Metformin is Associated with Decreased 30-Day Mortality Among Nursing Home Residents Infected with SARS-CoV2
et al., Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031, Jan 2021
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 775 nursing home residents in the USA, showing lower mortality with existing metformin use.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
Results may differ in countries with improved SOC.
|
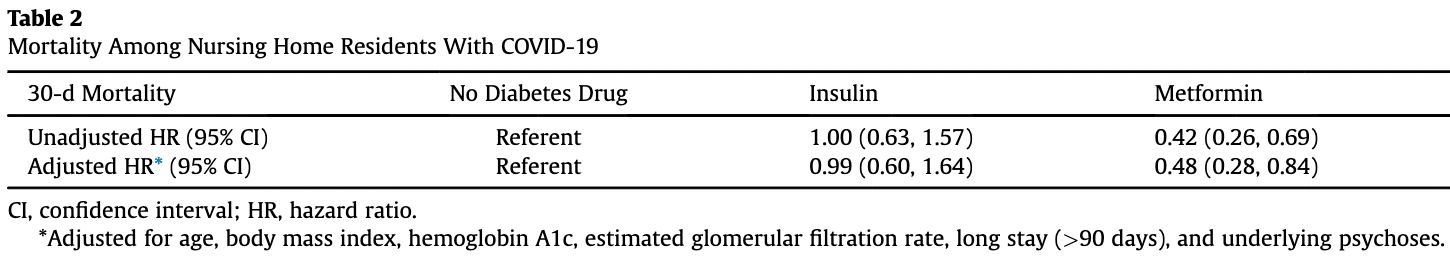
risk of death, 52.0% lower, HR 0.48, p = 0.009, treatment 16 of 127 (12.6%), control 144 of 648 (22.2%), NNT 10, adjusted per study, multivariable regression.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Lally et al., 31 Jan 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Metformin is Associated with Decreased 30-Day Mortality Among Nursing Home Residents Infected with SARS-CoV2
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031
Objectives: The COVID-19 pandemic presents an urgent need to investigate whether existing drugs can enhance or even worsen prognosis; metformin, a known mammalian target of rapamycin (m-TOR) inhibitor, has been identified as a potential agent. We sought to evaluate mortality benefit among older persons infected with SARS-CoV-2 who were taking metformin as compared to those who were not. Design: Retrospective cohort study. Setting and Participants: 775 nursing home residents infected with SARS-CoV-2 who resided in one of the 134 Community Living Centers (CLCs) of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) during March 1, 2020, to May 13, 2020, were included. Methods: Using a window of 14 days prior to SARS-CoV-2 testing, bar-coded medication administration records were examined for dispensing of medications for diabetes. The COVID-19einfected residents were divided into 4 groups: (1) residents administered metformin alone or in combination with other medications, (2) residents who used long-acting or daily insulin, (3) residents administered other diabetes medications, and (4) residents not administered diabetes medication, including individuals without diabetes and patients with untreated diabetes. Proportional hazard models adjusted for demographics, hemoglobin A1c, body mass index, and renal function. Results: Relative to those not receiving diabetes medications, residents taking metformin were at significantly reduced hazard of death [adjusted hazard ratio (HR) 0.48, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.28, 0.84] over the subsequent 30 days from COVID-19 diagnosis. There was no association with insulin (adjusted HR 0.99, 95% CI 0.60, 1.64) or other diabetes medications (adjusted HR 0.71, 95% CI 0.38, 1.32). Conclusions and Implications: Our data suggest a reduction in 30-day mortality following SARS-CoV-2 infection in residents who were on metformin-containing diabetes regimens. These findings suggest a relative survival benefit in nursing home residents on metformin, potentially through its mTOR inhibition effects. A prospective study should investigate the therapeutic benefits of metformin among persons with COVID-19. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of AMDA e The Society for Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Medicine. On December 31, 2019, an unforeseen health crisis emerged in Wuhan City, China. The World Health Organization reported a series of 44 pneumonia cases, 1 related to a new beta-coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2. By January 20, 2020, this newly termed coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was detected in the United States. 2 With COVID-19's rapid worldwide spread came the quick recognition of the major threat posed to the geriatric population, particularly the comorbid and frail. 3 Severe COVID-19 can occur in the presence of multiple chronic illnesses and age-related immunosenescence 4 ; grouped living conditions of many older people, particularly those in facilities, further ML and PT contributed equally and have agreed to share first..
References
Andrzejewski, Siegel, St-Pierre, Metabolic profiles associated with metformin efficacy in cancer, Front Endocrinol
Bailey, Metformin: Historical overview, Diabetologia
Boccardi, Ruggiero, Mecocci, COVID-19: A geriatric emergency, Geriatrics
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with COVID-19
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: The CORONADO study, Diabetologia
Cheng, Liu, Li, Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes
Dalan, Metformin, neutrophils and COVID-19 infection, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Drucker, Coronavirus infections and type 2 diabetesdShared pathways with therapeutic implications, Endocr Rev
Duca, Côté, Rasmussen, Metformin activates a duodenal AMPKdependent pathway to lower hepatic glucose production in rats [published correction appears in, Nat Med
Elixhauser, Steiner, Harris, Coffey, Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data, Med Care
Guo, Li, Dong, Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19, Diabetes Metab Res Rev
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obes Med
Harrison, Drug researchers pursue new lines of attack against COVID-19, Nature Biotechnol
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States, N Engl J Med
Kuss-Duerkop, Wang, Mena, Influenza virus differentially activates mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling to maximize late stage replication, PLOS Pathogens
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Maiese, The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR): Novel considerations as an antiviral treatment, Curr Neurovasc Res
Mannick, Giudice, Lattanzi, mTOR inhibition improves immune function in the elderly, Sci Transl Med
Mannick, Morris, Hockey, TORC1 inhibition enhances immune function and reduces infections in the elderly, Sci Transl Med
Mannick, Tomlinson, Shergill, TORC1 Inhibition with RTB101 as a potential pan-antiviral immunotherapy to decrease the incidence of respiratory tract infections due to multiple respiratory viruses in older adults, Open Forum Infect Dis
Moyo, Tanthuma, Cary, Cohort study of diabetes in HIV-infected adult patients: Evaluating the effect of diabetes mellitus on immune reconstitution, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Negrotto, Farez, Correale, Immunologic effects of metformin and pioglitazone treatment on metabolic syndrome and multiple sclerosis, JAMA Neurol
Nikolich-Zugich, Knox, Rios, SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in older adults: What we may expect regarding pathogenesis, immune responses, and outcomes, Geroscience
Sahra, Regazzetti, Robert, Metformin, independent of AMPK, induces mTOR inhibition and cell-cycle arrest through REDD1, Cancer Res
Scheen, Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes Metab
Sestan, Marinovi C S, Kavazovi C I, Virus-induced interferon-g causes insulin resistance in skeletal muscle and derails glycemic control in obesity, Immunity
Sharma, Ray, Sadasivam, Metformin in COVID-19: A possible role beyond diabetes, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Sukumar, Liu, Ji, Inhibiting glycolytic metabolism enhances CD8 þ T cell memory and antitumor function, J Clin Invest
Weinberg, Antimicrobial activities of biguanides, Ann N Y Acad Sci
Yin, Choi, Xu, Normalization of CD4 þ T cell metabolism reverses lupus, Sci Transl Med
Zheng, Li, Liu, Immunoregulation with mTOR inhibitors to prevent COVID-19 severity: A novel intervention strategy beyond vaccines and specific antiviral medicines, J Med Virol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031",
"ISSN": [
"1525-8610"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031",
"alternative-id": [
"S1525861020309245"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Metformin is Associated with Decreased 30-Day Mortality Among Nursing Home Residents Infected with SARS-CoV2"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of the American Medical Directors Association"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of AMDA - The Society for Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Medicine."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0716-4668",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lally",
"given": "Michelle A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4027-7891",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tsoukas",
"given": "Philip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Halladay",
"given": "Christopher W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Neill",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6000-6859",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gravenstein",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0259-4362",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rudolph",
"given": "James L.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Journal of the American Medical Directors Association"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"jamda.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-26T16:51:48Z",
"timestamp": 1603731108000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-29T21:58:22Z",
"timestamp": 1609279102000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"CIN 13-419",
"C19 20-213"
],
"name": "VA Health Services Research and Development"
},
{
"award": [
"3P01AG027296-11S2"
],
"name": "National Institute of Aging"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-16T06:08:34Z",
"timestamp": 1639634914067
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 20,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1525-8610"
}
],
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1525861020309245?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1525861020309245?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "193-198",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001191",
"article-title": "First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States",
"author": "Holshue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "929",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib2",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/geriatrics5020024",
"article-title": "COVID-19: A geriatric emergency",
"author": "Boccardi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "Geriatrics",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib3",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11357-020-00186-0",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in older adults: What we may expect regarding pathogenesis, immune responses, and outcomes",
"author": "Nikolich-Zugich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "Geroscience",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib4",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1567202616999191209142915",
"article-title": "The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR): Novel considerations as an antiviral treatment",
"author": "Maiese",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Curr Neurovasc Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib5",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1769",
"article-title": "Metformin, independent of AMPK, induces mTOR inhibition and cell-cycle arrest through REDD1",
"author": "Ben Sahra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4366",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib6",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.3787",
"article-title": "Metformin activates a duodenal AMPK-dependent pathway to lower hepatic glucose production in rats [published correction appears in Nat Med. 2016 Feb;22(2):217]",
"author": "Duca",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "506",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib7",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb27733.x",
"article-title": "Antimicrobial activities of biguanides",
"author": "Weinberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "587",
"journal-title": "Ann N Y Acad Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib8",
"volume": "148",
"year": "1968"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2013.12.042",
"article-title": "Cohort study of diabetes in HIV-infected adult patients: Evaluating the effect of diabetes mellitus on immune reconstitution",
"author": "Moyo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e34",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib9",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.4807",
"article-title": "Immunologic effects of metformin and pioglitazone treatment on metabolic syndrome and multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Negrotto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "520",
"journal-title": "JAMA Neurol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib10",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa0835",
"article-title": "Normalization of CD4+ T cell metabolism reverses lupus",
"author": "Yin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "274ra18",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib11",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-017-4318-z",
"article-title": "Metformin: Historical overview",
"author": "Bailey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1566",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib12",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1006635",
"article-title": "Influenza virus differentially activates mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling to maximize late stage replication",
"author": "Kuss-Duerkop",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1006635",
"journal-title": "PLOS Pathogens",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib13",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19",
"author": "Guo",
"first-page": "e3319",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183",
"article-title": "Metformin in COVID-19: A possible role beyond diabetes",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108183",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib15",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00005650-199801000-00004",
"article-title": "Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data",
"author": "Elixhauser",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "Med Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib16",
"volume": "36",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.3009892",
"article-title": "mTOR inhibition improves immune function in the elderly",
"author": "Mannick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "268ra179",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib18",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "TORC1 inhibition enhances immune function and reduces infections in the elderly",
"author": "Mannick",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofz415.2485",
"article-title": "LB2. TORC1 Inhibition with RTB101 as a potential pan-antiviral immunotherapy to decrease the incidence of respiratory tract infections due to multiple respiratory viruses in older adults",
"author": "Mannick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S993",
"issue": "Suppl 2",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib20",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endrev/bnaa011",
"article-title": "Coronavirus infections and type 2 diabetes—Shared pathways with therapeutic implications",
"author": "Drucker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Endocr Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib21",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2018.05.005",
"article-title": "Virus-induced interferon-γ causes insulin resistance in skeletal muscle and derails glycemic control in obesity",
"author": "Šestan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "164",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib22",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2018.00372",
"article-title": "Metabolic profiles associated with metformin efficacy in cancer",
"author": "Andrzejewski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "372",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib23",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI69589",
"article-title": "Inhibiting glycolytic metabolism enhances CD8+ T cell memory and antitumor function",
"author": "Sukumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4479",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib24",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108230",
"article-title": "Metformin, neutrophils and COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Dalan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108230",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib25",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with COVID-19",
"author": "Bramante",
"journal-title": "Preprint. medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes",
"author": "Crouse",
"journal-title": "Preprint. medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"article-title": "Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib28",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection",
"author": "Hariyanto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100290",
"journal-title": "Obes Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib29",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x",
"article-title": "Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: The CORONADO study",
"author": "Cariou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1500",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib30",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006",
"article-title": "Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality.",
"author": "Scheen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "423",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib31",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013",
"article-title": "Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "537",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib32",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41587-020-00013-z",
"article-title": "Drug researchers pursue new lines of attack against COVID-19",
"author": "Harrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "659",
"journal-title": "Nature Biotechnol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib33",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26009",
"article-title": "Immunoregulation with mTOR inhibitors to prevent COVID-19 severity: A novel intervention strategy beyond vaccines and specific antiviral medicines",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1495",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031_bib34",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Journal of the American Medical Directors Association"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Health Policy",
"General Medicine",
"General Nursing",
"Geriatrics and Gerontology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Metformin is Associated with Decreased 30-Day Mortality Among Nursing Home Residents Infected with SARS-CoV2"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "22"
}
