Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study
et al., Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552, May 2022
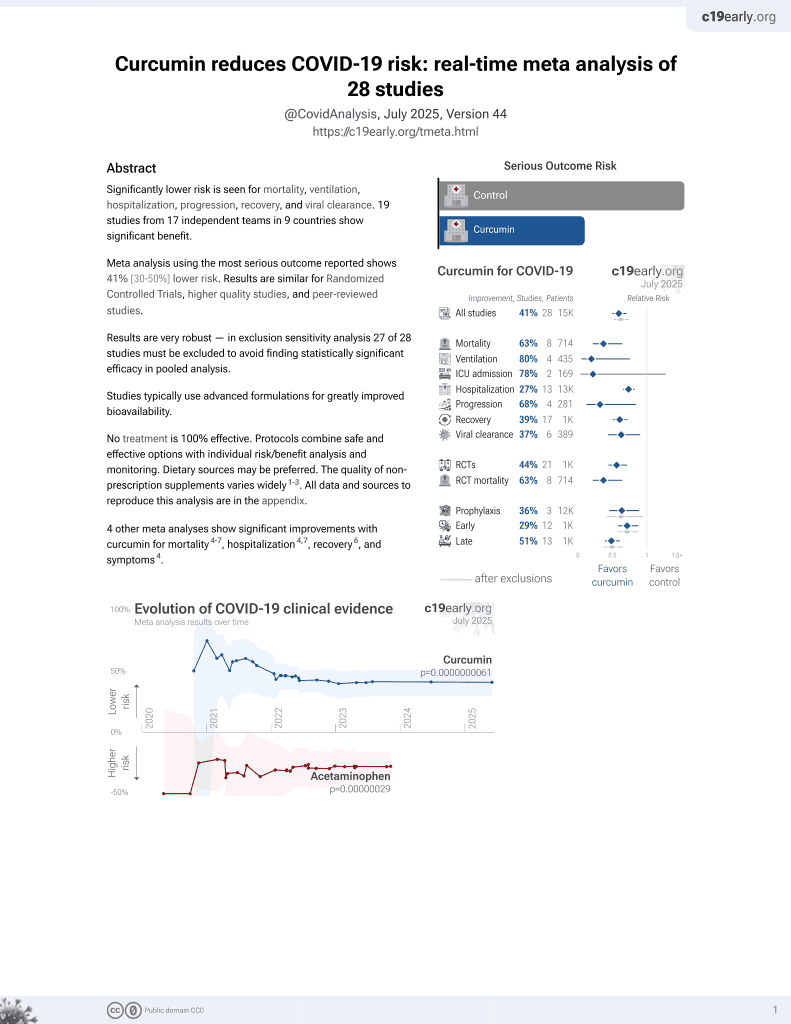
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In silico study showing showing significant inhibitory potential of curcumin for omicron.
62 preclinical studies support the efficacy of curcumin for COVID-19:
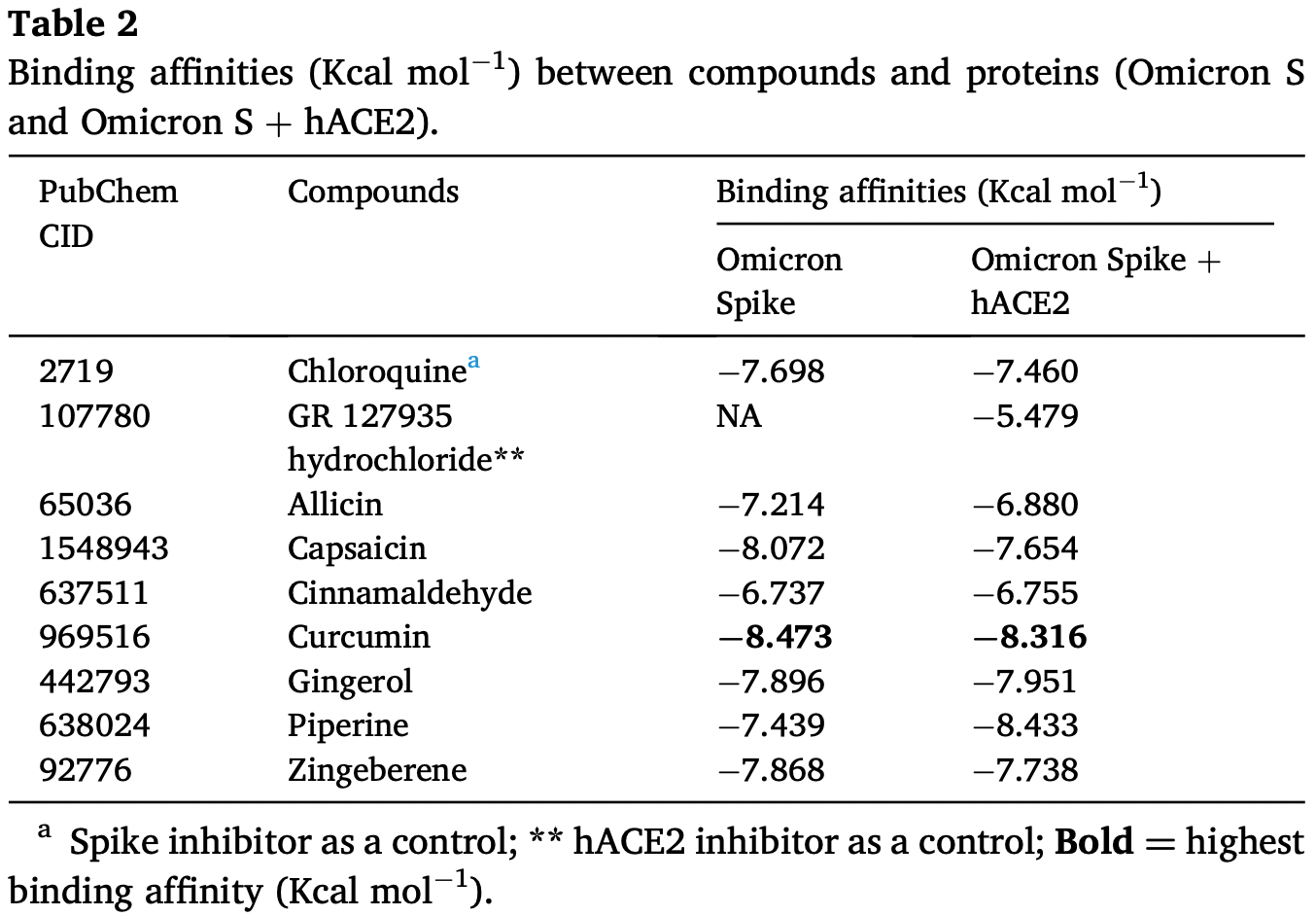
In silico studies predict inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 with curcumin or metabolites via binding to the spikeA,1,5,6,11,16,18,24,27 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,2,4,14,17,20 ), MproC,4-6,11,13,15-17,19,20,22,25,27,28,30,48 , RNA-dependent RNA polymeraseD,4-6,17,26 , PLproE,6, ACE2F,2,18,19,21 , nucleocapsidG,12,29 , nsp10H,29, and helicaseI,36 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3.
In vitro studies demonstrate inhibition of the spikeA,41 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,51), MproC,23,41,48,50 , ACE2F,51, and TMPRSS2K,51 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3,34 .
In vitro studies demonstrate efficacy in Calu-3L,49, A549M,41, A549-ATN,31, 293TO,7, HEK293-hACE2P,23,39 , 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2Q,40, Vero E6R,1,13,17,27,39,41,43,45,47,49 , and SH-SY5YS,38 cells.
Curcumin decreases pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by SARS-CoV-2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells47, alleviates SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-induced mitochondrial membrane damage and oxidative stress7, may limit COVID-19 induced cardiac damage by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway which mediates the profibrotic effects of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein on cardiac fibroblasts35, is predicted to inhibit the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain and the human ACE2 receptor for the delta and omicron variants14, lowers ACE2 and STAT3, curbing lung inflammation and ARDS in preclinical COVID-19 models32, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a ion channel activity, which contributes to viral pathogenicity and cytotoxicity42, has direct virucidal action by disrupting viral envelope integrity44, may inhibit viral replication and modulate inflammatory pathways like NF-κB via SIRT1 activation52, and can function as a photosensitizer in photodynamic therapy to generate reactive oxygen species that damage the virus44.
1.
Marzouk et al., Computational and Experimental Insights into the Antiviral Mechanism of Turmeric (Curcuma longa) against SARS-CoV-2 D614G, BIO Web of Conferences, doi:10.1051/bioconf/202519804002.
2.
Wu et al., Utilizing natural compounds as ligands to disrupt the binding of SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, impeding viral infection, Phytochemistry Letters, doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2025.102999.
3.
Najimi et al., Phytochemical Inhibitors of SARS‐CoV‐2 Entry: Targeting the ACE2‐RBD Interaction with l‐Tartaric Acid, l‐Ascorbic Acid, and Curcuma longa Extract, ChemistrySelect, doi:10.1002/slct.202406035.
4.
Rajamanickam et al., Exploring the Potential of Siddha Formulation MilagaiKudineer-Derived Phytotherapeutics Against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Investigation for Antiviral Intervention, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, doi:10.26502/fjppr.0105.
5.
Al balawi et al., Assessing multi-target antiviral and antioxidant activities of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2: an integrated in vitro and in silico study, Bioresources and Bioprocessing, doi:10.1186/s40643-024-00822-z.
6.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
7.
Zhang et al., Computational Discovery of Mitochondrial Dysfunction Biomarkers in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Facilitating Pytomedicine Screening, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784.
8.
Öztürkkan et al., In Silico investigation of the effects of curcuminoids on the spike protein of the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, Baku State University Journal of Chemistry and Material Sciences, 1:2, bsuj.bsu.edu.az/uploads/pdf/ec4204d62f7802de54e6092bf7860029.pdf.
9.
Yunze et al., Therapeutic effect and potential mechanism of curcumin, an active ingredient in Tongnao Decoction, on COVID-19 combined with stroke: a network pharmacology study and GEO database mining, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4329762/v1.
10.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
11.
Boseila et al., Throat spray formulated with virucidal Pharmaceutical excipients as an effective early prophylactic or treatment strategy against pharyngitis post-exposure to SARS CoV-2, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2024.114279.
12.
Hidayah et al., Bioinformatics study of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin and cyclocurcumin compounds in Curcuma longa as an antiviral agent via nucleocapsid on SARS-CoV-2 inhibition, International Conference on Organic and Applied Chemistry, doi:10.1063/5.0197724.
13.
Singh et al., Unlocking the potential of phytochemicals in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 M Pro protein - An in-silico and cell-based approach, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3888947/v1.
14.
Kant et al., Structure-based drug discovery to identify SARS-CoV2 spike protein–ACE2 interaction inhibitors, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2023.2300060.
15.
Naderi Beni et al., In silico studies of anti-oxidative and hot temperament-based phytochemicals as natural inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0295014.
16.
Moschovou et al., Exploring the Binding Effects of Natural Products and Antihypertensive Drugs on SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Investigation of Main Protease and Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242115894.
17.
Eleraky et al., Curcumin Transferosome-Loaded Thermosensitive Intranasal in situ Gel as Prospective Antiviral Therapy for SARS-Cov-2, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S423251.
18.
Singh (B) et al., Computational studies to analyze effect of curcumin inhibition on coronavirus D614G mutated spike protein, The Seybold Report, doi:10.17605/OSF.IO/TKEXJ.
19.
Thapa et al., In-silico Approach for Predicting the Inhibitory Effect of Home Remedies on Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2, Makara Journal of Science, doi:10.7454/mss.v27i3.1609.
20.
Srivastava et al., Paradigm of Well-Orchestrated Pharmacokinetic Properties of Curcuminoids Relative to Conventional Drugs for the Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 Receptors: An In Silico Approach, Stresses, doi:10.3390/stresses3030043.
21.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
22.
Winih Kinasih et al., Analisis in silico interaksi senyawa kurkuminoid terhadap enzim main protease 6LU7 dari SARS-CoV-2, Duta Pharma Journal, doi:10.47701/djp.v3i1.2904.
23.
Wu (B) et al., Potential Mechanism of Curcumin and Resveratrol against SARS-CoV-2, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2780614/v1.
24.
Nag et al., Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552.
25.
Rampogu et al., Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations Discover Curcumin Analogue as a Plausible Dual Inhibitor for SARS-CoV-2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23031771.
26.
Singh (C) et al., Potential of turmeric-derived compounds against RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2: An in-silico approach, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104965.
27.
Kandeil et al., Bioactive Polyphenolic Compounds Showing Strong Antiviral Activities against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10060758.
28.
Rajagopal et al., Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach, Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x.
29.
Suravajhala et al., Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin with COVID-19 Proteins, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v3.
30.
Sekiou et al., In-Silico Identification of Potent Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) from Natural Products: Quercetin, Hispidulin, and Cirsimaritin Exhibited Better Potential Inhibition than Hydroxy-Chloroquine Against COVID-19 Main Protease Active Site and ACE2, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12181404.v1.
31.
Grüneberg et al., Dose-dependent antiviral effects of glycyrrhizin, curcumin, and harmaline against clinical SARS-CoV-2 isolates, including D614G, Omicron BA.5, and Omicron XBB.1, BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, doi:10.1186/s12906-026-05253-1.
32.
Aktay et al., Oral Administration of Water-Soluble Curcumin Complex Prevents ARDS With the Potential for COVID-19 Treatment, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.70046.
33.
Olubiyi et al., Novel dietary herbal preparations with inhibitory activities against multiple SARS-CoV-2 targets: A multidisciplinary investigation into antiviral activities, Food Chemistry Advances, doi:10.1016/j.focha.2025.100969.
34.
Emam et al., Establishment of in-house assay for screening of anti-SARS-CoV-2 protein inhibitors, AMB Express, doi:10.1186/s13568-024-01739-8.
35.
Van Tin et al., Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Activates Cardiac Fibrogenesis through NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161331.
36.
Li et al., Thermal shift assay (TSA)-based drug screening strategy for rapid discovery of inhibitors against the Nsp13 helicase of SARS-CoV-2, Animals and Zoonoses, doi:10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001.
37.
Kamble et al., Nanoparticulate curcumin spray imparts prophylactic and therapeutic properties against SARS-CoV-2, Emergent Materials, doi:10.1007/s42247-024-00754-6.
38.
Nicoliche et al., Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin and curcuminoids in SH-SY5Y cells infected by SARS-CoV-2, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7.
39.
Nittayananta et al., A novel film spray containing curcumin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus infection and enhances mucosal immunity, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02282-x.
40.
Septisetyani et al., Curcumin and turmeric extract inhibited SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus cell entry and Spike mediated cell fusion, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.09.28.560070.
41.
Mohd Abd Razak et al., In Vitro Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activities of Curcumin and Selected Phenolic Compounds, Natural Product Communications, doi:10.1177/1934578X231188861.
42.
Fam et al., Channel activity of SARS-CoV-2 viroporin ORF3a inhibited by adamantanes and phenolic plant metabolites, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31764-9.
43.
Teshima et al., Antiviral activity of curcumin and its analogs selected by an artificial intelligence-supported activity prediction system in SARS-CoV-2-infected VeroE6 cells, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2023.2194647.
44.
Zupin et al., Optimization of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Treatments Based on Curcumin, Used Alone or Employed as a Photosensitizer, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14102132.
45.
Leka et al., In vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 of common herbal medicinal extracts and their bioactive compounds, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7463.
46.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
47.
Marín-Palma et al., Curcumin Inhibits In Vitro SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vero E6 Cells through Multiple Antiviral Mechanisms, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26226900.
48.
Bahun et al., Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro main protease by plant polyphenols, Food Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131594.
49.
Bormann et al., Turmeric Root and Its Bioactive Ingredient Curcumin Effectively Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13101914.
50.
Guijarro-Real et al., Potential In Vitro Inhibition of Selected Plant Extracts against SARS-CoV-2 Chymotripsin-Like Protease (3CLPro) Activity, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods10071503.
a.
The trimeric spike (S) protein is a glycoprotein that mediates viral entry by binding to the host ACE2 receptor, is critical for SARS-CoV-2's ability to infect host cells, and is a target of neutralizing antibodies. Inhibition of the spike protein prevents viral attachment, halting infection at the earliest stage.
b.
The receptor binding domain is a specific region of the spike protein that binds ACE2 and is a major target of neutralizing antibodies. Focusing on the precise binding site allows highly specific disruption of viral attachment with reduced potential for off-target effects.
c.
The main protease or Mpro, also known as 3CLpro or nsp5, is a cysteine protease that cleaves viral polyproteins into functional units needed for replication. Inhibiting Mpro disrupts the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle within the host cell, preventing the creation of new copies.
d.
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called nsp12, is the core enzyme of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex that copies the positive-sense viral RNA genome into negative-sense templates for progeny RNA synthesis. Inhibiting RdRp blocks viral genome replication and transcription.
e.
The papain-like protease (PLpro) has multiple functions including cleaving viral polyproteins and suppressing the host immune response by deubiquitination and deISGylation of host proteins. Inhibiting PLpro may block viral replication and help restore normal immune responses.
f.
The angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) protein is a host cell transmembrane protein that serves as the cellular receptor for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. ACE2 is expressed on many cell types, including epithelial cells in the lungs, and allows the virus to enter and infect host cells. Inhibition may affect ACE2's physiological function in blood pressure control.
g.
The nucleocapsid (N) protein binds and encapsulates the viral genome by coating the viral RNA. N enables formation and release of infectious virions and plays additional roles in viral replication and pathogenesis. N is also an immunodominant antigen used in diagnostic assays.
h.
Non-structural protein 10 (nsp10) serves as an RNA chaperone and stabilizes conformations of nsp12 and nsp14 in the replicase-transcriptase complex, which synthesizes new viral RNAs. Nsp10 disruption may destabilize replicase-transcriptase complex activity.
i.
The helicase, or nsp13, protein unwinds the double-stranded viral RNA, a crucial step in replication and transcription. Inhibition may prevent viral genome replication and the creation of new virus components.
j.
The interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the human ACE2 receptor is a primary method of viral entry, inhibiting this interaction can prevent the virus from attaching to and entering host cells, halting infection at an early stage.
k.
Transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) is a host cell protease that primes the spike protein, facilitating cellular entry. TMPRSS2 activity helps enable cleavage of the spike protein required for membrane fusion and virus entry. Inhibition may especially protect respiratory epithelial cells, buy may have physiological effects.
l.
Calu-3 is a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line with moderate ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. It provides a model of the human respiratory epithelium, but many not be ideal for modeling early stages of infection due to the moderate expression levels of ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
m.
A549 is a human lung carcinoma cell line with low ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Viral entry/replication can be studied but the cells may not replicate all aspects of lung infection.
n.
A549-AT is a human lung carcinoma cell line stably transfected with ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors. Unlike the parental line, this overexpression ensures stable infection and enhanced viral entry, allowing for the evaluation of antiviral efficacy against various SARS-CoV-2 variants.
o.
293T is a human embryonic kidney cell line that can be engineered for high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. 293T cells are easily transfected and support high protein expression.
p.
HEK293-hACE2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line with high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Cells have been transfected with a plasmid to express the human ACE2 (hACE2) protein.
q.
293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line engineered for high ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression, which mimics key aspects of human infection. 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 cells are very susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
r.
Vero E6 is an African green monkey kidney cell line with low/no ACE2 expression and high SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. The cell line is easy to maintain and supports robust viral replication, however the monkey origin may not accurately represent human responses.
s.
SH-SY5Y is a human neuroblastoma cell line that exhibits neuronal phenotypes. It is commonly used as an in vitro model for studying neurotoxicity, neurodegenerative diseases, and neuronal differentiation.
Nag et al., 1 May 2022, India, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: anish.nag@christuniversity.in.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study
Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552
Background: Omicron (B.1.1.529), a variant of SARS-CoV-2 is currently spreading globally as a dominant strain. Due to multiple mutations at its Spike protein, including 15 amino acid substitutions at the receptor binding domain (RBD), Omicron is a variant of concern (VOC) and capable of escaping vaccine generated immunity. So far, no specific treatment regime is suggested for this VOC. Methods: The three-dimensional structure of the Spike RBD domain of Omicron variant was constructed by incorporating 15 amino acid substitutions to the Native Spike (S) structure and structural changes were compared that of the Native S. Seven phytochemicals namely Allicin, Capsaicin, Cinnamaldehyde, Curcumin, Gingerol, Piperine, and Zingeberene were docked with Omicron S protein and Omicron S-hACE2 complex. Further, molecular dynamic simulation was performed between Crcumin and Omicron S protein to evaluate the structural stability of the complex in the physiological environment and compared with that of the control drug Chloroquine. Results: Curcumin, among seven phytochemicals, was found to have the most substantial inhibitory potential with Omicron S protein. Further, it was found that curcumin could disrupt the Omicron S-hACE2 complex. The molecular dynamic simulation demonstrated that Curcumin could form a stable structure with Omicron S in the physiological environment. Conclusion: To conclude, Curcumin can be considered as a potential therapeutic agent against the highly infectious Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2.
Author contributions A.N. conceived, designed the study & performed the experimentations; Primary data analysis & manuscript draft preparation were done by S.P. Secondary data analysis was done by RB and proof reading & manuscript finalisation was done by R.K. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Declaration of competing interest Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi. org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552.
References
Aliebrahimi, Montasser, Kouhsari, Ostad, Arab et al., Identification of phytochemicals targeting c-met kinase domain using consensus docking and molecular dynamics simulation studies, Cell Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1007/s12013-017-0821-6
Choudhary, Malik, Tomar, Identification of SARS-CoV-2 cell entry inhibitors by drug repurposing using in silico structure-based virtual screening approach, Front. Immunol
Cs De Magalhães, Almeida, Barbosa, Dardenne, A dynamic niching genetic algorithm strategy for docking highly flexible ligands, Inf. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ins.2014.08.002
Dedecker, O'brien, Fleming, Geiger, Jackson et al., The crystal structure of a hyperthermophilic archaeal TATA-box binding protein, J. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0697
Desta, Porter, Xia, Kozakov, Vajda, Performance and its limits in rigid body protein-protein docking, Structure, doi:10.1016/j.str.2020.06.006
Dolgin, Omicron thwarts some of the world's most-used COVID vaccines, Nature
Du, Qian, Xue, Molecular simulation of oncostatin M and receptor (OSM-OSMR) interaction as a potential therapeutic target for inflammatory bowel disease, Front. Mol. Biosci
Fu, Tu, Ping, Zheng, Yang et al., Subtype-selective mechanisms of negative allosteric modulators binding to group I metabotropic glutamate receptors, Acta Pharmacol. Sin, doi:10.1038/s41401-020-00541-z
Greaney, Starr, Bloom, An antibody-escape calculator for mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.04.471236
Gupta, Vemula, Donde, Gouda, Behera et al., In-silico approaches to detect inhibitors of the human severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein ion channel, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1751300
Harvey, Carabelli, Jackson, Gupta, Thomson et al., SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0
He, Hong, Pan, Lu, Wei, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: characteristics and prevention, MedComm, doi:10.1002/mco2.110
Jena, Kanungo, Nayak, Chainy Gbn, Dandapat, Catechin and curcumin interact with S protein of SARS-CoV2 and ACE2 of human cell membrane: insights from computational studies, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-81462-7
Korber, Fischer, Gnanakaran, Yoon, Theiler et al., Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike: evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043
Kumari, Kumar, Open Source Drug Discovery Consortium, A. Lynn, g_ mmpbsa-a GROMACS tool for high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations, J. Chem. Inf. Model, doi:10.1021/ci500020m
Kushwaha, Singh, Prajapati, Shuaib, Gupta et al., Phytochemicals present in Indian ginseng possess potential to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 virulence: a molecular docking and MD simulation study, Microb. Pathog, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104954
Kutzner, Páll, Fechner, Esztermann, De Groot et al., More bang for your buck: improved use of GPU nodes for GROMACS 2018, J. Comput. Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.26011
Li, Li, Hong, Wang, Fu et al., Clinical trials, progression-speed differentiating features and swiftness rule of the innovative targets of first-in-class drugs, Briefings Bioinf, doi:10.1093/bib/bby130
Li, Nie, Wu, Zhang, Ding et al., SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 variants lack higher infectivity but do have immune escape, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.042
Liu, Vanblargan, Bloyet, Rothlauf, Chen et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations that attenuate monoclonal and serum antibody neutralization, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2021.01.014
Marín-Palma, Tabares-Guevara, Zapata-Cardona, Flórez-Álvarez, Yepes et al., Curcumin inhibits in vitro SARS-CoV-2 infection in Vero E6 cells through multiple antiviral mechanisms, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26226900
Nag, Banerjee, Chowdhury, Venkatesh, Phytochemicals as potential drug candidates for targeting SARS CoV 2 proteins, an in silico study, Virus. Dis, doi:10.1007/s13337-021-00654-x
Nag, Paul, Banerjee, Kundu, In silico study of some selective phytochemicals against a hypothetical SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD using molecular docking tools, Comput. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104818
Pandurangan, Ochoa-Montaño, Ascher, Blundell, SDM: a server for predicting effects of mutations on protein stability, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkx439
Rao, Shetty, Evolutionary selectivity of amino acid is inspired from the enhanced structural stability and flexibility of the folded protein, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119774
Ren, Wang, Gao, Zhou, Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) of SARS-CoV-2: mutation, infectivity, transmission, and vaccine resistance, World J Clin Cases, doi:10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.1
Ribaudo, Coghi, Yang, Ng, Mastinu et al., Computational and experimental insights on the interaction of artemisinin, dihydroartemisinin and chloroquine with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptorbinding domain (RBD), Nat. Prod. Res, doi:10.1080/14786419.2021.1925894
Richards, Lim, An analysis of packing in the protein folding problem, Q. Rev. Biophys, doi:10.1017/s0033583500002845
Schüttelkopf, Van Aalten, PRODRG: a tool for high-throughput crystallography of protein-ligand complexes, Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr, doi:10.1107/S0907444904011679
Singh, Chauhan, Pandit, Sinha, Gupta et al., The dual role of phytochemicals on SARS-CoV-2 inhibition by targeting host and viral proteins, Complementary Altern. Med, doi:10.1016/j.jtcme.2021.09.001
Tong, Shi, Zhang, Shi, Tracking and controlling the spatiotemporal spread of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in South Africa, Trav. Med. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2021.102252
Wang, Schmidt, Weisblum, Muecksch, Barnes et al., mRNA vaccine-elicited antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and circulating variants, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03324-6
Xue, Wang, Tu, Yang, Zheng et al., Computational identification of the binding mechanism of a triple reuptake inhibitor amitifadine for the treatment of major depressive disorder, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys, doi:10.1039/C7CP07869B
Xue, Yang, Wang, Zheng, Chen et al., What contributes to serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors' dual-targeting mechanism? The key role of transmembrane domain 6 in human serotonin and norepinephrine transporters revealed by molecular dynamics simulation, ACS Chem. Neurosci, doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00490
Yang, Lin, Xing, Zhang, Zhang et al., Structure-based discovery of novel nonpeptide inhibitors targeting SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, J. Chem. Inf. Model, doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00355
Yang, Qin, Li, Tao, Zhou et al., Therapeutic target database update 2016: enriched resource for bench to clinical drug target and targeted pathway information, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkv1230
Yang, Yu, Chang, Liang, Tso et al., Effect of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 mutations on spike protein structure and function, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1038/s41594-021-00652-z
Yang, Zhang, Yang, Zhang, Wu et al., Computational design and modeling of nanobodies toward SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain, Chem. Biol. Drug Des, doi:10.1111/cbdd.13847
Zhang, Wu, Wu, Yang, Chen et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron strain exhibits potent capabilities for immune evasion and viral entrance, Signal Transduct, Targeted Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00852-5
Zhu, Shi, Qin, Tao, Liu et al., Therapeutic target database update 2012: a resource for facilitating target-oriented drug discovery, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkr797
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552",
"ISSN": [
"0010-4825"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552",
"alternative-id": [
"S0010482522003444"
],
"article-number": "105552",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Computers in Biology and Medicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9435-3795",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nag",
"given": "Anish",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Banerjee",
"given": "Ritesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paul",
"given": "Subhabrata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kundu",
"given": "Rita",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Computers in Biology and Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Computers in Biology and Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-27T14:56:12Z",
"timestamp": 1651071372000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-01T09:51:10Z",
"timestamp": 1651398670000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-01T10:11:25Z",
"timestamp": 1651399885136
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656633600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0010482522003444?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0010482522003444?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "105552",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib1",
"unstructured": "WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard n.d. https://covid19.who.int (accessed January 27, 2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mco2.110",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: characteristics and prevention",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "838",
"journal-title": "MedComm",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib2",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib3",
"unstructured": "INSACOG | Department of Biotechnology n.d. https://dbtindia.gov.in/insacog (accessed January 27, 2022)."
},
{
"article-title": "An antibody-escape calculator for mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain",
"author": "Greaney",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2021.102252",
"article-title": "Tracking and controlling the spatiotemporal spread of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in South Africa",
"author": "Tong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Trav. Med. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib5",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00852-5",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron strain exhibits potent capabilities for immune evasion and viral entrance",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Targeted Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib6",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "CDC",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043",
"article-title": "Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike: evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus",
"author": "Korber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "812",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib8",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-021-00652-z",
"article-title": "Effect of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 mutations on spike protein structure and function",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "731",
"journal-title": "Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib9",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-022-00079-6",
"article-title": "Omicron thwarts some of the world’s most-used COVID vaccines",
"author": "Dolgin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7893",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib10",
"volume": "601",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104818",
"article-title": "In silico study of some selective phytochemicals against a hypothetical SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD using molecular docking tools",
"author": "Nag",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Comput. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib11",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1751300",
"article-title": "In-silico approaches to detect inhibitors of the human severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein ion channel",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2617",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib12",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bib/bby130",
"article-title": "Clinical trials, progression-speed differentiating features and swiftness rule of the innovative targets of first-in-class drugs",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "649",
"journal-title": "Briefings Bioinf.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib13",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkv1230",
"article-title": "Therapeutic target database update 2016: enriched resource for bench to clinical drug target and targeted pathway information",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "D1069",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib14",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkr797",
"article-title": "Therapeutic target database update 2012: a resource for facilitating target-oriented drug discovery",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "D1128",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib15",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmolb.2020.00029",
"article-title": "Molecular simulation of oncostatin M and receptor (OSM–OSMR) interaction as a potential therapeutic target for inflammatory bowel disease",
"author": "Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Mol. Biosci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib16",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00490",
"article-title": "What contributes to serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors' dual-targeting mechanism? The key role of transmembrane domain 6 in human serotonin and norepinephrine transporters revealed by molecular dynamics simulation",
"author": "Xue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1128",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem. Neurosci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib17",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41401-020-00541-z",
"article-title": "Subtype-selective mechanisms of negative allosteric modulators binding to group I metabotropic glutamate receptors",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1354",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharmacol. Sin.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib18",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C7CP07869B",
"article-title": "Computational identification of the binding mechanism of a triple reuptake inhibitor amitifadine for the treatment of major depressive disorder",
"author": "Xue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6606",
"journal-title": "Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib19",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtcme.2021.09.001",
"article-title": "The dual role of phytochemicals on SARS-CoV-2 inhibition by targeting host and viral proteins",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Tradit., Complementary Altern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib20",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00355",
"article-title": "Structure-based discovery of novel nonpeptide inhibitors targeting SARS-CoV-2 Mpro",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3917",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inf. Model.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib21",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Phytochemicals as potential drug candidates for targeting SARS CoV 2 proteins, an in silico study",
"author": "Nag",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Virus. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cbdd.13847",
"article-title": "Computational design and modeling of nanobodies toward SARS‐CoV‐2 receptor binding domain",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Chem. Biol. Drug Des.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib23",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib24",
"unstructured": "GISAID - Initiative n.d. https://www.gisaid.org/(accessed January 27, 2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkx439",
"article-title": "SDM: a server for predicting effects of mutations on protein stability",
"author": "Pandurangan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W229",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib25",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.str.2020.06.006",
"article-title": "Performance and its limits in rigid body protein-protein docking",
"author": "Desta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1071",
"journal-title": "Structure",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib26",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14786419.2021.1925894",
"article-title": "Computational and experimental insights on the interaction of artemisinin, dihydroartemisinin and chloroquine with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor-binding domain (RBD)",
"author": "Ribaudo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat. Prod. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01664",
"article-title": "Identification of SARS-CoV-2 cell entry inhibitors by drug repurposing using in silico structure-based virtual screening approach",
"author": "Choudhary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib28",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ins.2014.08.002",
"article-title": "A dynamic niching genetic algorithm strategy for docking highly flexible ligands",
"author": "Magalhães",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "206",
"journal-title": "Inf. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib29",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.26011",
"article-title": "More bang for your buck: improved use of GPU nodes for GROMACS 2018",
"author": "Kutzner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2418",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib30",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444904011679",
"article-title": "PRODRG: a tool for high-throughput crystallography of protein-ligand complexes",
"author": "Schüttelkopf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1355",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib31",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ci500020m",
"article-title": "g_mmpbsa-a GROMACS tool for high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations",
"author": "Kumari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1951",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inf. Model.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib32",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119774",
"article-title": "Evolutionary selectivity of amino acid is inspired from the enhanced structural stability and flexibility of the folded protein",
"author": "Rao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib33",
"volume": "281",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0033583500002845",
"article-title": "An analysis of packing in the protein folding problem",
"author": "Richards",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "423",
"journal-title": "Q. Rev. Biophys.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib34",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/jmbi.1996.0697",
"article-title": "The crystal structure of a hyperthermophilic archaeal TATA-box binding protein",
"author": "DeDecker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1072",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib35",
"volume": "264",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape",
"author": "Harvey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "409",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib36",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.042",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 variants lack higher infectivity but do have immune escape",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2362",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib37",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2021.01.014",
"article-title": "Identification of SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations that attenuate monoclonal and serum antibody neutralization",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "477",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib38",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03324-6",
"article-title": "mRNA vaccine-elicited antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and circulating variants",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "616",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib39",
"volume": "592",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.1",
"article-title": "Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) of SARS-CoV-2: mutation, infectivity, transmission, and vaccine resistance",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "World J Clin Cases",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib40",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-81462-7",
"article-title": "Catechin and curcumin interact with S protein of SARS-CoV2 and ACE2 of human cell membrane: insights from computational studies",
"author": "Jena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2043",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib41",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26226900",
"article-title": "Curcumin inhibits in vitro SARS-CoV-2 infection in Vero E6 cells through multiple antiviral mechanisms",
"author": "Marín-Palma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6900",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib42",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104954",
"article-title": "Phytochemicals present in Indian ginseng possess potential to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 virulence: a molecular docking and MD simulation study",
"author": "Kushwaha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Microb. Pathog.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib43",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12013-017-0821-6",
"article-title": "Identification of phytochemicals targeting c-met kinase domain using consensus docking and molecular dynamics simulation studies",
"author": "Aliebrahimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "135",
"journal-title": "Cell Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552_bib44",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 44,
"references-count": 44,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0010482522003444"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Health Informatics",
"Computer Science Applications"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "146"
}