential Treatment for COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.675287 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "M Abd-Alkhalek",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Sci. Pharm. Sci.",
"key": "61662_CR27",
"unstructured": "Abd-Alkhalek, M. & A. & A Eldahshan, O.,. Managements of COVID-19 by Curcumin. Acta Sci. Pharm. Sci. 5, 1 (2020).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0929867327666200515101228",
"author": "K Rahimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1549",
"journal-title": "Curr. Med. Chem.",
"key": "61662_CR28",
"unstructured": "Rahimi, K. et al. Curcumin: A dietary phytochemical for targeting the phenotype and function of dendritic cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 28, 1549 (2020).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.643119",
"author": "JI Yuandani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "61662_CR29",
"unstructured": "Yuandani, J. I., Rohani, A. S. & Sumantri, I. B. Immunomodulatory effects and mechanisms of curcuma species and their bioactive compounds: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.643119 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcp.2007.08.016",
"author": "A Goel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "787",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Pharmacol.",
"key": "61662_CR30",
"unstructured": "Goel, A., Kunnumakkara, A. B. & Aggarwal, B. B. Curcumin as ‘Curecumin’: From kitchen to clinic. Biochem. Pharmacol. 75, 787 (2008).",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"author": "GJ Kelloff",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Semin. Oncol.",
"key": "61662_CR31",
"unstructured": "Kelloff, G. J. et al. Progress in clinical chemoprevention. Semin. Oncol. 24, 1 (1997).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"author": "M Ghandadi",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Curr. Pharm. Des.",
"key": "61662_CR32",
"unstructured": "Ghandadi, M. & Sahebkar, A. Curcumin: An Effective Inhibitor of Interleukin-6. Curr. Pharm. Des. 23, 1 (2016).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcad.2021.06.010",
"author": "M Ruscica",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Progress Cardiovasc. Dis.",
"key": "61662_CR33",
"unstructured": "Ruscica, M. et al. Impact of nutraceuticals on markers of systemic inflammation: Potential relevance to cardiovascular diseases—A position paper from the International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP). Progress Cardiovasc. Dis. 67, 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2021.06.010 (2021).",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6738",
"author": "F Zahedipour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Phytother. Res.",
"key": "61662_CR34",
"unstructured": "Zahedipour, F. et al. Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID-19 infection. Phytother. Res. 34, 1. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6738 (2020).",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22063168",
"author": "S Silvestro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "61662_CR35",
"unstructured": "Silvestro, S., Sindona, C., Bramanti, P. & Mazzon, E. A state of the art of antioxidant properties of curcuminoids in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063168 (2021).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C8CP06708B",
"author": "S Llano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3752",
"journal-title": "Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.",
"key": "61662_CR36",
"unstructured": "Llano, S., Gómez, S., Londoño, J. & Restrepo, A. Antioxidant activity of curcuminoids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 3752 (2019).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.53986/ibjm.2020.0054",
"author": "A Atia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "306",
"journal-title": "Iberoamerican J. Med.",
"key": "61662_CR37",
"unstructured": "Atia, A. & Abdullah, A. NQO1 Enzyme and its Role in Cellular Protection; an Insight. Iberoamerican J. Med. 2, 306–313 (2020).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.12.012",
"author": "M Battino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Biotechnol. Adv.",
"key": "61662_CR38",
"unstructured": "Battino, M. et al. Nrf2 as regulator of innate immunity: A molecular Swiss army knife!. Biotechnol. Adv. 36, 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.12.012 (2018).",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms18122772",
"author": "S Vomund",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "61662_CR39",
"unstructured": "Vomund, S., Schäfer, A., Parnham, M. J., Brüne, B. & Von Knethen, A. Nrf2, the master regulator of anti-oxidative responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122772 (2017).",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14020256",
"author": "A Vahedian-Azimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "61662_CR40",
"unstructured": "Vahedian-Azimi, A. et al. Effectiveness of curcumin on outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A systematic review of clinical trials. Nutrients 14, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020256 (2022).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110191",
"author": "FR Badoco",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Chem. Biol. Interact",
"key": "61662_CR41",
"unstructured": "Badoco, F. R. et al. EF24, a schistosomicidal curcumin analog: Insights from its synthesis and phenotypic, biochemical and cytotoxic activities. Chem. Biol. Interact 368, 1 (2022).",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics14020293",
"author": "AA Vigato",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceutics",
"key": "61662_CR42",
"unstructured": "Vigato, A. A. et al. Monoketonic curcuminoid-lidocaine co-deliver using thermosensitive organogels: From drug synthesis to epidermis structural studies. Pharmaceutics 14, 1 (2022).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2018.01.028",
"author": "N Hadzi-Petrushev",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "61662_CR43",
"unstructured": "Hadzi-Petrushev, N. et al. Comparative study of the antioxidant properties of monocarbonyl curcumin analogues C66 and B2BrBC in isoproteranol induced cardiac damage. Life Sci. 197, 1 (2018).",
"volume": "197",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/aps.2015.90",
"author": "ZW Cui",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharmacol Sin",
"key": "61662_CR44",
"unstructured": "Cui, Z. W. et al. Carvacrol protects neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against Fe2+-induced apoptosis by suppressing activation of MAPK/JNK-NF-κB signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36, 1 (2015).",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/brain/awac270",
"author": "AL Soung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Brain",
"key": "61662_CR45",
"unstructured": "Soung, A. L. et al. COVID-19 induces CNS cytokine expression and loss of hippocampal neurogenesis. Brain 145, 1 (2022).",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7004",
"author": "N Saber-Moghaddam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Phytother. Res.",
"key": "61662_CR46",
"unstructured": "Saber-Moghaddam, N. et al. Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in management of mild to moderate hospitalized coronavirus disease-19 patients: An open label nonrandomized clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 35, 1 (2021).",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107088",
"author": "H Valizadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "61662_CR47",
"unstructured": "Valizadeh, H. et al. Nano-curcumin therapy, a promising method in modulating inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 patients. Int. Immunopharmacol. 89, 1 (2020).",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.669362",
"author": "KS Pawar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "61662_CR48",
"unstructured": "Pawar, K. S. et al. Oral curcumin with piperine as adjuvant therapy for the treatment of COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. Front Pharmacol 12, 1 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13101914",
"author": "M Bormann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "61662_CR49",
"unstructured": "Bormann, M. et al. Turmeric root and its bioactive ingredient curcumin effectively neutralize sars-cov-2 in vitro. Viruses 13, 1 (2021).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26226900",
"author": "D Marín-Palma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "61662_CR50",
"unstructured": "Marín-Palma, D. et al. Curcumin inhibits in vitro sars-cov-2 infection in vero e6 cells through multiple antiviral mechanisms. Molecules 26, 1 (2021).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/D0RA03167D",
"author": "DPP Shanmugarajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "RSC Adv.",
"key": "61662_CR51",
"unstructured": "Shanmugarajan, D. P. P., Kumar, B. R. P. & Suresh, B. Curcumin to inhibit binding of spike glycoprotein to ACE2 receptors: Computational modelling, simulations, and ADMET studies to explore curcuminoids against novel SARS-CoV-2 targets. RSC Adv. 10, 1 (2020).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00491.x",
"author": "HN Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharmacol Sin",
"key": "61662_CR52",
"unstructured": "Zhang, H. N. et al. Curcumin downregulates homeobox gene NKX3.1 in prostate cancer cell LNCaP. Acta Pharmacol Sin 28, 1 (2007).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14163303",
"author": "C Germano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "61662_CR53",
"unstructured": "Germano, C. et al. Fetal Brain Damage during Maternal COVID-19: Emerging Hypothesis, Mechanism, and Possible Mitigation through Maternal-Targeted Nutritional Supplementation. Nutrients 14, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163303 (2022).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "C Giacobone",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Clin.",
"key": "61662_CR54",
"unstructured": "Giacobone, C., Leoni, V., Brambilla, P., Caccia, C. & Giuseppe, P. Metabolomic changes in COVID-19 patients. Biochim. Clin. 44, 1 (2020).",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27405",
"author": "M Manik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "61662_CR55",
"unstructured": "Manik, M. & Singh, R. K. Role of toll-like receptors in modulation of cytokine storm signaling in SARS-CoV-2-induced COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 94, 1. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.27405 (2022).",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.12.004",
"author": "S Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "61662_CR56",
"unstructured": "Cao, S. et al. Curcumin ameliorates oxidative stress-induced intestinal barrier injury and mitochondrial damage by promoting Parkin dependent mitophagy through AMPK-TFEB signal pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 147, 1 (2020).",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11064-020-03173-1",
"author": "B Xiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Neurochem. Res.",
"key": "61662_CR57",
"unstructured": "Xiang, B. et al. Curcumin ameliorates copper-induced neurotoxicity through inhibiting oxidative stress and mitochondrial apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem. Res. 46, 1 (2021).",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s12276-021-00596-w",
"author": "P Xue",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Exp. Mol. Med.",
"key": "61662_CR58",
"unstructured": "Xue, P. et al. Deficiency of optineurin enhances osteoclast differentiation by attenuating the NRF2-mediated antioxidant response. Exp. Mol. Med. 53, 1 (2021).",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "ML Pall",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sheng Li Xue Bao",
"key": "61662_CR59",
"unstructured": "Pall, M. L. & Levine, S. Nrf2, a master regulator of detoxification and also antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and other cytoprotective mechanisms, is raised by health promoting factors. Sheng Li Xue Bao 67, 1 (2015).",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12192-023-01379-0",
"author": "RS Hamad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Stress Chaperon.",
"key": "61662_CR60",
"unstructured": "Hamad, R. S. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and dysregulation of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway. Cell Stress Chaperon. 28, 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-023-01379-0 (2023).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0290-0",
"author": "TM Nguyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Res.",
"key": "61662_CR61",
"unstructured": "Nguyen, T. M., Zhang, Y. & Pandolfi, P. P. Virus against virus: a potential treatment for 2019-nCov (SARS-CoV-2) and other RNA viruses. Cell Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0290-0 (2020).",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2022.103827",
"author": "DG Ryan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "61662_CR62",
"unstructured": "Ryan, D. G. et al. Nrf2 activation reprograms macrophage intermediary metabolism and suppresses the type I interferon response. iScience 25, 1 (2022).",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27640",
"author": "H Gümüş",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "61662_CR63",
"unstructured": "Gümüş, H., Erat, T., Öztürk, İ, Demir, A. & Koyuncu, I. Oxidative stress and decreased Nrf2 level in pediatric patients with COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 94, 1 (2022).",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.03.020",
"author": "W Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Brain Res. Bull.",
"key": "61662_CR64",
"unstructured": "Dai, W. et al. Curcumin provides neuroprotection in model of traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Brain Res. Bull. 140, 65 (2018).",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13099-022-00481-5",
"author": "Y Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "Gut. Pathog.",
"key": "61662_CR65",
"unstructured": "Wang, Y., Dan, K., Xue, X., Chen, B. & Chen, C. Curcumin assists anti-EV71 activity of IFN-α by inhibiting IFNAR1 reduction in SH-SY5Y cells. Gut. Pathog. 14, 8 (2022).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14814/phy2.14707",
"author": "RMR Lemes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Physiol. Rep.",
"key": "61662_CR66",
"unstructured": "Lemes, R. M. R. et al. 17β-estradiol reduces SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. Physiol. Rep. 9, 1 (2021).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26226900",
"author": "D Marín-Palma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6900",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "61662_CR67",
"unstructured": "Marín-Palma, D. et al. Curcumin inhibits in vitro sars-cov-2 infection in vero e6 cells through multiple antiviral mechanisms. Molecules 26, 6900 (2021).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 67,
"references-count": 67,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-61662-7"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin and curcuminoids in SH-SY5Y cells infected by SARS-CoV-2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "14"
}