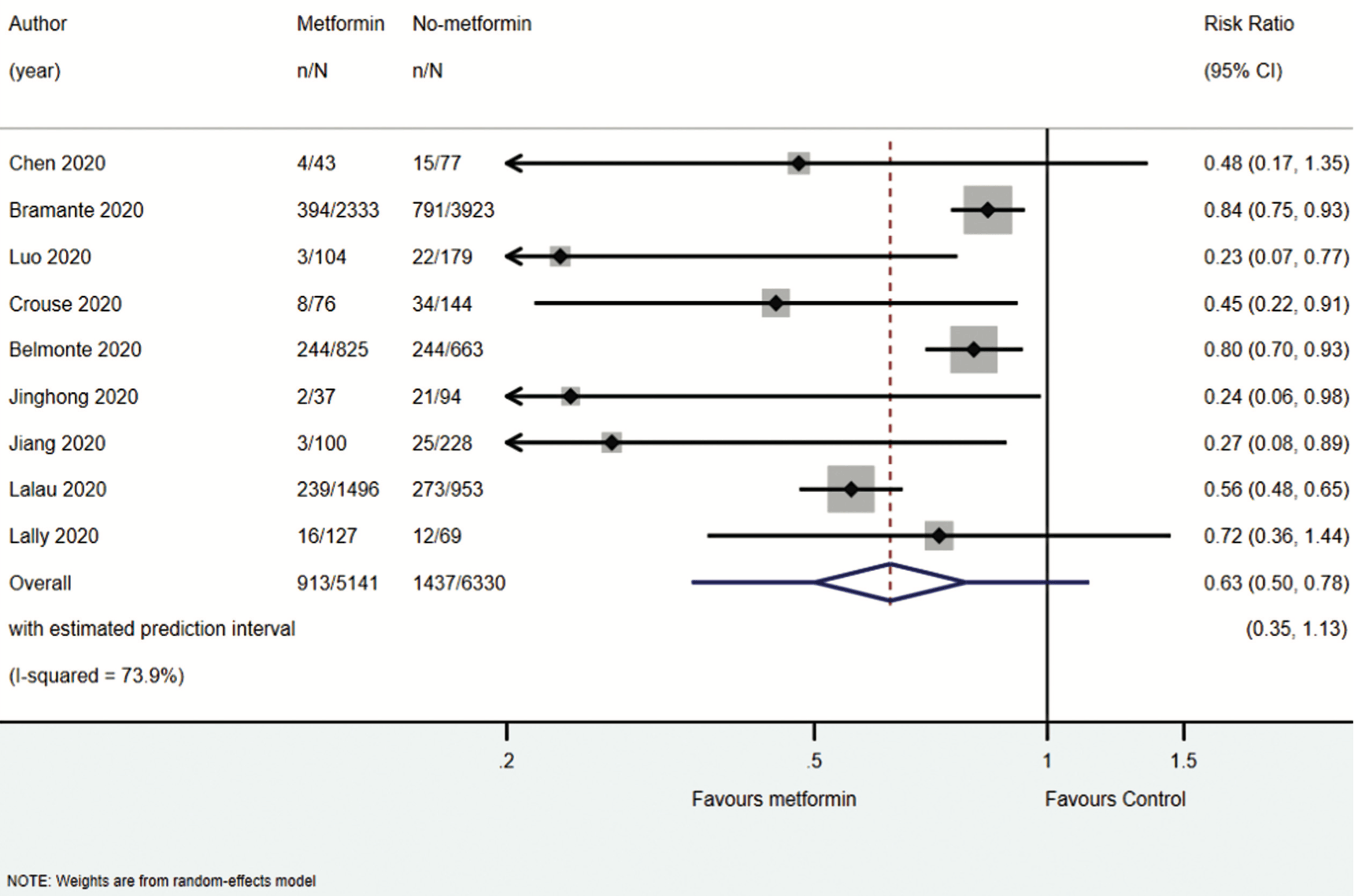
Association of Metformin with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
et al., Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India), doi:10.1055/s-0042-1760353, Jan 2023
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Systematic review and meta analysis showing significantly lower mortality with metformin.
24 meta-analyses show significant improvements with metformin for mortality1-23,
hospitalization7,13,23 ,
progression1, and
severity8,9,13 .
Currently there are 110 metformin for COVID-19 studies, showing 36% lower mortality [32‑40%], 29% lower ventilation [12‑43%], 19% lower ICU admission [8‑28%], 17% lower hospitalization [11‑23%], and 5% fewer cases [-4‑13%].
|
risk of death, 37.0% lower, RR 0.63, p < 0.001.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Yang et al., The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977.
2.
Lukito et al., The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006.
3.
Kow et al., Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26498.
4.
Hariyanto et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obesity Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290.
5.
Ma et al., Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282210.
6.
Parveen et al., Association of Metformin with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India), doi:10.1055/s-0042-1760353.
7.
Li et al., Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.704666.
8.
Schlesinger et al., Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-023-05928-1.
9.
Petrelli et al., Metformin and Covid-19: a systematic review of systematic reviews with meta-analysis, Acta Biomedica Atenei Parmensis, doi:10.23750/abm.v94iS3.14405.
10.
Oscanoa et al., Metformin therapy and severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a meta-analysis, Clinical Diabetology, doi:10.5603/DK.a2021.0035.
11.
Kan et al., Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.708494.
12.
Poly et al., Metformin Use Is Associated with Decreased Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes: Evidence from Retrospective Studies and Biological Mechanism, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10163507.
13.
Song et al., The Effect of Antihyperglycemic Medications on COVID-19: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review from Observational Studies, Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science, doi:10.1007/s43441-024-00633-6.
14.
Ganesh et al., Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15258.
15.
Nassar et al., Noninsulin‐based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis, Journal of Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13359.
16.
Zhan et al., Effect of Antidiabetic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/10600280221133577.
17.
Nguyen et al., Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155196.
18.
Han et al., Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002.
19.
Chen et al., The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458.
20.
Scheen, A., Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006.
21.
Sun et al., Is Metformin Use Associated With a Decreased Mortality for COVID-19 Diabetic Patients? A Meta-Analysis, Journal of the Endocrine Society, doi:10.1210/jendso/bvab048.709.
Parveen et al., 31 Jan 2023, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Contact: nidhi.bharal@gmail.com.
Association of Metformin with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India), doi:10.1055/s-0042-1760353
Studies have demonstrated high prevalence of mortality in coronavirus disease (COVID-19) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus; however, the effects of antidiabetic pharmacotherapy on COVID-19 complications need further exploration. The aim of the study was to explore the association of metformin use and mortality in COVID-19 patients. A literature search was conducted using the databases Medline (via PubMed) and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials until February 09, 2021. Nine studies were included in the meta-analysis, including 12,684 COVID-19 patients. The metaanalysis suggested 37% lower risk of mortality in patients receiving metformin (risk ratio: 0.63; 95% confidence interval: 0.50-0.78; p < 0.001). However, no significant difference in hospitalization days between the two groups (p ¼ 0.197) was observed. The analysis revealed significantly lower risk of having obesity (p < 0.001), hypertension (p < 0.001), heart failure (p < 0.001), and cerebrovascular disease (p ¼ 0.015) in the group receiving metformin. The analysis also demonstrated significantly lower risk of using anticoagulants (p ¼ 0.015), diuretics (p < 0.001), and antiplatelets (p ¼ 0.010) in patients receiving metformin. Our findings suggest that metformin use decreases mortality in COVID-19 patients. However, randomized studies demonstrating the consequences of metformin use are needed to understand the magnitude of the beneficial effects of metformin.
Conflict of Interest None declared.
References
Bailey, Gwilt, Diabetes, metformin and the clinical course of Covid-19: outcomes, mechanisms and suggestions on the therapeutic use of metformin, Front Pharmacol
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with Covid-19, Lancet Healthy Longev
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study, Diabetologia
Chen, Wu, Chen, Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study, BMJ
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Clinical Characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication, Diabetes Care
Cheng, Liu, Li, Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Might, Ovalle et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes, Front Endocrinol
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Might, Ovalle et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with Covid-19 and diabetes, Front Endocrinol
Dalton, Bolen, Mascha, Publication bias: the elephant in the review, Anesth Analg
Davis, Xie, Viollet, Zou, Activation of the AMP-activated kinase by antidiabetes drug metformin stimulates nitric oxide synthesis in vivo by promoting the association of heat shock protein 90 and endothelial nitric oxide synthase, Diabetes
Esam, A proposed mechanism for the possible therapeutic potential of Metformin in COVID-19, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Gao, Liu, Zhong, Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: a preliminary retrospective report, Clin Transl Sci
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obes Med
Hattori, Suzuki, Hattori, Kasai, Metformin inhibits cytokine-induced nuclear factor kappaB activation via AMP-activated protein kinase activation in vascular endothelial cells, Hypertension
Higgins, Green, Quality Assessment of Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis
Jiang, Chen, Yin, Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Kow, Hasan, Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: a meta-analysis, J Med Virol
Kow, Ramachandram, Hasan, Metformin in COVID-19: clinical trials are needed to prove its benefits, Ir J Med Sci
Lalau, Al-Salameh, Hadjadj, Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19, Diabetes Metab
Lally, Tsoukas, Halladay, Neill, Gravenstein et al., Metformin is associated with decreased 30-day mortality among nursing home residents infected with SARS-CoV2, J Am Med Dir Assoc
Li, Wei, Li, Metformin Use in Diabetes Prior to Hospitalization: Effects on Mortality in Covid-19, Endocr Pract
Li, Wei, Li, Metformin use in diabetes prior to hospitalization: effects on mortality in Covid-19, Endocr Pract
Lui, Tan, Is metformin a miracle or a menace in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes?, J Diabetes Investig
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Mclachlan, The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 are distinctly different paradigms, Clin Hypertens
Moher, Liberati, Tetzlaff, Altman, Group, Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement, PLoS Med
Parveen, Sehar, Bajpai, Agarwal, Association of diabetes and hypertension with disease severity in covid-19 patients: a systematic literature review and exploratory meta-analysis, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Pérez-Belmonte, Torres-Peña, Carmona, Mortality and other adverse outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus admitted for COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering drugs: a nationwide cohort study, BMC Med
Stroup, Berlin, Morton, Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Metaanalysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group, JAMA
Wong, Lui, Lui, Metformin use in relation to clinical outcomes and hyperinflammatory syndrome among COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: a propensity score analysis of a territory-wide cohort, Front Endocrinol
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0042-1760353",
"ISSN": [
"0379-038X",
"2454-5635"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-1760353",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Studies have demonstrated high prevalence of mortality in coronavirus disease (COVID-19) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus; however, the effects of antidiabetic pharmacotherapy on COVID-19 complications need further exploration. The aim of the study was to explore the association of metformin use and mortality in COVID-19 patients. A literature search was conducted using the databases Medline (via PubMed) and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials until February 09, 2021. Nine studies were included in the meta-analysis, including 12,684 COVID-19 patients. The meta-analysis suggested 37% lower risk of mortality in patients receiving metformin (risk ratio: 0.63; 95% confidence interval: 0.50–0.78; p < 0.001). However, no significant difference in hospitalization days between the two groups (p = 0.197) was observed. The analysis revealed significantly lower risk of having obesity (p < 0.001), hypertension (p < 0.001), heart failure (p < 0.001), and cerebrovascular disease (p = 0.015) in the group receiving metformin. The analysis also demonstrated significantly lower risk of using anticoagulants (p = 0.015), diuretics (p < 0.001), and antiplatelets (p = 0.010) in patients receiving metformin. Our findings suggest that metformin use decreases mortality in COVID-19 patients. However, randomized studies demonstrating the consequences of metformin use are needed to understand the magnitude of the beneficial effects of metformin.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Translational and Clinical Research, School of Chemical & Life Sciences, Jamia Hamdard, New Delhi, India"
}
],
"family": "Parveen",
"given": "Rizwana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Translational and Clinical Research, School of Chemical & Life Sciences, Jamia Hamdard, New Delhi, India"
}
],
"family": "Mishra",
"given": "Pinki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Translational and Clinical Research, School of Chemical & Life Sciences, Jamia Hamdard, New Delhi, India"
}
],
"family": "Luthra",
"given": "Reva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1227-2703",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, Keele University, Staffordshire, United Kingdom"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bajpai",
"given": "Ram",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2509-3026",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Translational and Clinical Research, School of Chemical & Life Sciences, Jamia Hamdard, New Delhi, India"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Agarwal",
"given": "Nidhi",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India)",
"container-title-short": "Ann Natl Acad Med Sci",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-23T00:00:45Z",
"timestamp": 1677110445000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-25T00:18:14Z",
"timestamp": 1679703494000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-25T00:41:07Z",
"timestamp": 1679704867854
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "01",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "01",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 52,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677024000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.thieme-connect.de/products/ejournals/pdf/10.1055/s-0042-1760353.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "194",
"original-title": [],
"page": "013-020",
"prefix": "10.1055",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
22
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Georg Thieme Verlag KG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108295",
"article-title": "Association of diabetes and hypertension with disease severity in covid-19 patients: a systematic literature review and exploratory meta-analysis",
"author": "R Parveen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108295",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "ref1",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdi.13484",
"article-title": "Is metformin a miracle or a menace in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes?",
"author": "D TW Lui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "479",
"issue": "04",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes Investig",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12897",
"article-title": "Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: a preliminary retrospective report",
"author": "Y Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1055",
"issue": "06",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1091",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study",
"author": "T Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1091",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "F Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x",
"article-title": "Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study",
"author": "B Cariou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1500",
"issue": "08",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26498",
"article-title": "Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: a meta-analysis",
"author": "C S Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "695",
"issue": "02",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diabetes.55.02.06.db05-1064",
"article-title": "Activation of the AMP-activated kinase by antidiabetes drug metformin stimulates nitric oxide synthesis in vivo by promoting the association of heat shock protein 90 and endothelial nitric oxide synthase",
"author": "B J Davis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "496",
"issue": "02",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.HYP.0000221429.94591.72",
"article-title": "Metformin inhibits cytokine-induced nuclear factor kappaB activation via AMP-activated protein kinase activation in vascular endothelial cells",
"author": "Y Hattori",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1183",
"issue": "06",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "ref9",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097",
"article-title": "Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement",
"author": "D Moher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1000097",
"issue": "07",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.283.15.2008",
"article-title": "Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group",
"author": "D F Stroup",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2008",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "283",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"author": "J Higgins",
"key": "ref13",
"volume-title": "Quality Assessment of Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1213/ANE.0000000000001596",
"article-title": "Publication bias: the elephant in the review",
"author": "J E Dalton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "812",
"issue": "04",
"journal-title": "Anesth Analg",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"article-title": "Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis",
"author": "P Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.600439",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with Covid-19 and diabetes",
"author": "A Crouse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "600439",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "13;11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7",
"article-title": "Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with Covid-19",
"author": "C T Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e34",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "Lancet Healthy Longev",
"key": "ref17",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-020-01832-2",
"article-title": "Mortality and other adverse outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus admitted for COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering drugs: a nationwide cohort study",
"author": "L M Pérez-Belmonte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "359",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013",
"article-title": "Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes",
"author": "X Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "537",
"issue": "04",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466",
"article-title": "Metformin use in diabetes prior to hospitalization: effects on mortality in Covid-19",
"author": "J Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1166",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Endocr Pract",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619",
"article-title": "Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "N Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108619",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "ref21",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19",
"author": "J-D Lalau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101216",
"issue": "05",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031",
"article-title": "Metformin is associated with decreased 30-day mortality among nursing home residents infected with SARS-CoV2",
"author": "M A Lally",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "193",
"issue": "01",
"journal-title": "J Am Med Dir Assoc",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0660",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication",
"author": "Y Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1399",
"issue": "07",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref24",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2022.810914",
"article-title": "Metformin use in relation to clinical outcomes and hyperinflammatory syndrome among COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: a propensity score analysis of a territory-wide cohort",
"author": "C KH Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "810914",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection",
"author": "T I Hariyanto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100290",
"journal-title": "Obes Med",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40885-020-00147-x",
"article-title": "The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 are distinctly different paradigms",
"author": "C S McLachlan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Clin Hypertens",
"key": "ref27",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.784459",
"article-title": "Diabetes, metformin and the clinical course of Covid-19: outcomes, mechanisms and suggestions on the therapeutic use of metformin",
"author": "C J Bailey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "784459",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11845-021-02869-9",
"article-title": "Metformin in COVID-19: clinical trials are needed to prove its benefits",
"author": "C S Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2641",
"issue": "06",
"journal-title": "Ir J Med Sci",
"key": "ref29",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.600439",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes",
"author": "A B Crouse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "600439",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108282",
"article-title": "A proposed mechanism for the possible therapeutic potential of Metformin in COVID-19",
"author": "Z Esam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108282",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "ref31",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466",
"article-title": "Metformin Use in Diabetes Prior to Hospitalization: Effects on Mortality in Covid-19",
"author": "J Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1166",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Endocr Pract",
"key": "ref32",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.thieme-connect.de/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-0042-1760353"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Association of Metformin with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "59"
}
