The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
et al., Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006, Nov 2020
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
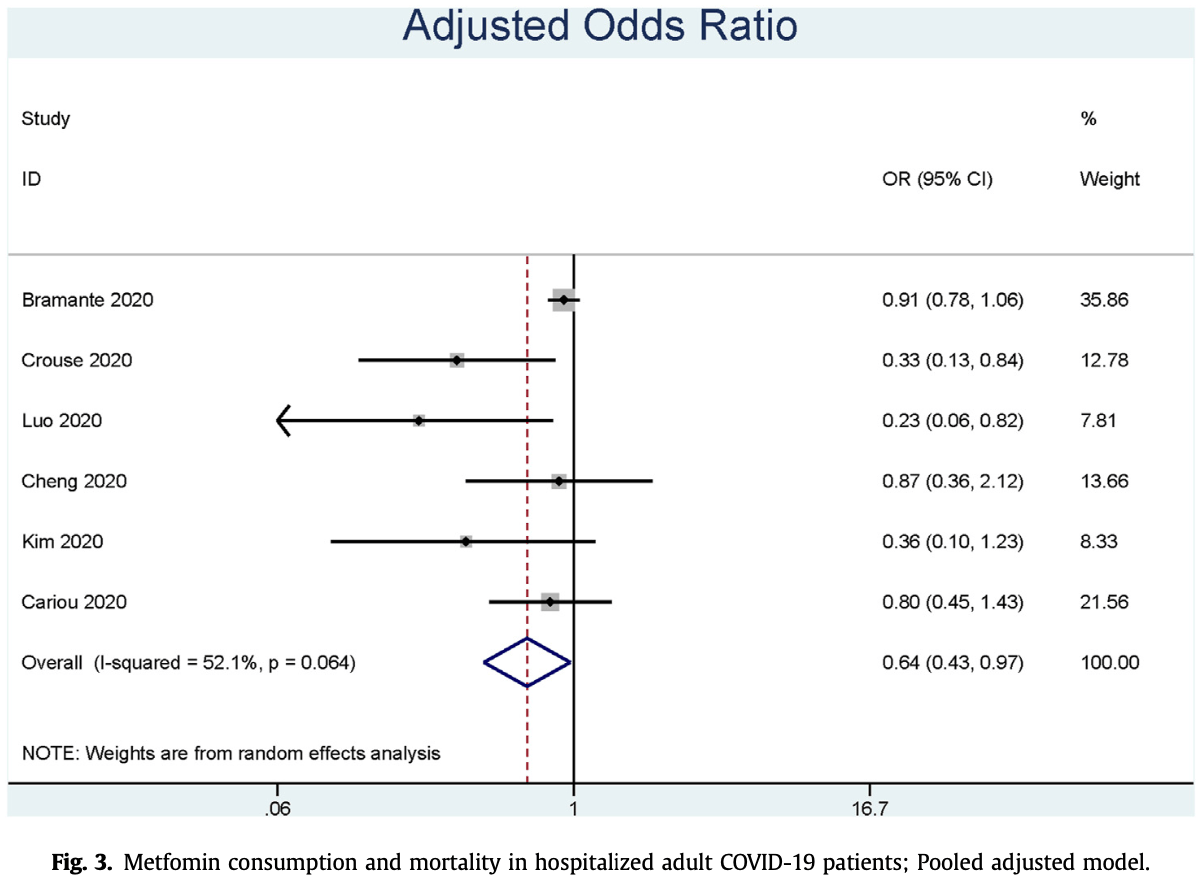
Meta analysis of 9 studies showing lower mortality with metformin use.
24 meta-analyses show significant improvements with metformin for mortality1-23,
hospitalization7,13,23 ,
progression1, and
severity8,9,13 .
Currently there are 110 metformin for COVID-19 studies, showing 36% lower mortality [32‑40%], 29% lower ventilation [12‑43%], 19% lower ICU admission [8‑28%], 17% lower hospitalization [11‑23%], and 5% fewer cases [-4‑13%].
|
risk of death, 36.0% lower, OR 0.64, p = 0.03, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Yang et al., The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977.
2.
Lukito et al., The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006.
3.
Kow et al., Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26498.
4.
Hariyanto et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obesity Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290.
5.
Ma et al., Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282210.
6.
Parveen et al., Association of Metformin with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India), doi:10.1055/s-0042-1760353.
7.
Li et al., Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.704666.
8.
Schlesinger et al., Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-023-05928-1.
9.
Petrelli et al., Metformin and Covid-19: a systematic review of systematic reviews with meta-analysis, Acta Biomedica Atenei Parmensis, doi:10.23750/abm.v94iS3.14405.
10.
Oscanoa et al., Metformin therapy and severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a meta-analysis, Clinical Diabetology, doi:10.5603/DK.a2021.0035.
11.
Kan et al., Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.708494.
12.
Poly et al., Metformin Use Is Associated with Decreased Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes: Evidence from Retrospective Studies and Biological Mechanism, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10163507.
13.
Song et al., The Effect of Antihyperglycemic Medications on COVID-19: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review from Observational Studies, Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science, doi:10.1007/s43441-024-00633-6.
14.
Ganesh et al., Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15258.
15.
Nassar et al., Noninsulin‐based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis, Journal of Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13359.
16.
Zhan et al., Effect of Antidiabetic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/10600280221133577.
17.
Nguyen et al., Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155196.
18.
Han et al., Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002.
19.
Chen et al., The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458.
20.
Scheen, A., Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006.
21.
Sun et al., Is Metformin Use Associated With a Decreased Mortality for COVID-19 Diabetic Patients? A Meta-Analysis, Journal of the Endocrine Society, doi:10.1210/jendso/bvab048.709.
Lukito et al., 11 Nov 2020, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006
Background and aims: Diabetes is one of the most common comorbidities, and it is associated with poorer outcomes in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 . Preliminary findings showed that mortality was reduced in those who consume metformin compared to those who did not, and given its low cost and widespread availability; metformin is an attractive and potential agent to mitigate excessive risk in diabetic populations. Methods: Several medical databases (Pubmed, EuropePMC, EBSCOhost, Proquest, Cochrane library) and two health-science preprint servers (preprint.org and Medrxiv) were systematically searched for relevant literature. Results: Nine studies with 10,233 subjects were included in the qualitative and quantitative synthesis. Meta-analysis showed that metformin is associated with lower mortality in pooled non-adjusted model (OR 0.45 [0.25, 0.81], p ¼ 0.008; I 2: 63.9%, p ¼ 0.026) and pooled adjusted model (OR 0.64 [0.43, 0.97], p ¼ 0.035; I 2 : 52.1%, p ¼ 0.064).
Conclusion: The analysis showed that metformin consumption was associated with lower mortality. Randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm this finding.
Ethics approval and consent to participate Not Applicable.
Consent for publication Not Applicable.
Conflicts of interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Abbreviations
ACE2 Angiotensin
References
Abu-Jamous, Anisimovich, Baxter, Mackillop, Vizcaychipi et al., Associations of comorbidities and medications with COVID-19 outcome: a retrospective analysis of real-world evidence data, doi:10.1101/2020.08.20.20174169
Bertrand, Samy, Matthieu, Al-Salameh, Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Marmor, Hoversten et al., Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with covid-19, MedRxiv Prepr Serv Heal Sci, doi:10.1101/2020.06.19.20135095
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Chen, Peng et al., Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0660
Cheng, Liu, Li, Zhang, Lei et al., Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab
Cochrance, Review manager (RevMan
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Might, Ovalle et al., Metformin use IS associated with reduced mortality IN a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes, MedRxiv Prepr Serv Heal Sci, doi:10.1101/2020.07.29.20164020
El-Arabey, Abdalla, Metformin and COVID-19: a novel deal of an old drug, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25958
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Huang, Lim, Pranata, Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia e a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression: diabetes and COVID-19, Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.018
Huang, Pranata, Lim, Oehadian, Alisjahbana, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, D-dimer, and ferritin in severe coronavirus disease-2019: a meta-analysis, Ther Adv Respir Dis, doi:10.1177/1753466620937175
Kim, Jeon, Kim, Moon, Cho et al., The clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with moderate-to-severe coronavirus disease 2019 infection and diabetes in daegu, South Korea, Diabetes Metab J, doi:10.4093/dmj.2020.0146
Li, Guan, Wu, Wang, Zhou et al., Early transmission dynamics in wuhan, China, of novel coronaviruseinfected pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001316
Lim, Exercise addiction and COVID-19-associated restrictions, J Ment Health, doi:10.1080/09638237.2020.1803234
Lim, Huang, Yonas, Vania, Pranata, A wave of non-communicable diseases following the COVID-19 pandemic, Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.06.050
Lim, Pranata, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) markedly increased mortality in patients with hip fracture e a systematic review and metaanalysis, J Clin Orthop Trauma, doi:10.1016/j.jcot.2020.09.015
Lim, Pranata, Huang, Yonas, Soeroto et al., Multiorgan failure with emphasis on acute kidney injury and severity of COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Can J Kidney Heal Dis, doi:10.1177/2054358120938573
Lim, Pranata, Sports activities during any pandemic lockdown, Ir J Med Sci, doi:10.1007/s11845-020-02300-9
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Liu, Zheng et al., Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Philipose, Smati, Wong, Aspey, Mendall, Obesity, old age and frailty are the true risk factors for COVID-19 mortality and not chronic disease or ethnicity in Croydon, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.12.20156257
Pranata, Huang, Lim, Wahjoepramono, July, Impact of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases on mortality and severity of COVID-19 -systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression, J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104949
Pranata, Lim, Huang, Raharjo, Lukito, Hypertension is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression, JRAAS -J Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst, doi:10.1177/14703203209268
Pranata, Lim, Yonas, Siswanto, Meyer, Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest prognosis during the COVID-19 pandemic, Intern Emerg Med, doi:10.1007/s11739-020-02428-7
Pranata, Lim, Yonas, Vania, Lukito et al., Body mass index and outcome in patients with COVID-19: a dose-response meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.005
Pranata, Permana, Huang, Lim, Soetedjo et al., The use of renin angiotensin system inhibitor on mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.06.047
Pranata, Soeroto, Huang, Lim, Santoso, Effect of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and smoking on the outcome of COVID-19, Int J Tubercul Lung Dis, doi:10.5588/ijtld.20.0278
Pranata, Tondas, Huang, Lim, Siswanto et al., Potential role of telemedicine in solving ST-segment elevation dilemmas in remote areas during the COVID-19 pandemic, Am J Emerg Med, doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.06.012
Sharma, Ray, Sadasivam, Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183
Ursini, Ciaffi, Landini, Meliconi, COVID-19 and diabetes: is metformin a friend or foe?, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108167
Yang, Lin, Ji, Guo, Binding of SARS coronavirus to its receptor damages islets and causes acute diabetes, Acta Diabetol, doi:10.1007/s00592-009-0109-4
Yonas, Alwi, Pranata, Huang, Lim et al., Effect of heart failure on the outcome of COVID-19 -a meta analysis and systematic review, Am J Emerg Med, doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.07.009
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006",
"ISSN": [
"1871-4021"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006",
"alternative-id": [
"S1871402120304719"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lukito",
"given": "Antonia Anna",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3998-6551",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pranata",
"given": "Raymond",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3763-2661",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Henrina",
"given": "Joshua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7631-6835",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Michael Anthonius",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawrensia",
"given": "Sherly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7895-382X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Suastika",
"given": "Ketut",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-11T22:28:51Z",
"timestamp": 1605133731000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-21T17:31:04Z",
"timestamp": 1608571864000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-28T16:09:55Z",
"timestamp": 1648483795681
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 49,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1871-4021"
}
],
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1604188800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1871402120304719?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1871402120304719?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2177-2183",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib1",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001316",
"article-title": "Early transmission dynamics in wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1199",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib2",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Hopkins University",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib4",
"series-title": "COVID-19 dashboard by the center for systems science and engineering (CSSE) at",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.018",
"article-title": "Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia – a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression: diabetes and COVID-19",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "395",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib5",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Metformin use IS associated with reduced mortality IN a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes",
"author": "Crouse",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv Prepr Serv Heal Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib7",
"series-title": "Cochrance. Review manager (RevMan)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Abu-Jamous",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib8",
"series-title": "Associations of comorbidities and medications with COVID-19 outcome: a retrospective analysis of real-world evidence data",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x",
"article-title": "Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study",
"author": "Bertrand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1500",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib9",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0660",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1399",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib10",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Cheng",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib11",
"series-title": "Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Obesity, old age and frailty are the true risk factors for COVID-19 mortality and not chronic disease or ethnicity in Croydon",
"author": "Philipose",
"first-page": "2020",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4093/dmj.2020.0146",
"article-title": "The clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with moderate-to-severe coronavirus disease 2019 infection and diabetes in daegu, South Korea",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "602",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab J",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib13",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"article-title": "Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib14",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with covid-19",
"author": "Bramante",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv Prepr Serv Heal Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.005",
"article-title": "Body mass index and outcome in patients with COVID-19: a dose-response meta-analysis",
"author": "Pranata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.06.050",
"article-title": "A wave of non-communicable diseases following the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "979",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib17",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Hypertension is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression",
"author": "Pranata",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "JRAAS - J Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.07.009",
"article-title": "Effect of heart failure on the outcome of COVID-19 - a meta analysis and systematic review",
"author": "Yonas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Am J Emerg Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-020-02428-7",
"article-title": "Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest prognosis during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Pranata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Intern Emerg Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.06.012",
"article-title": "Potential role of telemedicine in solving ST-segment elevation dilemmas in remote areas during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Pranata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Am J Emerg Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) markedly increased mortality in patients with hip fracture – a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Lim",
"journal-title": "J Clin Orthop Trauma",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5588/ijtld.20.0278",
"article-title": "Effect of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and smoking on the outcome of COVID-19",
"author": "Pranata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Tubercul Lung Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Multiorgan failure with emphasis on acute kidney injury and severity of COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Lim",
"journal-title": "Can J Kidney Heal Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib24",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104949",
"article-title": "Impact of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases on mortality and severity of COVID-19 - systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression",
"author": "Pranata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Sports activities during any pandemic lockdown",
"author": "Lim",
"issue": "1971",
"journal-title": "Ir J Med Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Exercise addiction and COVID-19-associated restrictions",
"author": "Lim",
"journal-title": "J Ment Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25958",
"article-title": "Metformin and COVID-19: a novel deal of an old drug",
"author": "El-Arabey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183",
"article-title": "Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108183",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib29",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1753466620937175",
"article-title": "C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, D-dimer, and ferritin in severe coronavirus disease-2019: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Ther Adv Respir Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib30",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108167",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes: is metformin a friend or foe?",
"author": "Ursini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108167",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib31",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.06.047",
"article-title": "The use of renin angiotensin system inhibitor on mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pranata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592-009-0109-4",
"article-title": "Binding of SARS coronavirus to its receptor damages islets and causes acute diabetes",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "193",
"journal-title": "Acta Diabetol",
"key": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006_bib33",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2010"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "14"
}
