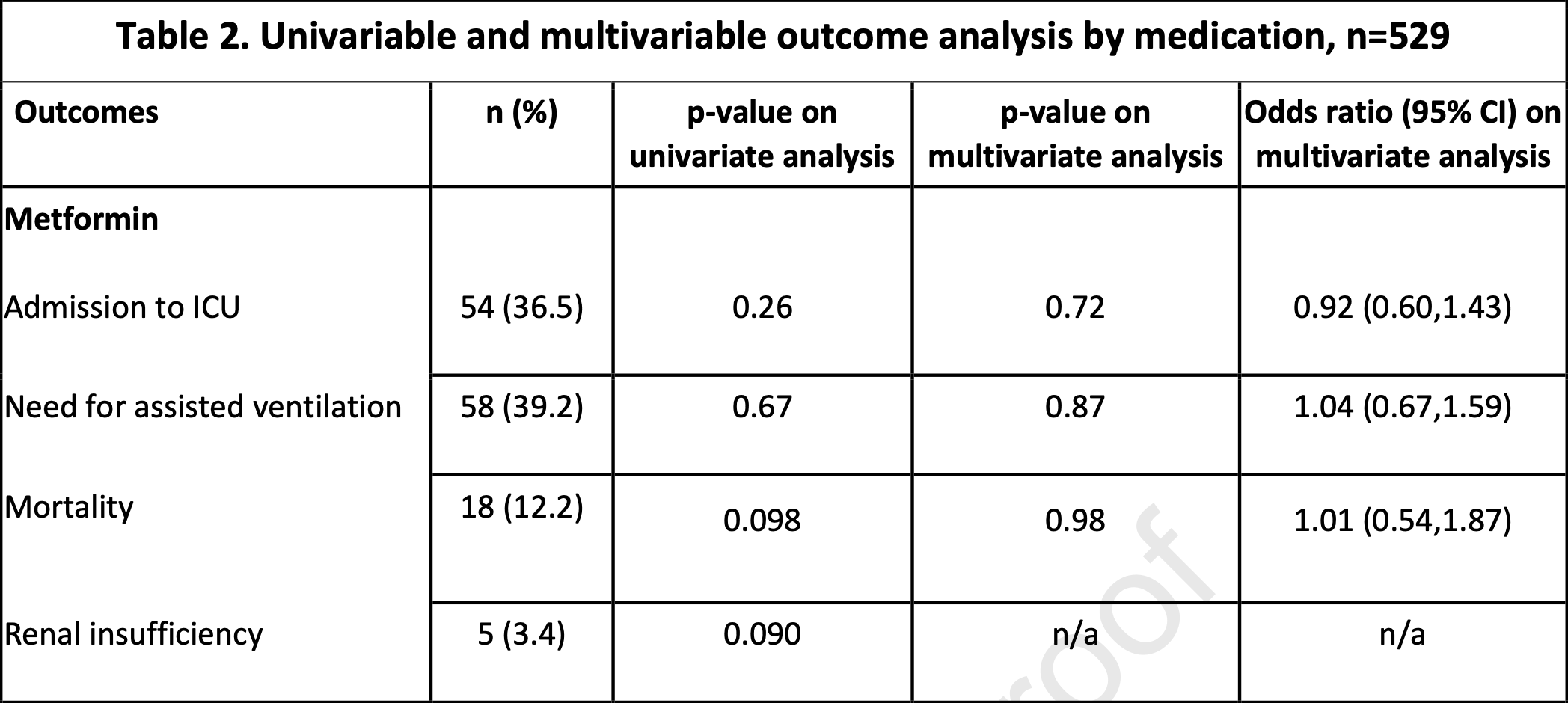
Association of metformin, dipeptidyl dipeptidase-4 inhibitors, and insulin with COVID-19-related hospital outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes
et al., Endocrine Practice, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001, Jun 2023
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 529 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes, showing no significant difference in outcomes with metformin use. This does not account for the different risk of being hospitalized based on metformin use.
Authors note that "there is a lower-than-expected proportion of metformin prescription in our population (28%) compared to the general US population", without noting that this may reflect the lower risk of being hospitalized for metformin patients, as shown in other studies1.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments2.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 1.0% higher, OR 1.01, p = 0.98, treatment 148, control 381, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 4.0% higher, OR 1.04, p = 0.87, treatment 148, control 381, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 8.0% lower, OR 0.92, p = 0.72, treatment 148, control 381, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Obiri-Yeboah et al., 8 Jun 2023, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, mean age 67.0, 8 authors.
Contact: lansanm@ccf.org.
Association of metformin, dipeptidyl dipeptidase-4 inhibitors, and insulin with COVID-19-related hospital outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes
Endocrine Practice, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
Bassendine, Bridge, Mccaughan, Gorrell, COVID-19 and comorbidities: A role for dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) in disease severity?, J Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13052
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with Covid-19, doi:10.1101/2020.06.19.20135095
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0660
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Might, Ovalle et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with covid-19 and diabetes, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.600439
Han, Ma, Sun, Association between anti-diabetic agents and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Arch Med Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002
Jehi, Ji, Milinovich, Individualizing Risk Prediction for Positive Coronavirus Disease 2019 Testing, Chest
Khunti, Knighton, Zaccardi, Prescription of glucose-lowering therapies and risk of COVID-19 mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide observational study in England, The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587
Li, Wei, Li, Metformin use in diabetes prior to hospitalization: effects on mortality in Covid-19, Endocrine Practice, doi:10.4158/EP-2020-0466
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Mirani, Favacchio, Carrone, Impact of comorbidities and glycemia at admission and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: A case series from an academic hospital in Lombardy, Italy. Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1340
Nauck, Meier, Reduced COVID-19 mortality with sitagliptin Treatment? Weighing the dissemination of potentially lifesaving findings against the assurance of high scientific standards, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dci20-0062
Prattichizzo, De Candia, Nicolucci, Ceriello, Elevated HbA1c levels in pre-Covid-19 infection increases the risk of mortality: A sistematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3476
Solerte, 'addio, Trevisan, Sitagliptin treatment at the time of hospitalization was associated with reduced mortality in patients with Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19: A multicenter, case-control, retrospective, observational Study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1521
Wander, Lowy, Beste, Prior glucose-lowering medication use and 30-day outcomes among 64,892 veterans with diabetes and COVID-19, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc21-1351
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001",
"ISSN": [
"1530-891X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001",
"alternative-id": [
"S1530891X23004299"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Association of metformin, dipeptidyl dipeptidase-4 inhibitors, and insulin with COVID-19-related hospital outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Endocrine Practice"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of the AACE."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Obiri-Yeboah",
"given": "Derrick",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bena",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alwakeel",
"given": "Mahmoud",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buehler",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Makin",
"given": "Vinni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Keren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pantalone",
"given": "Kevin M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7364-5550",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lansang",
"given": "M. Cecilia",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Endocrine Practice",
"container-title-short": "Endocrine Practice",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"aacejournalendocrinepractice.org",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-09T02:20:05Z",
"timestamp": 1686277205000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-10T23:17:41Z",
"timestamp": 1686439061000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-11T04:15:39Z",
"timestamp": 1686456939019
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1685577600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1530891X23004299?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1530891X23004299?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466",
"article-title": "Metformin use in diabetes prior to hospitalization: effects on mortality in Covid-19",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1166",
"journal-title": "Endocrine Practice",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib1",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.600439",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with covid-19 and diabetes",
"author": "Crouse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Endocrinology",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib2",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dci20-0062",
"article-title": "Reduced COVID-19 mortality with sitagliptin Treatment? Weighing the dissemination of potentially lifesaving findings against the assurance of high scientific standards",
"author": "Nauck",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2906",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib3",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1340",
"article-title": "Impact of comorbidities and glycemia at admission and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: A case series from an academic hospital in Lombardy, Italy",
"author": "Mirani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3042",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib4",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1521",
"article-title": "Sitagliptin treatment at the time of hospitalization was associated with reduced mortality in patients with Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19: A multicenter, case-control, retrospective, observational Study",
"author": "Solerte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2999",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib5",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0660",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1399",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib6",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00050-4",
"article-title": "Prescription of glucose-lowering therapies and risk of COVID-19 mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide observational study in England",
"author": "Khunti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib7",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc21-1351",
"article-title": "Prior glucose-lowering medication use and 30-day outcomes among 64,892 veterans with diabetes and COVID-19",
"author": "Wander",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2708",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib8",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.05.580",
"article-title": "Individualizing Risk Prediction for Positive Coronavirus Disease 2019 Testing",
"author": "Jehi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1364",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib9",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1753-0407.13052",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib10",
"unstructured": "Bassendine MF, Bridge SH, McCaughan GW, Gorrell MD. COVID-19 and comorbidities: A role for dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) in disease severity? J Diabetes. 2020 Sep;12(9):649-658. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13052. Epub 2020 May 27. PMID: 32394639."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7",
"article-title": "Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with Covid-19",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e34",
"journal-title": "Lacent Healthy Longev",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib11",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"article-title": "Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib12",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3476",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib13",
"unstructured": "Prattichizzo F, de Candia P, Nicolucci A, Ceriello A. Elevated HbA1c levels in pre-Covid-19 infection increases the risk of mortality: A sistematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2022 Jan;38(1):e3476. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3476. Epub 2021 May 28. PMID: 34018307; PMCID: PMC8209812."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002",
"article-title": "Association between anti-diabetic agents and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "186",
"journal-title": "Arch Med Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib14",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14744/nci.2022.34341",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib15",
"unstructured": "Erol RS, Sen EC, Ozturk FY, et al. Does DPP-4 inhibitor treatment affect the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients? North Clin Istanb. 2022 Jul 5;9(3):207-214. doi: 10.14744/nci.2022.34341. eCollection 2022."
},
{
"article-title": "The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib16",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13696998.2021.1886109",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.eprac.2023.06.001_bib17",
"unstructured": "Di Fusco M, Shea KM, Lin J, Nguyen JL, Angulo FJ, Benigno M, Malhotra D, Emir B, Sung AH, Hammond JL, Stoychev S, Charos A. Health outcomes and economic burden of hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the United States. J Med Econ. 2021 Jan-Dec;24(1):308-317. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2021.1886109. PMID: 33555956."
}
],
"reference-count": 17,
"references-count": 17,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1530891X23004299"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Association of metformin, dipeptidyl dipeptidase-4 inhibitors, and insulin with COVID-19-related hospital outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
