Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach
et al., Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x, Oct 2020
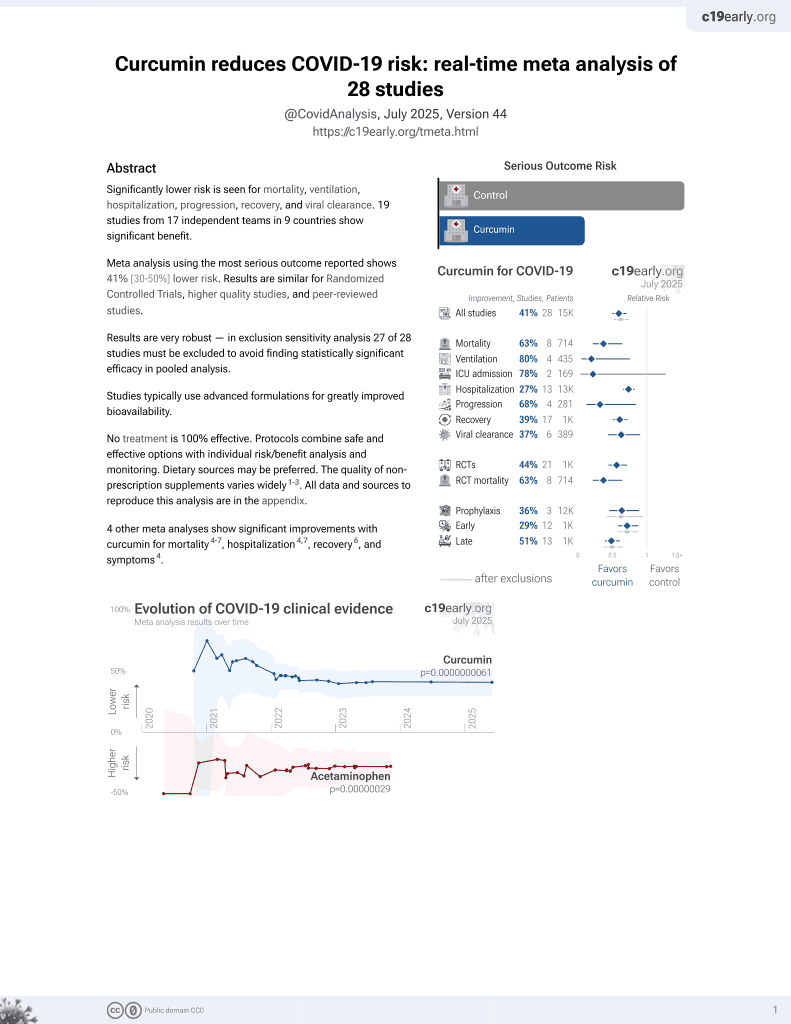
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
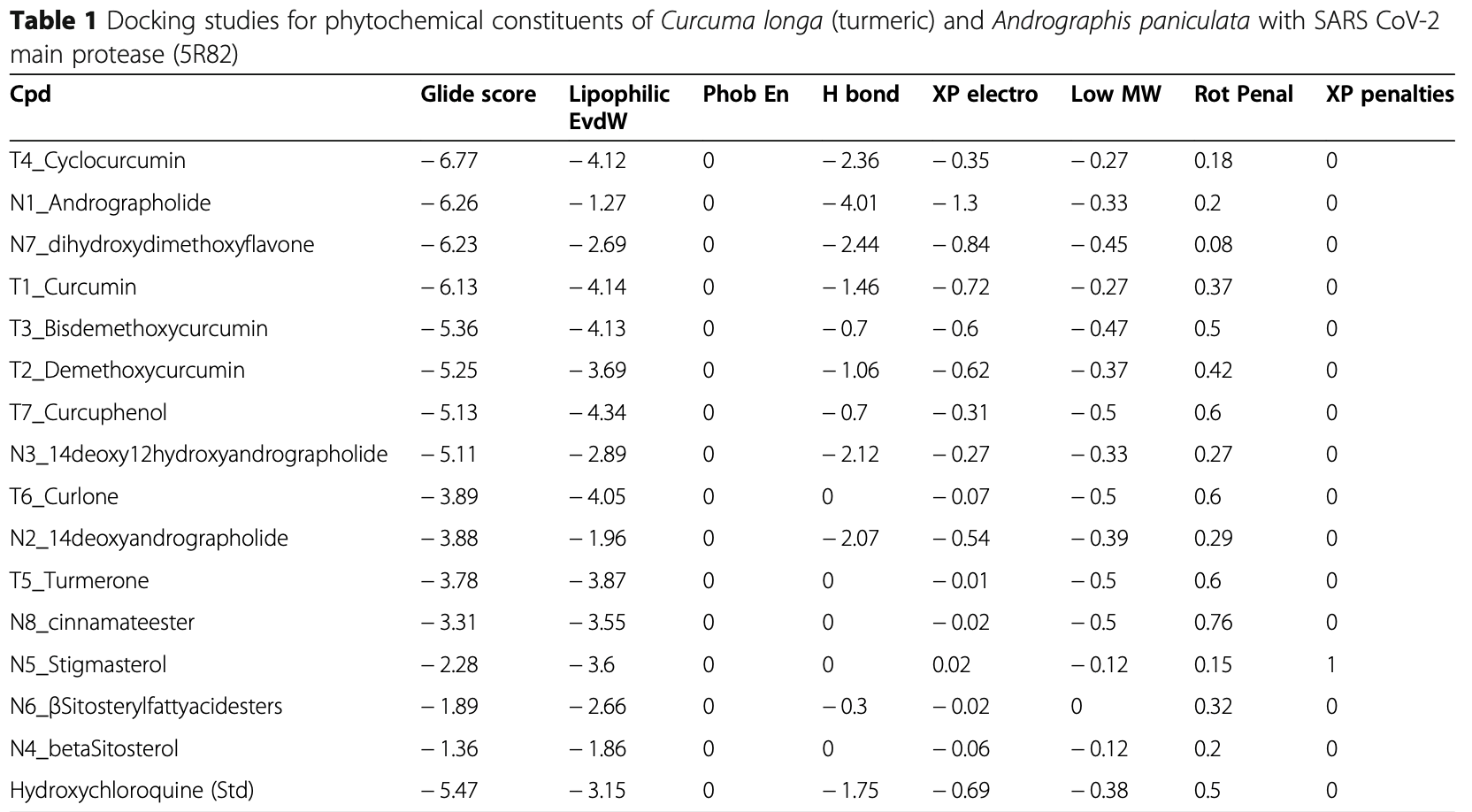
In silico study of several phytochemical compounds from Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata for their potential activity against COVID-19 by targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Molecular docking analysis found the turmeric compounds cyclocurcumin and curcumin and the Andrographis paniculata compounds andrographolide and dihydroxy dimethoxy flavone bind significantly stronger to the SARS-CoV-2 protease compared to hydroxychloroquine, with favorable ADMET properties. The ligands exhibited similar binding modes, with key interactions mediated by several conserved residues in the protease active site. MM-GBSA binding energy calculations further confirmed the stability of the ligand-protease complexes. Overall, the turmeric and Andrographis paniculata compounds show promising in silico activity against the SARS-CoV-2 protease, warranting further in vitro and in vivo evaluation of their potential benefits for COVID-19 treatment.
62 preclinical studies support the efficacy of curcumin for COVID-19:
In silico studies predict inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 with curcumin or metabolites via binding to the spikeA,1,5,6,11,16,18,24,27 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,2,4,14,17,20 ), MproC,4-6,11,13,15-17,19,20,22,25,27,28,30,48 , RNA-dependent RNA polymeraseD,4-6,17,26 , PLproE,6, ACE2F,2,18,19,21 , nucleocapsidG,12,29 , nsp10H,29, and helicaseI,36 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3.
In vitro studies demonstrate inhibition of the spikeA,41 (and specifically the receptor binding domainB,51), MproC,23,41,48,50 , ACE2F,51, and TMPRSS2K,51 proteins, and inhibition of spike-ACE2 interactionJ,3,34 .
In vitro studies demonstrate efficacy in Calu-3L,49, A549M,41, A549-ATN,31, 293TO,7, HEK293-hACE2P,23,39 , 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2Q,40, Vero E6R,1,13,17,27,39,41,43,45,47,49 , and SH-SY5YS,38 cells.
Curcumin decreases pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by SARS-CoV-2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells47, alleviates SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-induced mitochondrial membrane damage and oxidative stress7, may limit COVID-19 induced cardiac damage by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway which mediates the profibrotic effects of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein on cardiac fibroblasts35, is predicted to inhibit the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain and the human ACE2 receptor for the delta and omicron variants14, lowers ACE2 and STAT3, curbing lung inflammation and ARDS in preclinical COVID-19 models32, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a ion channel activity, which contributes to viral pathogenicity and cytotoxicity42, has direct virucidal action by disrupting viral envelope integrity44, may inhibit viral replication and modulate inflammatory pathways like NF-κB via SIRT1 activation52, and can function as a photosensitizer in photodynamic therapy to generate reactive oxygen species that damage the virus44.
Study covers curcumin and andrographolide.
1.
Marzouk et al., Computational and Experimental Insights into the Antiviral Mechanism of Turmeric (Curcuma longa) against SARS-CoV-2 D614G, BIO Web of Conferences, doi:10.1051/bioconf/202519804002.
2.
Wu et al., Utilizing natural compounds as ligands to disrupt the binding of SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, impeding viral infection, Phytochemistry Letters, doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2025.102999.
3.
Najimi et al., Phytochemical Inhibitors of SARS‐CoV‐2 Entry: Targeting the ACE2‐RBD Interaction with l‐Tartaric Acid, l‐Ascorbic Acid, and Curcuma longa Extract, ChemistrySelect, doi:10.1002/slct.202406035.
4.
Rajamanickam et al., Exploring the Potential of Siddha Formulation MilagaiKudineer-Derived Phytotherapeutics Against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Investigation for Antiviral Intervention, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, doi:10.26502/fjppr.0105.
5.
Al balawi et al., Assessing multi-target antiviral and antioxidant activities of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2: an integrated in vitro and in silico study, Bioresources and Bioprocessing, doi:10.1186/s40643-024-00822-z.
6.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
7.
Zhang et al., Computational Discovery of Mitochondrial Dysfunction Biomarkers in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Facilitating Pytomedicine Screening, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155784.
8.
Öztürkkan et al., In Silico investigation of the effects of curcuminoids on the spike protein of the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, Baku State University Journal of Chemistry and Material Sciences, 1:2, bsuj.bsu.edu.az/uploads/pdf/ec4204d62f7802de54e6092bf7860029.pdf.
9.
Yunze et al., Therapeutic effect and potential mechanism of curcumin, an active ingredient in Tongnao Decoction, on COVID-19 combined with stroke: a network pharmacology study and GEO database mining, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4329762/v1.
10.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
11.
Boseila et al., Throat spray formulated with virucidal Pharmaceutical excipients as an effective early prophylactic or treatment strategy against pharyngitis post-exposure to SARS CoV-2, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2024.114279.
12.
Hidayah et al., Bioinformatics study of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin and cyclocurcumin compounds in Curcuma longa as an antiviral agent via nucleocapsid on SARS-CoV-2 inhibition, International Conference on Organic and Applied Chemistry, doi:10.1063/5.0197724.
13.
Singh et al., Unlocking the potential of phytochemicals in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 M Pro protein - An in-silico and cell-based approach, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3888947/v1.
14.
Kant et al., Structure-based drug discovery to identify SARS-CoV2 spike protein–ACE2 interaction inhibitors, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2023.2300060.
15.
Naderi Beni et al., In silico studies of anti-oxidative and hot temperament-based phytochemicals as natural inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0295014.
16.
Moschovou et al., Exploring the Binding Effects of Natural Products and Antihypertensive Drugs on SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Investigation of Main Protease and Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242115894.
17.
Eleraky et al., Curcumin Transferosome-Loaded Thermosensitive Intranasal in situ Gel as Prospective Antiviral Therapy for SARS-Cov-2, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S423251.
18.
Singh (B) et al., Computational studies to analyze effect of curcumin inhibition on coronavirus D614G mutated spike protein, The Seybold Report, doi:10.17605/OSF.IO/TKEXJ.
19.
Thapa et al., In-silico Approach for Predicting the Inhibitory Effect of Home Remedies on Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2, Makara Journal of Science, doi:10.7454/mss.v27i3.1609.
20.
Srivastava et al., Paradigm of Well-Orchestrated Pharmacokinetic Properties of Curcuminoids Relative to Conventional Drugs for the Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 Receptors: An In Silico Approach, Stresses, doi:10.3390/stresses3030043.
21.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
22.
Winih Kinasih et al., Analisis in silico interaksi senyawa kurkuminoid terhadap enzim main protease 6LU7 dari SARS-CoV-2, Duta Pharma Journal, doi:10.47701/djp.v3i1.2904.
23.
Wu (B) et al., Potential Mechanism of Curcumin and Resveratrol against SARS-CoV-2, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2780614/v1.
24.
Nag et al., Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105552.
25.
Rampogu et al., Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations Discover Curcumin Analogue as a Plausible Dual Inhibitor for SARS-CoV-2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23031771.
26.
Singh (C) et al., Potential of turmeric-derived compounds against RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2: An in-silico approach, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104965.
27.
Kandeil et al., Bioactive Polyphenolic Compounds Showing Strong Antiviral Activities against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10060758.
28.
Rajagopal et al., Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach, Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x.
29.
Suravajhala et al., Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin with COVID-19 Proteins, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v3.
30.
Sekiou et al., In-Silico Identification of Potent Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) from Natural Products: Quercetin, Hispidulin, and Cirsimaritin Exhibited Better Potential Inhibition than Hydroxy-Chloroquine Against COVID-19 Main Protease Active Site and ACE2, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12181404.v1.
31.
Grüneberg et al., Dose-dependent antiviral effects of glycyrrhizin, curcumin, and harmaline against clinical SARS-CoV-2 isolates, including D614G, Omicron BA.5, and Omicron XBB.1, BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, doi:10.1186/s12906-026-05253-1.
32.
Aktay et al., Oral Administration of Water-Soluble Curcumin Complex Prevents ARDS With the Potential for COVID-19 Treatment, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.70046.
33.
Olubiyi et al., Novel dietary herbal preparations with inhibitory activities against multiple SARS-CoV-2 targets: A multidisciplinary investigation into antiviral activities, Food Chemistry Advances, doi:10.1016/j.focha.2025.100969.
34.
Emam et al., Establishment of in-house assay for screening of anti-SARS-CoV-2 protein inhibitors, AMB Express, doi:10.1186/s13568-024-01739-8.
35.
Van Tin et al., Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Activates Cardiac Fibrogenesis through NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161331.
36.
Li et al., Thermal shift assay (TSA)-based drug screening strategy for rapid discovery of inhibitors against the Nsp13 helicase of SARS-CoV-2, Animals and Zoonoses, doi:10.1016/j.azn.2024.06.001.
37.
Kamble et al., Nanoparticulate curcumin spray imparts prophylactic and therapeutic properties against SARS-CoV-2, Emergent Materials, doi:10.1007/s42247-024-00754-6.
38.
Nicoliche et al., Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin and curcuminoids in SH-SY5Y cells infected by SARS-CoV-2, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7.
39.
Nittayananta et al., A novel film spray containing curcumin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus infection and enhances mucosal immunity, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02282-x.
40.
Septisetyani et al., Curcumin and turmeric extract inhibited SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus cell entry and Spike mediated cell fusion, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.09.28.560070.
41.
Mohd Abd Razak et al., In Vitro Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activities of Curcumin and Selected Phenolic Compounds, Natural Product Communications, doi:10.1177/1934578X231188861.
42.
Fam et al., Channel activity of SARS-CoV-2 viroporin ORF3a inhibited by adamantanes and phenolic plant metabolites, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31764-9.
43.
Teshima et al., Antiviral activity of curcumin and its analogs selected by an artificial intelligence-supported activity prediction system in SARS-CoV-2-infected VeroE6 cells, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2023.2194647.
44.
Zupin et al., Optimization of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Treatments Based on Curcumin, Used Alone or Employed as a Photosensitizer, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14102132.
45.
Leka et al., In vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 of common herbal medicinal extracts and their bioactive compounds, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7463.
46.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
47.
Marín-Palma et al., Curcumin Inhibits In Vitro SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vero E6 Cells through Multiple Antiviral Mechanisms, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26226900.
48.
Bahun et al., Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro main protease by plant polyphenols, Food Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131594.
49.
Bormann et al., Turmeric Root and Its Bioactive Ingredient Curcumin Effectively Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13101914.
50.
Guijarro-Real et al., Potential In Vitro Inhibition of Selected Plant Extracts against SARS-CoV-2 Chymotripsin-Like Protease (3CLPro) Activity, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods10071503.
a.
The trimeric spike (S) protein is a glycoprotein that mediates viral entry by binding to the host ACE2 receptor, is critical for SARS-CoV-2's ability to infect host cells, and is a target of neutralizing antibodies. Inhibition of the spike protein prevents viral attachment, halting infection at the earliest stage.
b.
The receptor binding domain is a specific region of the spike protein that binds ACE2 and is a major target of neutralizing antibodies. Focusing on the precise binding site allows highly specific disruption of viral attachment with reduced potential for off-target effects.
c.
The main protease or Mpro, also known as 3CLpro or nsp5, is a cysteine protease that cleaves viral polyproteins into functional units needed for replication. Inhibiting Mpro disrupts the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle within the host cell, preventing the creation of new copies.
d.
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called nsp12, is the core enzyme of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex that copies the positive-sense viral RNA genome into negative-sense templates for progeny RNA synthesis. Inhibiting RdRp blocks viral genome replication and transcription.
e.
The papain-like protease (PLpro) has multiple functions including cleaving viral polyproteins and suppressing the host immune response by deubiquitination and deISGylation of host proteins. Inhibiting PLpro may block viral replication and help restore normal immune responses.
f.
The angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) protein is a host cell transmembrane protein that serves as the cellular receptor for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. ACE2 is expressed on many cell types, including epithelial cells in the lungs, and allows the virus to enter and infect host cells. Inhibition may affect ACE2's physiological function in blood pressure control.
g.
The nucleocapsid (N) protein binds and encapsulates the viral genome by coating the viral RNA. N enables formation and release of infectious virions and plays additional roles in viral replication and pathogenesis. N is also an immunodominant antigen used in diagnostic assays.
h.
Non-structural protein 10 (nsp10) serves as an RNA chaperone and stabilizes conformations of nsp12 and nsp14 in the replicase-transcriptase complex, which synthesizes new viral RNAs. Nsp10 disruption may destabilize replicase-transcriptase complex activity.
i.
The helicase, or nsp13, protein unwinds the double-stranded viral RNA, a crucial step in replication and transcription. Inhibition may prevent viral genome replication and the creation of new virus components.
j.
The interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the human ACE2 receptor is a primary method of viral entry, inhibiting this interaction can prevent the virus from attaching to and entering host cells, halting infection at an early stage.
k.
Transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) is a host cell protease that primes the spike protein, facilitating cellular entry. TMPRSS2 activity helps enable cleavage of the spike protein required for membrane fusion and virus entry. Inhibition may especially protect respiratory epithelial cells, buy may have physiological effects.
l.
Calu-3 is a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line with moderate ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. It provides a model of the human respiratory epithelium, but many not be ideal for modeling early stages of infection due to the moderate expression levels of ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
m.
A549 is a human lung carcinoma cell line with low ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Viral entry/replication can be studied but the cells may not replicate all aspects of lung infection.
n.
A549-AT is a human lung carcinoma cell line stably transfected with ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors. Unlike the parental line, this overexpression ensures stable infection and enhanced viral entry, allowing for the evaluation of antiviral efficacy against various SARS-CoV-2 variants.
o.
293T is a human embryonic kidney cell line that can be engineered for high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. 293T cells are easily transfected and support high protein expression.
p.
HEK293-hACE2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line with high ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Cells have been transfected with a plasmid to express the human ACE2 (hACE2) protein.
q.
293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line engineered for high ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression, which mimics key aspects of human infection. 293T/hACE2/TMPRSS2 cells are very susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
r.
Vero E6 is an African green monkey kidney cell line with low/no ACE2 expression and high SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. The cell line is easy to maintain and supports robust viral replication, however the monkey origin may not accurately represent human responses.
s.
SH-SY5Y is a human neuroblastoma cell line that exhibits neuronal phenotypes. It is commonly used as an in vitro model for studying neurotoxicity, neurodegenerative diseases, and neuronal differentiation.
Rajagopal et al., 16 Oct 2020, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: rkalirajan@ymail.com (corresponding author), rkalirajan@jssuni.edu.in.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach
Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x
Background: In early 2020, many scientists are rushing to discover novel drugs and vaccines against the coronavirus, and treatments for COVID-19, because coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a life-threatening viral disease, affected first in China and quickly spread throughout the world. In this article, in silico studies have been performed to explore the binding modes of chemical constituents for natural remedies like Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against COVID-19 (PDB ID 5R82) targeting coronavirus using Schrodinger suit 2019-4. The molecular docking studies are performed by the Glide module, in silico ADMET screening was performed by the QikProp module, and binding energy of ligands was calculated using the Prime MM-GB/SA module. Results: The chemical constituents from turmeric like cyclocurcumin and curcumin and from Andrographis paniculata like andrographolide and dihydroxy dimethoxy flavone are significantly binding with the active site of SARS CoV-2 main protease with Glide score more than -6 when compared to the currently used drugs hydroxychloroquine (-5.47) and nelfinavir (-5.93). When compared to remdesivir (-6.38), cyclocurcumin from turmeric is significantly more active. The docking results of the compounds exhibited similar mode of interactions with SARS CoV-2. Main protease and the residues THR24, THR25, THR26, LEU27, SER46, MET49, HIE41, GLN189, ARG188, ASP187, MET165, HIE164, PHE181, and THR54 play a crucial role in binding with ligands. Conclusion: Based on in silico investigations, the chemical constituents from turmeric like cyclocurcumin and curcumin and from Andrographis paniculata like andrographolide and dihydroxy dimethoxy flavone, significantly binding with the active site of SARS CoV-2 main protease, may produce significant activity and be useful for further development.
Abbreviations COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; MM-GBSA: Molecular mechanicsgeneralized Born surface area; PDB: Protein data bank; OPLS3: Optimized potentials for liquid simulations; XP: Extra precision
Authors' contributions The authors KR and GB contributed to the technical and preparation of the manuscript. PV and BA contributed to the collection of literature and preparation of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript and ensure that this is the case.
Ethics approval and consent to participate Not applicable
Consent for publication Not applicable
Competing interests The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Abe, Hashimoto, Horie, Curcumin inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production by human peripheral blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages, Pharmacol Res
Aggarwal, Kumar, Bharti, Anticancer potential of curcumin: preclinical and clinical studies, Anticancer Res
Akbar, Andrographis paniculata: a review of pharmacological activities and clinical effects, Altern Med Rev
Bhatia, Singh, Khanna, Effect of curcumin, its alkali salts and Curcuma longa oil in histamine-induced gastric ulceration, Indian J Exp Biol
Boopathi, Andrographis spp.: a source of bitter compounds for medicinal use, Anc Sci Life
Borhanuddin, Shamsuzzoha, Hussain, Hypoglycaemic effects of Andrographis paniculata Nees on nondiabetic rabbits, Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull
Calisher, Carroll, Colwell, Corley, Daszak et al., Statement in support of the scientists, public health professionals, and medical professionals of China combatting COVID-19, Lancet
Chang, Yan, Wang, Coronavirus disease 2019: coronaviruses and blood safety, Transfus Med Rev, doi:10.1016/j.tmrv.2020.02.003
Chaturvedi, Tomar, Tiwari, Singh, Clinical studies on Kalmegh (Andrographis paniculata Nees) in infective hepatitis, J Int Inst Ayurveda
Cross, Chloroquine's use to treat COVID-19 is backed by US government, but many questions remain, Drug Dev
Dua, Ojha, Roy, Joshi, Valecha et al., Antimalarial activity of some xanthones isolated from the roots of Andrographis paniculata, J Ethnopharmacol
Friesner, Murphy, Repasky, Frye, Greenwood et al., Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes, J Med Chem
Gu, Han, Wang, COVID-19: gastrointestinal manifestations and potential fecal-oral transmission, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054
Gupta, Ghosh, Curcuma longa inhibits TNF-alpha induced expression of adhesion molecules on human umbilical vein endothelial cells, Int J Immunopharmacol
Haddad, Sauvain, Deharo, Curcuma as a parasiticidal agent: a review, Planta Med, doi:10.1055/s-0030-1250549
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, Lindquist, Lofy et al., First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001191
Huang, Herrmann, Fast assessment of human receptor-binding capability of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), Bio Rxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.02.01.930537
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30183-5
Husen, Pihie, Nallappan, Screening for antihyperglycaemic activity in several local herbs of Malaysia, J Ethnopharmacol
Jacobson, Pincus, Rapp, Day, Honig et al., A hierarchical approach to all-atom protein loop prediction, Proteins
Jade, Suburb, Matthews, Hamzah, Lapis et al., Semisynthesis and in vitro anticancer activities of andrographolide analogues, Phytochem
Jarukamjorn, Nemoto, Pharmacological aspects of Andrographis paniculata on health and its major diterpenoid constituent andrographolide, J Health Sci
Kabir, Hasan, Rahman, Khan, Hoque et al., A survey of medicinal plants used by the Deb barma clan of the Tripura tribe of Moulvibazar district, Bangladesh, J Ethnobiol Ethnomed
Kalirajan, Gaurav, Pandiselvi, Gowramma, Sankar, Novel thiazine substituted 9-anilinoacridines: synthesis, antitumour activity and structure-activity relationships, Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem, doi:10.2174/1871520619666190408134224
Kalirajan, Gowramma, Jubie, Sankar, Molecular docking studies and in silico ADMET screening of some novel heterocyclic substituted 9anilinoacridines as topoisomerase II inhibitors, JSM Chem
Kalirajan, Mohammed Rafick, Jubie, Sankar, Docking studies, synthesis, characterization and evaluation of their antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of some novel isoxazole substituted 9-anilinoacridine derivatives, Sci World J, doi:10.1100/2012/165258
Kalirajan, Mohammed Rafick, Sankar, Gowramma, Green synthesis of some novel chalcone and isoxazole substituted 9anilinoacridine derivatives and evaluation of their antimicrobial and larvicidal activities, Indian J Chem
Kalirajan, Muralidharan, Jubie, Gowramma, Gomathy et al., Synthesis of some novel pyrazole substituted 9anilinoacridine derivatives and evaluation for their antioxidant and cytotoxic activities, J Heterocyclic Chem
Kalirajan, Muralidharan, Jubie, Sankar, Microwave assisted synthesis, characterization and evaluation for their antimicrobial activities of some novel pyrazole substituted 9-anilino acridine derivatives, Int J Health Allied Sci
Kalirajan, Pandiselvi, Gowramma, Balachandran, In-silico design, ADMET screening, MM-GBSA binding free energy of some novel isoxazole substituted9-anilinoacridines as HER2 inhibitors targeting breast cancer, Curr Drug Res Rev
Kalirajan, Rathore, Jubie, Gowramma, Gomathy et al., Microwave assisted synthesis of some novel pyrazole substituted benzimidazoles and evaluation of their biological activities, Indian J Chem
Kalirajan, Sankar, Jubie, Docking studies, synthesis, characterization of some novel oxazine substituted 9-anilinoacridine derivatives and evaluation for their anti-oxidant and anticancer activities as topo isomerase II inhibitors, Eur J Med Chem
Kalirajan, Sankar, Jubie, Gowramma, Molecular docking studies and in-silico ADMET screening of some novel oxazine substituted 9-anilinoacridines as topoisomerase II inhibitors, Indian J Pharm Educ Res
Kalirajan, Vivek, Sankar, Synthesis, characterization and evaluation for antitumour activity of some novel oxazine substituted 9anilinoacridines and their 3D-QSAR studies, Indian J Pharm Sci
Kim, Park, Kim, Curcuminoids from Curcuma longa L. (Zingiberaceae) that protect PC12 rat pheochromocytoma and normal human umbilical vein endothelial cells from betaA(1-42) insult, Neurosci Lett
Kuroda, Mimaki, Nishiyama, Kishida, Tsukagawa, Hypoglycemic effects of turmeric (Curcuma longa L. Rhizomes) on genetically diabetic KK-A y mice, Biol Pharm Bull
Li, Abel, Zhu, Cao, Zhao et al., The VSGB 2.0 model: a next generation energy model for high resolution protein structure modelling, Proteins
Lu, Zhao, Li, Niu, Yang et al., Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8
Parichatikanond, Suthisisang, Dhepakson, Herunsalee, Study of anti-inflammatory activities of the pure compounds from Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Nees and their effects on gene expression, Int Immunopharmacol
Parthasarathy, Chempakam, Zachariah, Chemistry of spices. United Kingdom
Prakash, Misra, Surin, Jain, Bhatta et al., Anti-platelet effects of Curcuma oil in experimental models of myocardial ischemiareperfusion and thrombosis, Thromb Res, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2010.11.007
Ramirez-Tortosa, Mesa, Aguilera, Quiles, Baro et al., Oral administration of a turmeric extract inhibits LDL oxidation and has hypocholesterolemic effects in rabbits with experimental atherosclerosis, Atherosclerosis
Sastry, Adzhigirey, Day, Annabhimoju, Sherman, Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments, J Comp Aided Mol Design
Srivastava, Dikshit, Srimal, Dhawan, Anti-thrombotic effect of curcumin, Thromb Res
To, Tsang, Yip, Chan, Wu et al., Consistent detection of 2019 novel coronavirus in saliva, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa149
Wang, Hu, Hu, Xiong, Zhao et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Zhang, Kang, Gong, Xu, Wang et al., The digestive system is a potential route of 2019-nCov infection: a bioinformatics analysis based on single-cell transcriptomes, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.01.30.927806
Zhou, Hou, Shen, Huang, Martin et al., Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2, Cell Discov
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A pneumonia associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x",
"ISSN": [
"2314-7253"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n<jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n<jats:p>In early 2020, many scientists are rushing to discover novel drugs and vaccines against the coronavirus, and treatments for COVID-19, because coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a life-threatening viral disease, affected first in China and quickly spread throughout the world. In this article, in silico studies have been performed to explore the binding modes of chemical constituents for natural remedies like <jats:italic>Curcuma longa</jats:italic> (turmeric) and <jats:italic>Andrographis paniculata</jats:italic> against COVID-19 (PDB ID 5R82) targeting coronavirus using Schrodinger suit 2019-4. The molecular docking studies are performed by the Glide module, in silico ADMET screening was performed by the QikProp module, and binding energy of ligands was calculated using the Prime MM-GB/SA module.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec><jats:sec>\n<jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n<jats:p>The chemical constituents from turmeric like cyclocurcumin and curcumin and from <jats:italic>Andrographis paniculata</jats:italic> like andrographolide and dihydroxy dimethoxy flavone are significantly binding with the active site of SARS CoV-2 main protease with Glide score more than − 6 when compared to the currently used drugs hydroxychloroquine (− 5.47) and nelfinavir (− 5.93). When compared to remdesivir (− 6.38), cyclocurcumin from turmeric is significantly more active. The docking results of the compounds exhibited similar mode of interactions with SARS CoV-2. Main protease and the residues THR24, THR25, THR26, LEU27, SER46, MET49, HIE41, GLN189, ARG188, ASP187, MET165, HIE164, PHE181, and THR54 play a crucial role in binding with ligands.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec><jats:sec>\n<jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Based on in silico investigations, the chemical constituents from turmeric like cyclocurcumin and curcumin and from <jats:italic>Andrographis paniculata</jats:italic> like andrographolide and dihydroxy dimethoxy flavone, significantly binding with the active site of SARS CoV-2 main protease, may produce significant activity and be useful for further development.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"126"
],
"article-number": "104",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "23 April 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "4 October 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "16 October 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "Not applicable"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Not applicable"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "The authors have no competing interests to declare."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3382-4316",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rajagopal",
"given": "Kalirajan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Varakumar",
"given": "Potlapati",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baliwada",
"given": "Aparma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Byran",
"given": "Gowramma",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences",
"container-title-short": "Futur J Pharm Sci",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-16T10:03:38Z",
"timestamp": 1602842618000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-16T06:56:48Z",
"timestamp": 1634367408000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-25T05:59:22Z",
"timestamp": 1700891962425
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 57,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1602806400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1602806400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
16
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"author": "D Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1061",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "126_CR1",
"unstructured": "Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Xiong, Zhao, Li, Wang X, Peng (2020) Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 323(11):1061–1069. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001191",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "126_CR2",
"unstructured": "Holshue ML, DeBolt C, Lindquist S, Lindquist S, Lofy KH, Wiesman J, Bruce H, Spitters C, Ericson K, Sara Wilkerson MN, Tural A, Diaz G, Cohn A, Fox LA, Patel A, Gerber SI, Kim L, Tong S, Lu X, Lindstrom S, Pallansch MA, Weldon WC, Biggs HM, Uyeki TM, Pillai SK (2020) First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States. N Engl J Med. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2001191"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-020-0153-3",
"author": "Y Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Cell Discov",
"key": "126_CR3",
"unstructured": "Zhou Y, Hou Y, Shen J, Huang Y, Martin W, Cheng F (2020) Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2. Cell Discov 6:14–18",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "126_CR4",
"unstructured": "Gu J, Han B, Wang J (2020) COVID-19: gastrointestinal manifestations and potential fecal-oral transmission. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30418-9",
"author": "C Calisher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e42",
"issue": "10226",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "126_CR5",
"unstructured": "Calisher C, Carroll D, Colwell R, Corley RB, Daszak P, Drosten C, Enjuanes L, Farrar J, Field H, Golding J (2020) Statement in support of the scientists, public health professionals, and medical professionals of China combatting COVID-19. Lancet. 395(10226):e42–e43",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa149",
"author": "KK-W To",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "841",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "126_CR6",
"unstructured": "To KK-W, Tsang OT-Y, Yip CC-Y, Chan K-H, Wu T-C, Chan JM-C, Leung W-S, Chik TS-H, Choi CY-C, Kandamby DH (2020) Consistent detection of 2019 novel coronavirus in saliva. Clin Infect Dis 71(15):841–843. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa149",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "126_CR7",
"unstructured": "Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H, Wang W, Song H, Huang B, Zhu N, Bi Y, Ma X, Zhan F, Liang W, Hu T, Zhou H, Hu Z, Zhou W, Zhao L, Chen J, Meng Y, Wang J, Yang L, Yuan J, Xie Z, Ma J, Liu WJ, Wang D, Xu W, Holmes EC, Gao GF, Wu G, Chen W, Shi W, Tan W (2020) Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"author": "P Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "126_CR8",
"unstructured": "Zhou P, Yang X-L, Wang X-G, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, Si H-R, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang C-L, Chen H-D, Chen J, Luo Y, Guo H, Jiang R-D, Liu M-Q, Chen Y, Shen X-R, Wang X, Zheng X-S, Zhao K, Chen Q-J, Deng F, Liu L-L, Yan B, Zhan F-X, Wang Y-Y, Xiao G-F, Shi Z-L (2020) A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 579:270–273. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.02.01.930537",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "126_CR9",
"unstructured": "Huang Q, Herrmann A (2020) Fast assessment of human receptor-binding capability of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Bio Rxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.01.930537"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.01.30.927806",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "126_CR10",
"unstructured": "Zhang H, Kang Z, Gong H, Xu D, Wang J, Li Z, Cui X, Xiao J, Meng T, Wang Z, Liu J, Xu H (2020) The digestive system is a potential route of 2019-nCov infection: a bioinformatics analysis based on single-cell transcriptomes. bioRxiv:927806. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.30.927806"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmrv.2020.02.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "126_CR11",
"unstructured": "Chang, L., Yan,Y., Wang, L. (2020) Coronavirus disease 2019: coronaviruses and blood safety. Transfus Med Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmrv.2020.02.003."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "126_CR12",
"unstructured": "Huang, C., Wang, Y., Li, X., Ren, L., Zhao, J., Hu, Y. (2020) Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan. China. Lancet. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30183-5."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2010.11.007",
"author": "P Prakash",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "111",
"journal-title": "Thromb Res",
"key": "126_CR13",
"unstructured": "Prakash P, Misra A, Surin WR, Jain M, Bhatta RS, Pal R (2011) Anti-platelet effects of Curcuma oil in experimental models of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion and thrombosis. Thromb Res 127:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2010.11.007",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1248/bpb.28.937",
"author": "M Kuroda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "937",
"journal-title": "Biol Pharm Bull",
"key": "126_CR14",
"unstructured": "Kuroda M, Mimaki Y, Nishiyama T, Mae T, Kishida H, Tsukagawa K (2005) Hypoglycemic effects of turmeric (Curcuma longa L. Rhizomes) on genetically diabetic KK-Ay mice. Biol Pharm Bull 5:937–939",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"author": "BB Aggarwal",
"first-page": "363",
"issue": "1A",
"journal-title": "Anticancer Res",
"key": "126_CR15",
"unstructured": "Aggarwal BB, Kumar A, Bharti AC (2003) Anticancer potential of curcumin: preclinical and clinical studies. Anticancer Res 23(1A):363–398",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1079/9781845934057.0000",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "126_CR16",
"unstructured": "Parthasarathy VA, Chempakam B, Zachariah TJ (2008) Chemistry of spices. United Kingdom. CABI:445–447"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0030-1250549",
"author": "M Haddad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "672",
"journal-title": "Planta Med",
"key": "126_CR17",
"unstructured": "Haddad M, Sauvain M, Deharo E (2010) Curcuma as a parasiticidal agent: a review. Planta Med 77:672–678. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1250549",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/phrs.1998.0404",
"author": "Y Abe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "41",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "126_CR18",
"unstructured": "Abe Y, Hashimoto S, Horie T (1999) Curcumin inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production by human peripheral blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages. Pharmacol Res 39(1):41–47",
"volume": "39",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0192-0561(99)00050-8",
"author": "B Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "745",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Int J Immunopharmacol",
"key": "126_CR19",
"unstructured": "Gupta B, Ghosh B (1999) Curcuma longa inhibits TNF-alpha induced expression of adhesion molecules on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int J Immunopharmacol 21(11):745–757",
"volume": "21",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0049-3848(85)90276-2",
"author": "R Srivastava",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "413",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Thromb Res",
"key": "126_CR20",
"unstructured": "Srivastava R, Dikshit M, Srimal RC, Dhawan BN (1985) Anti-thrombotic effect of curcumin. Thromb Res 40(3):413–417",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"author": "A Bhatia",
"first-page": "158",
"journal-title": "Indian J Exp Biol",
"key": "126_CR21",
"unstructured": "Bhatia A, Singh GB, Khanna NM (1964) Effect of curcumin, its alkali salts and Curcuma longa oil in histamine-induced gastric ulceration. Indian J Exp Biol 2:158–160",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1964"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0021-9150(99)00207-5",
"author": "MC Ramirez-Tortosa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "371",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Atherosclerosis",
"key": "126_CR22",
"unstructured": "Ramirez-Tortosa MC, Mesa MD, Aguilera MC, Quiles JL, Baro L, Ramirez-Tortosa CL, Martinez-Victoria E, Gil A (1999) Oral administration of a turmeric extract inhibits LDL oxidation and has hypocholesterolemic effects in rabbits with experimental atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 147(2):371–378",
"volume": "147",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0304-3940(01)01677-9",
"author": "DS Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "57",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Neurosci Lett",
"key": "126_CR23",
"unstructured": "Kim DS, Park SY, Kim JK (2001) Curcuminoids from Curcuma longa L. (Zingiberaceae) that protect PC12 rat pheochromocytoma and normal human umbilical vein endothelial cells from betaA(1-42) insult. Neurosci Lett 303(1):57–61",
"volume": "303",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"author": "C Boopathi",
"first-page": "164",
"issue": "3-4",
"journal-title": "Anc Sci Life",
"key": "126_CR24",
"unstructured": "Boopathi C (2000) Andrographis spp.: a source of bitter compounds for medicinal use. Anc Sci Life 19(3-4):164–168",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1248/jhs.54.370",
"author": "K Jarukamjorn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "370",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Health Sci",
"key": "126_CR25",
"unstructured": "Jarukamjorn K, Nemoto N (2008) Pharmacological aspects of Andrographis paniculata on health and its major diterpenoid constituent andrographolide. J Health Sci 54(4):370–381",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1746-4269-10-19",
"author": "MH Kabir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "19",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Ethnobiol Ethnomed",
"key": "126_CR26",
"unstructured": "Kabir MH, Hasan N, Rahman MM, Khan JA, Hoque NT, Quddus Bhuiyan MR, Mou SM, Jahan R, Rahmatullah M (2014) A survey of medicinal plants used by the Deb barma clan of the Tripura tribe of Moulvibazar district, Bangladesh. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed 10(1):19",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"author": "M Borhanuddin",
"first-page": "24",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull",
"key": "126_CR27",
"unstructured": "Borhanuddin M, Shamsuzzoha M, Hussain AH (1994) Hypoglycaemic effects of Andrographis paniculata Nees on nondiabetic rabbits. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 20(1):24–26",
"volume": "20",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"author": "S Akbar",
"first-page": "66",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Altern Med Rev",
"key": "126_CR28",
"unstructured": "Akbar S (2011) Andrographis paniculata: a review of pharmacological activities and clinical effects. Altern Med Rev 16(1):66–77",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"author": "GN Chaturvedi",
"first-page": "208",
"journal-title": "J Int Inst Ayurveda",
"key": "126_CR29",
"unstructured": "Chaturvedi GN, Tomar GS, Tiwari SK, Singh KP (1983) Clinical studies on Kalmegh (Andrographis paniculata Nees) in infective hepatitis. J Int Inst Ayurveda 2:208–211",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jep.2004.07.008",
"author": "VK Dua",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "247",
"journal-title": "J Ethnopharmacol",
"key": "126_CR30",
"unstructured": "Dua VK, Ojha VP, Roy R, Joshi BC, Valecha N, Devi CU et al (2004) Anti-malarial activity of some xanthones isolated from the roots of Andrographis paniculata. J Ethnopharmacol 95:247–251",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2010.08.002",
"author": "W Parichatikanond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1361",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "126_CR31",
"unstructured": "Parichatikanond W, Suthisisang C, Dhepakson P, Herunsalee A (2010) Study of anti-inflammatory activities of the pure compounds from Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Nees and their effects on gene expression. Int Immunopharmacol 10:1361–1373",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.11.031",
"author": "SR Jade",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "904",
"journal-title": "Phytochem",
"key": "126_CR32",
"unstructured": "Jade SR, Suburb GS, Matthews C, Hamzah AS, Lapis NH, Saad MS (2007) Semisynthesis and in vitro anticancer activities of andrographolide analogues. Phytochem 68:904–912",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jep.2004.07.004",
"author": "R Husen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "205",
"journal-title": "J Ethnopharmacol",
"key": "126_CR33",
"unstructured": "Husen R, Pihie AH, Nallappan M (2004) Screening for antihyperglycaemic activity in several local herbs of Malaysia. J Ethnopharmacol 95:205–208",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"author": "R Kalirajan",
"first-page": "583",
"journal-title": "Indian J Chem",
"key": "126_CR34",
"unstructured": "Kalirajan R, Mohammed rafick MH, Sankar S, Gowramma B (2018) Green synthesis of some novel chalcone and isoxazole substituted 9-anilinoacridine derivatives and evaluation of their antimicrobial and larvicidal activities. Indian J Chem 57B:583–590",
"volume": "57B",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2278-344X.115682",
"author": "R Kalirajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "81",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int J Health Allied Sci",
"key": "126_CR35",
"unstructured": "Kalirajan R, Muralidharan V, Jubie S, Sankar S (2013) Microwave assisted synthesis, characterization and evaluation for their antimicrobial activities of some novel pyrazole substituted 9-anilino acridine derivatives. Int J Health Allied Sci 2(2):81–87",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jhet.848",
"author": "R Kalirajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "748",
"journal-title": "J Heterocyclic Chem",
"key": "126_CR36",
"unstructured": "Kalirajan R, Muralidharan V, Jubie S, Gowramma B, Gomathy S, Sankar S, Elango K (2012) Synthesis of some novel pyrazole substituted 9-anilinoacridine derivatives and evaluation for their antioxidant and cytotoxic activities. J Heterocyclic Chem 49:748–754",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1100/2012/165258",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "126_CR37",
"unstructured": "Kalirajan R, Mohammed rafick MH, Jubie S, Sankar S (2012) Docking studies, synthesis, characterization and evaluation of their antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of some novel isoxazole substituted 9-anilinoacridine derivatives. Sci World J:165258. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/165258"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.08.025",
"author": "R Kalirajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "217",
"journal-title": "Eur J Med Chem",
"key": "126_CR38",
"unstructured": "Kalirajan R, kulshrestha V, Sankar S, Jubie S (2012) Docking studies, synthesis, characterization of some novel oxazine substituted 9-anilinoacridine derivatives and evaluation for their anti-oxidant and anticancer activities as topo isomerase II inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 56:217–224",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"author": "R Kalirajan",
"first-page": "1794",
"journal-title": "Indian J Chem",
"key": "126_CR39",
"unstructured": "Kalirajan R, Rathore L, Jubie S, Gowramma B, Gomathy S, Sankar S (2011) Microwave assisted synthesis of some novel pyrazole substituted benzimidazoles and evaluation of their biological activities. Indian J Chem 50B:1794–1801",
"volume": "50B",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5530/ijper.51.1.15",
"author": "R Kalirajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Indian J Pharm Educ Res",
"key": "126_CR40",
"unstructured": "Kalirajan R, Sankar S, Jubie S, Gowramma B (2017) Molecular docking studies and in-silico ADMET screening of some novel oxazine substituted 9-anilinoacridines as topoisomerase II inhibitors. Indian J Pharm Educ Res 51(1):110–115",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"author": "R Kalirajan",
"first-page": "1039",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "JSM Chem",
"key": "126_CR41",
"unstructured": "Kalirajan R, Gowramma B, Jubie S, Sankar S (2017) Molecular docking studies and in silico ADMET screening of some novel heterocyclic substituted 9-anilinoacridines as topoisomerase II inhibitors. JSM Chem 5(1):1039–1044",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1871520619666190408134224",
"author": "R Kalirajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1350",
"journal-title": "Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem",
"key": "126_CR42",
"unstructured": "Kalirajan R, Gaurav K, Pandiselvi A, Gowramma B, Sankar S (2019) Novel thiazine substituted 9-anilinoacridines: synthesis, antitumour activity and structure-activity relationships. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 11:1350–1358. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520619666190408134224",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4172/pharmaceutical-sciences.1000439",
"author": "R Kalirajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "921",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Indian J Pharm Sci",
"key": "126_CR43",
"unstructured": "Kalirajan R, Vivek kulshrestha, Sankar, S. (2018) Synthesis, characterization and evaluation for antitumour activity of some novel oxazine substituted 9-anilinoacridines and their 3D-QSAR studies. Indian J Pharm Sci 80(5):921–929",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/2589977511666190912154817",
"author": "R Kalirajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "118",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Curr Drug Res Rev",
"key": "126_CR44",
"unstructured": "Kalirajan R, Pandiselvi A, Gowramma B, Balachandran P (2019) In-silico design, ADMET screening, MM-GBSA binding free energy of some novel isoxazole substituted9-anilinoacridines as HER2 inhibitors targeting breast cancer. Curr Drug Res Rev 11(2):118–128",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10822-013-9644-8",
"author": "GM Sastry",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "221",
"journal-title": "J Comp Aided Mol Design",
"key": "126_CR45",
"unstructured": "Sastry GM, Adzhigirey M, Day T, Annabhimoju R, Sherman W (2013) Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J Comp Aided Mol Design 27:221–234",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/prot.10613",
"author": "MP Jacobson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "351",
"journal-title": "Proteins",
"key": "126_CR46",
"unstructured": "Jacobson MP, Pincus DL, Rapp CS, Day TJF, Honig B, Shaw DE, Friesner RA (2004) A hierarchical approach to all-atom protein loop prediction. Proteins 55:351–367",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jm051256o",
"author": "RA Friesner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6177",
"journal-title": "J Med Chem",
"key": "126_CR47",
"unstructured": "Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Halgren TA, Mainz DT (2006) Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein–ligand complexes. J Med Chem 49:6177–6196",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/prot.23106",
"author": "J Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2794",
"journal-title": "Proteins",
"key": "126_CR48",
"unstructured": "Li J, Abel R, Zhu K, Cao Y, Zhao S, Friesner RA (2011) The VSGB 2.0 model: a next generation energy model for high resolution protein structure modelling. Proteins 79:2794–2812",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"key": "126_CR49",
"unstructured": "Cross R (2020) Chloroquine’s use to treat COVID-19 is backed by US government, but many questions remain. Drug Dev 98(12)"
}
],
"reference-count": 49,
"references-count": 49,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://fjps.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "6"
}