Metformin use and mortality and length of stay among hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A multiracial, multiethnic, urban observational study
et al., Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.1002834, Nov 2022
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 4,462 COVID+ diabetes patients in the USA, showing no significant difference in outcomes with metformin use.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
Results may differ in countries with improved SOC.
|
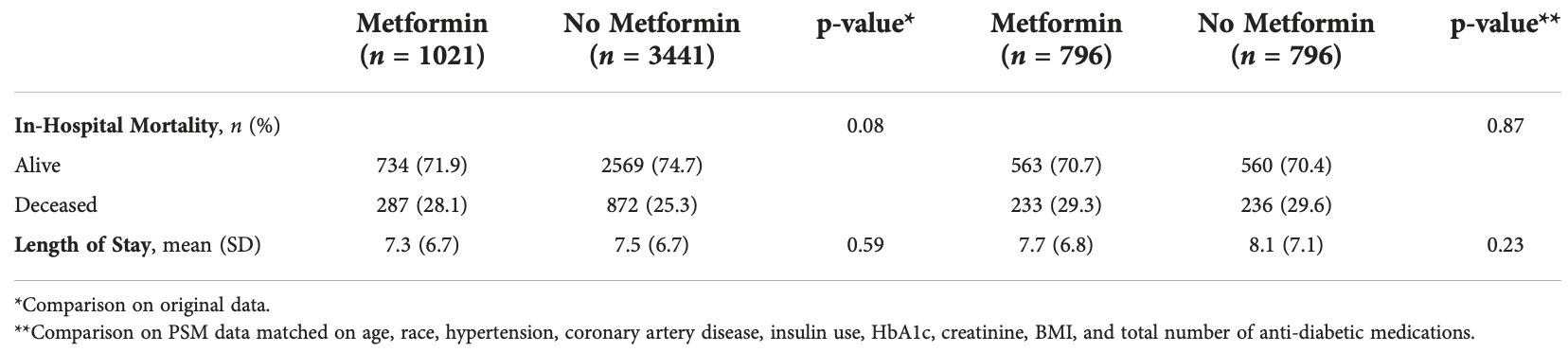
risk of death, 1.3% lower, RR 0.99, p = 0.91, treatment 233 of 796 (29.3%), control 236 of 796 (29.6%), NNT 265, propensity score matching.
|
|
hospitalization time, 4.9% lower, relative time 0.95, p = 0.23, treatment 796, control 796, propensity score matching.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Miao et al., 9 Nov 2022, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 1 January, 2020 - 7 May, 2020.
Metformin use and mortality and length of stay among hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A multiracial, multiethnic, urban observational study
Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.1002834
Introduction: Diabetes mellitus is a common comorbidity among patients with coronavirus disease 2019 . Diabetic patients with COVID-19 have a two-fold increased risk of death and tend to have more severe infection compared to the general population. Metformin, a first-line medication for diabetes management, has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Previous studies focusing on metformin and COVID-19 clinical outcomes have had mixed results, with some showing a mortality benefit or decreased complications with metformin use. To date, few studies have analyzed such outcomes among a diverse, multiracial community. Methods: This was a retrospective review of patients with Type 2 diabetes and a confirmed COVID-19 infection admitted to an urban academic medical center from January 1, 2020 to May 7, 2020. Baseline characteristics were collected. The primary outcomes of the study were in-hospital mortality and length of stay (LOS). Results: A total of 4462 patients with Type 2 diabetes and confirmed COVID-19 were identified. 41.3% were Black, and 41.5% were Hispanic. There were 1021 patients in the metformin group and 3441 in the non-metformin group. Of note, more participants in the metformin group had comorbid disease and/or advanced diabetes. We found no statistically significant differences between the metformin and non-metformin group in in-hospital mortality (28.1% vs 25.3%, P=0.08) or length of hospital stay in days (7.3 vs. 7.5, P=0.59), even after matching patients on various factors (29.3% vs. 29.6%, P=0.87; 7.7 vs. 8.1, P=0.23).
Ethics statement The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Montefiore Medical Center Institutional Review Board. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions EM: Design, data management, interpretation of data, and preparation of manuscript; KZ: Design, data management, interpretation of data, and preparation of manuscript; JiL: Data management, analysis, interpretation of data, preparation of manuscript; JuL: Data management, analysis, interpretation of data, preparation of manuscript; DY: Interpretation of data, preparation of manuscript; CG: Design, acquisition of subjects, data management, analysis, interpretation of data, preparation of manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Apicella, Campopiano, Mantuano, Mazoni, Coppelli et al., COVID-19 in people with diabetes: understanding the reasons for worse outcomes, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30238-2
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Chen, Peng et al., Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0660
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Might, Ovalle et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.600439
Ejaz, Alsrhani, Zafar, Javed, Junaid et al., COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients, J Infect Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014
Gao, Liu, Zhong, Liu, Zhou et al., Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: A preliminary retrospective report, Clin Transl Sci, doi:10.1111/cts.12897
Gaskin, Mcginty, Bower, Rohde, Young, Disparities in diabetes: the nexus of race, poverty, and place, Am J Public Health, doi:10.2105/AJPH.2013.301420
Guo, Li, Dong, Zhou, Zhang et al., Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19, Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3319
Heald, Jenkins, Williams, Sperrin, Mudaliar et al., Mortality in people with type 2 diabetes following SARS-CoV-2 infection: A population level analysis of potential risk factors, Diabetes Ther
Hou, Li, Zhang, Wu, Shi et al., Smoking is independently associated with an increased risk for COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analaysis based on adjusted effect estimates, Nicotine Tob Res, doi:10.1093/ntr/ntab112
Jiang, Chen, Liu, Yin, Yang et al., Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619
Lalau, Al-Salameh, Hadjadj, Goronflot, Wiernsperger et al., Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216
Lim, Bae, Kwon, Nauck, COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management, Nat Rev Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Liu, Zheng et al., Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Mackey, Ayers, Kondo, Saha, Advani et al., Racial and ethnic disparities in COVID-19-Related infections, hospitalizations, and deaths : A systematic review, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M20-6306
Oh, Song, Prior metformin therapy and 30-day mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a nationwide cohort study, Ann Palliative Med, doi:10.21037/apm.2020.04.25
Reis, Silva, Silva, Thabane, Milagres et al., Effect of early treatment with metformin on risk of emergency care and hospitalization among patients with COVID-19: The TOGETHER randomized platform clinical trial, Lancet Regional Health -Americas, doi:10.1016/j.lana.2021.100142
Singh, Singh, Saboo, Misra, Zangiabadian et al., The efficacy and potential mechanisms of metformin in the treatment of COVID-19 in the diabetics: A systematic review, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.645194
Yang, Sun, Zhang, Zhang, The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977
Zhu, She, Cheng, Qin, Zhang et al., Association of blood glucose control and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Lancet Healthy Longevity, doi:10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2022.1002834",
"ISSN": [
"1664-2392"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.1002834",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Introduction</jats:title><jats:p>Diabetes mellitus is a common comorbidity among patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Diabetic patients with COVID-19 have a two-fold increased risk of death and tend to have more severe infection compared to the general population. Metformin, a first-line medication for diabetes management, has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Previous studies focusing on metformin and COVID-19 clinical outcomes have had mixed results, with some showing a mortality benefit or decreased complications with metformin use. To date, few studies have analyzed such outcomes among a diverse, multiracial community.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>This was a retrospective review of patients with Type 2 diabetes and a confirmed COVID-19 infection admitted to an urban academic medical center from January 1, 2020 to May 7, 2020. Baseline characteristics were collected. The primary outcomes of the study were in-hospital mortality and length of stay (LOS).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 4462 patients with Type 2 diabetes and confirmed COVID-19 were identified. 41.3% were Black, and 41.5% were Hispanic. There were 1021 patients in the metformin group and 3441 in the non-metformin group. Of note, more participants in the metformin group had comorbid disease and/or advanced diabetes. We found no statistically significant differences between the metformin and non-metformin group in in-hospital mortality (28.1% vs 25.3%, P=0.08) or length of hospital stay in days (7.3 vs. 7.5, P=0.59), even after matching patients on various factors (29.3% vs. 29.6%, P=0.87; 7.7 vs. 8.1, P=0.23).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>While patients had more comorbid disease and advanced diabetes in the metformin group, there were no significant differences with regard to in-hospital mortality or length of stay due to COVID-19 compared to the non-metformin group. Prospective studies are needed to determine if there is clinical benefit for initiating, continuing, or re-initiating metformin in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fendo.2022.1002834"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miao",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Kaleena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Jianyou",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Juan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yoo",
"given": "Donna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "George",
"given": "Claudene J.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Endocrinology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Endocrinol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-09T05:49:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667972940000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-09T05:49:02Z",
"timestamp": 1667972942000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-10T05:58:39Z",
"timestamp": 1668059919194
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
9
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-09T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667952000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2022.1002834/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30238-2",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in people with diabetes: understanding the reasons for worse outcomes",
"author": "Apicella",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Endocrinol",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977",
"article-title": "The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108977",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3319",
"article-title": "Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021",
"article-title": "Association of blood glucose control and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1068",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7",
"article-title": "Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Healthy Longevity",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.026",
"article-title": "Non-insulin anti-diabetic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A critical appraisal of literature",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.645194",
"article-title": "The efficacy and potential mechanisms of metformin in the treatment of COVID-19 in the diabetics: A systematic review",
"author": "Zangiabadian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.600439",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes",
"author": "Crouse",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"article-title": "Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/apm.2020.04.25",
"article-title": "Prior metformin therapy and 30-day mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a nationwide cohort study",
"author": "Oh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Ann Palliative Med",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0660",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619",
"article-title": "Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108619",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12897",
"article-title": "Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: A preliminary retrospective report",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2105/AJPH.2013.301420",
"article-title": "Disparities in diabetes: the nexus of race, poverty, and place",
"author": "Gaskin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Am J Public Health",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-6306",
"article-title": "Racial and ethnic disparities in COVID-19-Related infections, hospitalizations, and deaths : A systematic review",
"author": "Mackey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients",
"author": "Ejaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19",
"author": "Lalau",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101216",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lana.2021.100142",
"article-title": "Effect of early treatment with metformin on risk of emergency care and hospitalization among patients with COVID-19: The TOGETHER randomized platform clinical trial",
"author": "Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100142",
"journal-title": "Lancet Regional Health - Americas",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13300-022-01259-3",
"article-title": "Mortality in people with type 2 diabetes following SARS-CoV-2 infection: A population level analysis of potential risk factors",
"author": "Heald",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Ther",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ntr/ntab112",
"article-title": "Smoking is independently associated with an increased risk for COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analaysis based on adjusted effect estimates",
"author": "Hou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nicotine Tob Res",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 21,
"references-count": 21,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2022.1002834/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Metformin use and mortality and length of stay among hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A multiracial, multiethnic, urban observational study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "13"
}
