Metformin Effectiveness in Reducing Mortality among Covid-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at a Tertiary Hospital in Indonesia
et al., Folia Medica Indonesiana, doi:10.20473/fmi.v59i3.46944, Sep 2023
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
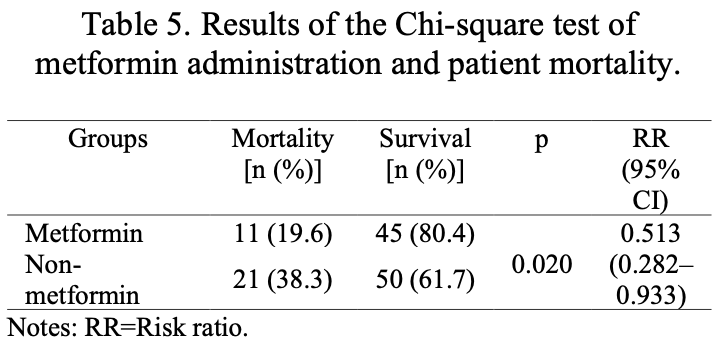
Retrospective 137 hospitalized mild to moderate COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes in Indonesia, showing a significantly lower mortality with metformin treatment.
|
risk of death, 48.7% lower, RR 0.51, p = 0.02, treatment 11 of 56 (19.6%), control 31 of 81 (38.3%), NNT 5.4.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zihono et al., 10 Sep 2023, retrospective, Indonesia, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: hany.yusmaini@gmail.com.
Metformin Effectiveness in Reducing Mortality among Covid-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at a Tertiary Hospital in Indonesia
Folia Medica Indonesiana, doi:10.20473/fmi.v59i3.46944
COVID-19 patients with comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes (T2DM), have a higher mortality rate compared to those without any comorbidities. T2DM patients usually receive metformin as their first-line treatment. However, the effectiveness of metformin in reducing mortality rates still requires further analysis. The objective of this study was to analyze the effectiveness of metformin in reducing mortality rates among COVID-19 patients with T2DM. An analytic observational design with a retrospective cohort approach was used in this study. Samples were acquired from hospitalized COVID-19 patients with T2DM medical records at Fatmawati Central General Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia, throughout 2020-2021. The samples were collected using a purposive sampling technique and analyzed using Chi-square test (p<0.05; RR<1). This study comprised 137 samples, with 56 samples receiving metformin and 81 not receiving metformin. The mortality rate in the sample group that received metformin was lower (19.6%) compared to the group that was not given the medication (38.3%). The Chi-square test results indicated a statistically significant relationship between metformin treatment and a lower mortality rate among COVID-19-contracted individuals with T2DM (p=0.020; RR=0.513). Therefore, this study concludes that the administration of metformin treatment reduces mortality among COVID-19 patients with T2DM.
Conflict of interest None.
Ethical consideration The study was ethically approved on 11/4/2023 by the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Pembangunan Nasional "Veteran" Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia, with approval letter No. 76/IV/2023/KEPK.
Author contribution YZ contributed to the conception and design, analysis and interpretation of the data, drafting of the article, and statistical expertise. HY, UH, EH, and DB contributed to the critical revision of the article for important intellectual content, final approval of the article, and statistical expertise. MIM contributed to the critical revision of the article for important intellectual content, final approval of the article, provision of study materials, and statistical expertise.
References
Alexaki, Henneicke, The role of glucocorticoids in the management of COVID-19, Hormone and Metabolic Research, doi:http://www.thieme-connect.de/DOI/DOI?10.1055/a-1300-2550
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort analysis, The Lancet Healthy Longevity, doi:10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7
Burhan, Susanto, Isbaniah, Pedoman tatalaksana COVID-19 edisi 4
Bwire, Coronavirus: Why men are more vulnerable to COVID-19 than women?, SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine, doi:10.1007/s42399-020-00341-w
Carfora, Spiniello, Ricciolino, Anticoagulant treatment in COVID-19: A narrative review, Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis, doi:10.1007/s11239-020-02242-0
Chen, Lv, Lin, The association between antidiabetic agents and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with diabetes: A bayesian network meta-analysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.895458/full
Cheng, Liu, Li, Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013
El Chakhtoura, Bonomo, Jump, Influence of aging and environment on presentation of infection in older adults, Infectious Disease Clinics of North America, doi:10.1016/j.idc.2017.07.017
Giorgino, Bhana, Czupryniak, Management of patients with diabetes and obesity in the COVID-19 era: Experiences and learnings from South and East Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108617
Groff, Kavanaugh, Ramgobin, Gastrointestinal manifestations of COVID-19: A review of what we know, Ochsner Journal, doi:10.31486/toj.20.0086
Harbuwono, Handayani, Wahyuningsih, Impact of diabetes mellitus on COVID-19 clinical symptoms and mortality: Jakarta's COVID-19 epidemiological registry, Primary Care Diabetes, doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2021.11.002
Holly, Biernacka, Maskell, Obesity, diabetes and COVID-19: An infectious disease spreading from the east collides with the consequences of an unhealthy western lifestyle, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.582870/full
Inzucchi, Management of diabetes mellitus in hospitalized patients
Jiang, Chen, Liu, Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619
John, Jacob, Kontoyiannis, When uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and severe COVID-19 converge: The perfect storm for mucormycosis, Journal of Fungi, doi:10.3390/jof7040298
Kamyshnyi, Matskevych, Lenchuk, Metformin to decrease COVID-19 severity and mortality: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112230
Kan, Zhang, Han, Mortality risk of antidiabetic agents for type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: A systematic review and metaanalysis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.708494/full
Kristanti, Yulia, Herawati, Analysis of antibiotic use in COVID-19 patients at a hospital in Sidoarjo, Jurnal Farmasi dan Ilmu Kefarmasian Indonesia, doi:10.20473/jfiki.v9i22022.200-208
Kshanti, Aji, Epriliawati, Clinical presentation and outcome of COVID-19 infection in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A preliminary data from a tertiary hospital in Jakarta during the early days of the pandemic, Bali Medical Journal, doi:10.15562/bmj.v9i3.1969
Lally, Tsoukas, Halladay, Metformin is associated with decreased 30-day mortality among nursing home residents infected with SARS-CoV2, Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.031
Li, Wei, Mccowen, Inpatient use of metformin and acarbose is associated with reduced mortality of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1002/edm2.301
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Mirani, Favacchio, Carrone, Impact of comorbidities and glycemia at admission and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in patients with Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A case series from an Academic Hospital in Lombardy, Italy, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1340
Nguyen, Ho, Nguyen, Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155196
Ouchi, Vilaplana-Carnerero, De Dios, Antidiabetic treatment and COVID-19 Outcomes: A population-based cohort study in primary health care in Catalonia during the first wave of the pandemic, Primary Care Diabetes, doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2022.10.001
Sutriyawan, Metodologi penelitian kedokteran dan kesehatan (dilengkapi tuntunan membuat proposal penelitian
Wang, Amin, Khanna, An observational cohort study of bacterial coinfection and implications for empirical antibiotic therapy in patients presenting with COVID-19 to hospitals in North West London, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dkaa475
Woolcott, Castilla-Bancayán, The effect of age on the association between diabetes and mortality in adult patients with COVID-19 in Mexico, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-88014-z
Yang, Sun, Zhang, The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108977
Yitao, Mu, Ling, Predictors of clinical deterioration in non-severe patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study, Current Medical Research and Opinion, doi:10.1080/03007995.2021.1876005
Zhang, Kong, Xia, Impaired fasting glucose and diabetes are related to higher risks of complications and mortality among patients with Coronavirus Disease, Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.00525/full
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.20473/fmi.v59i3.46944",
"ISSN": [
"2599-056X",
"2355-8393"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.20473/fmi.v59i3.46944",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Highlights:\n1. As there is a scarcity of publications on the use of metformin for COVID-19 in Indonesia, the findings of this present study may contribute more insight to the existing body of research and provide data specific to the Southeast Asian population.2. This study revealed a decreased mortality rate associated with metformin use in diabetic patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 infection.3. This study suggests that diabetic patients may continue metformin treatment during a COVID-19 infection as the medication has sustained therapeutic effects.\n \nAbstract\nCOVID-19 patients with comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes (T2DM), have a higher mortality rate compared to those without any comorbidities. T2DM patients usually receive metformin as their first-line treatment. However, the effectiveness of metformin in reducing mortality rates still requires further analysis. The objective of this study was to analyze the effectiveness of metformin in reducing mortality rates among COVID-19 patients with T2DM. An analytic observational design with a retrospective cohort approach was used in this study. Samples were acquired from hospitalized COVID-19 patients with T2DM medical records at Fatmawati Central General Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia, throughout 2020–2021. The samples were collected using a purposive sampling technique and analyzed using Chi-square test (p<0.05; RR<1). This study comprised 137 samples, with 56 samples receiving metformin and 81 not receiving metformin. The mortality rate in the sample group that received metformin was lower (19.6%) compared to the group that was not given the medication (38.3%). The Chi-square test results indicated a statistically significant relationship between metformin treatment and a lower mortality rate among COVID-19-contracted individuals with T2DM (p=0.020; RR=0.513). Therefore, this study concludes that the administration of metformin treatment reduces mortality among COVID-19 patients with T2DM.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yudivaniel Zihono",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hany Yusmaini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Uswatun Hasanah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Erna Harfiani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Md Ikhsan Mokoagow",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dicky Budiman",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Folia Medica Indonesiana",
"container-title-short": "FMI",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-07T01:50:07Z",
"timestamp": 1701913807000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-07T01:50:14Z",
"timestamp": 1701913814000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-07T05:37:11Z",
"timestamp": 1701927431166
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
10
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1694304000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://e-journal.unair.ac.id/FMI/article/download/46944/27185",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://e-journal.unair.ac.id/FMI/article/download/46944/27185",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8420",
"original-title": [],
"page": "267-273",
"prefix": "10.20473",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Universitas Airlangga",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://e-journal.unair.ac.id/FMI/article/view/46944"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Engineering"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Metformin Effectiveness in Reducing Mortality among Covid-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at a Tertiary Hospital in Indonesia",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "59"
}
