Antidiabetic agent use and clinical outcomes in patients with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
et al., Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2024.1482853, PROSPERO CRD42023476297, Jan 2025
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
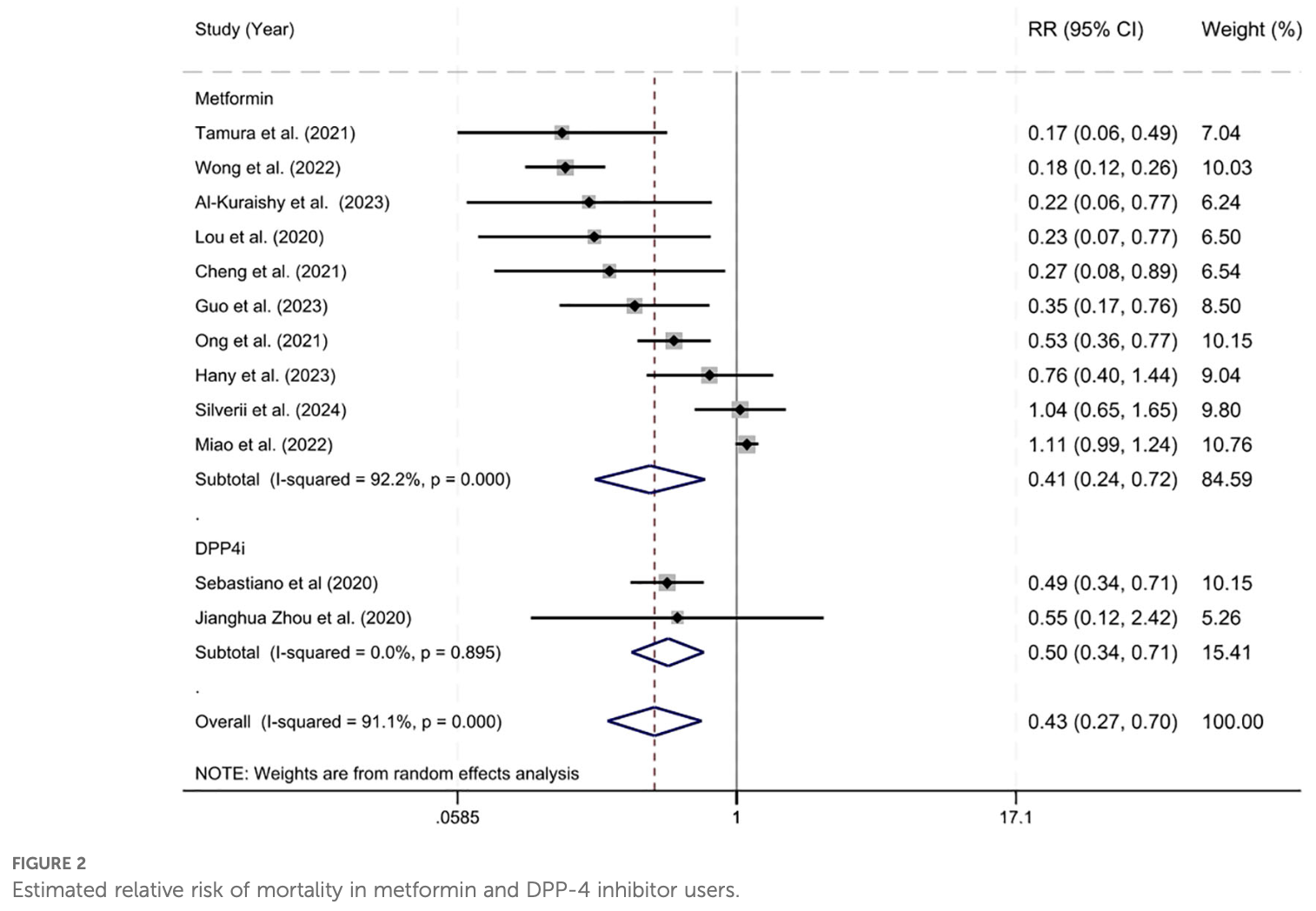
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Systematic review and meta-analysis of 35 studies showing lower mortality with metformin and DPP-4 inhibitor treatment for COVID-19 patients with diabetes.
24 meta-analyses show significant improvements with metformin for mortality1-23,
hospitalization7,13,23 ,
progression1, and
severity8,9,13 .
Currently there are 110 metformin for COVID-19 studies, showing 36% lower mortality [32‑40%], 29% lower ventilation [12‑43%], 19% lower ICU admission [8‑28%], 17% lower hospitalization [11‑23%], and 5% fewer cases [-4‑13%].
|
risk of death, 59.0% lower, RR 0.41, p = 0.002.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Yang et al., The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977.
2.
Lukito et al., The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006.
3.
Kow et al., Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26498.
4.
Hariyanto et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obesity Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290.
5.
Ma et al., Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282210.
6.
Parveen et al., Association of Metformin with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India), doi:10.1055/s-0042-1760353.
7.
Li et al., Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.704666.
8.
Schlesinger et al., Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-023-05928-1.
9.
Petrelli et al., Metformin and Covid-19: a systematic review of systematic reviews with meta-analysis, Acta Biomedica Atenei Parmensis, doi:10.23750/abm.v94iS3.14405.
10.
Oscanoa et al., Metformin therapy and severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a meta-analysis, Clinical Diabetology, doi:10.5603/DK.a2021.0035.
11.
Kan et al., Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.708494.
12.
Poly et al., Metformin Use Is Associated with Decreased Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes: Evidence from Retrospective Studies and Biological Mechanism, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10163507.
13.
Song et al., The Effect of Antihyperglycemic Medications on COVID-19: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review from Observational Studies, Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science, doi:10.1007/s43441-024-00633-6.
14.
Ganesh et al., Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15258.
15.
Nassar et al., Noninsulin‐based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis, Journal of Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13359.
16.
Zhan et al., Effect of Antidiabetic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/10600280221133577.
17.
Nguyen et al., Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155196.
18.
Han et al., Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002.
19.
Chen et al., The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458.
20.
Scheen, A., Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006.
21.
Sun et al., Is Metformin Use Associated With a Decreased Mortality for COVID-19 Diabetic Patients? A Meta-Analysis, Journal of the Endocrine Society, doi:10.1210/jendso/bvab048.709.
Keels et al., 6 Jan 2025, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD42023476297.
Contact: keelsj@bc.edu, jordan.keels@bc.edu.
Antidiabetic agent use and clinical outcomes in patients with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2024.1482853
Background: The effect of antidiabetic agents on mortality outcomes is unclear for individuals with diabetes mellitus (DM) who are hospitalized for COVID-19. Purpose: To examine the relationship between antidiabetic agent use and clinical outcomes in individuals with DM hospitalized for COVID-19. Methods: A systematic review of the literature (2020-2024) was performed across five databases. Included articles reported primary research (English) reporting clinical outcomes of adult patients (≥18 yrs.) with DM receiving antidiabetic agents who were hospitalized for COVID-19. Following PRISMA guidelines articles underwent independent dual review. Quality appraisal was completed for included studies. Independent reviewers used a structured data extraction form to retrieve relevant data. Aggregated data were synthesized by treatment regimen and reported descriptively. Random effects meta-analyses were performed to assess relative risk and prevalence of mortality. Results: After removing duplicates, title and abstract screening of 4,898 articles identified 118 articles for full-text review and 35 articles were retained for analysis. Included articles were primarily from China (15/35, 43%) and retrospective in nature (31/35, 89%). Fourteen studies (40%) assessed multiple antidiabetic agents, fifteen studies (42%) focused on metformin, three studies (9%) assessed the use of DPP-4 inhibitors, and three single studies (9%) investigated the use of insulin, TZD, and SGLT2 inhibitors. Despite differences among studies, the overall relative risk of mortality among metformin and DPP-4 inhibitor users was 0.432 (95% CI = 0.268-0.695, z = 3.45, p < 0.001) and the overall prevalence of mortality among all antidiabetic users was 16% (95% CI = 13%-19%, z = 10.70, p < 0.001). Conclusions and implications: Synthesis of findings suggest that patients who remained on oral agents (with/without supplemental insulin therapy) exhibited decreased mortality and lower inflammatory markers. Results indicate that
Author contributions
Funding The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of article. This study was funded by the Endocrine Nurses Society.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2024. 1482853/full#supplementary-material .
References
Abbaszadeh, Mir, Hasanvand, Metformin and its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects; new concepts, J Renal Inj Prev, doi:10.15171/jrip.2019.11
Abdi, Jalilian, Sarbarzeh, Vlaisavljevic, Diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review on the current evidences, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108347
Abuhasira, Ayalon-Dangur, Zaslavsky, Koren, Keller et al., A randomized clinical trial of linagliptin vs. Standard of care in patients hospitalized with diabetes and COVID-19, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.794382
Ahmad, Lim, Lamptey, Webb, Davies, Type 2 diabetes, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01655-5
Baagar, Alessa, Abu-Farha, Abubaker, Alhumaidi et al., Effect of pioglitazone on inflammatory response and clinical outcome in T2DM patients with COVID-19: a randomized multicenter double-blind clinical trial, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1369918
Bo, Yuli, Ye, Junfeng L Xiaolin, Yan, Immune-inflammatory biomarkers and the risk of cardiac in COVID-19 patients with diabetes: a retrospective cohort study, Cardiovasc Diabetol, doi:10.1186/s12933-022-01625-2
Bramante, Buse, Liebovitz, Nicklas, Puskarich et al., Outpatient treatment of COVID-19 and incidence of post-COVID-19 condition over 10 months (COVID-OUT): a multicentre, randomised, quadruple-blind, parallel-group, phase 3 trial, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00299-2
Chen, Lv, Lin, Arshad, Dai, The association between antidiabetic agents and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with diabetes: A bayesian network meta-analysis, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458
Cheng, Liu, Li, Zhang, Lei et al., Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013
Cheng, Xin, Chen, Li, Li, Effects of metformin, insulin on COVID-19 patients with pre-existed type 2 diabetes: A multicentral retrospective study, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119371
Cheung, Vijayakumar, A guide to conducting a meta-analysis, Neuropsychol Rev, doi:10.1007/s11065-016-9319-z
Committee, Diabetes care in the hospital: standards of care in diabetes-2024, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc24-S016
Dimeglio, Evans-Molina, Oram, Type 1 diabetes, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31320-5
Du, Wang, Chen, The potential effects of DPP-4 inhibitors on cardiovascular system in COVID-19 patients, J Cell Mol Med, doi:10.1111/jcmm.v24.18
Elibol, Eren, Erdogȃn, Elmaagȃçm, Dizdar et al., Factors influencing on development of COVID-19 pneumonia and association with oral antidiabetic drugs in hospitalized patients with diabetes mellitus, Prim Care Diabetes, doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2021.08.001
Fu, Hu, Ren, Zuo, Chen et al., Prognostic factors for COVID-19 hospitalized patients with preexisting type 2 diabetes, Int J Endocrinol, doi:10.1155/2022/9322332
Gao, Liu, Zhong, Liu R Zhou, Huang, Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: A preliminary retrospective report, Clin Transl Sci, doi:10.1111/cts.12897
Gonikman, Kustovs, Antidiabetic drug efficacy in reduction of mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic, Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina59101810
Guo, Gao, Xie, Ye, Zhao, Effects of metformin on COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective study, Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, doi:10.2147/DMSO.S417925
Han, Hossain, Mahboob, Nissapatorn, Wilairatana et al., Association between anti-diabetic agents and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Arch Med Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002
Hm, Gareeb, Alblihed, Cruz-Martins, Batiha, COVID-19 and risk of acute ischemic stroke and acute lung injury in patients with type II diabetes mellitus: the anti-inflammatory role of metformin, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.644295
Hm, Gareeb, Albogami, Jean-Marc, Nadwa et al., Potential therapeutic benefits of metformin alone and in combination with sitagliptin in the management of type 2 diabetes patients with COVID-19, Pharm, doi:10.3390/ph15111361
Hm, Gareeb, Kholy, El-Khateeb, Alexiou et al., The potential therapeutic effect of metformin in type 2 diabetic patients with severe COVID-19, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, doi:10.26355/eurrev_202312_34583
Jiang, Chen, Liu, Yin, Yang et al., Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619
Kan, Zhang, Han, Xu, Ye et al., Mortality risk of antidiabetic agents for type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.708494
Kliim-Hansen, Johansson, Gasbjerg, Jimenez-Solem, Petersen et al., The impact of type 2 diabetes and glycaemic control on mortality and clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the capital region of Denmark, Diabetes Obes Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.15302
Kow, Hasan, Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26498
Lai, Yang, Sun, Pan, Wang et al., Risk of incident diabetes after COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155330
Lewandowski, Bronowicka-Szydełko, Rabczyński, Bednarska-Chabowska, Adamiec-Mroczek et al., Insulin and metformin administration: unravelling the multifaceted association with mortality across various clinical settings considering type 2 diabetes mellitus and COVID-19, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines12030605
Li, Shen, Yang, Fairley, Chai et al., Global diabetes prevalence in COVID-19 patients and contribution to COVID-19-related severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc22-1943
Li, Wei, Mccowen, Xiong, Liu et al., Inpatient use of metformin and acarbose is associated with reduced mortality of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, Endocrinol Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1002/edm2.v5.1
Liberati, Altman, Tetzlaff, Mulrow, Gøtzsche et al., The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration, PloS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
Liu, Bai, Han, Jiang, Qiu et al., The association of diabetes and the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective study, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108386
Lukito, Pranata, Henrina, Lim, Lawrensia et al., The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Liu, Zheng et al., Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Ma, Krishnamurthy, Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282210
Metwally, Mehta, Johnson, Nagarjuna, Snyder, COVID-19induced new-onset diabetes: trends and technologies, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/dbi21-0029
Miao, Zhang, Liu, Yoo, George, Metformin use and mortality and length of stay among hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A multiracial, multiethnic, urban observational study, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.1002834
Miyashita, Hozumi, Furuhashi, Nakatani, Inoue et al., Changes in the characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 patients from the early pandemic to the delta variant epidemic: a nationwide population-based study, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2022.2155250
Nassar, Ma, Sun, Zhang, Qu et al., Noninsulin-based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13359
Nguyen, Ho, Nguyen, Ho, Li et al., Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155196
Nyland, Raja-Khan, Bettermann, Haouzi, Leslie et al., Diabetes, drug treatment, and mortality in COVID-19: A multinational retrospective cohort study, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/db21-0385
Obiri-Yeboah, Bena, Alwakeel, Buehler, Makin et al., Association of metformin, dipeptidyl dipeptidase-4 inhibitors, and insulin with coronavirus disease 2019-related hospital outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes, Endocr Pract, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001
Ong, Tan, Cañete, Lim, Robles, Association between metformin use and mortality among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19 infection, J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc, doi:10.15605/jafes.036.02.20
Ozbek, Can, The effect of dapagliflozin use on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Int J Diabetes Developing Countries, doi:10.1007/s13410-023-01287-0
Patoulias, Doumas, Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and COVID-19related deaths among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of observational studies, Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.3803/EnM.2021.1048
Paul, Hossain, Mahboob, Nissapatorn, Wilairatana et al., Does oxidative stress management help alleviation of COVID-19 symptoms in patients experiencing diabetes?, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14020321
Petrelli, Grappasonni, Nguyen, Tesauro, Pantanetti et al., Metformin and Covid-19: a systematic review of systematic reviews with meta-analysis, Acta BioMed, doi:10.23750/abm.v94iS3.14405
Reuters, Endnote, None
Samuel, Varghese, Büsselberg, Therapeutic potential of metformin in COVID-19: reasoning for its protective role, Trends Microbiol, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2021.03.004
Shacham, Maman, Ishay, Blood glucose control with different treatment regimens in type 2 diabetes patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection: A retrospective study, Med, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000032650
Sharma, Behl, Sharma, Singh, Grewal et al., COVID-19 and diabetes: Association intensify risk factors for morbidity and mortality, BioMed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113089
Shaseb, Ghaffary, Garjani, Zoghi, Dizaji et al., Long and short-term metformin consumption as a potential therapy to prevent complications of COVID-19, Adv Pharm Bull, doi:10.34172/apb.2023.066
Silverii, Fumagalli, Rozzini, Milani, Mannucci et al., Is metformin use associated with a more favorable COVID-19 course in people with diabetes?, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm13071874
Solerte, 'addio, Trevisan, Lovati, Rossi et al., Sitagliptin treatment at the time of hospitalization was associated with reduced mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A multicenter, case-control, retrospective, observational study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1521
Tamura, Said, De Freitas, Rubio, Outcome and death risk of diabetes patients with Covid-19 receiving pre-hospital and in-hospital metformin therapies, Diabetol Metab Syndr, doi:10.1186/s13098-021-00695-8
Tang, Uhl, Zhang, Xue, Li et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection induces beta cell transdifferentiation, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.015
Tisch, Xourgia, Exadaktylos, Ziaka, Potential use of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors during acute illness: a systematic review based on COVID-19, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-024-03758-8
Van Baal, Reinold, Benson, Diehl, Witzke et al., Implications of an hbA1c-based diabetes screening on prevalence and effect of dysglycemia in patients with COVID-19, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgac590
Vasbinder, Anderson, Shadid, Berlin, Pan et al., Inflammation, hyperglycemia, and adverse outcomes in individuals with diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc21-2102
Viera, Garrett, Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic, Fam Med
Wong, Lui, Lui, Low, Kwok et al., Metformin use in relation to clinical outcomes and hyperinflammatory syndrome among COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: A propensity score analysis of a territory-wide cohort, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.810914
Xu, He, Yu, Zhong, Zhou et al., Effects of different treatments for type 2 diabetes mellitus on mortality of coronavirus disease from 2019 to 2021 in China: a multi-institutional retrospective study, Mol BioMed, doi:10.1186/s43556-024-00183-1
Yang, Sun, Zhang, Zhang, The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977
Yu, Li, Sun, Wang, Insulin treatment is associated with increased mortality in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.014
Zein, Raffaello, Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-IV) inhibitor was associated with mortality reduction in COVID-19 -A systematic review and meta-analysis, Prim Care Diabetes, doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2021.12.008
Zhan, Weng, Qi, Wang, Lin et al., Effect of antidiabetic therapy on clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Ann Pharmacother, doi:10.1177/10600280221133577
Zhang, Wang, Zhu, Mao, Bai et al., Risk factors for poor outcomes of diabetes patients with COVID-19: A single-center, retrospective study in early outbreak in China, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.571037
Zhou, Wu, Lei, Cheng, Qin, No significant association between dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and adverse outcomes of COVID-19, World J Clin cases, doi:10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5576
Zihono, Yusmaini, Hasanah, Harfiani, Mokoagow et al., Metformin Effectiveness in Reducing Mortality among Covid-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at a Tertiary Hospital in Indonesia, Folia Med Indonesiana, doi:10.20473/fmi.v59i3.46944
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2024.1482853",
"ISSN": [
"1664-2392"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2024.1482853",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>The effect of antidiabetic agents on mortality outcomes is unclear for individuals with diabetes mellitus (DM) who are hospitalized for COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Purpose</jats:title><jats:p>To examine the relationship between antidiabetic agent use and clinical outcomes in individuals with DM hospitalized for COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>A systematic review of the literature (2020-2024) was performed across five databases. Included articles reported primary research (English) reporting clinical outcomes of adult patients (≥18 yrs.) with DM receiving antidiabetic agents who were hospitalized for COVID-19. Following PRISMA guidelines articles underwent independent dual review. Quality appraisal was completed for included studies. Independent reviewers used a structured data extraction form to retrieve relevant data. Aggregated data were synthesized by treatment regimen and reported descriptively. Random effects meta-analyses were performed to assess relative risk and prevalence of mortality.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>After removing duplicates, title and abstract screening of 4,898 articles identified 118 articles for full-text review and 35 articles were retained for analysis. Included articles were primarily from China (15/35, 43%) and retrospective in nature (31/35, 89%). Fourteen studies (40%) assessed multiple antidiabetic agents, fifteen studies (42%) focused on metformin, three studies (9%) assessed the use of DPP-4 inhibitors, and three single studies (9%) investigated the use of insulin, TZD, and SGLT2 inhibitors. Despite differences among studies, the overall relative risk of mortality among metformin and DPP-4 inhibitor users was 0.432 (95% CI = 0.268-0.695, z = 3.45, p &lt; 0.001) and the overall prevalence of mortality among all antidiabetic users was 16% (95% CI = 13%–19%, z = 10.70, p &lt; 0.001).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions and implications</jats:title><jats:p>Synthesis of findings suggest that patients who remained on oral agents (with/without supplemental insulin therapy) exhibited decreased mortality and lower inflammatory markers. Results indicate that individuals with DM should continue oral antidiabetic agents with additional basal insulin as needed to improve glycemic control and reduce mortality. Further work is needed to uncover mechanism(s) and clarify medical management approaches.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fendo.2024.1482853"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keels",
"given": "Jordan N.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDonald",
"given": "Isabella R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Christopher S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dwyer",
"given": "Andrew A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Endocrinology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Endocrinol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-06T05:22:54Z",
"timestamp": 1736140974000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-06T05:23:01Z",
"timestamp": 1736140981000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-07T05:07:55Z",
"timestamp": 1736226475321,
"version": "3.32.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1736121600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2024.1482853/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.015",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection induces beta cell transdifferentiation",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1577",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31320-5",
"article-title": "Type 1 diabetes",
"author": "DiMeglio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "391",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01655-5",
"article-title": "Type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Ahmad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113089",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes: Association intensify risk factors for morbidity and mortality",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "113089",
"journal-title": "BioMed Pharmacother",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc22-1943",
"article-title": "Global diabetes prevalence in COVID-19 patients and contribution to COVID-19- related severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155330",
"article-title": "Risk of incident diabetes after COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155330",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dbi21-0029",
"article-title": "COVID-19-induced new-onset diabetes: trends and technologies",
"author": "Metwally",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgac590",
"article-title": "Implications of an hbA1c-based diabetes screening on prevalence and effect of dysglycemia in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Van Baal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.708494",
"article-title": "Mortality risk of antidiabetic agents for type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Kan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108347",
"article-title": "Diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review on the current evidences",
"author": "Abdi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108347",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619",
"article-title": "Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108619",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100",
"article-title": "The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration",
"author": "Liberati",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS Med",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"article-title": "EndNote",
"author": "Reuters",
"key": "B13",
"volume-title": "EndNote",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B14",
"unstructured": "Covidence systematic review software\n \n \n 2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11065-016-9319-z",
"article-title": "A guide to conducting a meta-analysis",
"author": "Cheung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Neuropsychol Rev",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic",
"author": "Viera",
"journal-title": "Fam Med",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/DMSO.S417925",
"article-title": "Effects of metformin on COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective study",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43556-024-00183-1",
"article-title": "Effects of different treatments for type 2 diabetes mellitus on mortality of coronavirus disease from 2019 to 2021 in China: a multi-institutional retrospective study",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "Mol BioMed",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5576",
"article-title": "No significant association between dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and adverse outcomes of COVID-19",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "World J Clin cases",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12897",
"article-title": "Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: A preliminary retrospective report",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013",
"article-title": "Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "537",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119371",
"article-title": "Effects of metformin, insulin on COVID-19 patients with pre-existed type 2 diabetes: A multicentral retrospective study",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119371",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "275",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"article-title": "Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2022.810914",
"article-title": "Metformin use in relation to clinical outcomes and hyperinflammatory syndrome among COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: A propensity score analysis of a territory-wide cohort",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.014",
"article-title": "Insulin treatment is associated with increased mortality in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.571037",
"article-title": "Risk factors for poor outcomes of diabetes patients with COVID-19: A single-center, retrospective study in early outbreak in China",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/edm2.v5.1",
"article-title": "Inpatient use of metformin and acarbose is associated with reduced mortality of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol Diabetes Metab",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/9322332",
"article-title": "Prognostic factors for COVID-19 hospitalized patients with preexisting type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9322332",
"journal-title": "Int J Endocrinol 2022",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108386",
"article-title": "The association of diabetes and the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective study",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108386",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "169",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12933-022-01625-2",
"article-title": "Immune-inflammatory biomarkers and the risk of cardiac injury in COVID-19 patients with diabetes: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Bo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "188",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Diabetol",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001",
"article-title": "Association of metformin, dipeptidyl dipeptidase-4 inhibitors, and insulin with coronavirus disease 2019-related hospital outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Obiri-Yeboah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocr Pract",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2022.1002834",
"article-title": "Metformin use and mortality and length of stay among hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A multiracial, multiethnic, urban observational study",
"author": "Miao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc21-2102",
"article-title": "Inflammation, hyperglycemia, and adverse outcomes in individuals with diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19",
"author": "Vasbinder",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "692",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26355/eurrev_202312_34583",
"article-title": "The potential therapeutic effect of metformin in type 2 diabetic patients with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Al-Kuraishy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.644295",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and risk of acute ischemic stroke and acute lung injury in patients with type II diabetes mellitus: the anti-inflammatory role of metformin",
"author": "Al-Kuraishy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph15111361",
"article-title": "Potential therapeutic benefits of metformin alone and in combination with sitagliptin in the management of type 2 diabetes patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Al-Kuraishy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pharm (Basel)",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.794382",
"article-title": "A randomized clinical trial of linagliptin vs. Standard of care in patients hospitalized with diabetes and COVID-19",
"author": "Abuhasira",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000032650",
"article-title": "Blood glucose control with different treatment regimens in type 2 diabetes patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection: A retrospective study",
"author": "Chertok Shacham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Med (Baltimore)",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm13071874",
"article-title": "Is metformin use associated with a more favorable COVID-19 course in people with diabetes",
"author": "Silverii",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1521",
"article-title": "Sitagliptin treatment at the time of hospitalization was associated with reduced mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A multicenter, case-control, retrospective, observational study",
"author": "Solerte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2999",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15605/jafes.036.02.20",
"article-title": "Association between metformin use and mortality among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Ong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcd.2021.08.001",
"article-title": "Factors influencing on development of COVID-19 pneumonia and association with oral anti-diabetic drugs in hospitalized patients with diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Elibol",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Prim Care Diabetes",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13410-023-01287-0",
"article-title": "The effect of dapagliflozin use on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients hospitalized with COVID-19",
"author": "Ozbek",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Diabetes Developing Countries",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13098-021-00695-8",
"article-title": "Outcome and death risk of diabetes patients with Covid-19 receiving pre-hospital and in-hospital metformin therapies",
"author": "Tamura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Diabetol Metab Syndr",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20473/fmi.v59i3.46944",
"article-title": "Metformin Effectiveness in Reducing Mortality among Covid-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at a Tertiary Hospital in Indonesia",
"author": "Zihono",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Folia Med Indonesiana",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.34172/apb.2023.066",
"article-title": "Long and short-term metformin consumption as a potential therapy to prevent complications of COVID-19",
"author": "Shaseb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Adv Pharm Bull",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.15302",
"article-title": "The impact of type 2 diabetes and glycaemic control on mortality and clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the capital region of Denmark",
"author": "Kliim-Hansen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes Metab",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines12030605",
"article-title": "Insulin and metformin administration: unravelling the multifaceted association with mortality across various clinical settings considering type 2 diabetes mellitus and COVID-19",
"author": "Lewandowski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2024.1369918",
"article-title": "Effect of pioglitazone on inflammatory response and clinical outcome in T2DM patients with COVID-19: a randomized multicenter double-blind clinical trial",
"author": "Baagar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db21-0385",
"article-title": "Diabetes, drug treatment, and mortality in COVID-19: A multinational retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Nyland",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/10600280221133577",
"article-title": "Effect of antidiabetic therapy on clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Zhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Ann Pharmacother",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2022.895458",
"article-title": "The association between antidiabetic agents and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with diabetes: A bayesian network meta-analysis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977",
"article-title": "The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108977",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.23750/abm.v94iS3.14405",
"article-title": "Metformin and Covid-19: a systematic review of systematic reviews with meta-analysis",
"author": "Petrelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Acta BioMed",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0282210",
"article-title": "Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155196",
"article-title": "Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis",
"author": "Nguyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155196",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1753-0407.13359",
"article-title": "Noninsulin-based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Nassar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "86",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002",
"article-title": "Association between anti-diabetic agents and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Arch Med Res",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcd.2021.12.008",
"article-title": "Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-IV) inhibitor was associated with mortality reduction in COVID-19 - A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Zein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Prim Care Diabetes",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3803/EnM.2021.1048",
"article-title": "Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and COVID-19-related deaths among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of observational studies",
"author": "Patoulias",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol Metab (Seoul)",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26498",
"article-title": "Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis",
"author": "Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14020321",
"article-title": "Does oxidative stress management help alleviation of COVID-19 symptoms in patients experiencing diabetes",
"author": "Paul",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tim.2021.03.004",
"article-title": "Therapeutic potential of metformin in COVID-19: reasoning for its protective role",
"author": "Samuel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "894",
"journal-title": "Trends Microbiol",
"key": "B63",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006",
"article-title": "The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Lukito",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "B64",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15171/jrip.2019.11",
"article-title": "Metformin and its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects; new concepts",
"author": "Abbaszadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "54",
"journal-title": "J Renal Inj Prev",
"key": "B65",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00299-2",
"article-title": "Outpatient treatment of COVID-19 and incidence of post-COVID-19 condition over 10 months (COVID-OUT): a multicentre, randomised, quadruple-blind, parallel-group, phase 3 trial",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "B66",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jcmm.v24.18",
"article-title": "The potential effects of DPP-4 inhibitors on cardiovascular system in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Cell Mol Med",
"key": "B67",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc22-S016",
"article-title": "Diabetes care in the hospital: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S244",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B68",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina59101810",
"article-title": "Antidiabetic drug efficacy in reduction of mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Gonikman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Medicina (Kaunas)",
"key": "B69",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-024-03758-8",
"article-title": "Potential use of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors during acute illness: a systematic review based on COVID-19",
"author": "Tisch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "B70",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2155250",
"article-title": "Changes in the characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 patients from the early pandemic to the delta variant epidemic: a nationwide population-based study",
"author": "Miyashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2155250",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "B71",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc24-S016",
"article-title": "16. Diabetes care in the hospital: standards of care in diabetes—2024",
"author": "Committee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B72",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 72,
"references-count": 72,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2024.1482853/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Antidiabetic agent use and clinical outcomes in patients with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "15"
}
