The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
et al., Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458, PROSPERO CRD42021288200, May 2022
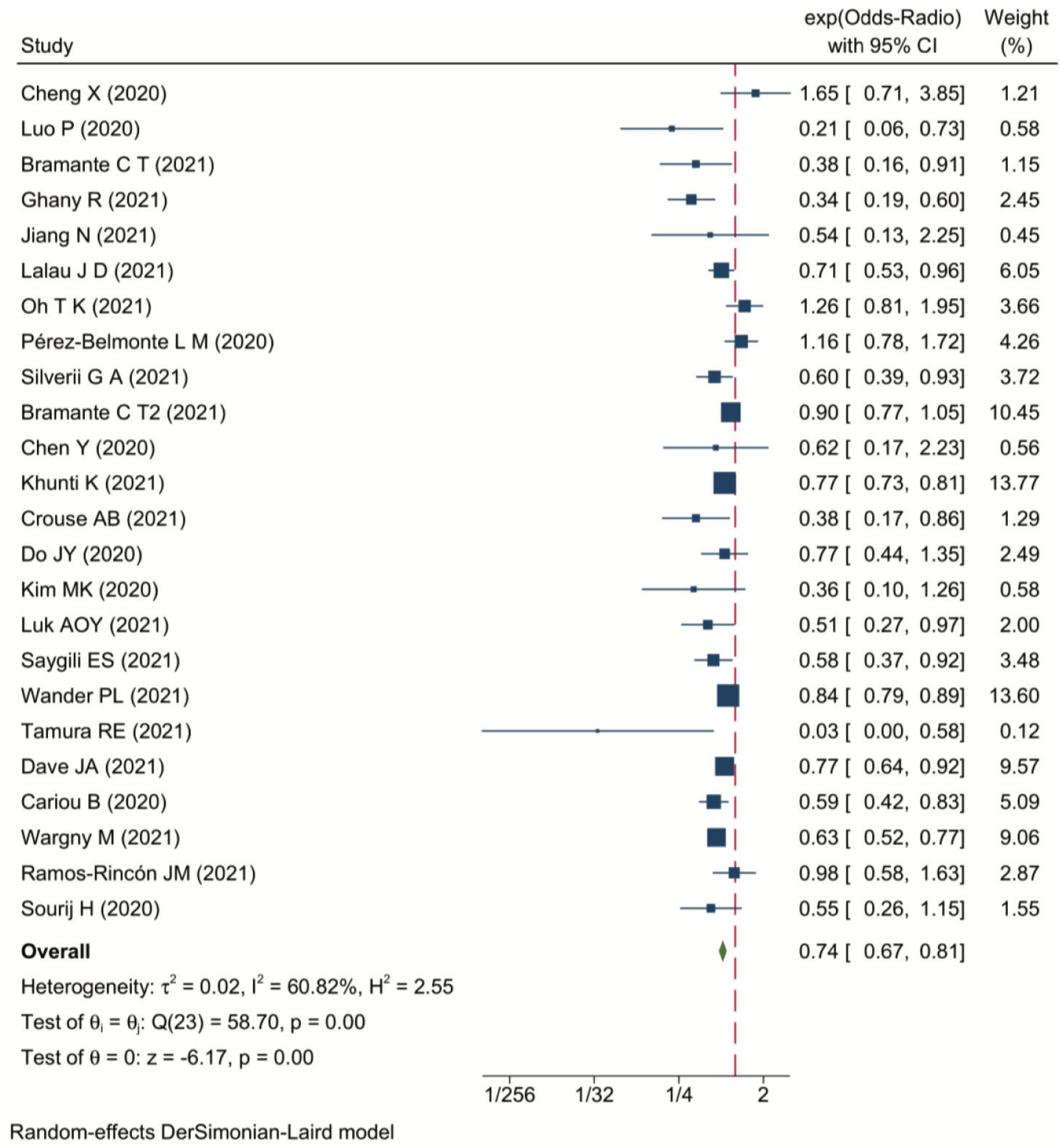
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Meta-analysis of 42 studies (25 for metformin) with 7 antidiabetic agents, showing metformin, DPP4i, SGLT2i, and GLP1RA were associated with lower COVID-19 mortality in patients with diabetes compared to non-users, while insulin was associated with higher mortality.
24 meta-analyses show significant improvements with metformin for mortality1-23,
hospitalization7,13,23 ,
progression1, and
severity8,9,13 .
Currently there are 110 metformin for COVID-19 studies, showing 36% lower mortality [32‑40%], 29% lower ventilation [12‑43%], 19% lower ICU admission [8‑28%], 17% lower hospitalization [11‑23%], and 5% fewer cases [-4‑13%].
|
risk of death, 26.0% lower, OR 0.74, p < 0.001, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Yang et al., The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977.
2.
Lukito et al., The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006.
3.
Kow et al., Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26498.
4.
Hariyanto et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obesity Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290.
5.
Ma et al., Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282210.
6.
Parveen et al., Association of Metformin with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India), doi:10.1055/s-0042-1760353.
7.
Li et al., Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.704666.
8.
Schlesinger et al., Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-023-05928-1.
9.
Petrelli et al., Metformin and Covid-19: a systematic review of systematic reviews with meta-analysis, Acta Biomedica Atenei Parmensis, doi:10.23750/abm.v94iS3.14405.
10.
Oscanoa et al., Metformin therapy and severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a meta-analysis, Clinical Diabetology, doi:10.5603/DK.a2021.0035.
11.
Kan et al., Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.708494.
12.
Poly et al., Metformin Use Is Associated with Decreased Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes: Evidence from Retrospective Studies and Biological Mechanism, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10163507.
13.
Song et al., The Effect of Antihyperglycemic Medications on COVID-19: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review from Observational Studies, Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science, doi:10.1007/s43441-024-00633-6.
14.
Ganesh et al., Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15258.
15.
Nassar et al., Noninsulin‐based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis, Journal of Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13359.
16.
Zhan et al., Effect of Antidiabetic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/10600280221133577.
17.
Nguyen et al., Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155196.
18.
Han et al., Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002.
19.
Chen et al., The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458.
20.
Scheen, A., Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006.
21.
Sun et al., Is Metformin Use Associated With a Decreased Mortality for COVID-19 Diabetic Patients? A Meta-Analysis, Journal of the Endocrine Society, doi:10.1210/jendso/bvab048.709.
Chen et al., 27 May 2022, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD42021288200.
Contact: daimengjun@sjtu.edu.cn.
The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458
Aims: This study aimed to assess the impact of different antidiabetic agents on individuals with diabetes and COVID-19. Methods: We searched PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases from inception to October 31, 2021 and included seven antidiabetic agents. The data were pooled via traditional pairwise meta-analysis and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Results: The pairwise meta-analysis included 35 studies. Metformin (odds ratio (OR), 0.74; P=0.001), dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4i) (OR, 0.88; P=0.04), sodiumglucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) (OR, 0.82; P=0.001), and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP1RA) (OR, 0.91; P=0.02) treatment were associated with lower COVID-19 mortality in individuals with diabetes compared to respective nonusers. However, insulin treatment resulted in higher mortality (OR, 1.8; P=0.001). Mortality did not significantly differ in sulfonylurea (OR, 0.97; P=0.56) and thiazolidinediones (TZDs) (OR, 1.00; P=0.96) users. Furthermore, due to limited data, we analyzed five antidiabetic agents (metformin, DPP4i, sulfonylurea, insulin, and SGLT2i) and found no association between them and severe disease risk (all P>0.05). The Bayesian network meta-analysis included 18 studies. GLP1RA and SGLT2i had the highest first and second rank probability (67.3% and 62.5%, respectively). Insulin showed the maximum probability of ranking seventh (97.0%). Metformin had the third and fourth highest rank probability of 44.8% and 38.9%, respectively. Meanwhile, DPP4i had the fifth-highest rank probability of 42.4%, followed by sulfonylurea at 45.1%.
Conclusion: Metformin, DPP4i, SGLT2i, and GLP1RA treatments were highly possible to reduced COVID-19 mortality risk in individuals with diabetes, while insulin might be related to increased mortality risk. Sulfonylurea and TZDs treatments were not associated with
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS YC, XL, and SL: Conceptualization, methodology, data curation, investigation, and writing -original draft preparation. MA and MD: Supervision, writing -reviewing and editing, and funding acquisition. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2022.895458/ full#supplementary-material Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Publisher's Note: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aroda, A Review of Glp-1 Receptor Agonists: Evolution and Advancement, Through the Lens of Randomised Controlled Trials, Diabetes Obes Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.13162
Bavishi, Whelton, Mancia, Corrao, Messerli, Renin-Angiotensin-System Inhibitors and All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Covid-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies, J Hypertens, doi:10.1097/hjh.0000000000002784
Bonora, Avogaro, Fadini, Disentangling Conflicting Evidence on Dpp-4 Inhibitors and Outcomes of Covid-19: Narrative Review and Meta-Analysis, J Endocrinol Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01515-6
Bramante, Buse, Tamaritz, Palacio, Cohen et al., Outpatient Metformin Use Is Associated With Reduced Severity of Covid-19 Disease in Adults With Overweight or Obesity, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26873
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Marmor, Hovertsen et al., Metformin and Risk of Mortality in Patients Hospitalised With Covid-19: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis, Lancet Healthy Longevity, doi:10.1016/s2666-7568(20)30033-7
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Pichelin, Al-Salameh et al., Phenotypic Characteristics and Prognosis of Inpatients With Covid-19 and Diabetes: The Coronado Study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Chen, Peng et al., Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients With Diabetes and Covid-19 in Association With Glucose-Lowering Medication, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0660
Cheng, Liu, Li, Zhang, Lei et al., Metformin Is Associated With Higher Incidence of Acidosis, But Not Mortality, in Individuals With Covid-19 and Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013
Cheng, Xin, Chen, Li, Li, Effects of Metformin, Insulin on Covid-19 Patients With Pre-Existed Type 2 Diabetes: A Multicentral Retrospective Study, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119371
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Might, Ovalle et al., Metformin Use Is Associated With Reduced Mortality in a Diverse Population With Covid-19 and Diabetes, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.600439
Dai, Zhang, Li, Chen, Zhang, The Effect of Prophylactic Balloon Occlusion in Patients With Placenta Accreta Spectrum: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, Eur Radiol, doi:10.1007/s00330-021-08423-6
Dalan, Ang, Tan, Fong, Tay et al., The Association of Hypertension and Diabetes Pharmacotherapy With Covid-19 Severity and Immune Signatures: An Observational Study, Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother, doi:10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa098
Dalan, Metformin, Neutrophils and Covid-19 Infection, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108230
Das, Dutta, Sglt2 Inhibition and Covid-19: The Road Not Taken, Eur J Clin Invest, doi:10.1111/eci.13339
Dave, Tamuhla, Tiffin, Levitt, Ross et al., Risk Factors for Covid-19 Hospitalisation and Death in People Living With Diabetes: A Virtual Cohort Study From the Western Cape Province, South Africa, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108925
Dias, Welton, Sutton, Caldwell, Lu et al., Evidence Synthesis for Decision Making 4: Inconsistency in Networks of Evidence Based on Randomized Controlled Trials, Med Decision Making, doi:10.1177/0272989X12455847
Do, Kim, Park, Cho, Kang, Is There an Association Between Metformin Use and Clinical Outcomes in Diabetes Patients With Covid-19?, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.10.006
Elibol, Eren, Erdogȃn, Elmaagȃçm, Dizdar et al., Factors Influencing on Development of Covid-19 Pneumonia and Association With Oral Anti-Diabetic Drugs in Hospitalized Patients With Diabetes Mellitus, Primary Care Diabetes, doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2021.08.001
Fadini, Albiero, Avogaro, Direct Effects of Dpp-4 Inhibition on the Vasculature. Reconciling Basic Evidence With Lack of Clinical Evidence, Vascul Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.vph.2015.08.004
Fadini, Morieri, Longato, Bonora, Pinelli et al., Exposure to Dipeptidyl-Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Covid-19 Among People With Type 2 Diabetes: A Case-Control Study, Diabetes Obes Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.14097
Filgueiras, Capelozzi, Martins, Jancar, Sepsis-Induced Lung Inflammation Is Modulated by Insulin, BMC Pulm Med, doi:10.1186/1471-2466-14-177
Gao, Liu, Zhong, Liu, Zhou et al., Risk of Metformin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes With Covid-19: A Preliminary Retrospective Report, Clin Transl Sci, doi:10.1111/cts.12897
Ghany, Palacio, Dawkins, Chen, Mccarter et al., Metformin Is Associated With Lower Hospitalizations, Mortality and Severe Coronavirus Infection Among Elderly Medicare Minority Patients in 8 States in USA, Diabetes Metab Syndrome, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.022
Han, Ma, Sun, Zhang, Qu et al., The Association Between Anti-Diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of Covid-19 in Patients With Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Arch Med Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002
Hariyanto, Intan, Hananto, Putri, Kurniawan, Pre-Admission Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist (Glp-1ra) and Mortality From Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19): A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109031
Higgins, Thomas, Chandler, Cumpston, Li et al., Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions
Israelsen, Pottegård, Sandholdt, Madsbad, Thomsen et al., Comparable Covid-19 Outcomes With Current Use of Glp-1 Receptor Agonists, Dpp-4 Inhibitors or Sglt-2 Inhibitors Among Patients With Diabetes Who Tested Positive for Sars-Cov-2, Diabetes Obes Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.14329
Jiang, Chen, Liu, Yin, Yang et al., Association of Metformin With Mortality or Ards in Patients With Covid-19 and Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619
Kahkoska, Abrahamsen, Alexander, Bennett, Chute et al., Association Between Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Use and Covid-19 Outcomes, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc21-0065
Kan, Zhang, Han, Xu, Ye et al., Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With Covid-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.708494
Katsanos, Spiliopoulos, Karunanithy, Krokidis, Sabharwal et al., Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis of Nitinol Stents, Covered Stents, Drug-Eluting Stents, and Drug-Coated Balloons in the Femoropopliteal Artery, J Vasc Surg, doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2014.01.041
Khunti, Knighton, Zaccardi, Bakhai, Barron et al., Prescription of Glucose-Lowering Therapies and Risk of Covid-19 Mortality in People With Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Observational Study in England, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00050-4
Kim, Jeon, Kim, Moon, Cho et al., The Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients With Moderate-To-Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Diabetes in Daegu, South Korea, Diabetes Metab J, doi:10.4093/dmj.2020.0146
Kosiborod, Esterline, Furtado, Oscarsson, Gasparyan et al., Dapagliflozin in Patients With Cardiometabolic Risk Factors Hospitalised With Covid-19 (Dare-19): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00180-7
Koufakis, Karras, Zebekakis, Ajjan, Kotsa, Should the Last Be First? Questions and Dilemmas Regarding Early Short-Term Insulin Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Expert Opin Biol Ther, doi:10.1080/14712598.2018.1526278
Koufakis, Pavlidis, Metallidis, Kotsa, Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Covid-19: Meeting at the Crossroads Between Heart, Diabetes and Infectious Diseases, Int J Clin Pharm, doi:10.1007/s11096-021-01256-9
Lalau, Al-Salameh, Hadjadj, Goronflot, Wiernsperger et al., Metformin Use Is Associated With a Reduced Risk of Mortality in Patients With Diabetes Hospitalised for Covid-19, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216
Lally, Tsoukas, Halladay, Neill, Gravenstein et al., Metformin Is Associated With Decreased 30-Day Mortality Among Nursing Home Residents Infected With Sars-Cov2, J Am Med Dir Assoc, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031
Li, Wei, Mccowen, Xiong, Liu et al., Inpatient Use of Metformin and Acarbose Is Associated With Reduced Mortality of Covid-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Endocrinol Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1002/edm2.301
Lim, Bae, Kwon, Nauck, Covid-19 and Diabetes Mellitus: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Management, Nat Rev Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4
Liu, Mei, Chen, Ye, Comparison of Antidiabetic Medications During the Treatment of Atherosclerosis in T2dm Patients, Mediat Inflamm, doi:10.1155/2017/5032708
Luk, Yip, Zhang, Kong, Wong et al., Glucose-Lowering Drugs and Outcome From Covid-19 Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Wide Analysis in Hong Kong, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052310
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Liu, Zheng et al., Metformin Treatment Was Associated With Decreased Mortality in Covid-19 Patients With Diabetes in a Retrospective Analysis, Am J Trop Med Hygiene, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Meijer, Hoekstra, Van Den Oever, Simsek, Van Den Bergh et al., Treatment With a Dpp-4 Inhibitor at Time of Hospital Admission for Covid-19 Is Not Associated With Improved Clinical Outcomes: Data From the Covid-Predict Cohort Study in the Netherlands, J Diabetes Metab Disord, doi:10.1007/s40200-021-00833-z
Noh, Oh, Jeong, Filion, Yu et al., Association Between Dpp-4 Inhibitors and Covid-19-Related Outcomes Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1824
Nomoto, Kimachi, Miyoshi, Kameda, Cho et al., Effects of 50 Mg Vildagliptin Twice Daily Vs. 50 Mg Sitagliptin Once Daily on Blood Glucose Fluctuations by Long-Term Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose, Endocr J, doi:10.1507/endocrj.EJ16-0546
Nyland, Raja-Khan, Bettermann, Haouzi, Leslie et al., Diabetes, Drug Treatment and Mortality in Covid-19: A Multinational Retrospective Cohort Study, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/db21-0385
Oh, Song, Metformin Use and Risk of Covid-19 Among Patients With Type Ii Diabetes Mellitus: An Nhis-Covid-19 Database Cohort Study, Acta Diabetol, doi:10.1007/s00592-020-01666-7
Orioli, Servais, Belkhir, Laterre, Thissen et al., Clinical Characteristics and Short-Term Prognosis of in-Patients With Diabetes and Covid-19: A Retrospective Study From an Academic Center in Belgium, Diabetes Metab syndrome, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.020
Patoulias, Doumas, Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Covid-19-Related Deaths Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies, Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.3803/EnM.2021.1048
Peŕez-Belmonte, Torres-Peña, Loṕez-Carmona, Ayala-Gutieŕrez, Fuentes-Jimeńez et al., Mortality and Other Adverse Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Admitted for Covid-19 in Association With Glucose-Lowering Drugs: A Nationwide Cohort Study, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-020-01832-2
Pranata, Henrina, Raffaello, Lawrensia, Huang, Diabetes and Covid-19: The Past, the Present, and the Future, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154814
Rakhmat, Kusmala, Handayani, Juliastuti, Nawangsih et al., Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (Dpp-4) Inhibitor and Mortality in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) -a Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression, Diabetes Metab Syndrome, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.027
Ramos-Rincoń, Peŕez-Belmonte, Carrasco-Sańchez, Jansen-Chaparro, De-Sousa-Baena et al., Cardiometabolic Therapy and Mortality in Very Old Patients With Diabetes Hospitalized Due to Covid-19, journals gerontology Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci, doi:10.1093/gerona/glab124
Rhee, Lee, Nam, Kyoung, Shin et al., Effects of a Dpp-4 Inhibitor and Ras Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients With Diabetes and Covid-19, Diabetes Metab J, doi:10.4093/dmj.2020.0206
Rogliani, Matera, Calzetta, Hanania, Page et al., Long-Term Observational Study on the Impact of Glp-1r Agonists on Lung Function in Diabetic Patients, Respir Med, doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2019.06.015
Roussel, Darmon, Pichelin, Goronflot, Abouleka et al., Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Prognosis of Covid-19 in Hospitalized Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score Analysis From the Coronado Study, Diabetes Obes Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.14324
Saygili, Karakiliçe, Mert, Sȩner, Mirci, Preadmission Usage of Metformin and Mortality in Covid-19 Patients Including the Post-Discharge Period, Irish J Med Sci, doi:10.1007/s11845-021-02823-9
Schaschkow, Mura, Dal, Langlois, Seyfritz et al., Impact of the Type of Continuous Insulin Administration on Metabolism in a Diabetic Rat Model, J Diabetes Res, doi:10.1155/2016/8310516
Silverii, Monami, Cernigliaro, Vigneri, Guarnotta et al., Are Diabetes and Its Medications Risk Factors for the Development of Covid-19? Data From a Population-Based Study in Sicily, Nutrition Metabolism Cardiovasc Dis NMCD, doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2020.09.028
Solerte, 'addio, Trevisan, Lovati, Rossi et al., Sitagliptin Treatment at the Time of Hospitalization Was Associated With Reduced Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Covid-19: A Multicenter, Case-Control, Retrospective, Observational Study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1521
Sourij, Aziz, Bräuer, Ciardi, Clodi et al., Covid-19 Fatality Prediction in People With Diabetes and Prediabetes Using a Simple Score Upon Hospital Admission, Diabetes Obes Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.14256
Stang, Critical Evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for the Assessment of the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analyses, Eur J Epidemiol, doi:10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
Stroup, Berlin, Morton, Olkin, Williamson et al., Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology: A Proposal for Reporting. Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (Moose) Group, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.283.15.2008
Tamura, Said, De Freitas, Rubio, Outcome and Death Risk of Diabetes Patients With Covid-19 Receiving Pre-Hospital and in-Hospital Metformin Therapies, Diabetol Metab Syndrome, doi:10.1186/s13098-021-00695-8
Wander, Lowy, Beste, Tulloch-Palomino, Korpak et al., Prior Glucose-Lowering Medication Use and 30-Day Outcomes Among 64,892 Veterans With Diabetes and Covid-19, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc21-1351
Wargny, Potier, Gourdy, Pichelin, Amadou et al., Predictors of Hospital Discharge and Mortality in Patients With Diabetes and Covid-19: Updated Results From the Nationwide Coronado Study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w
Yang, Cai, Zhang, Dpp-4 Inhibitors May Improve the Mortality of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Meta-Analysis, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0251916
Yang, Cai, Zhang, Insulin Treatment May Increase Adverse Outcomes in Patients With Covid-19 and Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.696087
Yang, Sun, Zhang, Zhang, The Effect of Metformin on Mortality and Severity in Covid-19 Patients With Diabetes Mellitus, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977
Zangiabadian, Nejadghaderi, Zahmatkesh, Hajikhani, Mirsaeidi et al., The Efficacy and Potential Mechanisms of Metformin in the Treatment of Covid-19 in the Diabetics: A Systematic Review, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.645194
Zhou, Tang, Han, Yang, Simór, Impact of Antidiabetic Agents on Dementia Risk: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154265
Zhou, Wu, Wang, Lei, Cheng et al., No Significant Association Between Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Adverse Outcomes of Covid-19, World J Clin Cases, doi:10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5576
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2022.895458",
"ISSN": [
"1664-2392"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.895458",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Aims</jats:title><jats:p>This study aimed to assess the impact of different antidiabetic agents on individuals with diabetes and COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>We searched PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases from inception to October 31, 2021 and included seven antidiabetic agents. The data were pooled <jats:italic>via</jats:italic> traditional pairwise meta-analysis and Bayesian network meta-analysis.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>The pairwise meta-analysis included 35 studies. Metformin (odds ratio (OR), 0.74; P=0.001), dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4i) (OR, 0.88; P=0.04), sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) (OR, 0.82; P=0.001), and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP1RA) (OR, 0.91; P=0.02) treatment were associated with lower COVID-19 mortality in individuals with diabetes compared to respective non-users. However, insulin treatment resulted in higher mortality (OR, 1.8; P=0.001). Mortality did not significantly differ in sulfonylurea (OR, 0.97; P=0.56) and thiazolidinediones (TZDs) (OR, 1.00; P=0.96) users. Furthermore, due to limited data, we analyzed five antidiabetic agents (metformin, DPP4i, sulfonylurea, insulin, and SGLT2i) and found no association between them and severe disease risk (all P&gt;0.05). The Bayesian network meta-analysis included 18 studies. GLP1RA and SGLT2i had the highest first and second rank probability (67.3% and 62.5%, respectively). Insulin showed the maximum probability of ranking seventh (97.0%). Metformin had the third and fourth highest rank probability of 44.8% and 38.9%, respectively. Meanwhile, DPP4i had the fifth-highest rank probability of 42.4%, followed by sulfonylurea at 45.1%.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Metformin, DPP4i, SGLT2i, and GLP1RA treatments were highly possible to reduced COVID-19 mortality risk in individuals with diabetes, while insulin might be related to increased mortality risk. Sulfonylurea and TZDs treatments were not associated with mortality. None of the antidiabetic agents studied were associated with the risk of severe disease. Additionally, GLP1RA probably had the most significant protective effect against death, followed by SGLT2i and metformin.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Systematic Review Registration</jats:title><jats:p>PROSPERO (CRD42021288200)</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fendo.2022.895458"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Yidan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lv",
"given": "Xingfei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Sang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arshad",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dai",
"given": "Mengjun",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Endocrinology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Endocrinol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-27T12:17:43Z",
"timestamp": 1653653863000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-27T12:17:46Z",
"timestamp": 1653653866000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-11T09:03:30Z",
"timestamp": 1715418210799
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 20,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1653609600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2022.895458/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002",
"article-title": "The Association Between Anti-Diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of Covid-19 in Patients With Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Arch Med Res",
"key": "B1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154814",
"article-title": "Diabetes and Covid-19: The Past, the Present, and the Future",
"author": "Pranata",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.708494",
"article-title": "Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With Covid-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Kan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109031",
"article-title": "Pre-Admission Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist (Glp-1ra) and Mortality From Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19): A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression",
"author": "Hariyanto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "179",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.283.15.2008",
"article-title": "Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology: A Proposal for Reporting. Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (Moose) Group",
"author": "Stroup",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "283",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z",
"article-title": "Critical Evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for the Assessment of the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analyses",
"author": "Stang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur J Epidemiol",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154265",
"article-title": "Impact of Antidiabetic Agents on Dementia Risk: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/hjh.0000000000002784",
"article-title": "Renin-Angiotensin-System Inhibitors and All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Covid-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies",
"author": "Bavishi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Hypertens",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/9781119536604",
"author": "Higgins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "264 p",
"key": "B9",
"volume-title": "Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00330-021-08423-6",
"article-title": "The Effect of Prophylactic Balloon Occlusion in Patients With Placenta Accreta Spectrum: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur Radiol",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0272989X12455847",
"article-title": "Evidence Synthesis for Decision Making 4: Inconsistency in Networks of Evidence Based on Randomized Controlled Trials",
"author": "Dias",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Med Decision Making",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.numecd.2020.09.028",
"article-title": "Are Diabetes and Its Medications Risk Factors for the Development of Covid-19? Data From a Population-Based Study in Sicily",
"author": "Silverii",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutrition Metabolism Cardiovasc Dis NMCD",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc21-0065",
"article-title": "Association Between Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Use and Covid-19 Outcomes",
"author": "Kahkoska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/glab124",
"article-title": "Cardiometabolic Therapy and Mortality in Very Old Patients With Diabetes Hospitalized Due to Covid-19",
"author": "Ramos-Rincón",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "journals gerontology Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.020",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics and Short-Term Prognosis of in-Patients With Diabetes and Covid-19: A Retrospective Study From an Academic Center in Belgium",
"author": "Orioli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab syndrome",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14329",
"article-title": "Comparable Covid-19 Outcomes With Current Use of Glp-1 Receptor Agonists, Dpp-4 Inhibitors or Sglt-2 Inhibitors Among Patients With Diabetes Who Tested Positive for Sars-Cov-2",
"author": "Israelsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes Metab",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14256",
"article-title": "Covid-19 Fatality Prediction in People With Diabetes and Prediabetes Using a Simple Score Upon Hospital Admission",
"author": "Sourij",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes Metab",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db21-0385",
"article-title": "Diabetes, Drug Treatment and Mortality in Covid-19: A Multinational Retrospective Cohort Study",
"author": "Nyland",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119371",
"article-title": "Effects of Metformin, Insulin on Covid-19 Patients With Pre-Existed Type 2 Diabetes: A Multicentral Retrospective Study",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "275",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcd.2021.08.001",
"article-title": "Factors Influencing on Development of Covid-19 Pneumonia and Association With Oral Anti-Diabetic Drugs in Hospitalized Patients With Diabetes Mellitus",
"author": "Elibol",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Primary Care Diabetes",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052310",
"article-title": "Glucose-Lowering Drugs and Outcome From Covid-19 Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Wide Analysis in Hong Kong",
"author": "Luk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/edm2.301",
"article-title": "Inpatient Use of Metformin and Acarbose Is Associated With Reduced Mortality of Covid-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol Diabetes Metab",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031",
"article-title": "Metformin Is Associated With Decreased 30-Day Mortality Among Nursing Home Residents Infected With Sars-Cov2",
"author": "Lally",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Am Med Dir Assoc",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.600439",
"article-title": "Metformin Use Is Associated With Reduced Mortality in a Diverse Population With Covid-19 and Diabetes",
"author": "Crouse",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-020-01832-2",
"article-title": "Mortality and Other Adverse Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Admitted for Covid-19 in Association With Glucose-Lowering Drugs: A Nationwide Cohort Study",
"author": "Pérez-Belmonte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w",
"article-title": "Predictors of Hospital Discharge and Mortality in Patients With Diabetes and Covid-19: Updated Results From the Nationwide Coronado Study",
"author": "Wargny",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00050-4",
"article-title": "Prescription of Glucose-Lowering Therapies and Risk of Covid-19 Mortality in People With Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Observational Study in England",
"author": "Khunti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1521",
"article-title": "Sitagliptin Treatment at the Time of Hospitalization Was Associated With Reduced Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Covid-19: A Multicenter, Case-Control, Retrospective, Observational Study",
"author": "Solerte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2999",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40200-021-00833-z",
"article-title": "Treatment With a Dpp-4 Inhibitor at Time of Hospital Admission for Covid-19 Is Not Associated With Improved Clinical Outcomes: Data From the Covid-Predict Cohort Study in the Netherlands",
"author": "Meijer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes Metab Disord",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013",
"article-title": "Metformin Is Associated With Higher Incidence of Acidosis, But Not Mortality, in Individuals With Covid-19 and Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "537",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"article-title": "Metformin Treatment Was Associated With Decreased Mortality in Covid-19 Patients With Diabetes in a Retrospective Analysis",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hygiene",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26873",
"article-title": "Outpatient Metformin Use Is Associated With Reduced Severity of Covid-19 Disease in Adults With Overweight or Obesity",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.022",
"article-title": "Metformin Is Associated With Lower Hospitalizations, Mortality and Severe Coronavirus Infection Among Elderly Medicare Minority Patients in 8 States in USA",
"author": "Ghany",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndrome",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619",
"article-title": "Association of Metformin With Mortality or Ards in Patients With Covid-19 and Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216",
"article-title": "Metformin Use Is Associated With a Reduced Risk of Mortality in Patients With Diabetes Hospitalised for Covid-19",
"author": "Lalau",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592-020-01666-7",
"article-title": "Metformin Use and Risk of Covid-19 Among Patients With Type Ii Diabetes Mellitus: An Nhis-Covid-19 Database Cohort Study",
"author": "Oh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Acta Diabetol",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2666-7568(20)30033-7",
"article-title": "Metformin and Risk of Mortality in Patients Hospitalised With Covid-19: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Healthy Longevity",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0660",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients With Diabetes and Covid-19 in Association With Glucose-Lowering Medication",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.10.006",
"article-title": "Is There an Association Between Metformin Use and Clinical Outcomes in Diabetes Patients With Covid-19",
"author": "Do",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101208",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12897",
"article-title": "Risk of Metformin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes With Covid-19: A Preliminary Retrospective Report",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4093/dmj.2020.0146",
"article-title": "The Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients With Moderate-To-Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Diabetes in Daegu, South Korea",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab J",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11845-021-02823-9",
"article-title": "Preadmission Usage of Metformin and Mortality in Covid-19 Patients Including the Post-Discharge Period",
"author": "Saygili",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Irish J Med Sci",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc21-1351",
"article-title": "Prior Glucose-Lowering Medication Use and 30-Day Outcomes Among 64,892 Veterans With Diabetes and Covid-19",
"author": "Wander",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13098-021-00695-8",
"article-title": "Outcome and Death Risk of Diabetes Patients With Covid-19 Receiving Pre-Hospital and in-Hospital Metformin Therapies",
"author": "Tamura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Diabetol Metab Syndrome",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108925",
"article-title": "Risk Factors for Covid-19 Hospitalisation and Death in People Living With Diabetes: A Virtual Cohort Study From the Western Cape Province, South Africa",
"author": "Dave",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x",
"article-title": "Phenotypic Characteristics and Prognosis of Inpatients With Covid-19 and Diabetes: The Coronado Study",
"author": "Cariou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14097",
"article-title": "Exposure to Dipeptidyl-Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Covid-19 Among People With Type 2 Diabetes: A Case-Control Study",
"author": "Fadini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes Metab",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4093/dmj.2020.0206",
"article-title": "Effects of a Dpp-4 Inhibitor and Ras Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients With Diabetes and Covid-19",
"author": "Rhee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab J",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa098",
"article-title": "The Association of Hypertension and Diabetes Pharmacotherapy With Covid-19 Severity and Immune Signatures: An Observational Study",
"author": "Dalan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1824",
"article-title": "Association Between Dpp-4 Inhibitors and Covid-19-Related Outcomes Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes",
"author": "Noh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14324",
"article-title": "Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Prognosis of Covid-19 in Hospitalized Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score Analysis From the Coronado Study",
"author": "Roussel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes Metab",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5576",
"article-title": "No Significant Association Between Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Adverse Outcomes of Covid-19",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "World J Clin Cases",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00180-7",
"article-title": "Dapagliflozin in Patients With Cardiometabolic Risk Factors Hospitalised With Covid-19 (Dare-19): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial",
"author": "Kosiborod",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jvs.2014.01.041",
"article-title": "Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis of Nitinol Stents, Covered Stents, Drug-Eluting Stents, and Drug-Coated Balloons in the Femoropopliteal Artery",
"author": "Katsanos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1123",
"journal-title": "J Vasc Surg",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.645194",
"article-title": "The Efficacy and Potential Mechanisms of Metformin in the Treatment of Covid-19 in the Diabetics: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Zangiabadian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-021-01515-6",
"article-title": "Disentangling Conflicting Evidence on Dpp-4 Inhibitors and Outcomes of Covid-19: Narrative Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Bonora",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Endocrinol Invest",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108230",
"article-title": "Metformin, Neutrophils and Covid-19 Infection",
"author": "Dalan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977",
"article-title": "The Effect of Metformin on Mortality and Severity in Covid-19 Patients With Diabetes Mellitus",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0251916",
"article-title": "Dpp-4 Inhibitors May Improve the Mortality of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.027",
"article-title": "Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (Dpp-4) Inhibitor and Mortality in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) - a Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression",
"author": "Rakhmat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndrome",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3803/EnM.2021.1048",
"article-title": "Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Covid-19-Related Deaths Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies",
"author": "Patoulias",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol Metab (Seoul Korea)",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2017/5032708",
"article-title": "Comparison of Antidiabetic Medications During the Treatment of Atherosclerosis in T2dm Patients",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mediat Inflamm",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "2017",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1507/endocrj.EJ16-0546",
"article-title": "Effects of 50 Mg Vildagliptin Twice Daily Vs. 50 Mg Sitagliptin Once Daily on Blood Glucose Fluctuations Evaluated by Long-Term Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose",
"author": "Nomoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocr J",
"key": "B63",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vph.2015.08.004",
"article-title": "Direct Effects of Dpp-4 Inhibition on the Vasculature. Reconciling Basic Evidence With Lack of Clinical Evidence",
"author": "Fadini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Vascul Pharmacol",
"key": "B64",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4",
"article-title": "Covid-19 and Diabetes Mellitus: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Management",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Endocrinol",
"key": "B65",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.696087",
"article-title": "Insulin Treatment May Increase Adverse Outcomes in Patients With Covid-19 and Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B66",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14712598.2018.1526278",
"article-title": "Should the Last Be First? Questions and Dilemmas Regarding Early Short-Term Insulin Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus",
"author": "Koufakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin Biol Ther",
"key": "B67",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2016/8310516",
"article-title": "Impact of the Type of Continuous Insulin Administration on Metabolism in a Diabetic Rat Model",
"author": "Schaschkow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes Res",
"key": "B68",
"volume": "2016",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2466-14-177",
"article-title": "Sepsis-Induced Lung Inflammation Is Modulated by Insulin",
"author": "Filgueiras",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMC Pulm Med",
"key": "B69",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.13162",
"article-title": "A Review of Glp-1 Receptor Agonists: Evolution and Advancement, Through the Lens of Randomised Controlled Trials",
"author": "Aroda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "22",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes Metab",
"key": "B70",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2019.06.015",
"article-title": "Long-Term Observational Study on the Impact of Glp-1r Agonists on Lung Function in Diabetic Patients",
"author": "Rogliani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "86",
"journal-title": "Respir Med",
"key": "B71",
"volume": "154",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11096-021-01256-9",
"article-title": "Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Covid-19: Meeting at the Crossroads Between Heart, Diabetes and Infectious Diseases",
"author": "Koufakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Pharm",
"key": "B72",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/eci.13339",
"article-title": "Sglt2 Inhibition and Covid-19: The Road Not Taken",
"author": "Das",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Invest",
"key": "B73",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 73,
"references-count": 73,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2022.895458/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "13"
}
