Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19
et al., Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216, Dec 2020
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
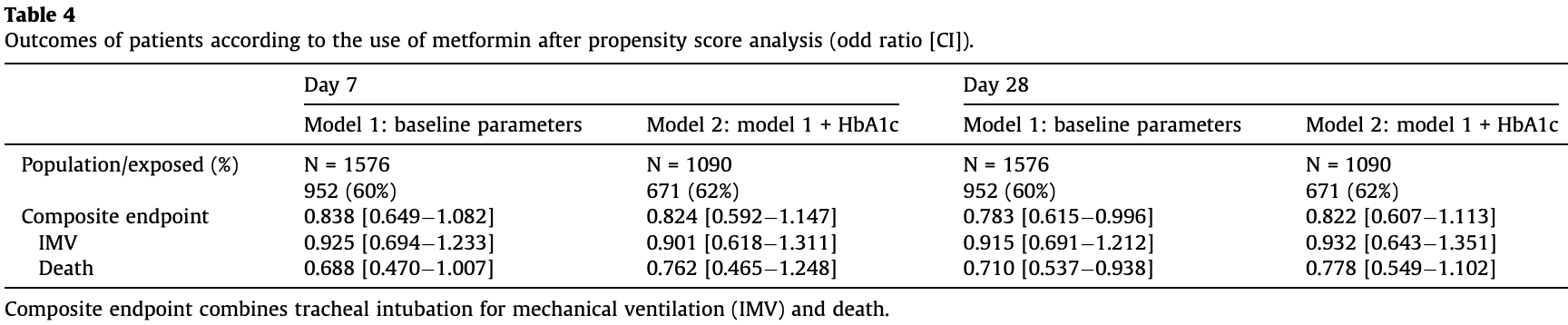
Retrospective 2,449 hospitalized COVID-19 diabetes patients in France, 1,496 with existing metformin use, showing lower mortality with treatment. Statistical significance was reached in model 1 but not in models 2-4 which also adjust for HbA1c, eGFR, and diabetes duration, but have a lower number of patients. CORONADO (Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and Diabetes Outcomes).
|
risk of death, 22.2% lower, OR 0.78, p = 0.16, treatment 671, control 419, day 28, model 2, propensity score matching, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of death/intubation, 17.8% lower, OR 0.82, p = 0.21, treatment 671, control 419, day 28, model 2, propensity score matching, primary outcome, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 6.8% lower, OR 0.93, p = 0.72, treatment 671, control 419, day 28, model 2, propensity score matching, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Lalau et al., 10 Dec 2020, retrospective, France, peer-reviewed, 33 authors, study period 10 March, 2020 - 10 April, 2020.
Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19
Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216
Metformin exerts anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. We addressed the impact of prior metformin use on prognosis in patients with type 2 diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19. Methods. -CORONADO is a nationwide observational study that included patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19 between March 10 and April 10, 2020 in 68 French centres. The primary outcome combined tracheal intubation and/or death within 7 days of admission. A Kaplan-Meier survival curve was reported for death up to day 28. The association between metformin use and outcomes was then estimated in a logistic regression analysis after applying a propensity score inverse probability of treatment weighting approach. Results. -Among the 2449 patients included, 1496 were metformin users and 953 were not. Compared with non-users, metformin users were younger with a lower prevalence of diabetic complications, but had more severe features of COVID-19 on admission. The primary endpoint occurred in 28.0% of metformin users (vs 29.0% in non-users, P = 0.6134) on day 7 and in 32.6% (vs 38.7%, P = 0.0023) on day 28. The mortality rate was lower in metformin users on day 7 (8.2 vs 16.1%, P < 0.0001) and on day 28 (16.0 vs 28.6%, P < 0.0001). After propensity score weighting was applied, the odds ratios for primary outcome and death (OR [95%CI], metformin users vs non-users) were 0.838 [0.649À1.082] and 0.688 [0.470À1.007] on day 7, then 0.783 [0.615À0.996] and 0.710 [0.537À0.938] on day 28, respectively. Conclusion. -Metformin use appeared to be associated with a lower risk of death in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19.
Conflict of interest JDL reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Brothier, Lilly, MSD, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Sanofi. AAS reports personal fees from AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk. SH reports personal fees and non-financial support from AstraZeneca, grants and personal fees from Bayer, personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, grants from Dinno Sante ´, personal fees from Eli Lilly, non-financial support from LVL, personal fees and non-financial support from MSD, personal fees from Novartis, grants from Pierre Fabre Sante ´, personal fees and non-financial support from Sanofi, personal fees and non-financial support from Servier, and personal fees from Valbiotis. MP reports personal fees and non-financial support from Novo Nordisk, nonfinancial support from Sanofi, and non-financial support from Amgen. JFG reports personal fees and non-financial support from Eli Lilly, personal fees and non-financial support from Novo Nordisk, personal fees and non-financial support from Gilead, and personal fees and non-financial support from AstraZeneca. MJ reports personal fees and non-financial support from Sanofi, personal fees and non-financial support from Eli Lilly, personal fees and non-financial support from Novo Nordisk, grants and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Medtronic, personal fees and non-financial support from Abbott, personal fees and non-financial support from BMS, personal fees and non-financial support from..
References
Ac (african Or Caribbean, As, HbA1c corresponds to the glycated haemoglobin determined in the first 7 days following hospital admission or in the 6 months prior hospitalisation
Arb, angiotensin-2 receptor-blocker
Austin, The performance of different propensity-score methods for estimating differences in proportions (risk differences or absolute risk reductions) in observational studies, Stat Med, doi:10.1002/sim.3854
Austin, The relative ability of different propensity score methods to balance measured covariates between treated and untreated subjects in observational studies, Med Decis Mak Int J Soc Med Decis Mak, doi:10.1177/0272989X09341755
Bailey, Metformin: historical overview, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4318-z
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Marmor, Hoversten et al., Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with Covid-19, MedRxiv Prepr Serv Health Sci, doi:10.1101/2020.06.19.20135095
Broe, Kajbaf, Lalau, Renoprotective effects of metformin, Nephron, doi:10.1159/000481951
Buse, Wexler, Tsapas, Rossing, Mingrone et al., Update to: management of hyperglycemia in Type 2 diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dci19-0066
Cameron, Morrison, Levin, Mohan, Forteath et al., Antiinflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445
Cariou, Goronflot, Rimbert, Boullu, May et al., Routine use of statins and increased mortality related to COVID-19 in inpatients with type 2 diabetes: results from the CORONADO study, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.10.001
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Pichelin, Al-Salameh et al., Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x
Cheng, Liu, Li, Zhang, Lei et al., Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with Covid-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Might, Ovalle et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with covid-19 and diabetes, MedRxiv Prepr Serv Health Sci, doi:10.1101/2020.07.29.20164020
Crowley, Diamantidis, Mcduffie, Cameron, Stanifer et al., Clinical outcomes of metformin use in populations with chronic kidney disease, congestive heart failure, or chronic liver disease: a systematic review, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M16-1901
Do, Kim, Park, Cho, Kang, Is there an association between metformin use and clinical outcomes in diabetes patients with COVID-19?, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.10.006
Foretz, Guigas, Viollet, Understanding the glucoregulatory mechanisms of metformin in type 2 diabetes mellitus, Nat Rev Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-019-0242-2
Gao, Liu, Zhong, Liu, Zhou et al., Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with Covid-19: a preliminary retrospective report, Clin Transl Sci, doi:10.1111/cts.12897
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obes Med, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290
Heckman-Stoddard, Decensi, Sahasrabuddhe, Ford, Repurposing metformin for the prevention of cancer and cancer recurrence, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4372-6
Kheirollahi, Wasnick, Biasin, Vazquez-Armendariz, Chu et al., Metformin induces lipogenic differentiation in myofibroblasts to reverse lung fibrosis, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-019-10839-0
Kulkarni, Gubbi, Barzilai, Benefits of metformin in attenuating the hallmarks of aging, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.001
Lalau, Al-Salameh, Hadjadj, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, Diabetes & Metabolism
Lalau, Al-Salameh, Hadjadj, None, Diabetes & Metabolism
Lalau, Management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30231-X
Liang, Ding, Li, Wang, Kan et al., Association of preadmission metformin use and mortality in patients with sepsis and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies, Crit Care Lond Engl, doi:10.1186/s13054-019-2346-4
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Liu, Zheng et al., Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in Covid-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Malik, Mehdi, Ali, Patel, Basharat et al., Is metformin poised for a second career as an antimicrobial?, Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.2975
Mao, Li, Propensity score weighting methods for dichotomous treatments; R package version
Marcucci, Romeo, Caserta, Rumio, Lefoulon, Context-dependent pharmacological effects of metformin on the immune system, Trends Pharmacol Sci, doi:10.1016/j.tips.2020.01.003
Maruthur, Tseng, Hutfless, Wilson, Suarez-Cuervo et al., Diabetes Medications as monotherapy or metformin-based combination therapy for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M15-2650
Menendez, Metformin and SARS-CoV-2: mechanistic lessons on air pollution to weather the cytokine/thrombotic storm in COVID-19, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.103347
Messerli, Siontis, Rexhaj, COVID-19 and renin angiotensin blockers: current evidence and recommendations, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047022
Mra, mineralocorticoid-receptor antagonist (i.e. spironolactone and eplerenone)
Pe ´rez-Belmonte, Torres-Pen ˜a, Lo ´pez-Carmona, Ayala-Gutie ´rrez, Fuentes-Jime ´nez et al., Mortality and other adverse outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus admitted for COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering drugs: a nationwide cohort study, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-020-01832-2
Robert, Fendri, Hary, Lacroix, Andre ´jak et al., Kinetics of plasma and erythrocyte metformin after acute administration in healthy subjects, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/s1262-3636(07)70037-x
Rotermund, Machetanz, Fitzgerald, The therapeutic potential of metformin in neurodegenerative diseases, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2018.00400
Roussel, Travert, Pasquet, Wilson, Smith et al., Metformin use and mortality among patients with diabetes and atherothrombosis, Arch Intern Med, doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2010.409
Scheen, Marre, Thivolet, Prognostic factors in patients with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19: findings from the CORONADO study and other recent reports, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.05.008
Scheen, Metformin and COVID-19: from cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006
Singh, Singh, Is metformin ahead in the race as a repurposed hostdirected therapy for patients with diabetes and COVID-19?, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108268
Wiernsperger, Metformin as a cellular protector; a synoptic view of modern evidences, J Nephropharmacology
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Bacon, Bates et al., Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4
Zhu, She, Cheng, Qin, Zhang et al., Association of Blood Glucose control and outcomes in patients with Covid-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216",
"ISSN": [
"1262-3636"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216",
"alternative-id": [
"S1262363620302731"
],
"article-number": "101216",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Diabetes & Metabolism"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lalau",
"given": "Jean-Daniel",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7951-9926",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Al-Salameh",
"given": "Abdallah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hadjadj",
"given": "Samy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1019-9821",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Goronflot",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiernsperger",
"given": "Nicolas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pichelin",
"given": "Matthieu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allix",
"given": "Ingrid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0581-7592",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Amadou",
"given": "Coralie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7348-7161",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bourron",
"given": "Olivier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duriez",
"given": "Thierry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gautier",
"given": "Jean-François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dutour",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gonfroy",
"given": "Céline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gouet",
"given": "Didier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8731-7355",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Joubert",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Julier",
"given": "Ingrid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Larger",
"given": "Etienne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9101-5002",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Marchand",
"given": "Lucien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marre",
"given": "Michel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3687-5522",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Meyer",
"given": "Laurent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olivier",
"given": "Frédérique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prevost",
"given": "Gaëtan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quiniou",
"given": "Pascale",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raffaitin-Cardin",
"given": "Christelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roussel",
"given": "Ronan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saulnier",
"given": "Pierre-Jean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seret-Begue",
"given": "Dominique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0696-974X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Thivolet",
"given": "Charles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vatier",
"given": "Camille",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9976-7938",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Desailloud",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wargny",
"given": "Matthieu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gourdy",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1580-8040",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cariou",
"given": "Bertrand",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Diabetes & Metabolism"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-10T18:01:01Z",
"timestamp": 1607623261000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-04T01:17:24Z",
"timestamp": 1635988644000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100009406",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nantes"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100008966",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Société Francophone du Diabète"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-09T01:26:15Z",
"timestamp": 1641691575407
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 19,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1262-3636"
}
],
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1630454400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1262363620302731?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1262363620302731?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "101216",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"article-title": "Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0005",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dci19-0066",
"article-title": "2019 Update to: management of hyperglycemia in Type 2 diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD)",
"author": "Buse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "487",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0010",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M15-2650",
"article-title": "Diabetes Medications as monotherapy or metformin-based combination therapy for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Maruthur",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "740",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0015",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000481951",
"article-title": "Renoprotective effects of metformin",
"author": "De Broe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "261",
"journal-title": "Nephron",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0020",
"volume": "138",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-017-4372-6",
"article-title": "Repurposing metformin for the prevention of cancer and cancer recurrence",
"author": "Heckman-Stoddard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1639",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0025",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2018.00400",
"article-title": "The therapeutic potential of metformin in neurodegenerative diseases",
"author": "Rotermund",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "400",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0030",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.001",
"article-title": "Benefits of metformin in attenuating the hallmarks of aging",
"author": "Kulkarni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0035",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Metformin as a cellular protector; a synoptic view of modern evidences",
"author": "Wiernsperger",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "J Nephropharmacology",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0040",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-019-0242-2",
"article-title": "Understanding the glucoregulatory mechanisms of metformin in type 2 diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Foretz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "569",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0045",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-019-2346-4",
"article-title": "Association of preadmission metformin use and mortality in patients with sepsis and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies",
"author": "Liang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "50",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Lond Engl",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0050",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-017-4318-z",
"article-title": "Metformin: historical overview",
"author": "Bailey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1566",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0055",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.2975",
"article-title": "Is metformin poised for a second career as an antimicrobial?",
"author": "Malik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2975",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0060",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"article-title": "A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0065",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tips.2020.01.003",
"article-title": "Context-dependent pharmacological effects of metformin on the immune system",
"author": "Marcucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "162",
"journal-title": "Trends Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0070",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status",
"author": "Cameron",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "652",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0075",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103347",
"article-title": "Metformin and SARS-CoV-2: mechanistic lessons on air pollution to weather the cytokine/thrombotic storm in COVID-19",
"author": "Menendez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8760",
"journal-title": "Aging",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0080",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-019-10839-0",
"article-title": "Metformin induces lipogenic differentiation in myofibroblasts to reverse lung fibrosis",
"author": "Kheirollahi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2987",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0085",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30231-X",
"article-title": "Management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Lalau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "666",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0090",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study",
"author": "Cariou",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0095",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.3854",
"article-title": "The performance of different propensity-score methods for estimating differences in proportions (risk differences or absolute risk reductions) in observational studies",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2137",
"journal-title": "Stat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0100",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0272989X09341755",
"article-title": "The relative ability of different propensity score methods to balance measured covariates between treated and untreated subjects in observational studies",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "661",
"journal-title": "Med Decis Mak Int J Soc Med Decis Mak",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0105",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"author": "Mao",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0110",
"series-title": "Propensity score weighting methods for dichotomous treatments",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047022",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and renin angiotensin blockers: current evidence and recommendations",
"author": "Messerli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2042",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0115",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Routine use of statins and increased mortality related to COVID-19 in inpatients with type 2 diabetes: results from the CORONADO study",
"author": "Cariou",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0120",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1262-3636(07)70037-X",
"article-title": "Kinetics of plasma and erythrocyte metformin after acute administration in healthy subjects",
"author": "Robert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "279",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0125",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006",
"article-title": "Metformin and COVID-19: from cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality",
"author": "Scheen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108268",
"article-title": "Is metformin ahead in the race as a repurposed host-directed therapy for patients with diabetes and COVID-19?",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0135",
"volume": "165",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection",
"author": "Hariyanto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100290",
"journal-title": "Obes Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0140",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"article-title": "Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in Covid-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0145",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with Covid-19",
"author": "Bramante",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv Prepr Serv Health Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0150",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with covid-19 and diabetes",
"author": "Crouse",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv Prepr Serv Health Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0155",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013",
"article-title": "Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with Covid-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "537",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0160",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Is there an association between metformin use and clinical outcomes in diabetes patients with COVID-19?",
"author": "Do",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0165",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-020-01832-2",
"article-title": "Mortality and other adverse outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus admitted for COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering drugs: a nationwide cohort study",
"author": "Pérez-Belmonte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0170",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12897",
"article-title": "Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with Covid-19: a preliminary retrospective report",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0175",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021",
"article-title": "Association of Blood Glucose control and outcomes in patients with Covid-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1068",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0180",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.05.008",
"article-title": "Prognostic factors in patients with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19: findings from the CORONADO study and other recent reports",
"author": "Scheen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0185",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M16-1901",
"article-title": "Clinical outcomes of metformin use in populations with chronic kidney disease, congestive heart failure, or chronic liver disease: a systematic review",
"author": "Crowley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "191",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0190",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archinternmed.2010.409",
"article-title": "Metformin use and mortality among patients with diabetes and atherothrombosis",
"author": "Roussel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1892",
"journal-title": "Arch Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216_bib0195",
"volume": "170",
"year": "2010"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Diabetes & Metabolism"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology",
"General Medicine",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "47"
}
