Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis
et al., British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15258, PROSPERO CRD42020221842, Feb 2022
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
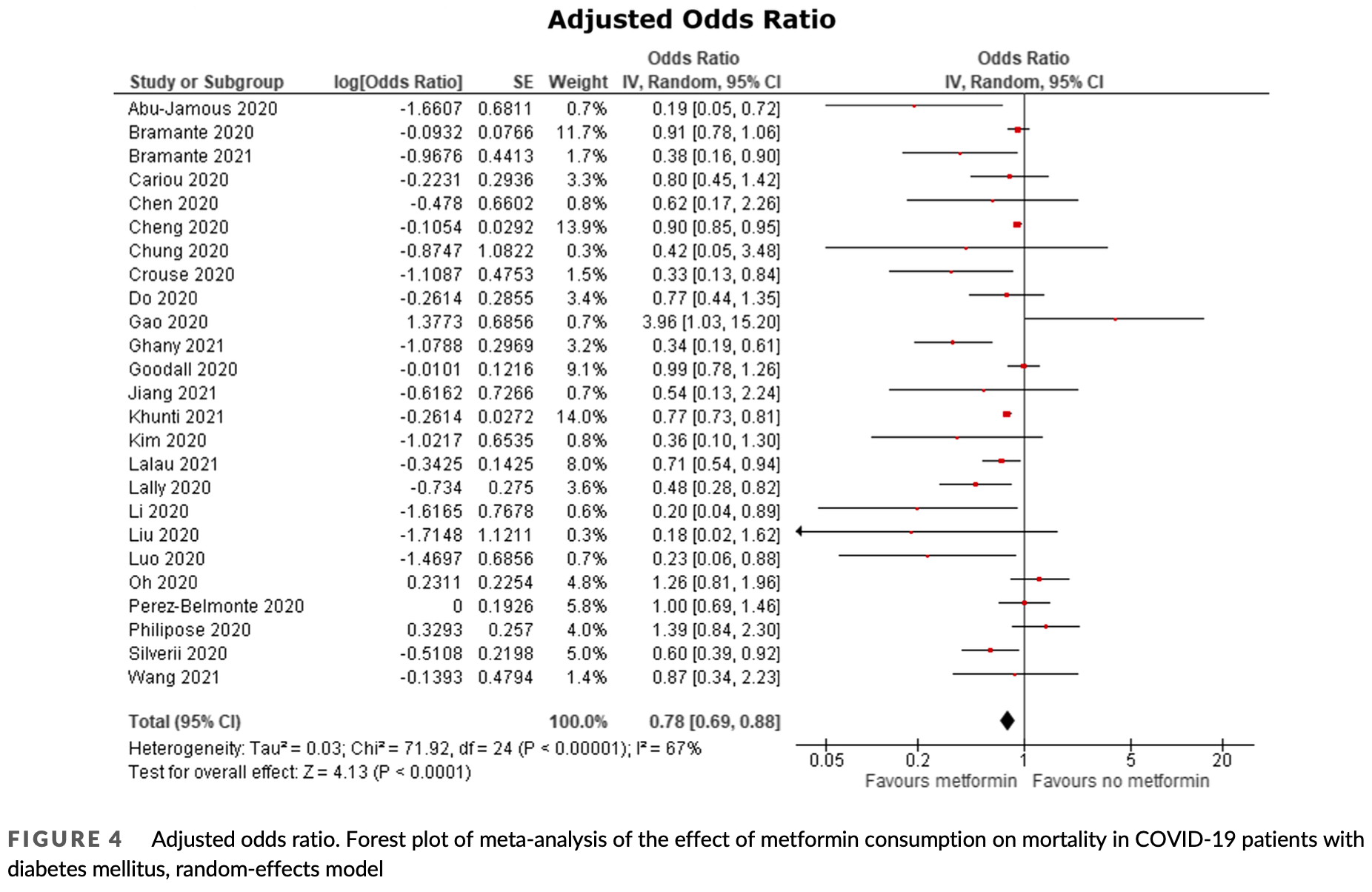
Meta analysis of 32 cohort studies with 2,916,231 patients showing significantly lower mortality with metformin treatment in COVID-19 patients with diabetes, with an unadjusted odds ratio of 0.61 (95% CI: 0.53-0.71) and an adjusted odds ratio of 0.78 (95% CI: 0.69-0.88). The study suggests metformin may improve outcomes in these patients through multiple mechanisms, including attenuating cytokine storms, improving adaptive and innate immunity, and decreasing viral entry.
24 meta-analyses show significant improvements with metformin for mortality1-23,
hospitalization7,13,23 ,
progression1, and
severity8,9,13 .
Currently there are 110 metformin for COVID-19 studies, showing 36% lower mortality [32‑40%], 29% lower ventilation [12‑43%], 19% lower ICU admission [8‑28%], 17% lower hospitalization [11‑23%], and 5% fewer cases [-4‑13%].
|
risk of death, 22.0% lower, OR 0.78, p < 0.001, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Yang et al., The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977.
2.
Lukito et al., The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006.
3.
Kow et al., Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26498.
4.
Hariyanto et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obesity Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290.
5.
Ma et al., Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282210.
6.
Parveen et al., Association of Metformin with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India), doi:10.1055/s-0042-1760353.
7.
Li et al., Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.704666.
8.
Schlesinger et al., Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-023-05928-1.
9.
Petrelli et al., Metformin and Covid-19: a systematic review of systematic reviews with meta-analysis, Acta Biomedica Atenei Parmensis, doi:10.23750/abm.v94iS3.14405.
10.
Oscanoa et al., Metformin therapy and severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a meta-analysis, Clinical Diabetology, doi:10.5603/DK.a2021.0035.
11.
Kan et al., Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.708494.
12.
Poly et al., Metformin Use Is Associated with Decreased Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes: Evidence from Retrospective Studies and Biological Mechanism, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10163507.
13.
Song et al., The Effect of Antihyperglycemic Medications on COVID-19: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review from Observational Studies, Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science, doi:10.1007/s43441-024-00633-6.
14.
Ganesh et al., Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15258.
15.
Nassar et al., Noninsulin‐based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis, Journal of Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13359.
16.
Zhan et al., Effect of Antidiabetic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/10600280221133577.
17.
Nguyen et al., Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155196.
18.
Han et al., Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002.
19.
Chen et al., The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458.
20.
Scheen, A., Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006.
21.
Sun et al., Is Metformin Use Associated With a Decreased Mortality for COVID-19 Diabetic Patients? A Meta-Analysis, Journal of the Endocrine Society, doi:10.1210/jendso/bvab048.709.
Ganesh et al., 23 Feb 2022, peer-reviewed, 2 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD42020221842.
Contact: adithanganesh321@gmail.com.
Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15258
Aims: The COVID-19 pandemic is a global public health emergency and patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) are disproportionately affected, exhibiting more severe outcomes. Recent studies have shown that metformin is associated with improved outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and DM and may be a potential candidate for drug repurposing. We aimed to investigate the effects of metformin on outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and DM. Methods: Databases (PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, EMBASE, Clinicaltrials.gov and Cochrane library) were searched up to 10 April 2021 for studies reporting data on metformin use in COVID-19 patients with DM. The risk of bias was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale. Certainty of evidence was rated using the GRADE approach. The primary outcome was mortality reported as odds ratio (OR). A random-effects meta-analysis was carried out on both unadjusted and adjusted ORs. This study is registered with PROSPERO, CRD42020221842. Results: In total, 2 916 231 patients from 32 cohort studies were included in the quantitative and qualitative synthesis. The meta-analysis showed that metformin was significantly associated with lower mortality in COVID-19 patients with DM in both unadjusted (OR 0.61 [95% confidence interval: 0.53-0.71], P < .00001, I 2 = 70%) and adjusted (OR 0.78 [95% confidence interval: 0.69-0.88], P < .00001, I 2 = 67%) models.
Conclusion: Poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients with DM can be attributed to inadequate glycaemic control and weakened immune responses. Metformin has multiple effects that can improve outcomes in patients with DM and our findings highlight a possible role of its use. However, robust randomised trials are needed to thoroughly assess its use.
COMPETING INTERESTS None.
References
Abu-Jamous, Anisimovich, Baxter, Associations of comorbidities and medications with COVID-19 outcome: A retrospective analysis of real-world evidence data, MedRxiv
Alexander, Christopoulos, Davenport, Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID-19 patients with new or pre-existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and metaanalysis, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:info:doi/10.1111/bcp.15258
Booth, Clinical Features and Short-term Outcomes of 144 Patients With SARS in the Greater Toronto Area, JAMA, doi:info:doi/10.1001/jama.289.21.JOC30885
Bramante, Buse, Tamaritz, Outpatient metformin use is associated with reduced severity of COVID-19 disease in adults with overweight or obesity, J Med Virol, doi:info:doi/10.1002/jmv.26873
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis, Lancet Healthy Longevity, doi:info:doi/10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7
Cameron, Morrison, Levin, Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Metformin Irrespective of Diabetes Status, Circ Res, doi:info:doi/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORO-NADO study, Diabetologia, doi:info:doi/10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients With Diabetes and COVID-19 in Association With Glucose-Lowering Medication, Diabetes Care, doi:info:doi/10.2337/dc20-0660
Cheng, Liu, Li, Metformin Is Associated with Higher Incidence of Acidosis, but Not Mortality, in Individuals with COVID-19 and Pre-existing Type 2 Diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013
Cheng, Xin, Chen, Effects of metformin, insulin on COVID-19 patients with pre-existed type 2 diabetes: A multicentral retrospective study, Life Sci, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119371
Chung, Lee, Ha, The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Diabetes Metab J, doi:info:doi/10.4093/dmj.2020.0105
Critchley, Carey, Harris, Dewilde, Hosking et al., Glycemic Control and Risk of Infections Among People With Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes in a Large Primary Care Cohort Study, Diabetes Care, doi:info:doi/10.2337/dc18-0287
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Might, Ovalle et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes, MedRxiv
Dashti, Bates, Roche, Fiskio, Mora et al., Clinical Characteristics and Severity of COVID-19 Disease in Patients from Boston Area Hospitals, MedRxiv
Do, Kim, Park, Cho, Kang, Is there an association between metformin use and clinical outcomes in diabetes patients with COVID-19?, Diabetes Metab, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.diabet.2020.10.006
Fernandez-Real, Valdes, Manco, Surfactant Protein D, a Marker of Lung Innate Immunity, Is Positively Associated With Insulin Sensitivity, Diabetes Care, doi:info:doi/10.2337/dc09-0542
Foretz, Guigas, Bertrand, Pollak, Viollet, Metformin: From Mechanisms of Action to Therapies, Cell Metab, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.09.018
Gao, Liu, Zhong, Risk of Metformin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Preliminary Retrospective Report, Clin Transl Sci, doi:info:doi/10.1111/cts.12897
Ghany, Palacio, Dawkins, Metformin is associated with lower hospitalizations, mortality and severe coronavirus infection among elderly medicare minority patients in 8 states in USA, Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.022
Goodall, Reed, Ardissino, Risk factors for severe disease in patients admitted with COVID-19 to a hospital in London, England: a retrospective cohort study, Epidemiol Infect, doi:info:doi/10.1017/S0950268820002472
Guan, Liang, Zhao, Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis, Eur Respir J, doi:info:doi/10.1183/13993003.00547-2020
Guo, Li, Dong, Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of <scp > COVID</scp > À19, Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:info:doi/10.1002/dmrr.3319
Guyatt, Oxman, Santesso, GRADE guidelines: 12. Preparing Summary of Findings tables-binary outcomes, J Clin Epidemiol, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.01.012
Guyatt, Oxman, Vist, GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations, BMJ, doi:info:doi/10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD
Henry, Frias, Walsh, Improved glycemic control with minimal systemic metformin exposure: Effects of Metformin Delayed-Release (Metformin DR) targeting the lower bowel over 16 weeks in a randomized trial in subjects with type 2 diabetes, PLOS One, doi:info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0203946
Ho, Huang, Tsai, Lai, Yu, Metformin use mitigates the adverse prognostic effect of diabetes mellitus in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Respir Res, doi:info:doi/10.1186/s12931-019-1035-9
Izzi-Engbeaya, Distaso, Amin, Severe COVID-19 and Diabetes -A Retrospective Cohort Study from Three London Teaching Hospitals, MedRxiv
Jiang, Chen, Liu, Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619
Joober, Schmitz, Annable, Boksa, Publication bias: What are the challenges and can they be overcome?, J Psychiatry Neurosci, doi:info:doi/10.1503/jpn.120065
Jornayvaz, Assouline, Pugin, Gariani, Extremely high-dose insulin requirement in a diabetic patient with COVID-19: a case report, BMC Endocr Disord, doi:info:doi/10.1186/s12902-020-00632-2
Kartika, Purnamasari, Pradipta, Larasati, Wibowo, Impact of low interferon-γ and il-10 levels on tnf-α and il-6 production by pha-induced pbmcs in type 2 diabetes mellitus, J Inflamm Res, doi:info:doi/10.2147/JIR.S245064
Khunti, Knighton, Zaccardi, Prescription of glucoselowering therapies and risk of COVID-19 mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide observational study in England, Lancet Diabetes Endo, doi:info:doi/10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00050-4
Kim, Jeon, Kim, The clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with moderate-to-severe coronavirus disease 2019 infection and diabetes in Daegu, South Korea Diab Metab J, doi:info:doi/10.4093/dmj.2020.0146
Kulcsar, Coleman, Beck, Frieman, Comorbid diabetes results in immune dysregulation and enhanced disease severity following MERS-CoV infection, JCI Insight, doi:info:doi/10.1172/jci.insight.131774
Kumar, Arora, Sharma, Is diabetes mellitus associated with mortality and severity of COVID-19? A meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044
Kuwabara, Yokota, Curi, Tc, Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes mellitus induce lipopolysaccharide tolerance in rat neutrophils, Sci Rep, doi:info:doi/10.1038/s41598-018-35809-2
Lalau, Al-Salameh, Hadjadj, Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19, Diabetes Metab, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216
Lally, Tsoukas, Halladay, Neill, Gravenstein et al., Metformin Is Associated With Decreased 30-Day Mortality Among Nursing Home Residents Infected With SARS-CoV2, J Am Med Dir Assoc, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031
Lecube, Pach On, Petriz, Hernández, Sim O R, Phagocytic Activity Is Impaired in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Increases after Metabolic Improvement, PLoS ONE, doi:info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0023366
Lemkes, Hermanides, Devries, Holleman, Meijers et al., Hyperglycemia: a prothrombotic factor?, J Thromb Haemost, doi:info:doi/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03910.x
Li, Tian, Chen, Newly diagnosed diabetes is associated with a higher risk of mortality than known diabetes in hospitalized patients with <scp > COVID</scp > À19, Diabetes Obes Metab, doi:info:doi/10.1111/dom.14099
Li, Wei, Li, TO HOSPITALIZATION: EFFECTS ON MORTALITY IN COVID-19, Endocr Pract, doi:info:doi/10.4158/EP-2020-0466
Li, Wei, Mccowen, Inpatient Use of Metformin and Acarbose Is Associated with Reduced Mortality of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Research Square
Liang, Ding, Li, Association of preadmission metformin use and mortality in patients with sepsis and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies, Crit Care, doi:info:doi/10.1186/s13054-019-2346-4
Liu, Bai, Han, The association of diabetes and the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective study, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108386
Liu, Li, Lu, AMPK: a balancer of the renin-angiotensin system, Biosci Rep, doi:info:doi/10.1042/BSR20181994
Lukito, Pranata, Henrina, Lim, Lawrensia et al., The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Metformin Treatment Was Associated with Decreased Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes in a Retrospective Analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:info:doi/10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Matsiukevich, Piraino, Lahni, Metformin ameliorates gender-and age-dependent hemodynamic instability and myocardial injury in murine hemorrhagic shock, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) -Mol Basis Dis, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.05.027
Mendy, Gopal, Alcorn, Forno, Reduced mortality from lower respiratory tract disease in adult diabetic patients treated with metformin, Respirology, doi:info:doi/10.1111/resp.13486
Menendez, Metformin and SARS-CoV-2: mechanistic lessons on air pollution to weather the cytokine/thrombotic storm in COVID-19, Aging, doi:info:doi/10.18632/aging.103347
Oh, Song, Metformin use and risk of COVID-19 among patients with type II diabetes mellitus: an NHIS-COVID-19 database cohort study, Acta Diabetol, doi:info:doi/10.1007/s00592-020-01666-7
Orioli, Servais, Belkhir, Clinical characteristics and shortterm prognosis of in-patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A retrospective study from an academic center in Belgium, Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.020
Ouyang, Isnard, Lin, Metformin effect on gut microbiota: insights for HIV-related inflammation, AIDS Res Therapy, doi:info:doi/10.1186/s12981-020-00267-2
Pal, Bhansali, COVID-19, diabetes mellitus and ACE2: The conundrum, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108132
Philipose, Smati, Wong, Aspey, Mendall, Obesity, old age, and frailty are the true risk factors for COVID-19 mortality and not chronic disease or ethnicity, MedRxiv
Pérez-Belmonte, Torres-Peña, Opez-Carmona, Mortality and other adverse outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus admitted for COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering drugs: a nationwide cohort study, BMC Med, doi:info:doi/10.1186/s12916-020-01832-2
Rayman, Lumb, Kennon, Guidance on the management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in the exceptional circumstances of the COVID-19 pandemic, Diabet Med, doi:info:doi/10.1111/dme.14328
Ruan, Likelihood of survival of coronavirus disease 2019, Infect Dis, doi:info:doi/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30257-7
Scheen, Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes Metab, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006
Schuiveling, Vazirpanah, Radstake, Zimmermann, Broen, Metformin, A New Era for an Old Drug in the Treatment of Immune Mediated Disease?, Curr Drug Targets, doi:info:doi/10.2174/1389450118666170613081730
Silverii, Monami, Cernigliaro, Are diabetes and its medications risk factors for the development of COVID-19? Data from a population-based study in Sicily, Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.numecd.2020.09.028
Simonnet, Chetboun, Poissy, High Prevalence of Obesity in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) Requiring Invasive Mechanical Ventilation, Obesity, doi:info:doi/10.1002/oby.22831
Singh, Singh, Suhail, AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Restricts Zika Virus Replication in Endothelial Cells by Potentiating Innate Antiviral Responses and Inhibiting Glycolysis, J Immunol, doi:info:doi/10.4049/jimmunol.1901310
Skelly, Dettori, Brodt, Assessing bias: the importance of considering confounding, Evidence-Based Spine-Care J, doi:info:doi/10.1055/s-0031-1298595
Stang, Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses, Eur J Epidemiol, doi:info:doi/10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
Stefan, Birkenfeld, Schulze, Ludwig, Obesity and impaired metabolic health in patients with COVID-19, Nature Reviews, doi:info:doi/10.1038/s41574-020-0364-6
Terpos, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, Elalamy, Hematological findings and complications of <scp > COVID</scp > À19, Am J Hematol, doi:info:doi/10.1002/ajh.25829
Ursini, Ciaffi, Landini, Meliconi, COVID-19 and diabetes: Is metformin a friend or foe?, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108167
Wang, Cooper, Gokhale, Association of Metformin with Susceptibility to COVID-19 in People with Type 2 Diabetes, J Clin Endocrinol Metabol, doi:info:doi/10.1210/clinem/dgab067
Yang, Feng, Yuan, Plasma glucose levels and diabetes are independent predictors for mortality and morbidity in patients with SARS, Diabet Med, doi:info:doi/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2006.01861.x
Yang, Lin, Guo, Binding of SARS coronavirus to its receptor damages islets and causes acute diabetes, Acta Diabetol, doi:info:doi/10.1007/s00592-009-0109-4
Zhang, He, Impacts of metformin on tuberculosis incidence and clinical outcomes in patients with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Eur J Clin Pharmacol, doi:info:doi/10.1007/s00228-019-02786-y
Zhang, Kong, Xia, Impaired Fasting Glucose and Diabetes Are Related to Higher Risks of Complications and Mortality Among Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019, Front Endocrinol, doi:info:doi/10.3389/fendo.2020.00525
Zhang, Wei, Chen, Wan, Chen, Clinical analysis of risk tors for severe COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes, J Diabetes Complications, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107666
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, The Lancet, doi:info:doi/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
Zhu, She, Cheng, Association of Blood Glucose Control and Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19 and Pre-existing Type 2 Diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.15258",
"ISSN": [
"0306-5251",
"1365-2125"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bcp.15258",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Aims</jats:title><jats:p>The COVID‐19 pandemic is a global public health emergency and patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) are disproportionately affected, exhibiting more severe outcomes. Recent studies have shown that metformin is associated with improved outcomes in patients with COVID‐19 and DM and may be a potential candidate for drug repurposing. We aimed to investigate the effects of metformin on outcomes in patients with COVID‐19 and DM.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>Databases (PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, EMBASE, <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" xlink:href=\"http://Clinicaltrials.gov\">Clinicaltrials.gov</jats:ext-link> and Cochrane library) were searched up to 10 April 2021 for studies reporting data on metformin use in COVID‐19 patients with DM. The risk of bias was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa scale. Certainty of evidence was rated using the GRADE approach. The primary outcome was mortality reported as odds ratio (OR). A random‐effects meta‐analysis was carried out on both unadjusted and adjusted ORs. This study is registered with PROSPERO, CRD42020221842.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>In total, 2 916 231 patients from 32 cohort studies were included in the quantitative and qualitative synthesis. The meta‐analysis showed that metformin was significantly associated with lower mortality in COVID‐19 patients with DM in both unadjusted (OR 0.61 [95% confidence interval: 0.53–0.71], <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> < .00001, <jats:italic>I</jats:italic><jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 70%) and adjusted (OR 0.78 [95% confidence interval: 0.69–0.88], <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> < .00001, <jats:italic>I</jats:italic><jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 67%) models.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Poor outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with DM can be attributed to inadequate glycaemic control and weakened immune responses. Metformin has multiple effects that can improve outcomes in patients with DM and our findings highlight a possible role of its use. However, robust randomised trials are needed to thoroughly assess its use.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/bcp.15258"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4772-5928",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences University of Nottingham UK"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ganesh",
"given": "Adithan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences University of Nottingham UK"
}
],
"family": "Randall",
"given": "Michael D.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Brit J Clinical Pharma",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-05T02:59:29Z",
"timestamp": 1644029969000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-23T21:50:21Z",
"timestamp": 1692827421000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000837",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "University of Nottingham"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-11T09:07:52Z",
"timestamp": 1715418472001
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 26,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1645574400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/bcp.15258",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1111/bcp.15258",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/bcp.15258",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2642-2656",
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_2_9_2_1",
"unstructured": "COVID Live Update: 141400793 Cases and 3 026 206 Deaths from the Coronavirus ‐ Worldometern.d.https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/(accessed April 18 2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473‐3099(20)30257‐7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc18‐0287",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1464‐5491.2006.01861.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.289.21.JOC30885",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3319",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0023366",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.131774",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598‐018‐35809‐2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.25829",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JIR.S245064",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc09‐0542",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.29.20164020",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_9_16_1",
"unstructured": "CrouseAB GrimesT LiP MightM OvalleF ShalevA.Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID‐19 and diabetes. MedRxiv2020;Preprint."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666‐7568(20)30033‐7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125‐020‐05180‐x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213‐8587(21)00050‐4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2014.09.018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931‐019‐1035‐9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228‐019‐02786‐y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/jpn.120065",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654‐010‐9491‐z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.01.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916‐020‐01832‐2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.10.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20‐0660",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12897",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4093/dmj.2020.0146",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20‐0375",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.12.20156257",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_9_35_1",
"unstructured": "PhiliposeZ SmatiN WongCS AspeyK MendallM.Obesity old age and frailty are the true risk factors for COVID‐19 mortality and not chronic disease or ethnicity. MedRxiv2020;Preprint."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4093/dmj.2020.0105",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.20.20174169",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_9_37_1",
"unstructured": "Abu‐JamousB AnisimovichA BaxterJ et al.Associations of comorbidities and medications with COVID‐19 outcome: A retrospective analysis of real‐world evidence data. MedRxiv2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108386",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107666",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.numecd.2020.09.028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.00525",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4158/EP‐2020‐0466",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119371",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26873",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592‐020‐01666‐7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_46_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Inpatient Use of Metformin and Acarbose Is Associated with Reduced Mortality of COVID‐19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus",
"author": "Li J",
"first-page": "e00301",
"journal-title": "Research Square",
"key": "e_1_2_9_47_1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268820002472",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_48_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.07.20160275",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_9_49_1",
"unstructured": "Izzi‐EngbeayaC DistasoW AminA et al.Severe COVID‐19 and Diabetes ‐ A Retrospective Cohort Study from Three London Teaching Hospitals. MedRxiv2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.27.20163071",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_9_50_1",
"unstructured": "DashtiH BatesDW RocheE FiskioJ MoraS DemlerOV.Clinical Characteristics and Severity of COVID‐19 Disease in Patients from Boston Area Hospitals. MedRxiv2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab067",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_51_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_52_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_53_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_54_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_55_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_56_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00547‐2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_57_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1538‐7836.2010.03910.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_58_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22831",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_59_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574‐020‐0364‐6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_60_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108132",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_61_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592‐009‐0109‐4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_62_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14099",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_63_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12902‐020‐00632‐2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_64_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dme.14328",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_65_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BSR20181994",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_66_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108167",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_67_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1901310",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_68_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_69_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389450118666170613081730",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_70_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103347",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_71_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12981‐020‐00267‐2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_72_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.05.027",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_73_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054‐019‐2346‐4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_74_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/resp.13486",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_75_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0203946",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_76_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140‐6736(20)30566‐3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_77_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s‐0031‐1298595",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_78_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.14748",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_79_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 78,
"references-count": 78,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bcp.15258"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "88"
}
