Effects of different treatments for type 2 diabetes mellitus on mortality of coronavirus disease from 2019 to 2021 in China: a multi-institutional retrospective study
et al., Molecular Biomedicine, doi:10.1186/s43556-024-00183-1, May 2024
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
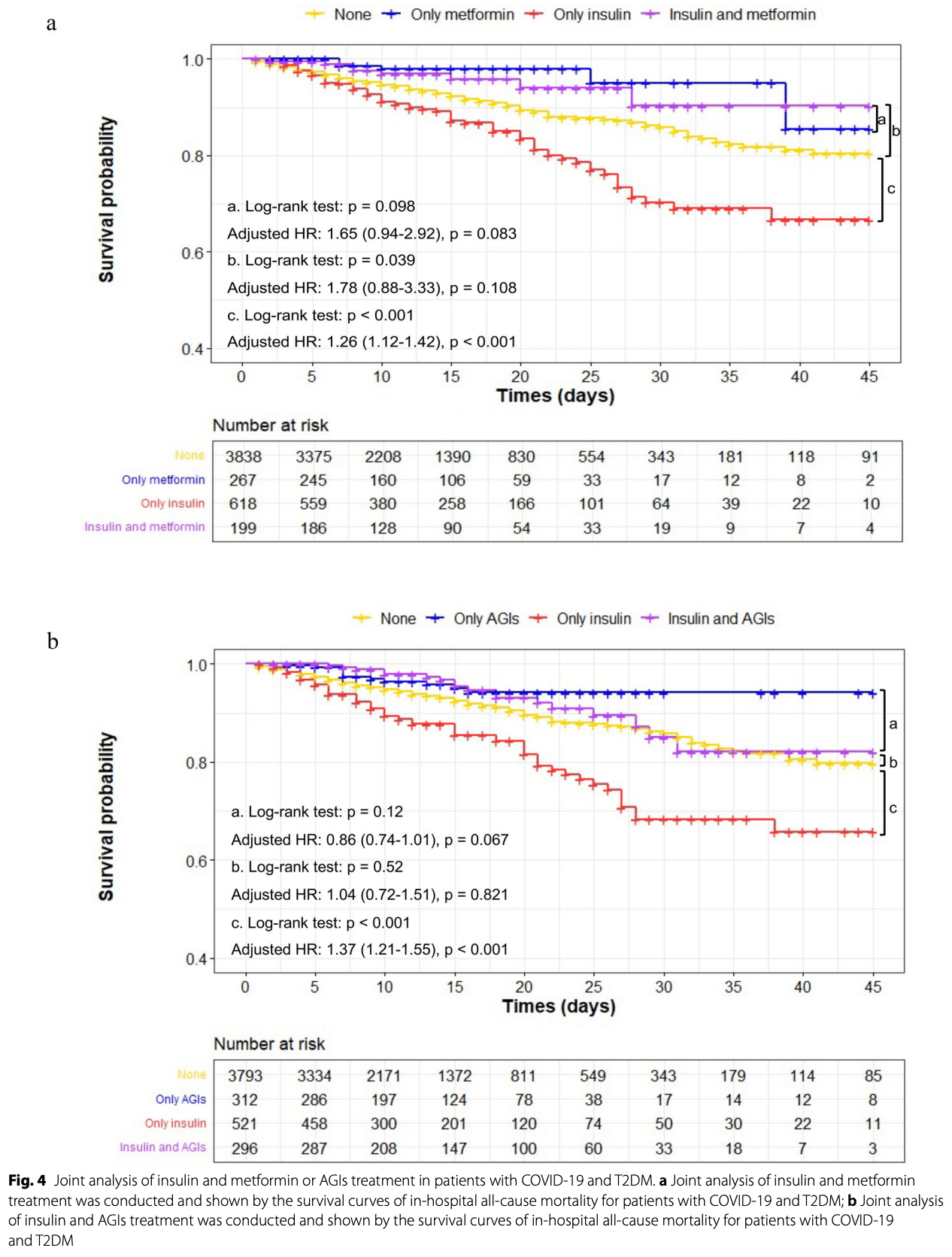
Retrospective 4,922 COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes in China, showing lower mortality with metformin and alpha-glucosidase inhibitor treatment and higher mortality with insulin treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of death, 52.0% lower, HR 0.48, p = 0.01, treatment 405, control 405, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of death, 59.0% lower, HR 0.41, p = 0.001, treatment 466, control 4,456, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 54.0% lower, HR 0.46, p = 0.007, treatment 466, control 4,456, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, Table S7.
|
|
risk of ARDS, 72.0% lower, HR 0.28, p = 0.04, treatment 466, control 4,456, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, Table S7.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Xu et al., 17 May 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: dwwang@tjh.tjmu.edu.cn.
Effects of different treatments for type 2 diabetes mellitus on mortality of coronavirus disease from 2019 to 2021 in China: a multi-institutional retrospective study
Molecular Biomedicine, doi:10.1186/s43556-024-00183-1
The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic has continued for 5 years. Sporadic cases continue to occur in different locations. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with a high risk of a poor prognosis in patients with COVID-19. Successful control of blood glucose levels can effectively decrease the risks of severe infections and mortality. However, the effects of different treatments were reported differently and even adversely. This retrospective study included 4,922 patients who have been diagnosed as COVID-19 and T2DM from 138 Hubei hospitals. The clinical characteristics and outcomes were compared and calculated their risk for death using multivariate Cox regression and Kaplan-Meier curves. After adjustment of age, sex, comorbidities, and in-hospital medications, metformin and alpha-glucosidase inhibitor (AGI) use performed lower all-cause mortality (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.41; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.24-0.71; p = 0.001 for metformin; 0.53, 0.35-0.80, p = 0.002 for AGIs), while insulin use was associated with increased all-cause mortality (adjusted HR, 2.07, 95% CI, 1.61-2.67, p < 0.001). After propensity score-matched (PSM) analysis, adjusted HRs for insulin, metformin, and AGIs associated with all-cause mortality were 1.32 (95% CI, 1.03-1.81; p = 0.012), 0.48 (95% CI, 0.23-0.83, p = 0.014), and 0.59 (95% CI, 0.35-0.98, p = 0.05). Therefore, metformin and AGIs might be more suitable for patients with COVID-19 and T2DM while insulin might be used with caution.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1186/ s43556-024-00183-1.
Supplementary Material 1. Authors' contributions KX designed the study, collected and analyzed data, performed the statistical analysis, and wrote the manuscript. WH, BY, KZ and DZ completed the data collation and was responsible for quality control. DWW designed the project, edited the manuscript, and supervised the study. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College (no. TJ-IRB20210138). Owing to the retrospective nature and anonymity in this study, the Research Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College waived the requirement for obtaining written informed consent.
Competing interests The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Badawi, Ryoo, Prevalence of diabetes in the 2009 Influenza A (H1N1) and the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: a systematic review and Meta-analysis, J Public Health Res, doi:10.4081/jphr.2016.733
Bailey, Gwilt, Diabetes, metformin and the clinical course of Covid-19: outcomes, mechanisms and suggestions on the therapeutic use of metformin, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.784459
Bornstein, Rubino, Khunti, Mingrone, Hopkins et al., Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30152-2
Bramante, Buse, Tamaritz, Palacio, Cohen et al., Outpatient metformin use is associated with reduced severity of COVID-19 disease in adults with overweight or obesity, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv26873
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Buse, Liebovitz et al., Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2201662
Chan, Casiraghi, Laraway, Coleman, Blau et al., Metformin is associated with reduced COVID-19 severity in patients with prediabetes, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2022.110157
Cheng, Liu, Li, Zhang, Lei et al., Metformin is Associated with higher incidence of Acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013
Fukushi, Yoshinaka, Matsuoka, Hatakeyama, Ishizaka et al., Monitoring of S protein maturation in the endoplasmic reticulum by calnexin is important for the infectivity of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.01250-12
Ghany, Palacio, Dawkins, Chen, Mccarter et al., Metformin is associated with lower hospitalizations, mortality and severe coronavirus infection among elderly medicare minority patients in 8 states in USA, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.022
Gianchandani, Esfandiari, Ang, Iyengar, Knotts et al., Managing hyperglycemia in the COVID-19 inflammatory storm, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/dbi20-0022
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9
Guo, Shi, Zhang, Wang, Vale Moreira et al., Comorbid diabetes and the risk of disease severity or death among 8807 COVID-19 patients in China: a meta-analysis, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108346
Gupta, Ghosh, Singh, Misra, Clinical considerations for patients with diabetes in times of COVID-19 epidemic, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.03.002
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30183-5
Jia, Weng, Zhu, Lu, Zhou, Standards of medical care for type 2 diabetes in China 2019, Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3158
Jolobe, Post-COVID-19 diabetes in the context of long COVID, Am J Emerg Med, doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2022.07.015
Katulanda, Dissanayake, Ranathunga, Ratnasamy, Wijewickrama et al., Prevention and management of COVID-19 among patients with diabetes: an appraisal of the literature, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05164-x
Kunal, Madan, Tarke, Gautam, Kinkar et al., Emerging spectrum of post-COVID-19 syndrome, Postgrad Med J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139585
Li, Wei, Mccowen, Xiong, Liu et al., Inpatient use of metformin and acarbose is associated with reduced mortality of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, Endocrinol Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1002/edm2.301
Llauradó, Vlacho, Wargny, Ruan, Franch-Nadal et al., The association between macrovascular complications and intensive care admission, invasive mechanical ventilation, and mortality in people with diabetes hospitalized for coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), Cardiovasc Diabetol, doi:10.1186/s12933-022-01657-8
Longo, Caruso, Maiorino, Bellastella, Giugliano et al., Treating type 2 diabetes in COVID-19 patients: the potential benefits of injective therapies, Cardiovasc Diabetol, doi:10.1186/s12933-020-01090-9
Mcgurnaghan, Weir, Bishop, Kennedy, Blackbourn et al., Risks of and risk factors for COVID-19 disease in people with diabetes: a cohort study of the total population of Scotland, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30405-8
Postler, Peng, Bhatt, Ghosh, Metformin selectively dampens the acute inflammatory response through an AMPK-dependent mechanism, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-97441-x
Rajasekharan, Bonotto, Alves, Kazungu, Poggianella et al., Inhibitors of protein glycosylation are active against the coronavirus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13050808
Ritchie, Harvey, Feldmann, Stroeher, Feldmann et al., Identification of N-linked carbohydrates from severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) spike glycoprotein, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2009.12.020
Roca-Ho, Riera, Palau, Pascual, Soler, Characterization of ACE and ACE2 expression within different organs of the NOD mouse, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms18030563
Sardu, Onofrio, Balestrieri, Barbieri, Rizzo et al., Outcomes in patients with hyperglycemia affected by COVID-19: can we do more on glycemic control?, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0723
Schaller, Sharma, Dupee, Nguyen, Urueña et al., Ex vivo SARS-CoV-2 infection of human lung reveals heterogeneous host defense and therapeutic responses, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.148003
Singh, Khunti, COVID-19 and diabetes, Annu Rev Med
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Williams, Borger, α-glucosidase inhibitors as host-directed antiviral agents with potential for the treatment of COVID-19, Biochem Soc Trans, doi:10.1042/bst20200505
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Bacon, Bates et al., Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using Open-SAFELY, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4
Xian, Liu, Nilsson, Gatchalian, Crother et al., Metformin inhibition of mitochondrial ATP and DNA synthesis abrogates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pulmonary inflammation, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2021.05.004
Yang, Feng, Yuan, Yuan, Fu et al., Plasma glucose levels and diabetes are independent predictors for mortality and morbidity in patients with SARS, Diabet Med, doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2006.01861.x
Yu, Li, Sun, Wang, Insulin treatment is associated with increased mortality in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.014
Zhang, Luo, Li, Wang, Chen et al., Risk factors for death among the First 80 543 coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases in China: relationships between age, underlying disease, case severity, and region, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab493
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30566-3
Zhu, She, Cheng, Qin, Zhang et al., Association of blood glucose control and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and preexisting type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43556-024-00183-1",
"ISSN": [
"2662-8651"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s43556-024-00183-1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic has continued for 5 years. Sporadic cases continue to occur in different locations. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with a high risk of a poor prognosis in patients with COVID-19. Successful control of blood glucose levels can effectively decrease the risks of severe infections and mortality. However, the effects of different treatments were reported differently and even adversely. This retrospective study included 4,922 patients who have been diagnosed as COVID-19 and T2DM from 138 Hubei hospitals. The clinical characteristics and outcomes were compared and calculated their risk for death using multivariate Cox regression and Kaplan–Meier curves. After adjustment of age, sex, comorbidities, and in-hospital medications, metformin and alpha-glucosidase inhibitor (AGI) use performed lower all-cause mortality (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.41; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.24–0.71; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.001 for metformin; 0.53, 0.35–0.80, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.002 for AGIs), while insulin use was associated with increased all-cause mortality (adjusted HR, 2.07, 95% CI, 1.61–2.67, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.001). After propensity score-matched (PSM) analysis, adjusted HRs for insulin, metformin, and AGIs associated with all-cause mortality were 1.32 (95% CI, 1.03–1.81; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.012), 0.48 (95% CI, 0.23–0.83, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.014), and 0.59 (95% CI, 0.35–0.98, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.05). Therefore, metformin and AGIs might be more suitable for patients with COVID-19 and T2DM while insulin might be used with caution.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"183"
],
"article-number": "18",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "27 November 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "12 April 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "17 May 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College (no. TJ-IRB20210138). Owing to the retrospective nature and anonymity in this study, the Research Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College waived the requirement for obtaining written informed consent."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0004-0512-785X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Ke",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "He",
"given": "Wu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Bo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhong",
"given": "Kaineng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Da",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Dao Wen",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Molecular Biomedicine",
"container-title-short": "Mol Biomed",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-17T00:02:04Z",
"timestamp": 1715904124000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-17T00:02:55Z",
"timestamp": 1715904175000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82241034",
"C-0052",
"82100526"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"award": [
"Top-Notch Talent Program of Hubei Province"
],
"name": "Top-Notch Talent Program of Hubei Province"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100015640",
"award": [
"2021YBJRC005"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Tongji Hospital"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82330010"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "National Nature Science Foundation of China"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-18T00:43:06Z",
"timestamp": 1715992986748
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
17
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-17T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1715904000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-17T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1715904000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s43556-024-00183-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s43556-024-00183-1/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s43556-024-00183-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
17
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05164-x",
"author": "P Katulanda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1440",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "183_CR1",
"unstructured": "Katulanda P, Dissanayake HA, Ranathunga I, Ratnasamy V, Wijewickrama PSA, Yogendranathan N, et al. Prevention and management of COVID-19 among patients with diabetes: an appraisal of the literature. Diabetologia. 2020;63(8):1440–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-020-05164-x.",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021",
"author": "L Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1068",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "183_CR2",
"unstructured": "Zhu L, She ZG, Cheng X, Qin JJ, Zhang XJ, Cai J, et al. Association of blood glucose control and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2020;31(6):1068–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"author": "EJ Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "430",
"issue": "7821",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "183_CR3",
"unstructured": "Williamson EJ, Walker AJ, Bhaskaran K, Bacon S, Bates C, Morton CE, et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature. 2020;584(7821):430–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4.",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"author": "C Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "183_CR4",
"unstructured": "Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30183-5.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dbi20-0022",
"author": "R Gianchandani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2048",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "183_CR5",
"unstructured": "Gianchandani R, Esfandiari NH, Ang L, Iyengar J, Knotts S, Choksi P, et al. Managing hyperglycemia in the COVID-19 inflammatory storm. Diabetes. 2020;69(10):2048–53. https://doi.org/10.2337/dbi20-0022.",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.07.015",
"author": "OMP Jolobe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "208",
"journal-title": "Am J Emerg Med",
"key": "183_CR6",
"unstructured": "Jolobe OMP. Post-COVID-19 diabetes in the context of long COVID. Am J Emerg Med. 2022;61:208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2022.07.015.",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139585",
"author": "S Kunal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "633",
"issue": "1162",
"journal-title": "Postgrad Med J",
"key": "183_CR7",
"unstructured": "Kunal S, Madan M, Tarke C, Gautam DK, Kinkar JS, Gupta K, et al. Emerging spectrum of post-COVID-19 syndrome. Postgrad Med J. 2022;98(1162):633–43. https://doi.org/10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139585.",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.03.002",
"author": "R Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "211",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "183_CR8",
"unstructured": "Gupta R, Ghosh A, Singh AK, Misra A. Clinical considerations for patients with diabetes in times of COVID-19 epidemic. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020;14(3):211–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.03.002.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12933-020-01090-9",
"author": "M Longo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "115",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Diabetol",
"key": "183_CR9",
"unstructured": "Longo M, Caruso P, Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Giugliano D, Esposito K. Treating type 2 diabetes in COVID-19 patients: the potential benefits of injective therapies. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020;19(1):115. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-020-01090-9.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2022.110157",
"author": "LE Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110157",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "183_CR10",
"unstructured": "Chan LE, Casiraghi E, Laraway B, Coleman B, Blau H, Zaman A, et al. Metformin is associated with reduced COVID-19 severity in patients with prediabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;194:110157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2022.110157.",
"volume": "194",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.784459",
"author": "CJ Bailey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "784459",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "183_CR11",
"unstructured": "Bailey CJ, Gwilt M. Diabetes, metformin and the clinical course of Covid-19: outcomes, mechanisms and suggestions on the therapeutic use of metformin. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:784459. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.784459.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv26873",
"author": "CT Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4273",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "183_CR12",
"unstructured": "Bramante CT, Buse J, Tamaritz L, Palacio A, Cohen K, Vojta D, et al. Outpatient metformin use is associated with reduced severity of COVID-19 disease in adults with overweight or obesity. J Med Virol. 2021;93(7):4273–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv26873.",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.022",
"author": "R Ghany",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "513",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "183_CR13",
"unstructured": "Ghany R, Palacio A, Dawkins E, Chen G, McCarter D, Forbes E, et al. Metformin is associated with lower hospitalizations, mortality and severe coronavirus infection among elderly medicare minority patients in 8 states in USA. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021;15(2):513–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.022.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.014",
"author": "B Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "65",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "183_CR14",
"unstructured": "Yu B, Li C, Sun Y, Wang DW. Insulin treatment is associated with increased mortality in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2021;33(1):65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.014.",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30152-2",
"author": "SR Bornstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "546",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "183_CR15",
"unstructured": "Bornstein SR, Rubino F, Khunti K, Mingrone G, Hopkins D, Birkenfeld AL, et al. Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8(6):546–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30152-2.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30405-8",
"author": "SJ McGurnaghan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "82",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "183_CR16",
"unstructured": "McGurnaghan SJ, Weir A, Bishop J, Kennedy S, Blackbourn LAK, McAllister DA, et al. Risks of and risk factors for COVID-19 disease in people with diabetes: a cohort study of the total population of Scotland. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9(2):82–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30405-8.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab493",
"author": "Y Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "630",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "183_CR17",
"unstructured": "Zhang Y, Luo W, Li Q, Wang X, Chen J, Song Q, et al. Risk factors for death among the First 80 543 coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases in China: relationships between age, underlying disease, case severity, and region. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;74(4):630–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab493.",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"author": "F Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1054",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "183_CR18",
"unstructured": "Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30566-3.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108346",
"author": "L Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108346",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "183_CR19",
"unstructured": "Guo L, Shi Z, Zhang Y, Wang C, Do Vale Moreira NC, Zuo H, et al. Comorbid diabetes and the risk of disease severity or death among 8807 COVID-19 patients in China: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;166:108346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108346.",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12933-022-01657-8",
"author": "G Llauradó",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "216",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Diabetol",
"key": "183_CR20",
"unstructured": "Llauradó G, Vlacho B, Wargny M, Ruan Y, Franch-Nadal J, Domingo P, et al. The association between macrovascular complications and intensive care admission, invasive mechanical ventilation, and mortality in people with diabetes hospitalized for coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022;21(1):216. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-022-01657-8.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"author": "D Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1061",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "183_CR21",
"unstructured": "Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1061–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.1585.",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "183_CR22",
"unstructured": "The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41(2):145−51. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.003."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4081/jphr.2016.733",
"author": "A Badawi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "733",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Public Health Res",
"key": "183_CR23",
"unstructured": "Badawi A, Ryoo SG. Prevalence of diabetes in the 2009 Influenza A (H1N1) and the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Public Health Res. 2016;5(3):733. https://doi.org/10.4081/jphr.2016.733.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1464-5491.2006.01861.x",
"author": "JK Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "623",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Diabet Med",
"key": "183_CR24",
"unstructured": "Yang JK, Feng Y, Yuan MY, Yuan SY, Fu HJ, Wu BY, et al. Plasma glucose levels and diabetes are independent predictors for mortality and morbidity in patients with SARS. Diabet Med. 2006;23(6):623–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2006.01861.x.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"author": "M Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "271",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "183_CR25",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181(2):271–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052.",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms18030563",
"author": "H Roca-Ho",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "563",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "183_CR26",
"unstructured": "Roca-Ho H, Riera M, Palau V, Pascual J, Soler MJ. Characterization of ACE and ACE2 expression within different organs of the NOD mouse. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030563.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-med-042220-011857",
"author": "AK Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Med",
"key": "183_CR27",
"unstructured": "Singh AK, Khunti K. COVID-19 and diabetes. Annu Rev Med. 2022;73:129–47.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013",
"author": "X Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "537",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "183_CR28",
"unstructured": "Cheng X, Liu YM, Li H, Zhang X, Lei F, Qin JJ, et al. Metformin is Associated with higher incidence of Acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2020;32(4):537–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"author": "DE Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "459",
"issue": "7816",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "183_CR29",
"unstructured": "Gordon DE, Jang GM, Bouhaddou M, Xu J, Obernier K, White KM, et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature. 2020;583(7816):459–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9.",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.148003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "183_CR30",
"unstructured": "Schaller MA, Sharma Y, Dupee Z, Nguyen D, Urueña J, Smolchek R, et al. Ex vivo SARS-CoV-2 infection of human lung reveals heterogeneous host defense and therapeutic responses. JCI Insight. 2021;6. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.148003."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-97441-x",
"author": "TS Postler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "18721",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "183_CR31",
"unstructured": "Postler TS, Peng V, Bhatt DM, Ghosh S. Metformin selectively dampens the acute inflammatory response through an AMPK-dependent mechanism. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):18721. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-97441-x.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2021.05.004",
"author": "H Xian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1463",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "183_CR32",
"unstructured": "Xian H, Liu Y, Rundberg Nilsson A, Gatchalian R, Crother TR, Tourtellotte WG, et al. Metformin inhibition of mitochondrial ATP and DNA synthesis abrogates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pulmonary inflammation. Immunity. 2021;54(7):1463–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2021.05.004.",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2201662",
"author": "CT Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "599",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "183_CR33",
"unstructured": "Bramante CT, Huling JD, Tignanelli CJ, Buse JB, Liebovitz DM, Nicklas JM, et al. Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(7):599–610. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2201662.",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2009.12.020",
"author": "G Ritchie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "257",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "183_CR34",
"unstructured": "Ritchie G, Harvey DJ, Feldmann F, Stroeher U, Feldmann H, Royle L, et al. Identification of N-linked carbohydrates from severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) spike glycoprotein. Virology. 2010;399(2):257–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2009.12.020.",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.01250-12",
"author": "M Fukushi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11745",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "183_CR35",
"unstructured": "Fukushi M, Yoshinaka Y, Matsuoka Y, Hatakeyama S, Ishizaka Y, Kirikae T, et al. Monitoring of S protein maturation in the endoplasmic reticulum by calnexin is important for the infectivity of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J Virol. 2012;86(21):11745–53. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01250-12.",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bst20200505",
"author": "SJ Williams",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1287",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Biochem Soc Trans",
"key": "183_CR36",
"unstructured": "Williams SJ, Goddard-Borger ED. α-glucosidase inhibitors as host-directed antiviral agents with potential for the treatment of COVID-19. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020;48(3):1287–95. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst20200505.",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13050808",
"author": "S Rajasekharan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "808",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "183_CR37",
"unstructured": "Rajasekharan S, Milan Bonotto R, Nascimento Alves L, Kazungu Y, Poggianella M, Martinez-Orellana P, et al. Inhibitors of protein glycosylation are active against the coronavirus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Viruses. 2021;13(5):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050808.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/edm2.301",
"author": "J Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e00301",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol Diabetes Metab",
"key": "183_CR38",
"unstructured": "Li J, Wei Q, McCowen KC, Xiong W, Liu J, Jiang W, et al. Inpatient use of metformin and acarbose is associated with reduced mortality of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2022;5(1):e00301. https://doi.org/10.1002/edm2.301.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0723",
"author": "C Sardu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1408",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "183_CR39",
"unstructured": "Sardu C, D’Onofrio N, Balestrieri ML, Barbieri M, Rizzo MR, Messina V, et al. Outcomes in patients with hyperglycemia affected by COVID-19: can we do more on glycemic control? Diabetes Care. 2020;43(7):1408–15. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc20-0723.",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3158",
"author": "W Jia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e3158",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev",
"key": "183_CR40",
"unstructured": "Jia W, Weng J, Zhu D, Ji L, Lu J, Zhou Z, et al. Standards of medical care for type 2 diabetes in China 2019. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2019;35(6):e3158. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3158.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1186/s43556-024-00183-1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effects of different treatments for type 2 diabetes mellitus on mortality of coronavirus disease from 2019 to 2021 in China: a multi-institutional retrospective study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "5"
}
