Effect of Antidiabetic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
et al., Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/10600280221133577, Oct 2022
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
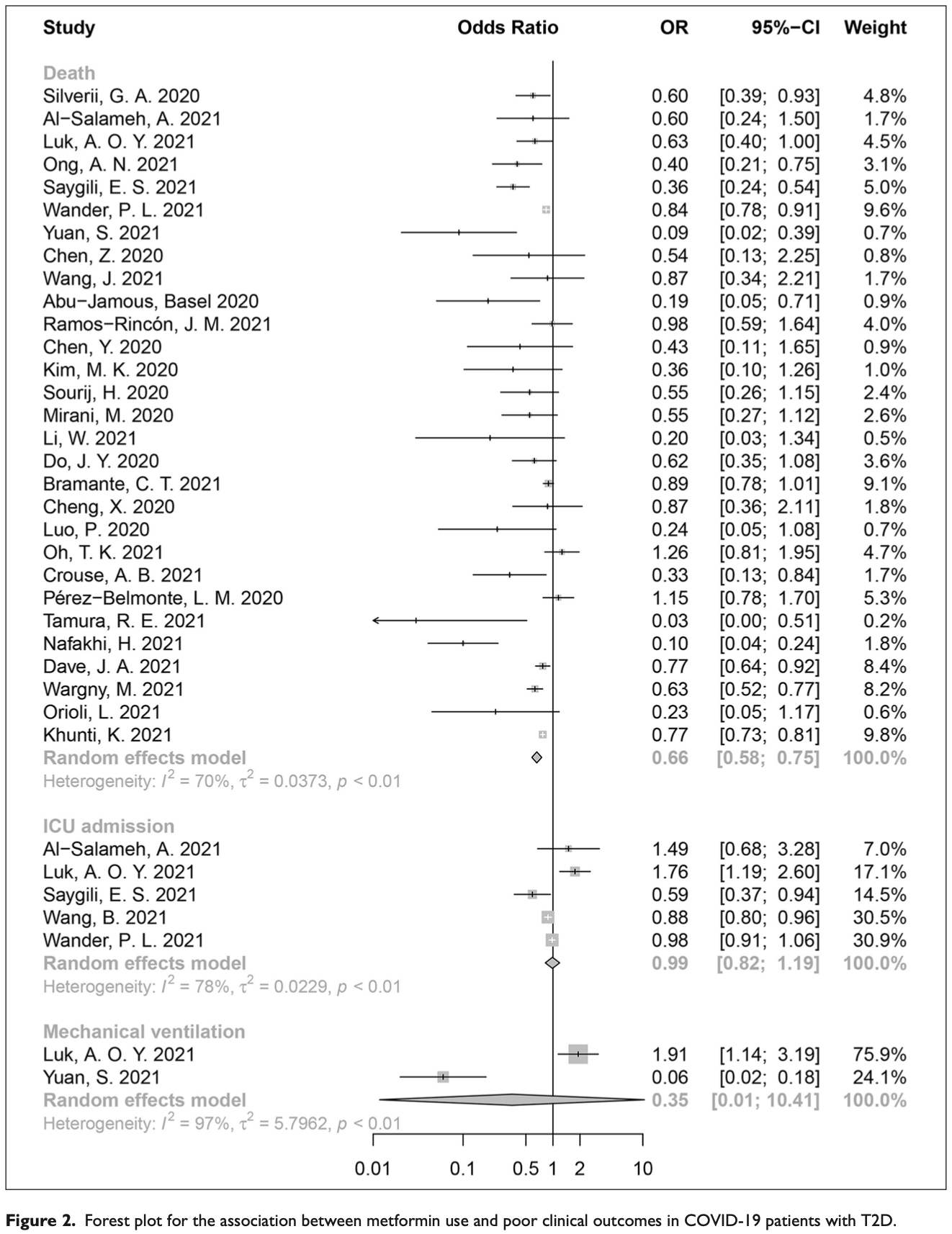
Meta analysis of 54 studies (34 for metformin) with a total of over 314,000 patients showing lower mortality with metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes. Metformin, SGLT-2i, and GLP-1ra were associated with 34%, 20%, and 17% lower mortality risk respectively. However, insulin was associated with 52% higher mortality risk and higher ICU admission risk. No significant associations were found for DPP-4 inhibitors, sulfonylureas, α-glycosidase inhibitors, and thiazolidinediones.
24 meta-analyses show significant improvements with metformin for mortality1-23,
hospitalization7,13,23 ,
progression1, and
severity8,9,13 .
Currently there are 110 metformin for COVID-19 studies, showing 36% lower mortality [32‑40%], 29% lower ventilation [12‑43%], 19% lower ICU admission [8‑28%], 17% lower hospitalization [11‑23%], and 5% fewer cases [-4‑13%].
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments24.
|
risk of death, 34.0% lower, OR 0.66, p < 0.001, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 65.0% lower, OR 0.35, p = 0.57, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 1.0% lower, OR 0.99, p = 0.92, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Yang et al., The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977.
2.
Lukito et al., The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006.
3.
Kow et al., Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26498.
4.
Hariyanto et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obesity Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290.
5.
Ma et al., Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282210.
6.
Parveen et al., Association of Metformin with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India), doi:10.1055/s-0042-1760353.
7.
Li et al., Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.704666.
8.
Schlesinger et al., Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-023-05928-1.
9.
Petrelli et al., Metformin and Covid-19: a systematic review of systematic reviews with meta-analysis, Acta Biomedica Atenei Parmensis, doi:10.23750/abm.v94iS3.14405.
10.
Oscanoa et al., Metformin therapy and severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a meta-analysis, Clinical Diabetology, doi:10.5603/DK.a2021.0035.
11.
Kan et al., Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.708494.
12.
Poly et al., Metformin Use Is Associated with Decreased Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes: Evidence from Retrospective Studies and Biological Mechanism, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10163507.
13.
Song et al., The Effect of Antihyperglycemic Medications on COVID-19: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review from Observational Studies, Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science, doi:10.1007/s43441-024-00633-6.
14.
Ganesh et al., Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15258.
15.
Nassar et al., Noninsulin‐based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis, Journal of Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13359.
16.
Zhan et al., Effect of Antidiabetic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/10600280221133577.
17.
Nguyen et al., Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155196.
18.
Han et al., Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002.
19.
Chen et al., The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458.
20.
Scheen, A., Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006.
21.
Sun et al., Is Metformin Use Associated With a Decreased Mortality for COVID-19 Diabetic Patients? A Meta-Analysis, Journal of the Endocrine Society, doi:10.1210/jendso/bvab048.709.
22.
Keels et al., Antidiabetic agent use and clinical outcomes in patients with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2024.1482853.
Zhan et al., 29 Oct 2022, China, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: jhong_lz@163.com, xymacq@hotmail.com, xymacq@tmmu.edu.cn.
Effect of Antidiabetic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/10600280221133577
Background: No study has yet systematically evaluated the effect of antidiabetic therapy on clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). Objective: We aimed to evaluate the effect of different antidiabetic therapy on clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with T2D. Methods: We comprehensively retrieved the published research which examined the effect of antidiabetic therapy on clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with T2D. The odds ratio (OR) and its 95% confidence interval (95% CI) for clinical outcomes were calculated using the random-effects model, and meta-regression was adopted to evaluate the potential sources of heterogeneity between studies. Results: A total of 54 studies were included in this study. We found that the use of metformin (OR = 0.66, 95% CI: 0.58-0.75), SGLT-2i (OR = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.73-0.88), and GLP-1ra (OR = 0.83, 95% CI: 0.70-0.98) were significantly associated with lower mortality risk in COVID-19 patients with T2D, while insulin use might unexpectedly increase the ICU admission rate (OR = 2.32, 95% CI: 1.34-4.01) and risk of death (OR = 1.52, 95% CI: 1.32-1.75). No statistically significant associations were identified for DPP-4i, SUs, AGIs, and TZDs. Conclusion and Relevance: We demonstrated that the usage of metformin, SGLT-2i, and GLP-1ra could significantly decrease mortality in COVID-19 patients with T2D. The heterogeneity across the studies, baseline characteristics of the included patients, shortage of dosage and the duration of antidiabetic drugs and autonomy of drug selection might limit the objectivity and accuracy of results. Further adequately powered and high-quality randomized controlled trials are warranted for conclusive findings.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
ORCID iDs Luhan Wang https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7917-9071 Xiangyu Ma https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7967-3950
Supplemental Material Supplemental material for this article is available online.
References
Al-Salameh, Bennis, Cariou, Lalau, The association between metformin treatment and COVID-19 outcomes according to metformin continuation during hospitalisation, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.dia-bet.2021.101297
Alessi, De Oliveira, Schaan, Telo, Dexamethasone in the era of COVID-19: friend or foe? An essay on the effects of dexamethasone and the potential risks of its inadvertent use in patients with diabetes, Diabetol Metab Syndr, doi:10.1186/s13098-020-00583-7
Attri, Goyal, Gupta, Tandon, Basal-bolus insulin regimen for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: a practical approach, Diabetes Ther, doi:10.1007/s13300-020-00873-3
Barron, Bakhai, Kar, Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a whole-population study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2
Bossi, Forloni, Colombelli, Lack of efficacy of SGLT2-i in severe pneumonia related to novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection: no little help from our friends, Diabetes Ther, doi:10.1007/s13300-020-00844-8
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis, Lancet Healthy Longev, doi:10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7
Chen, Chien, Yang, Role of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in patients with diabetes infected with coronavirus-19, J Chin Med Assoc, doi:10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000338
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Cheng, Liu, Li, Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Might, Ovalle et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.600439
Dalan, Is DPP4 inhibition a comrade or adversary in COVID-19 infection, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108216
Dandona, Ghanim, Diabetes, obesity, COVID-19, insulin, and other antidiabetes drugs, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dci21-0003
Das, Rastogi, Harikumar, Diagnosis and management considerations in steroid-related hyperglycemia in COVID-19: a position statement from the endocrine society of India, Indian J Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.4103/ijem.ijem_227_21
Fang, Li, Yu, Epidemiological, comorbidity factors with severity and prognosis of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.103579
Fang, Ming, Cen, Post-sequelae one year after hospital discharge among older COVID-19 patients: a multicenter prospective cohort study, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.12.005
Ganesh, Randall, Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID-19 patients with new or pre-existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta-analysis, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bcp.15258
Gianchandani, Esfandiari, Ang, Managing hyperglycemia in the COVID-19 inflammatory storm, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/dbi20-0022
Gupta, Hussain, Misra, Diabetes and COVID-19: evidence, current status and unanswered research questions, Eur J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0652-1
Han, Ma, Sun, The association between antidiabetic agents and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Arch Med Res, doi:10.1016/j.arc-med.2021.08.002
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Kalra, Mukherjee, Venkataraman, Hypoglycemia: the neglected complication, Indian J Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.4103/2230-8210.117219
Koufakis, Metallidis, Zebekakis, Ajjan, Kotsa, Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in the era of COVID-19 pandemic: is the benefit to risk ratio still favorable, J Diabetes Sci Technol, doi:10.1177/1932296820932155
Lee, Jun, Anti-inflammatory effects of GLP-1based therapies beyond glucose control, Mediators Inflamm, doi:10.1155/2016/3094642
Li, Fang, Cheng, Development and validation of a prognostic nomogram for predicting in-hospital mortality of COVID-19: a multicenter retrospective cohort study of 4086 cases in China, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.202605
Li, Xu, Yu, Risk factors for severity and mortality in adult COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.006
Liu, Bai, Han, The association of diabetes and the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: a retrospective study, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108386
Maranta, Cianfanelli, Rizzo, Cianflone, Filling the gap between Guidelines and Real World in the cardiovascular approach to the diabetic patients: the need for a call to action, Int J Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.12.074
Meijer, Hoekstra, Van Den Oever, Treatment with a DPP-4 inhibitor at time of hospital admission for COVID-19 is not associated with improved clinical outcomes: data from the COVID-PREDICT cohort study in The Netherlands, J Diabetes Metab Disord, doi:10.1007/s40200-021-00833-z
Mendes, Câmara-De-Souza, Halpern, Hospital management of hyperglycemia in the context of COVID-19: evidence-based clinical considerations, Diabetol Metab Syndr, doi:10.1186/s13098-022-00808-x
Mirabelli, Chiefari, Puccio, Potential benefits and harms of novel antidiabetic drugs during COVID-19 crisis, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph17103664
Nyland, Raja-Khan, Bettermann, Diabetes, drug treatment and mortality in COVID-19: a multinational retrospective cohort study, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/db21-0385
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Pal, Banerjee, Mukherjee, Bhogal, Kaur et al., Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use and mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis, Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1177/2042018821996482
Papadopoulos, Koutroulos, Zikoudi, Diabetes-related acute metabolic emergencies in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetol Int, doi:10.1007/s13340-021-00502-9
Poly, Islam, Li, Lin, Hsu et al., Metformin use is associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes: evidence from retrospective studies and biological mechanism, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10163507
Pérez-Belmonte, Torres-Peña, Md, Mortality and other adverse outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus admitted for COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering drugs: a nationwide cohort study, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-020-01832-2
Rados, Viecceli, Pinto, Metabolic effects of antihyperglycemic agents and mortality: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-69738-w
Riahi, Lo, Anastasopoulou, Insulin use and poor COVID-19 outcomes among diabetes patients: association not necessarily causation, Endocr Res, doi:10.1080/07435800.2021.1894821
Sachinidis, Nikolic, Stoian, Cardiovascular outcomes trials with incretin-based medications: a critical review of data available on GLP-1 receptor agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154343
Samuel, Varghese, Busselberg, Therapeutic potential of metformin in COVID-19: reasoning for its protective role, Trends Microbiol, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2021.03.004
Shang, Wang, Zhang, The relationship between diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 prognosis: a retrospective cohort study in Wuhan, China, Am J Med, doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.05.033
Silverii, Monami, Cernigliaro, Are diabetes and its medications risk factors for the development of COVID-19? Data from a population-based study in Sicily, Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, doi:10.1016/j.num-ecd.2020.09.028
Stroup, Berlin, Morton, Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting: meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.283.15.2008
Suh, Park, Glucocorticoid-induced diabetes mellitus: an important but overlooked problem, Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.180
Tan, Goh, Khoo, Self-reported hypoglycaemia in insulin-treated patients with diabetes mellitus: results from the Singapore cohort of the International Operations Hypoglycaemia Assessment Tool study, Singapore Med J, doi:10.11622/smedj.2019081
Varghese, Samuel, Liskova, Kubatka, Büsselberg, Diabetes and coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): molecular mechanism of Metformin intervention and the scientific basis of drug repurposing, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009634
Wander, Lowy, Beste, Risk factors for adverse outcomes among 35 879 veterans with and without diabetes after diagnosis with COVID-19, BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care, doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002252
Wang, Cooper, Gokhale, Association of metformin with susceptibility to COVID-19 in people with type 2 diabetes, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab067
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Wargny, Potier, Gourdy, Predictors of hospital discharge and mortality in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: updated results from the nationwide CORONADO study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w
Who, WHO COVID-19 dashboard
Xu, Wang, Wang, The impact of type 2 diabetes and its management on the prognosis of patients with severe COVID-19, J Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13084
Yang, Sun, Zhang, Zhang, The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977
Yang, Yu, Xu, Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5
Zhan, Zhang, Wang, Glycemic control and COVID-19 outcomes: the missing metabolic players, QJM, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac044
Zhan, Zhang, Wang, Response to letter to editor by Dr. Pranav Ish entitled "COVID-19 and diabetes-double whammy, QJM, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac048
Zhan, Zhang, Wang, Short and long-term prognosis of glycemic control in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes, QJM, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac020
Zhang, Wang, Shen, Symptoms and health outcomes among survivors of COVID-19 infection 1 year after discharge from hospitals in Wuhan, China, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanet-workopen.2021.27403
Zhu, She, Cheng, Association of blood glucose control and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and preexisting type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/10600280221133577",
"ISSN": [
"1060-0280",
"1542-6270"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/10600280221133577",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background:</jats:title><jats:p> No study has yet systematically evaluated the effect of antidiabetic therapy on clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective:</jats:title><jats:p> We aimed to evaluate the effect of different antidiabetic therapy on clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with T2D. </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods:</jats:title><jats:p> We comprehensively retrieved the published research which examined the effect of antidiabetic therapy on clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with T2D. The odds ratio (OR) and its 95% confidence interval (95% CI) for clinical outcomes were calculated using the random-effects model, and meta-regression was adopted to evaluate the potential sources of heterogeneity between studies. </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results:</jats:title><jats:p> A total of 54 studies were included in this study. We found that the use of metformin (OR = 0.66, 95% CI: 0.58-0.75), SGLT-2i (OR = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.73-0.88), and GLP-1ra (OR = 0.83, 95% CI: 0.70-0.98) were significantly associated with lower mortality risk in COVID-19 patients with T2D, while insulin use might unexpectedly increase the ICU admission rate (OR = 2.32, 95% CI: 1.34-4.01) and risk of death (OR = 1.52, 95% CI: 1.32-1.75). No statistically significant associations were identified for DPP-4i, SUs, AGIs, and TZDs. </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion and Relevance:</jats:title><jats:p> We demonstrated that the usage of metformin, SGLT-2i, and GLP-1ra could significantly decrease mortality in COVID-19 patients with T2D. The heterogeneity across the studies, baseline characteristics of the included patients, shortage of dosage and the duration of antidiabetic drugs and autonomy of drug selection might limit the objectivity and accuracy of results. Further adequately powered and high-quality randomized controlled trials are warranted for conclusive findings. </jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/10600280221133577"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "College of Public Health, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, College of Preventive Medicine, Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University), Chongqing, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhan",
"given": "Kegang",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Orthopedics, Chongqing Key Laboratory of Pediatrics, Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Child Development and Disorders, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health and Disorders, Children’s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China"
}
],
"family": "Weng",
"given": "Liuqi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease Control and Prevention, Chongqing Municipal Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Chongqing, China"
}
],
"family": "Qi",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7917-9071",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, College of Preventive Medicine, Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University), Chongqing, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Luhan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "West China School of Clinical Medicine, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China"
}
],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, College of Preventive Medicine, Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University), Chongqing, China"
}
],
"family": "Fang",
"given": "Xiaoyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "College of Public Health, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Jia",
"given": "Hong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7967-3950",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, College of Preventive Medicine, Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University), Chongqing, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Xiangyu",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Annals of Pharmacotherapy",
"container-title-short": "Ann Pharmacother",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-29T09:36:20Z",
"timestamp": 1667036180000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-24T20:17:24Z",
"timestamp": 1687637844000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"CQYC202005003"
],
"name": "Chongqing Talents: Exceptional Young Talents Project"
},
{
"award": [
"cstc2020jcyj-jqX0014"
],
"name": "Outstanding Youth Science Foundation of Chongqing"
},
{
"name": "Science Foundation for Outstanding Young People of the Army Medical University"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-11T09:12:57Z",
"timestamp": 1715418777471
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/page/policies/text-and-data-mining-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667001600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/10600280221133577",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/10600280221133577",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/10600280221133577",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"page": "776-786",
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
29
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"key": "bibr1-10600280221133577",
"unstructured": "WHO. WHO COVID-19 dashboard 2022. https://covid19.who.int/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr2-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr3-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr4-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.27403.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr5-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.12.005.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr6-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr7-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.202605.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr8-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103579.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr9-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr10-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcac020.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr11-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr12-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcac048.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr13-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcac044.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr14-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db21-0385.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr15-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108386.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr16-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.numecd.2020.09.028.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr17-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-020-01832-2.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr18-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13300-020-00844-8.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr19-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr20-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0652-1.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr21-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2042018821996482.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr22-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40200-021-00833-z.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr23-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10163507.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr24-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009634.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr25-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr26-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.15258.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr27-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr28-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr29-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab067.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr30-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.283.15.2008.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr31-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n71.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr32-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr33-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.600439.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr34-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tim.2021.03.004.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr35-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dbi20-0022.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr36-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07435800.2021.1894821.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr37-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.05.033.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr38-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dci21-0003.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr39-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13300-020-00873-3.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr40-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.117219.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr41-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.11622/smedj.2019081.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr42-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13098-022-00808-x.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr43-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13098-020-00583-7.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr44-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.180.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr45-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1753-0407.13084.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr46-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.006.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr47-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijem.ijem_227_21.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr48-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000338.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr49-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108216.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr50-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr51-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002252.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr52-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2016/3094642.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr53-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph17103664.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr54-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154343.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr55-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.12.074.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr56-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-69738-w.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr57-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13340-021-00502-9.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr58-10600280221133577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1932296820932155.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr59-10600280221133577"
}
],
"reference-count": 59,
"references-count": 59,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/10600280221133577"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of Antidiabetic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy",
"volume": "57"
}
