Inpatient use of metformin and acarbose is associated with reduced mortality of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
et al., Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1002/edm2.301, Sep 2021
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
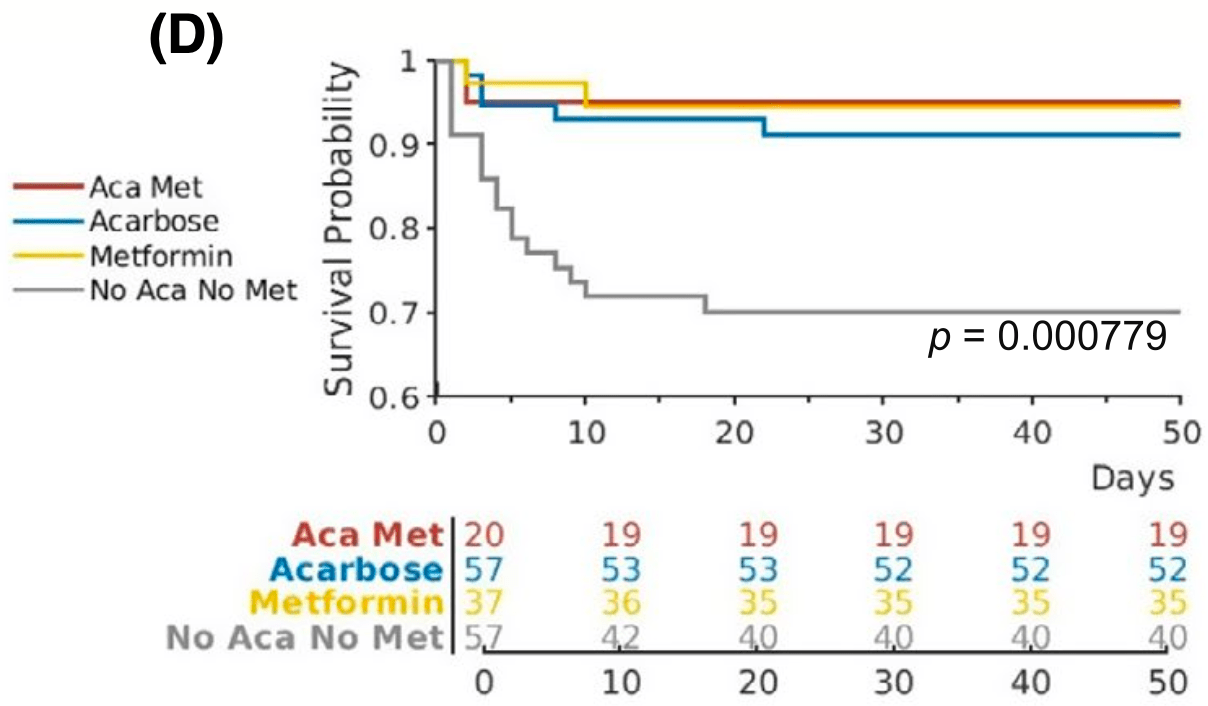
Retrospective 131 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes, showing lower mortality with metformin treatment and acarbose treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
|
risk of death, 75.8% lower, RR 0.24, p = 0.02, treatment 2 of 37 (5.4%), control 21 of 94 (22.3%), NNT 5.9.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Li et al., 29 Sep 2021, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 13 authors.
Contact: nianxiong@hust.edu.cn, wxli@health.ucsd.edu.
Inpatient use of metformin and acarbose is associated with reduced mortality of COVID‐19 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1002/edm2.301
This is an open access article under the terms of the Creat ive Commo ns Attri bution License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
DATA AVA I L A B I L I T Y S TAT E M E N T The data that support the findings of this study are available upon request from the lead author, J.L.
O RCI D Willis X. Li https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9041-7341
R E FE R E N C E S
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of covid-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Bergmark, Bhatt, Mcguire, Metformin use and clinical outcomes among patients with diabetes mellitus with or without heart failure or kidney dysfunction: observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 trial, Circulation
Berlin, Gulick, Martinez, Severe covid-19, N Engl J Med
Clement, Braithwaite, Magee, Management of diabetes and hyperglycemia in hospitals, Diabetes Care
Gabir, Hanson, Dabelea, Plasma glucose and prediction of microvascular disease and mortality: evaluation of 1997 American diabetes association and 1999 world health organization criteria for diagnosis of diabetes, Diabetes Care
Geleris, Sun, Platt, Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Gu, Shi, Tang, Comparison of glucose lowering effect of metformin and acarbose in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a metaanalysis, PLoS One
Gu, Wang, Li, Analyses of gut microbiota and plasma bile acids enable stratification of patients for antidiabetic treatment, Nat Commun
Hanefeld, The role of acarbose in the treatment of noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, J Diabetes Complications
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid-19-preliminary report, N Engl J Med
Jarcho, Ingelfinger, Hamel, Agostino, Harrington, Inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and covid-19, N Engl J Med
Jia, Weng, Zhu, Standards of medical care for type 2 diabetes in China 2019, Diabetes Metab Res Rev
Kavanagh, Mccowen, Clinical practice. glycemic control in the ICU, N Engl J Med
Li, Wei, Li, Metformin use in diabetes prior to hospitalization: effects on mortality in covid-19, Endocr Pract
Malhotra, Hepokoski, Mccowen, Shyy, Metformin, and COVID-19, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2020.101425
Malhotra, Intensive insulin in intensive care, N Engl J Med
Mo, Liu, Ma, Effects of acarbose and metformin on the inflammatory state in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients: a one-year randomized clinical study, Drug Des Devel Ther
Rosas, Bräu, Waters, Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe Covid-19 Pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Rosenberg, Dufort, Udo, Association of treatment with hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York State, JAMA
Salama, Han, Yau, Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Stone, Frigault, Boyd, Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Venter, Richter, Towards effective diagnostic assays for COVID-19: a review, J Clin Pathol
Wang, Zhang, Du, Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk Factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med
Xu, Han, Li, Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/edm2.301",
"ISSN": [
"2398-9238",
"2398-9238"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/edm2.301",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/edm2.301"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-07-05"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-09-18"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-09-29"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine University of California La Jolla California USA"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jinghong",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology Wuhan Red Cross Hospital Wuhan Hubei China"
}
],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Qi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine University of California La Jolla California USA"
}
],
"family": "McCowen",
"given": "Karen C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology Wuhan Red Cross Hospital Wuhan Hubei China"
}
],
"family": "Xiong",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology Wuhan Red Cross Hospital Wuhan Hubei China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Jiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology Wuhan Red Cross Hospital Wuhan Hubei China"
}
],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Wenlijun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine University of California La Jolla California USA"
}
],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Robert L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine University of California La Jolla California USA"
}
],
"family": "Hepokoski",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine University of California La Jolla California USA"
}
],
"family": "He",
"given": "Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine University of California La Jolla California USA"
}
],
"family": "Shyy",
"given": "John Y. J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine University of California La Jolla California USA"
}
],
"family": "Malhotra",
"given": "Atul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology Wuhan Red Cross Hospital Wuhan Hubei China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Neurology Union Hospital Tongji Medical College Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wuhan Hubei China"
}
],
"family": "Xiong",
"given": "Nian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9041-7341",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine University of California La Jolla California USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Li",
"given": "Willis X.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism",
"container-title-short": "Endocrino Diabet & Metabol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-29T20:27:59Z",
"timestamp": 1632947279000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-12T17:42:45Z",
"timestamp": 1642009365000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100008897",
"award": [
"R01HL085188",
"R01HL125643"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Nihon Superior"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-13T10:07:57Z",
"timestamp": 1665655677570
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1632873600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1632873600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/edm2.301",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/edm2.301",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/edm2.301",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
29
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_2_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid‐19‐preliminary report",
"author": "Horby P",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "e_1_2_8_3_1",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009575",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diacare.27.2.553",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3158",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp1001115",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe058304",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2020.101425",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1056-8727(97)00123-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-017-01682-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206685",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diacare.23.8.1113",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2012410",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.8630",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028700",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028836",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2030340",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe2012924",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.040144",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0126704",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/DDDT.S208327",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_27_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 26,
"references-count": 26,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/edm2.301"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Inpatient use of metformin and acarbose is associated with reduced mortality of COVID‐19 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "5"
}
