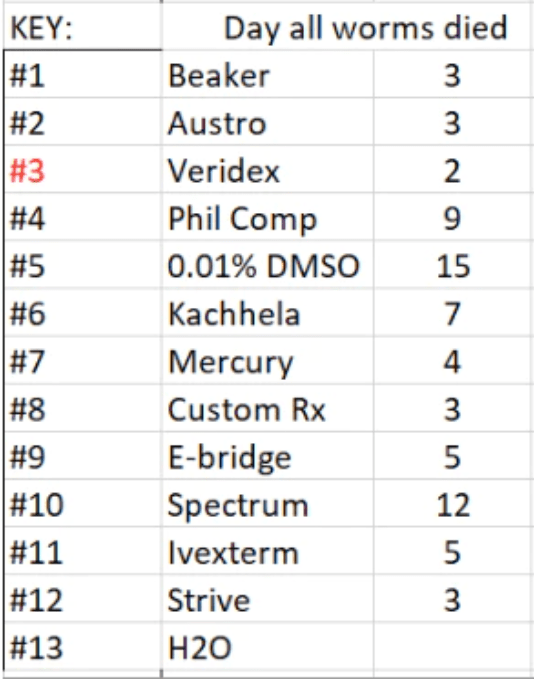
Not All Ivermectin Is Created Equal: Comparing The Quality of 11 Different Ivermectin Sources
, T., Do Your Own Research, Jun 2022
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro analysis of ivermectin from 11 different sources showing highly variable antiparasitic efficacy. Multiple sources and brands were more effective than the US mass produced Edenbridge brand.
74 preclinical studies support the efficacy of ivermectin for COVID-19:
Ivermectin, better known for antiparasitic activity, is a broad spectrum antiviral with activity against many viruses including H7N771, Dengue37,72,73 , HIV-173, Simian virus 4074, Zika37,75,76 , West Nile76, Yellow Fever77,78, Japanese encephalitis77, Chikungunya78, Semliki Forest virus78, Human papillomavirus57, Epstein-Barr57, BK Polyomavirus79, and Sindbis virus78.
Ivermectin inhibits importin-α/β-dependent nuclear import of viral proteins71,73,74,80 , shows spike-ACE2 disruption at 1nM with microfluidic diffusional sizing38, binds to glycan sites on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein preventing interaction with blood and epithelial cells and inhibiting hemagglutination41,81, shows dose-dependent inhibition of wildtype and omicron variants36, exhibits dose-dependent inhibition of lung injury61,66, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 via IMPase inhibition37, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 induced formation of fibrin clots resistant to degradation9, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro54, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RdRp activity28, may minimize viral myocarditis by inhibiting NF-κB/p65-mediated inflammation in macrophages60, may be beneficial for COVID-19 ARDS by blocking GSDMD and NET formation82, may interfere with SARS-CoV-2's immune evasion via ORF8 binding4, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by disrupting CD147 interaction83-86, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 attachment to lipid rafts via spike NTD binding2, shows protection against inflammation, cytokine storm, and mortality in an LPS mouse model sharing key pathological features of severe COVID-1959,87, may be beneficial in severe COVID-19 by binding IGF1 to inhibit the promotion of inflammation, fibrosis, and cell proliferation that leads to lung damage8, may minimize SARS-CoV-2 induced cardiac damage40,48, may counter immune evasion by inhibiting NSP15-TBK1/KPNA1 interaction and restoring IRF3 activation88, may disrupt SARS-CoV-2 N and ORF6 protein nuclear transport and their suppression of host interferon responses1, reduces TAZ/YAP nuclear import, relieving SARS-CoV-2-driven suppression of IRF3 and NF-κB antiviral pathways35, increases Bifidobacteria which play a key role in the immune system89, has immunomodulatory51 and anti-inflammatory70,90 properties, and has an extensive and very positive safety profile91.
1.
Gayozo et al., Binding affinities analysis of ivermectin, nucleocapsid and ORF6 proteins of SARS-CoV-2 to human importins α isoforms: A computational approach, Biotecnia, doi:10.18633/biotecnia.v27.2485.
2.
Lefebvre et al., Characterization and Fluctuations of an Ivermectin Binding Site at the Lipid Raft Interface of the N-Terminal Domain (NTD) of the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16121836.
3.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
4.
Bagheri-Far et al., Non-spike protein inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by natural products through the key mediator protein ORF8, Molecular Biology Research Communications, doi:10.22099/mbrc.2024.50245.2001.
5.
de Oliveira Só et al., In Silico Comparative Analysis of Ivermectin and Nirmatrelvir Inhibitors Interacting with the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202404.1825.v1.
6.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
7.
Oranu et al., Validation of the binding affinities and stabilities of ivermectin and moxidectin against SARS-CoV-2 receptors using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation, GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.30574/gscbps.2024.26.1.0030.
8.
Zhao et al., Identification of the shared gene signatures between pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension using bioinformatics analysis, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1197752.
9.
Vottero et al., Computational Prediction of the Interaction of Ivermectin with Fibrinogen, Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms241411449.
10.
Chellasamy et al., Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors, Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277.
11.
Umar et al., Inhibitory potentials of ivermectin, nafamostat, and camostat on spike protein and some nonstructural proteins of SARS-CoV-2: Virtual screening approach, Jurnal Teknologi Laboratorium, doi:10.29238/teknolabjournal.v11i1.344.
12.
Alvarado et al., Interaction of the New Inhibitor Paxlovid (PF-07321332) and Ivermectin With the Monomer of the Main Protease SARS-CoV-2: A Volumetric Study Based on Molecular Dynamics, Elastic Networks, Classical Thermodynamics and SPT, Computational Biology and Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2022.107692.
13.
Aminpour et al., In Silico Analysis of the Multi-Targeted Mode of Action of Ivermectin and Related Compounds, Computation, doi:10.3390/computation10040051.
14.
Parvez et al., Insights from a computational analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Host–pathogen interaction, pathogenicity, and possible drug therapeutics, Immunity, Inflammation and Disease, doi:10.1002/iid3.639.
15.
Francés-Monerris et al., Microscopic interactions between ivermectin and key human and viral proteins involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, doi:10.1039/D1CP02967C.
16.
González-Paz et al., Comparative study of the interaction of ivermectin with proteins of interest associated with SARS-CoV-2: A computational and biophysical approach, Biophysical Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677.
17.
González-Paz (B) et al., Structural Deformability Induced in Proteins of Potential Interest Associated with COVID-19 by binding of Homologues present in Ivermectin: Comparative Study Based in Elastic Networks Models, Journal of Molecular Liquids, doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284.
18.
Rana et al., A Computational Study of Ivermectin and Doxycycline Combination Drug Against SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-755838/v1.
19.
Muthusamy et al., Virtual Screening Reveals Potential Anti-Parasitic Drugs Inhibiting the Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein, Journal of Virology & Antiviral Research, www.scitechnol.com/abstract/virtual-screening-reveals-potential-antiparasitic-drugs-inhibiting-the-receptor-binding-domain-of-sarscov2-spike-protein-16398.html.
20.
Qureshi et al., Mechanistic insights into the inhibitory activity of FDA approved ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2: old drug with new implications, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1906750.
21.
Schöning et al., Highly-transmissible Variants of SARS-CoV-2 May Be More Susceptible to Drug Therapy Than Wild Type Strains, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-379291/v1.
22.
Bello et al., Elucidation of the inhibitory activity of ivermectin with host nuclear importin α and several SARS-CoV-2 targets, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1911857.
23.
Udofia et al., In silico studies of selected multi-drug targeting against 3CLpro and nsp12 RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase proteins of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV, Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics, doi:10.1007/s13721-021-00299-2.
24.
Choudhury et al., Exploring the binding efficacy of ivermectin against the key proteins of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: an in silico approach, Future Medicine, doi:10.2217/fvl-2020-0342.
25.
Kern et al., Modeling of SARS-CoV-2 Treatment Effects for Informed Drug Repurposing, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.625678.
26.
Saha et al., The Binding mechanism of ivermectin and levosalbutamol with spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, Structural Chemistry, doi:10.1007/s11224-021-01776-0.
27.
Eweas et al., Molecular Docking Reveals Ivermectin and Remdesivir as Potential Repurposed Drugs Against SARS-CoV-2, Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.592908.
28.
Parvez (B) et al., Prediction of potential inhibitors for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 using comprehensive drug repurposing and molecular docking approach, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.098.
29.
Francés-Monerris (B) et al., Has Ivermectin Virus-Directed Effects against SARS-CoV-2? Rationalizing the Action of a Potential Multitarget Antiviral Agent, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12782258.v1.
30.
Kalhor et al., Repurposing of the approved small molecule drugs in order to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 S protein and human ACE2 interaction through virtual screening approaches, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1824816.
31.
Swargiary, A., Ivermectin as a promising RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor and a therapeutic drug against SARS-CoV2: Evidence from in silico studies, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-73308/v1.
32.
Maurya, D., A Combination of Ivermectin and Doxycycline Possibly Blocks the Viral Entry and Modulate the Innate Immune Response in COVID-19 Patients, American Chemical Society (ACS), doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12630539.v1.
33.
Lehrer et al., Ivermectin Docks to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-binding Domain Attached to ACE2, In Vivo, 34:5, 3023-3026, doi:10.21873/invivo.12134.
34.
Suravajhala et al., Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin with COVID-19 Proteins, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v3.
35.
Kofler et al., M-Motif, a potential non-conventional NLS in YAP/TAZ and other cellular and viral proteins that inhibits classic protein import, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2025.112105.
36.
Shahin et al., The selective effect of Ivermectin on different human coronaviruses; in-vitro study, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4180797/v1.
37.
Jitobaom et al., Identification of inositol monophosphatase as a broad‐spectrum antiviral target of ivermectin, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29552.
38.
Fauquet et al., Microfluidic Diffusion Sizing Applied to the Study of Natural Products and Extracts That Modulate the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD/ACE2 Interaction, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28248072.
39.
García-Aguilar et al., In Vitro Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Ivermectin Interaction, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242216392.
40.
Liu et al., SARS-CoV-2 viral genes Nsp6, Nsp8, and M compromise cellular ATP levels to impair survival and function of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, Stem Cell Research & Therapy, doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03485-3.
41.
Boschi et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induces Hemagglutination: Implications for COVID-19 Morbidities and Therapeutics and for Vaccine Adverse Effects, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.11.24.517882.
42.
De Forni et al., Synergistic drug combinations designed to fully suppress SARS-CoV-2 in the lung of COVID-19 patients, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0276751.
43.
Saha (B) et al., Manipulation of Spray-Drying Conditions to Develop an Inhalable Ivermectin Dry Powder, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14071432.
44.
Jitobaom (B) et al., Synergistic anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of repurposed anti-parasitic drug combinations, BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology, doi:10.1186/s40360-022-00580-8.
45.
Croci et al., Liposomal Systems as Nanocarriers for the Antiviral Agent Ivermectin, International Journal of Biomaterials, doi:10.1155/2016/8043983.
46.
Zheng et al., Red blood cell-hitchhiking mediated pulmonary delivery of ivermectin: Effects of nanoparticle properties, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121719.
47.
Delandre et al., Antiviral Activity of Repurposing Ivermectin against a Panel of 30 Clinical SARS-CoV-2 Strains Belonging to 14 Variants, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15040445.
48.
Liu (B) et al., Genome-wide analyses reveal the detrimental impacts of SARS-CoV-2 viral gene Orf9c on human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, Stem Cell Reports, doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.01.014.
49.
Segatori et al., Effect of Ivermectin and Atorvastatin on Nuclear Localization of Importin Alpha and Drug Target Expression Profiling in Host Cells from Nasopharyngeal Swabs of SARS-CoV-2- Positive Patients, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13102084.
50.
Jitobaom (C) et al., Favipiravir and Ivermectin Showed in Vitro Synergistic Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-941811/v1.
51.
Munson et al., Niclosamide and ivermectin modulate caspase-1 activity and proinflammatory cytokine secretion in a monocytic cell line, British Society For Nanomedicine Early Career Researcher Summer Meeting, 2021, web.archive.org/web/20230401070026/https://michealmunson.github.io/COVID.pdf.
52.
Mountain Valley MD, Mountain Valley MD Receives Successful Results From BSL-4 COVID-19 Clearance Trial on Three Variants Tested With Ivectosol™, 5/18, www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2021/05/18/2231755/0/en/Mountain-Valley-MD-Receives-Successful-Results-From-BSL-4-COVID-19-Clearance-Trial-on-Three-Variants-Tested-With-Ivectosol.html.
53.
Yesilbag et al., Ivermectin also inhibits the replication of bovine respiratory viruses (BRSV, BPIV-3, BoHV-1, BCoV and BVDV) in vitro, Virus Research, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198384.
54.
Mody et al., Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents, Communications Biology, doi:10.1038/s42003-020-01577-x.
55.
Jeffreys et al., Remdesivir-ivermectin combination displays synergistic interaction with improved in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2022.106542.
56.
Surnar et al., Clinically Approved Antiviral Drug in an Orally Administrable Nanoparticle for COVID-19, ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci., doi:10.1021/acsptsci.0c00179.
57.
Li et al., Quantitative proteomics reveals a broad-spectrum antiviral property of ivermectin, benefiting for COVID-19 treatment, J. Cellular Physiology, doi:10.1002/jcp.30055.
58.
Caly et al., The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787.
59.
Zhang et al., Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice, Inflammation Research, doi:10.1007/s00011-008-8007-8.
60.
Gao et al., Ivermectin ameliorates acute myocarditis via the inhibition of importin-mediated nuclear translocation of NF-κB/p65, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112073.
61.
Abd-Elmawla et al., Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome by ivermectin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis, Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B, doi:10.1631/jzus.B2200385.
62.
Uematsu et al., Prophylactic administration of ivermectin attenuates SARS-CoV-2 induced disease in a Syrian Hamster Model, The Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.1038/s41429-023-00623-0.
63.
Albariqi et al., Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Inhaled Ivermectin in Mice as a Potential COVID-19 Treatment, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121688.
64.
Errecalde et al., Safety and Pharmacokinetic Assessments of a Novel Ivermectin Nasal Spray Formulation in a Pig Model, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2021.01.017.
65.
Madrid et al., Safety of oral administration of high doses of ivermectin by means of biocompatible polyelectrolytes formulation, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05820.
66.
Ma et al., Ivermectin contributes to attenuating the severity of acute lung injury in mice, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113706.
67.
de Melo et al., Attenuation of clinical and immunological outcomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection by ivermectin, EMBO Mol. Med., doi:10.15252/emmm.202114122.
68.
Arévalo et al., Ivermectin reduces in vivo coronavirus infection in a mouse experimental model, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-86679-0.
69.
Chaccour et al., Nebulized ivermectin for COVID-19 and other respiratory diseases, a proof of concept, dose-ranging study in rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-74084-y.
70.
Yan et al., Anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin in mouse model of allergic asthma, Inflammation Research, doi:10.1007/s00011-011-0307-8.
71.
Götz et al., Influenza A viruses escape from MxA restriction at the expense of efficient nuclear vRNP import, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/srep23138.
72.
Tay et al., Nuclear localization of dengue virus (DENV) 1–4 non-structural protein 5; protection against all 4 DENV serotypes by the inhibitor Ivermectin, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.002.
73.
Wagstaff et al., Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin α/β-mediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus, Biochemical Journal, doi:10.1042/BJ20120150.
74.
Wagstaff (B) et al., An AlphaScreen®-Based Assay for High-Throughput Screening for Specific Inhibitors of Nuclear Import, SLAS Discovery, doi:10.1177/1087057110390360.
75.
Barrows et al., A Screen of FDA-Approved Drugs for Inhibitors of Zika Virus Infection, Cell Host & Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2016.07.004.
76.
Yang et al., The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104760.
77.
Mastrangelo et al., Ivermectin is a potent inhibitor of flavivirus replication specifically targeting NS3 helicase activity: new prospects for an old drug, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dks147.
78.
Varghese et al., Discovery of berberine, abamectin and ivermectin as antivirals against chikungunya and other alphaviruses, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.12.012.
79.
Bennett et al., Role of a nuclear localization signal on the minor capsid Proteins VP2 and VP3 in BKPyV nuclear entry, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2014.10.013.
80.
Kosyna et al., The importin α/β-specific inhibitor Ivermectin affects HIF-dependent hypoxia response pathways, Biological Chemistry, doi:10.1515/hsz-2015-0171.
81.
Scheim et al., Sialylated Glycan Bindings from SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Blood and Endothelial Cells Govern the Severe Morbidities of COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242317039.
82.
Liu (C) et al., Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and immune regulation: insights into pathobiology and therapeutic implications of transfusion-related acute lung injury, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324021.
83.
Shouman et al., SARS-CoV-2-associated lymphopenia: possible mechanisms and the role of CD147, Cell Communication and Signaling, doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01718-3.
84.
Scheim (B), D., Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-Threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-Mediated Vascular Occlusion, SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3636557.
85.
Scheim (C), D., From Cold to Killer: How SARS-CoV-2 Evolved without Hemagglutinin Esterase to Agglutinate and Then Clot Blood Cells, Center for Open Science, doi:10.31219/osf.io/sgdj2.
86.
Behl et al., CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target, Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072.
87.
DiNicolantonio et al., Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350.
88.
Mothae et al., SARS-CoV-2 host-pathogen interactome: insights into more players during pathogenesis, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2025.110607.
89.
Hazan et al., Treatment with Ivermectin Increases the Population of Bifidobacterium in the Gut, ACG 2023, acg2023posters.eventscribe.net/posterspeakers.asp.
Williams et al., 14 Jun 2022, preprint, 1 author.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.