Metformin for Long COVID: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
et al., Authorea Inc., doi:10.22541/au.176460133.31712164/v1, Dec 2025
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
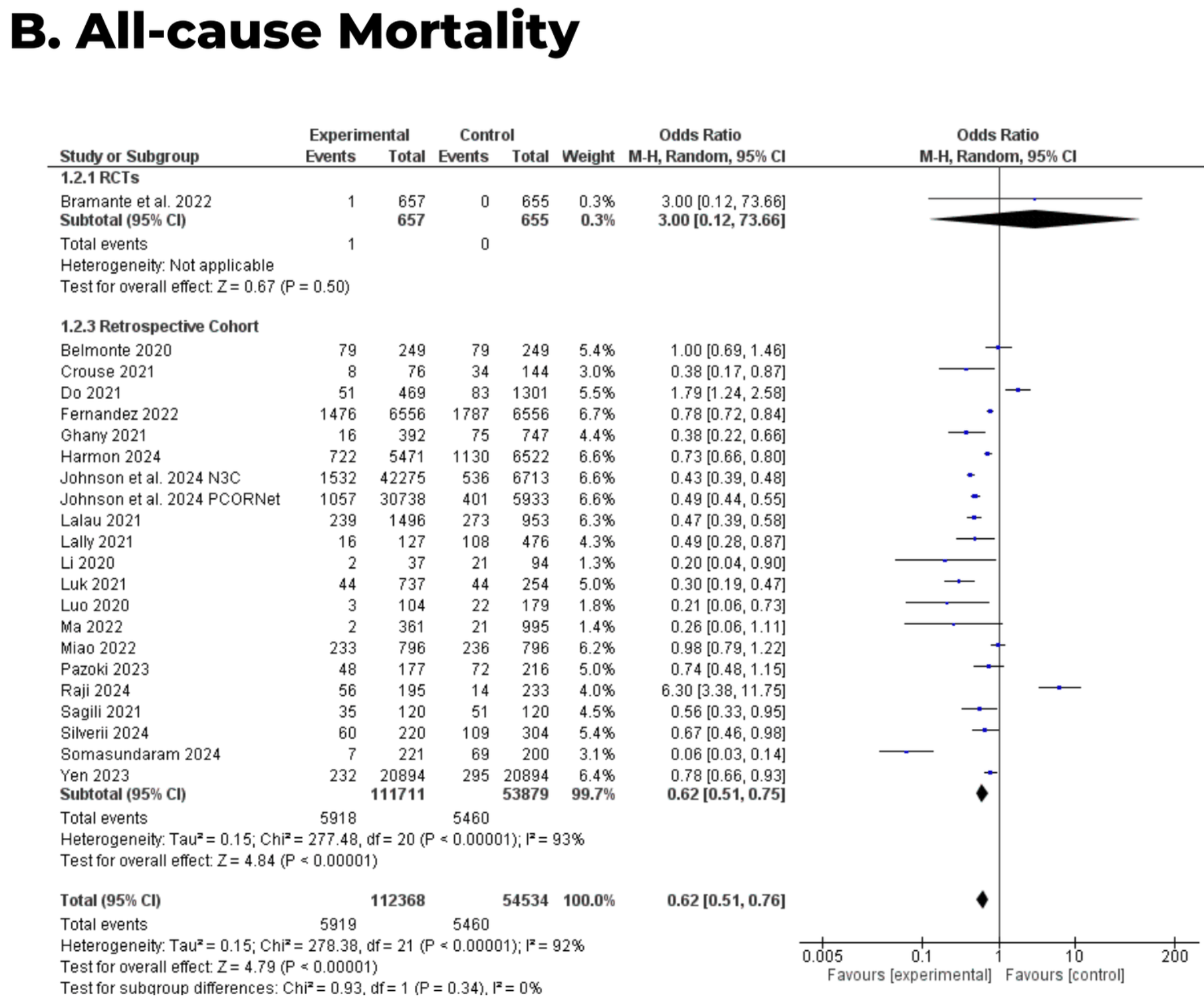
Systematic review and meta-analysis of 26 studies showing lower mortality, hospitalization, and long COVID wiht metformin treatment.
24 meta-analyses show significant improvements with metformin for mortality1-23,
hospitalization7,13,23 ,
progression1, and
severity8,9,13 .
Currently there are 110 metformin for COVID-19 studies, showing 36% lower mortality [32‑40%], 29% lower ventilation [12‑43%], 19% lower ICU admission [8‑28%], 17% lower hospitalization [11‑23%], and 5% fewer cases [-4‑13%].
1.
Yang et al., The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977.
2.
Lukito et al., The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006.
3.
Kow et al., Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26498.
4.
Hariyanto et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obesity Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290.
5.
Ma et al., Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282210.
6.
Parveen et al., Association of Metformin with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India), doi:10.1055/s-0042-1760353.
7.
Li et al., Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.704666.
8.
Schlesinger et al., Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-023-05928-1.
9.
Petrelli et al., Metformin and Covid-19: a systematic review of systematic reviews with meta-analysis, Acta Biomedica Atenei Parmensis, doi:10.23750/abm.v94iS3.14405.
10.
Oscanoa et al., Metformin therapy and severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a meta-analysis, Clinical Diabetology, doi:10.5603/DK.a2021.0035.
11.
Kan et al., Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.708494.
12.
Poly et al., Metformin Use Is Associated with Decreased Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes: Evidence from Retrospective Studies and Biological Mechanism, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10163507.
13.
Song et al., The Effect of Antihyperglycemic Medications on COVID-19: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review from Observational Studies, Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science, doi:10.1007/s43441-024-00633-6.
14.
Ganesh et al., Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15258.
15.
Nassar et al., Noninsulin‐based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis, Journal of Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13359.
16.
Zhan et al., Effect of Antidiabetic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/10600280221133577.
17.
Nguyen et al., Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155196.
18.
Han et al., Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002.
19.
Chen et al., The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458.
20.
Scheen, A., Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006.
21.
Sun et al., Is Metformin Use Associated With a Decreased Mortality for COVID-19 Diabetic Patients? A Meta-Analysis, Journal of the Endocrine Society, doi:10.1210/jendso/bvab048.709.
Ling et al., 1 Dec 2025, Malaysia, preprint, 4 authors.
Metformin for Long COVID: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
doi:10.22541/au.176460133.31712164/v1
Background: Long COVID affects millions worldwide, yet no therapy has shown consistent benefit. Early studies suggest metformin may reduce long COVID risk, but its impact on both long COVID and acute COVID-19 severity has not been fully synthesized. This study evaluated whether metformin lowers long COVID incidence and acute severe outcomes. Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational cohort studies of adults with SARS-CoV-2 infection comparing metformin with placebo or standard care. Random-effects models using adjusted estimates were applied, and heterogeneity was assessed with the I 2 statistic. Findings: Twenty-six studies ( n=181,197) were included; five reported long COVID outcomes and 23 reported acute outcomes. Metformin was associated with a reduced risk of long COVID (OR 0.79, 95% CI 0.71-0.89; I 2 =0%), consistent across study designs. During acute illness, metformin was linked to lower all-cause mortality (OR 0.62, 95% CI 0.51-0.76) and hospitalisation (OR 0.74, 95% CI 0.61-0.89). Associations with ICU admission favored metformin but were not statistically significant, and a non-significant increase in mechanical ventilation risk was observed. Interpretation: Metformin may lower the risk of long COVID; its low cost, safety, and accessibility make it a promising option needing confirmation in large, high-quality randomized trials.
Hosted file Manuscript_Metformin for Long COVID.docx available at https://authorea.com/users/1005634/ articles/1365931-metformin-for-long-covid-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis
Posted on 1 Dec 2025 -The copyright holder is the author/funder. All rights reserved. No reuse without permission. - https://doi.org/10.22541/au.176460133.31712164/v1 -This is a preprint and has not been peer-reviewed. Data may be preliminary. Tables_Metformin for Long COVID.docx available at https://authorea.com/users/1005634/ articles/1365931-metformin-for-long-covid-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.22541/au.176460133.31712164/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.22541/au.176460133.31712164/v1",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
1
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Monash University Malaysia Jeffrey Cheah School of Medicine and Health Sciences"
}
],
"family": "Ling",
"given": "Victor Shiing Hieng",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Monash University Malaysia Jeffrey Cheah School of Medicine and Health Sciences"
}
],
"family": "Ling",
"given": "Chieng Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Monash University Malaysia Jeffrey Cheah School of Medicine and Health Sciences"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Ling Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0000-3324-8705",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Monash University Malaysia Jeffrey Cheah School of Medicine and Health Sciences"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Low",
"given": "Zhen Xuen Brandon",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-01T15:02:17Z",
"timestamp": 1764601337000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-01T15:02:17Z",
"timestamp": 1764601337000
},
"group-title": "Preprints",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-01T15:04:55Z",
"timestamp": 1764601495294,
"version": "3.46.0"
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Authorea Inc."
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
1
]
]
},
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
1
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.22541",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.authorea.com/users/1005634/articles/1365931-metformin-for-long-covid-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis?commit=f3b04bedb87e5e5e61aab6b56912306991c0a0b3"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Metformin for Long COVID: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"type": "posted-content"
}
