Metformin Use in Diabetes Prior to Hospitalization: Effects on Mortality in Covid-19
et al., Endocrine Practice, doi:10.4158/EP-2020-0466, Oct 2020
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 131 type II diabetes patients with COVID pneumonia, showing lower mortality with existing metformin use. Acarbose (commonly used in China as an initial therapy for diabetes) did not have a similar association with mortality, suggesting that the result may not be explained by metformin being used early in type II diabetes.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
|
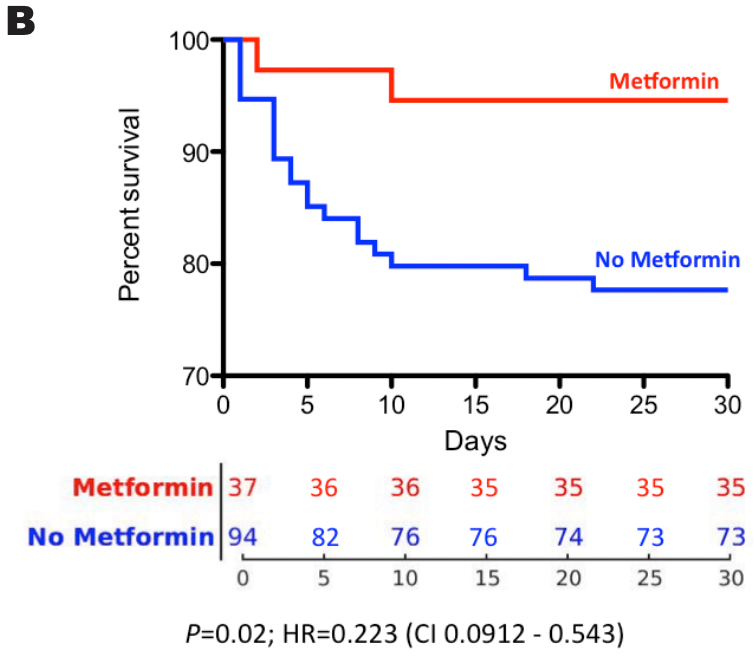
risk of death, 77.7% lower, HR 0.22, p = 0.02, treatment 2 of 37 (5.4%), control 21 of 94 (22.3%), NNT 5.9, adjusted per study, multivariable.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 27.0% higher, RR 1.27, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 37 (2.7%), control 2 of 94 (2.1%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Li et al., 1 Oct 2020, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 16 authors, study period 23 January, 2020 - 19 March, 2020.
Metformin Use in Diabetes Prior to Hospitalization: Effects on Mortality in Covid-19
Endocrine Practice, doi:10.4158/ep-2020-0466
Objective: Although type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been reported as a risk factor for coronavirus disease 2019 , the effect of pharmacologic agents used to treat T2DM, such as metformin, on COVID-19 outcomes remains unclear. Metformin increases the expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2, a known receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Data from people with T2DM hospitalized for COVID-19 were used to test the hypothesis that metformin use is associated with improved survival in this population. Methods: Retrospective analyses were performed on de-identified clinical data from a major hospital in Wuhan, China, that included patients with T2DM hospitalized for COVID-19 during the recent epidemic. One hundred and thirty-one patients diagnosed with COVID-19 and T2DM were used in this study. The primary outcome was mortality. Demographic, clinical characteristics, laboratory data, diabetes medications, and respiratory therapy data were also included in the analysis. Results: Of these 131 patients, 37 used metformin with or without other antidiabetes medications. Among the 37 metformin-taking patients, 35 (94.6%) survived and 2 (5.4%) did not survive. The mortality rates in the metformin-taking group versus the non-metformin group were 5.4% (2/37) versus 22.3% (21/94). Using multivariate analysis, metformin was found to be an independent predictor of survival in this cohort (P = .02).
Conclusion: This study reveals a significant association between metformin use and survival in people with T2DM diagnosed with COVID-19. These clinical data are consistent with potential benefits of the use of metformin for COVID-19 patients with T2DM.
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 -preliminary report, N Engl J Med
Bergmark, Bhatt, Mcguire, Metformin use and clinical outcomes among patients with diabetes mellitus with or without heart failure or kidney dysfunction: observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 trial, Circulation
Berlin, Gulick, Martinez, Severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19
El Messaoudi, Rongen, De Boer, Riksen, The cardioprotective effects of metformin, Curr Opin Lipidol
Fang, Karakiulakis, Roth, Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?, Lancet Respir Med
Gabir, Hanson, Dabelea, Plasma glucose and prediction of microvascular disease and mortality: evaluation of 1997 American Diabetes Association and 1999 World Health Organization criteria for diagnosis of diabetes, Diabetes Care
Garcia, Flumamine, a new synthetic analgesic and anti-flu drug, J Philipp Med Assoc
Geleris, Sun, Platt, Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Guo, Li, Dong, Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19, Diabetes Metab Res Rev
Jarcho, Ingelfinger, Hamel, Sr, Harrington, Inhibitors of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Kavanagh, Mccowen, Clinical practice. Glycemic control in the ICU, N Engl J Med
Lan, Ge, Yu, Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor, Nature
Li, Liu, Wang, Wang, Chen, Metformin in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Biomed Rep
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Malhotra, Hepokoski, Mccowen, Shyy, ACE2, metformin and COVID-19, iScience
Malhotra, Intensive insulin in intensive care, N Engl J Med
Mccowen, Malhotra, Bistrian, Stress induced hyperglycemia, Crit Care Clin
Norrie, Remdesivir for COVID-19: challenges of underpowered studies, Lancet
Patel, Verma, COVID-19 and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: what is the evidence?, JAMA
Pernicova, Korbonits, Metformin--mode of action and clinical implications for diabetes and cancer, Nat Rev Endocrinol
Ramnath, Mcsharry, Malhotra, Do no harm: reaffirming the value of evidence and equipoise while minimizing cognitive bias in the COVID-19 era, Chest
Rosenberg, Dufort, Udo, Association of treatment with hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York State, JAMA
Schädle, Tschritter, Kellerer, Metformin associated lactic acidosis in clinical practice -a case series, Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes
Tsakiris, Donald, Rutishauser, Banchero, Wood, Cardiovascular responses to hypertension and hypotension in dogs with denervated hearts, J Appl Physiol
Ursini, Ciaffi, Landini, Meliconi, COVID-19 and diabetes: is metformin a friend or foe?, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Vaduganathan, Vardeny, Michel, Mcmurray, Pfeffer et al., Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors in patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Venter, Richter, Towards effective diagnostic assays for COVID-19: a review, J Clin Pathol
Wang, Zhang, Du, Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med
Xu, Han, Li, Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Zhang, Dong, Martin, AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in endothelium mitigates pulmonary hypertension, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Zhu, She, Cheng, Association of blood glucose control and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4158/ep-2020-0466",
"ISSN": [
"1530-891X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4158/ep-2020-0466",
"alternative-id": [
"S1530891X20482229"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jinghong",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Qi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Willis X",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCowen",
"given": "Karen C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xiong",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Jiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Wenlijun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marin",
"given": "Traci",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Robert L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "He",
"given": "Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gongol",
"given": "Brendan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hepokoski",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Jason X-J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shyy",
"given": "John Y-J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xiong",
"given": "Nian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Malhotra",
"given": "Atul",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Endocrine Practice"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-02T23:44:21Z",
"timestamp": 1604360661000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-04T15:35:48Z",
"timestamp": 1636040148000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-14T20:13:10Z",
"timestamp": 1639512790957
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 8,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1530-891X"
}
],
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1601510400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1530891X20482229?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1530891X20482229?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1166-1172",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009575",
"article-title": "Severe Covid-19",
"author": "Berlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0010",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0749-0704(05)70154-8",
"article-title": "Stress induced hyperglycemia",
"author": "McCowen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Clin.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0015",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe058304",
"article-title": "Intensive insulin in intensive care",
"author": "Malhotra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "516",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0020",
"volume": "354",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp1001115",
"article-title": "Clinical practice. Glycemic control in the ICU",
"author": "Kavanagh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2540",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0025",
"volume": "363",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021",
"article-title": "Association of blood glucose control and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1068",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0030",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19",
"author": "Guo",
"first-page": "e3319",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0035",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30116-8",
"article-title": "Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?",
"author": "Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e21",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0040",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MOL.0b013e32834ae1a7",
"article-title": "The cardioprotective effects of metformin",
"author": "El Messaoudi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "445",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Lipidol.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0045",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/br.2012.18",
"article-title": "Metformin in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "Biomed Rep.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0050",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrendo.2013.256",
"article-title": "Metformin--mode of action and clinical implications for diabetes and cancer",
"author": "Pernicova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "143",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0055",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/jappl.1969.27.6.817",
"article-title": "Cardiovascular responses to hypertension and hypotension in dogs with denervated hearts",
"author": "Tsakiris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "817",
"journal-title": "J Appl Physiol.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0060",
"volume": "27",
"year": "1969"
},
{
"article-title": "Flumamine, a new synthetic analgesic and anti-flu drug",
"author": "Garcia",
"first-page": "287",
"journal-title": "J Philipp Med Assoc.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0065",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1950"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201712-2570OC",
"article-title": "AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in endothelium mitigates pulmonary hypertension",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0070",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5",
"article-title": "Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor",
"author": "Lan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "215",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0075",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.040144",
"article-title": "Metformin use and clinical outcomes among patients with diabetes mellitus with or without heart failure or kidney dysfunction: observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 trial",
"author": "Bergmark",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1004",
"journal-title": "Circulation.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0080",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206685",
"article-title": "Towards effective diagnostic assays for COVID-19: a review",
"author": "Venter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "370",
"journal-title": "J Clin Pathol.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0085",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diacare.23.8.1113",
"article-title": "Plasma glucose and prediction of microvascular disease and mortality: evaluation of 1997 American Diabetes Association and 1999 World Health Organization criteria for diagnosis of diabetes",
"author": "Gabir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1113",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0090",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0095",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2020.101425",
"article-title": "ACE2, metformin and COVID-19",
"author": "Malhotra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101425",
"journal-title": "iScience.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0100",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31023-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for COVID-19: challenges of underpowered studies",
"author": "Norrie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1525",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0105",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1569",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0110",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - preliminary report",
"author": "Beigel",
"first-page": "2007764",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2012410",
"article-title": "Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Geleris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2411",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0120",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.8630",
"article-title": "Association of treatment with hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York State",
"author": "Rosenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2493",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0125",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.05.548",
"article-title": "Do no harm: reaffirming the value of evidence and equipoise while minimizing cognitive bias in the COVID-19 era",
"author": "Ramnath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "873",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0130",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"article-title": "Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10970",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0135",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe2012924",
"article-title": "Inhibitors of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Covid-19",
"author": "Jarcho",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2462",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0140",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Metformin associated lactic acidosis in clinical practice - a case series",
"author": "Schädle",
"journal-title": "Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0145",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108167",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes: is metformin a friend or foe?",
"author": "Ursini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108167",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0150",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsr2005760",
"article-title": "Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors in patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Vaduganathan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1653",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0155",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: what is the evidence?",
"author": "Patel",
"first-page": "1769",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0160",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19",
"author": "Bramante",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0165",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"article-title": "Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg.",
"key": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466_bb0170",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Endocrine Practice"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology",
"General Medicine",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Metformin Use in Diabetes Prior to Hospitalization: Effects on Mortality in Covid-19"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "26"
}
