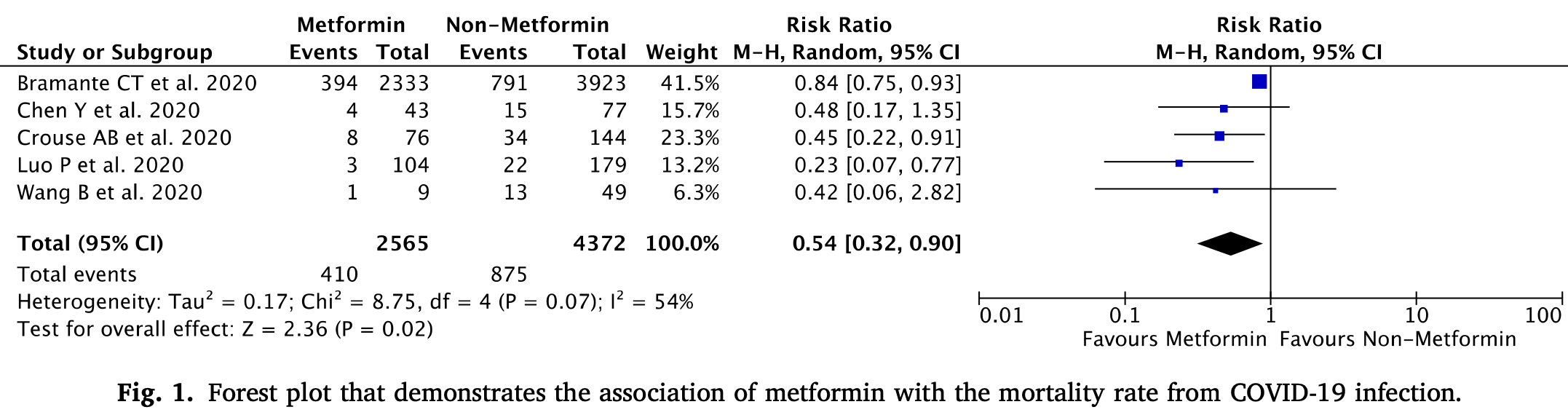
Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection
et al., Obesity Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290, Aug 2020
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Meta analysis of 5 studies showing lower mortality with metformin use.
24 meta-analyses show significant improvements with metformin for mortality1-23,
hospitalization7,13,23 ,
progression1, and
severity8,9,13 .
Currently there are 110 metformin for COVID-19 studies, showing 36% lower mortality [32‑40%], 29% lower ventilation [12‑43%], 19% lower ICU admission [8‑28%], 17% lower hospitalization [11‑23%], and 5% fewer cases [-4‑13%].
1.
Yang et al., The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977.
2.
Lukito et al., The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006.
3.
Kow et al., Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26498.
4.
Hariyanto et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obesity Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290.
5.
Ma et al., Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282210.
6.
Parveen et al., Association of Metformin with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India), doi:10.1055/s-0042-1760353.
7.
Li et al., Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.704666.
8.
Schlesinger et al., Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-023-05928-1.
9.
Petrelli et al., Metformin and Covid-19: a systematic review of systematic reviews with meta-analysis, Acta Biomedica Atenei Parmensis, doi:10.23750/abm.v94iS3.14405.
10.
Oscanoa et al., Metformin therapy and severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a meta-analysis, Clinical Diabetology, doi:10.5603/DK.a2021.0035.
11.
Kan et al., Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.708494.
12.
Poly et al., Metformin Use Is Associated with Decreased Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes: Evidence from Retrospective Studies and Biological Mechanism, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10163507.
13.
Song et al., The Effect of Antihyperglycemic Medications on COVID-19: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review from Observational Studies, Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science, doi:10.1007/s43441-024-00633-6.
14.
Ganesh et al., Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15258.
15.
Nassar et al., Noninsulin‐based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis, Journal of Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13359.
16.
Zhan et al., Effect of Antidiabetic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/10600280221133577.
17.
Nguyen et al., Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155196.
18.
Han et al., Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002.
19.
Chen et al., The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458.
20.
Scheen, A., Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006.
21.
Sun et al., Is Metformin Use Associated With a Decreased Mortality for COVID-19 Diabetic Patients? A Meta-Analysis, Journal of the Endocrine Society, doi:10.1210/jendso/bvab048.709.
Hariyanto et al., 18 Aug 2020, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection
Obesity Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290
Background and aims: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has caused a significant impact on all aspects of life. One of the comorbidities associated with severe outcome and mortality of COVID-19 is diabetes. Metformin is one of the drugs which is most commonly used for the treatment of diabetes patients. This study aims to analyze the potential benefit of metformin use in reducing the mortality rate from COVID-19 infection. Methods: We systematically searched the Google Scholar database using specific keywords related to our aims until August 3rd, 2020. All articles published on COVID-19 and metformin were retrieved. Statistical analysis was done using Review Manager 5.4 software. Results: A total of 5 studies with a total of 6937 patients were included in our analysis. Our meta-analysis showed that metformin use is associated with reduction in mortality rate from COVID-19 infections [RR 0.54 (95% CI 0.32-0.90), p = 0.02, I 2 = 54%, random-effect modelling]. Conclusion: Metformin has shown benefits in reducing the mortality rate from COVID-19 infections. Patients with diabetes should be advised to continue taking metformin drugs despite COVID-19 infection status.
References
Al-Benna, Association of high level gene expression of ACE2 in adipose tissue with mortality of COVID-19 infection in obese patients, Obes Med, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100283
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Marmor, Hoversten et al., Observational Study of Metformin and Risk of Mortality in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19, doi:10.1101/2020.06.19.20135095
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Chen, Peng et al., Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0660
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Might, Ovalle et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes, doi:10.1101/2020.07.29.20164020
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Dyslipidemia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.07.054
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Thyroid disease is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.07.044
Huang, Lim, Pranata, Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia -a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.018
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Liu, Zheng et al., Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Sharma, Ray, Sadasivam, Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183
Singh, Gupta, Ghosh, Misra, Diabetes in COVID-19: prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.004
Ursini, Ciaffi, Landini, Meliconi, COVID-19 and diabetes: is metformin a friend or foe?, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108167
Wang, Van Oekelen, Mouhieddine, Del, Valle et al., A tertiary center experience of multiple myeloma patients with COVID-19: lessons learned and the path forward, J. Hematol. Oncol, doi:10.1186/s13045-020-00934-x
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290",
"ISSN": [
"2451-8476"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290",
"alternative-id": [
"S245184762030110X"
],
"article-number": "100290",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Obesity Medicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hariyanto",
"given": "Timotius Ivan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5219-9029",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kurniawan",
"given": "Andree",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Obesity Medicine"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-18T17:44:19Z",
"timestamp": 1597772659000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-25T06:11:48Z",
"timestamp": 1606284708000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-28T12:48:26Z",
"timestamp": 1648471706104
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 61,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "2451-8476"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1598918400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S245184762030110X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S245184762030110X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100290",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100283",
"article-title": "Association of high level gene expression of ACE2 in adipose tissue with mortality of COVID-19 infection in obese patients",
"author": "Al-Benna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100283",
"journal-title": "Obes Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Bramante",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib2",
"series-title": "Observational Study of Metformin and Risk of Mortality in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0660",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1399",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib3",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes",
"author": "Crouse",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.07.044",
"article-title": "Thyroid disease is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection",
"author": "Hariyanto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1429",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib5",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.07.054",
"article-title": "Dyslipidemia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection",
"author": "Hariyanto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1463",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib6",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.018",
"article-title": "Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia - a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "395",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib7",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"article-title": "Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg.",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib8",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183",
"article-title": "Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108183",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib9",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.004",
"article-title": "Diabetes in COVID-19: prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "303",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib10",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108167",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes: is metformin a friend or foe?",
"author": "Ursini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108167",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib11",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13045-020-00934-x",
"article-title": "A tertiary center experience of multiple myeloma patients with COVID-19: lessons learned and the path forward",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "94",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Hematol. Oncol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290_bib12",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Obesity Medicine"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "19"
}
