Metformin use and risk of COVID-19 among patients with type II diabetes mellitus: an NHIS-COVID-19 database cohort study
et al., Acta Diabetologica, doi:10.1007/s00592-020-01666-7, Feb 2021
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
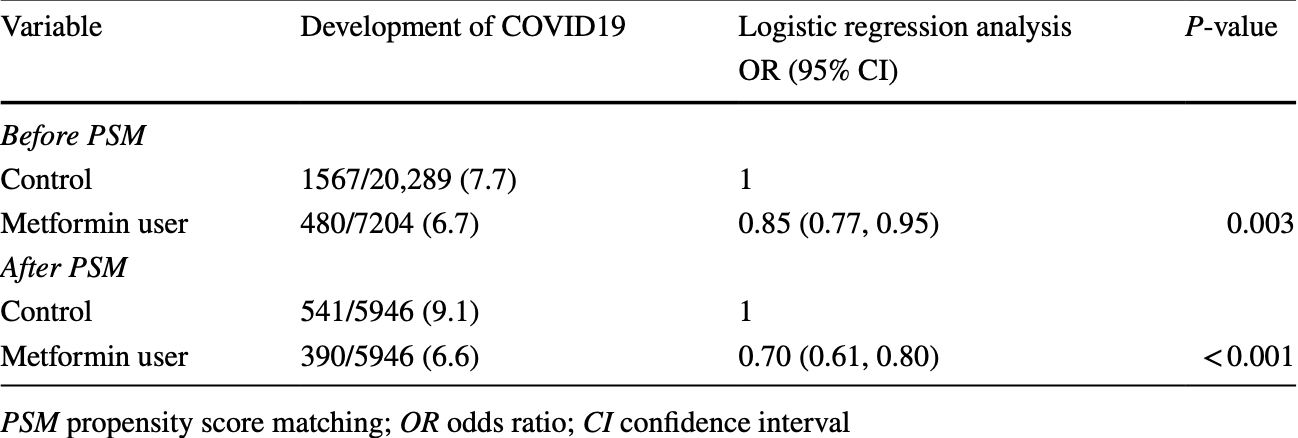
Retrospective 27,493 type II diabetes patients in the USA, 7,204 on metformin, showing significantly lower COVID-19 cases, but no significant difference in mortality.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 26.0% higher, OR 1.26, p = 0.30, treatment 5,946, control 5,946, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 28.0% lower, RR 0.72, p < 0.001, treatment 390 of 5,946 (6.6%), control 541 of 5,946 (9.1%), NNT 39, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, propensity score matching.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Oh et al., 13 Feb 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
Metformin use and risk of COVID-19 among patients with type II diabetes mellitus: an NHIS-COVID-19 database cohort study
Acta Diabetologica, doi:10.1007/s00592-020-01666-7
Aims The relationship between metformin therapy and the risk of coronavirus disease has not been reported among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). We aimed to investigate whether metformin therapy was associated with the incidence of COVID-19 among type 2 DM patients in South Korea. Methods The National Health Insurance Service-COVID-19 cohort database, comprising COVID-19 patients from 1 January 2020 to 4 June 2020, was used for this study. Among them, adult patients with type 2 DM were included in this study. Metformin users were defined as those who had been prescribed continuous oral metformin for over a period of ≥ 90 days, and the control group was defined as all other patients. Results Overall, 27,493 patients with type 2 DM (7204, metformin user group; 20,289, control group) were included. After propensity score matching, 11,892 patients (5946 patients in each group) were included in the final analysis. In the logistic regression analysis, the odds of metformin users developing COVID-19 was 30% lower than that of the control group [odds ratio (OR): 0.70, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.61-0.80; P < 0.001]. However, in the multivariate model, metformin use was not associated with hospital mortality when compared with that of the control group (OR: 1.26, 95% CI: 0.81-1.95; P = 0.301). Conclusions Metformin therapy might have potential benefits for the prevention of COVID-19 among patients with type 2 DM in South Korea. However, it did not affect the hospital mortality of type 2 DM patients diagnosed with COVID-19.
Keywords Antidiabetic drug • Cohort study • Metformin • Type 2 diabetes Managed by Massimo Federici .
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https ://doi.org/10.1007/s0059 2-020-01666 -7. Author contributions TK Oh designed the study, analysed the data, interpreted the data, and drafted the manuscript; In-Ae Song contributed to the study conceptualization, acquisition of data, and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have given approved the final version of the manuscript.
Data availability The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Compliance with ethical standards Conflicts of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (X-2004-604-905) and the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (NHIS-2020-1-291).
Informed consent The requirement of informed consent was waived because data analyses were performed retrospectively using anonymised data retrieved from the South Korean National Health Insurance Service database. Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Apicella, Campopiano, Mantuano, Mazoni, Coppelli et al., COVID-19 in people with diabetes: understanding the reasons for worse outcomes, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30238-2
Bailey, Metformin: historical overview, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4318-z
Bedford, Enria, Giesecke, COVID-19: towards controlling of a pandemic, The Lancet
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with Covid-19, doi:10.1101/2020.06.19.20135095
Cai, Sex difference and smoking predisposition in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30117-X
Cameron, Morrison, Levin, Anti-Inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445
Clements, Gao, Yeap, Wong, Ali et al., Metformin in prostate cancer: two for the price of one, Ann Oncol, doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr037
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with Covid-19 and diabetes, doi:10.1101/2020.07.29.20164020
El-Arabey, Abdalla, Metformin and COVID-19: a novel deal of an old drug, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25958
Elm, Altman, Egger, Pocock, Gøtzsche et al., The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies, Ann Intern Med
Esam, A proposed mechanism for the possible therapeutic potential of Metformin in COVID-19, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108282
Gu, Mack, sis using electronic health records data in Michigan medicine, doi:10.1101/2020.06.16.20133140
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Ingraham, Barakat, Reilkoff, Understanding the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-SARS-CoV axis: a comprehensive review, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00912-2020
Jang, Lee, Hong, Kwok, Cho et al., Metformin enhances the immunomodulatory potential of adiposederived mesenchymal stem cells through STAT1 in an animal model of lupus, Rheumatology, doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kez631
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Liu, Zheng et al., Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Moore, Report, Disparities in incidence of COVID-19 among underrepresented racial/ethnic groups in counties identified as hotspots during june 5-18, 2020-22 states
Negrotto, Farez, Correale, Immunologic effects of metformin and pioglitazone treatment on metabolic syndrome and multiple sclerosis, JAMA Neurol, doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.4807
Prattichizzo, Giuliani, Mensa, Pleiotropic effects of metformin: Shaping the microbiome to manage type 2 diabetes and postpone ageing, Ageing Res Rev, doi:10.1016/j.arr.2018.10.003
Qi, Qian, Zhang, Zhang, Single cell RNA sequencing of 13 human tissues identify cell types and receptors of human coronaviruses, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.044
Rosenbaum, Db, Reducing bias in observational studies using subclassification on the propensity score, J Am Stat Assoc
Rothan, Byrareddy, The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak, J Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433
Seifarth, Schehler, Schneider, Effectiveness of metformin on weight loss in non-diabetic individuals with obesity, Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes, doi:10.1055/s-0032-1327734
Sharma, Ray, Sadasivam, Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183
Solerte, 'addio, Trevisan, Sitagliptin treatment at the time of hospitalization was associated with reduced mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: a multicenter, case-control, retrospective, observational study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1521
Solerte, Sabatino, Galli, Fiorina, Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibition in COVID-19, Acta Diabetol, doi:10.1007/s00592-020-01539-z
Tu, Tu, Gao, Shao, Jjjoi, The epidemiological and clinical features of COVID-19 and lessons from this global infectious public health event
Tufan, Guler, Matucci-Cerinic, COVID-19, immune system response, hyperinflammation and repurposing antirheumatic drugs, Turk J Med Sci, doi:10.3906/sag-2004-168
Wang, Wang, Chen, Qin, Unique epidemiological and clinical features of the emerging 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) implicate special control measures, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25748
Zangrillo, Beretta, Scandroglio, Oh, Characteristics, treatment, outcomes and cause of death of invasively ventilated patients with COVID-19 ARDS in Milan. Italy, Crit Care Resusc 30, Ann Palliat Med, doi:10.21037/apm.2020.04.25
Zhou, Chi, Lv, Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19), Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3377
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592-020-01666-7",
"ISSN": [
"0940-5429",
"1432-5233"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00592-020-01666-7",
"alternative-id": [
"1666"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "7 September 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "26 December 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "13 February 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Compliance with ethical standards",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflicts of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (X-2004–604-905) and the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (NHIS-2020–1-291)."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Informed consent",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The requirement of informed consent was waived because data analyses were performed retrospectively using anonymised data retrieved from the South Korean National Health Insurance Service database."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oh",
"given": "Tak Kyu",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7814-4253",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Song",
"given": "In-Ae",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Acta Diabetologica"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-14T13:43:58Z",
"timestamp": 1613310238000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-10T08:12:28Z",
"timestamp": 1620634348000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-20T02:15:20Z",
"timestamp": 1639966520923
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 4,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0940-5429"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1432-5233"
}
],
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
13
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1613174400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1613174400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s00592-020-01666-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00592-020-01666-7/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s00592-020-01666-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "771-778",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
13
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
13
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25748",
"author": "Y Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "568",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "1666_CR1",
"unstructured": "Wang Y, Wang Y, Chen Y, Qin Q (2020) Unique epidemiological and clinical features of the emerging 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) implicate special control measures. J Med Virol 92(6):568–576. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25748",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.003",
"author": "Epidemiology Working Group for NCIP Epidemic Response, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "145",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi",
"key": "1666_CR2",
"unstructured": "Epidemiology Working Group for NCIP Epidemic Response, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (2020) The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 41(2):145–151. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.003",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30673-5",
"author": "J Bedford",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1015",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "The Lancet",
"key": "1666_CR3",
"unstructured": "Bedford J, Enria D, Giesecke J et al (2020) COVID-19: towards controlling of a pandemic. The Lancet 395(10229):1015–1018",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6933e1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1666_CR4",
"unstructured": "Moore JTJMM, Report MW (2020) Disparities in incidence of COVID-19 among underrepresented racial/ethnic groups in counties identified as hotspots during june 5–18, 2020—22 states, february–june 2020. 69"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433",
"author": "HA Rothan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102433",
"journal-title": "J Autoimmun",
"key": "1666_CR5",
"unstructured": "Rothan HA, Byrareddy SN (2020) The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. J Autoimmun 109:102433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4324/9781003141402-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1666_CR6",
"unstructured": "Tu H, Tu S, Gao S, Shao A, Sheng JJJoI (2020) The epidemiological and clinical features of COVID-19 and lessons from this global infectious public health event"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30117-X",
"author": "H Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e20",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "1666_CR7",
"unstructured": "Cai H (2020) Sex difference and smoking predisposition in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Respir Med 8(4):e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30117-X",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"author": "WJ Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1708",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "1666_CR8",
"unstructured": "Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y et al (2020) Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med 382(18):1708–1720. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.16.20133140",
"author": "T Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "1666_CR9",
"unstructured": "Gu T, Mack JA, Salvatore M et al (2020) COVID-19 outcomes, risk factors and associations by race: a comprehensive analysis using electronic health records data in Michigan medicine. medRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.16.20133140",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30238-2",
"author": "M Apicella",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "782",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "1666_CR10",
"unstructured": "Apicella M, Campopiano MC, Mantuano M, Mazoni L, Coppelli A, Del Prato S (2020) COVID-19 in people with diabetes: understanding the reasons for worse outcomes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 8(9):782–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30238-2",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-017-4318-z",
"author": "CJ Bailey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1566",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "1666_CR11",
"unstructured": "Bailey CJ (2017) Metformin: historical overview. Diabetologia 60(9):1566–1576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-017-4318-z",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.29.20164020",
"author": "A Crouse",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "1666_CR12",
"unstructured": "Crouse A, Grimes T, Li P et al (2020) Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with Covid-19 and diabetes. medRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.29.20164020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25958",
"author": "AA El-Arabey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "1666_CR13",
"unstructured": "El-Arabey AA, Abdalla M (2020) Metformin and COVID-19: a novel deal of an old drug. J Med Virol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25958",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108282",
"author": "Z Esam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "1666_CR14",
"unstructured": "Esam Z (2020) A proposed mechanism for the possible therapeutic potential of Metformin in COVID-19. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108282",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"author": "P Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "69",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "1666_CR15",
"unstructured": "Luo P, Qiu L, Liu Y, Liu XL, Zheng JL, Xue HY, Liu WH, Liu D, Li J (2020) Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 103(1):69–72. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3906/sag-2004-168",
"author": "A Tufan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Turk J Med Sci",
"key": "1666_CR16",
"unstructured": "Tufan A, Avanoglu Guler A, Matucci-Cerinic M (2020) COVID-19, immune system response, hyperinflammation and repurposing antirheumatic drugs. Turk J Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-2004-168",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445",
"author": "AR Cameron",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "652",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "1666_CR17",
"unstructured": "Cameron AR, Morrison VL, Levin D et al (2016) Anti-Inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status. Circ Res 119(5):652–665. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00912-2020",
"author": "NE Ingraham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "1666_CR18",
"unstructured": "Ingraham NE, Barakat AG, Reilkoff R et al (2020) Understanding the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-SARS-CoV axis: a comprehensive review. Eur Respir J. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00912-2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-147-8-200710160-00010",
"author": "E Von Elm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "573",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "1666_CR19",
"unstructured": "Von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP (2007) The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Ann Intern Med 147(8):573–577",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/01621459.1984.10478078",
"author": "PR Rosenbaum",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "516",
"issue": "387",
"journal-title": "J Am Stat Assoc",
"key": "1666_CR20",
"unstructured": "Rosenbaum PR, Rubin DB (1984) Reducing bias in observational studies using subclassification on the propensity score. J Am Stat Assoc 79(387):516–524",
"volume": "79",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/rheumatology/kez631",
"author": "SG Jang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1426",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Rheumatology (Oxford)",
"key": "1666_CR21",
"unstructured": "Jang SG, Lee J, Hong SM, Kwok SK, Cho ML, Park SH (2020) Metformin enhances the immunomodulatory potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells through STAT1 in an animal model of lupus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 59(6):1426–1438. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez631",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.4807",
"author": "L Negrotto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "520",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA Neurol",
"key": "1666_CR22",
"unstructured": "Negrotto L, Farez MF, Correale J (2016) Immunologic effects of metformin and pioglitazone treatment on metabolic syndrome and multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol 73(5):520–528. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.4807",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arr.2018.10.003",
"author": "F Prattichizzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "87",
"journal-title": "Ageing Res Rev",
"key": "1666_CR23",
"unstructured": "Prattichizzo F, Giuliani A, Mensa E et al (2018) Pleiotropic effects of metformin: Shaping the microbiome to manage type 2 diabetes and postpone ageing. Ageing Res Rev 48:87–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2018.10.003",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0032-1327734",
"author": "C Seifarth",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "27",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes",
"key": "1666_CR24",
"unstructured": "Seifarth C, Schehler B, Schneider HJ (2013) Effectiveness of metformin on weight loss in non-diabetic individuals with obesity. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 121(1):27–31. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1327734",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3377",
"author": "Y Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev",
"key": "1666_CR25",
"unstructured": "Zhou Y, Chi J, Lv W et al (2020) Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3377",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/annonc/mdr037",
"author": "A Clements",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2556",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Ann Oncol",
"key": "1666_CR26",
"unstructured": "Clements A, Gao B, Yeap SHO, Wong MKY, Ali SS, Gurney H (2011) Metformin in prostate cancer: two for the price of one. Ann Oncol 22(12):2556–2560. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdr037",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183",
"author": "S Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108183",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "1666_CR27",
"unstructured": "Sharma S, Ray A, Sadasivam B (2020) Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 164:108183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.19.20135095",
"author": "C Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "1666_CR28",
"unstructured": "Bramante C, Ingraham N, Murray T et al (2020) Observational study of metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with Covid-19. medRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.19.20135095",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "A Zangrillo",
"key": "1666_CR29",
"unstructured": "Zangrillo A, Beretta L, Scandroglio AM (2020) Characteristics, treatment, outcomes and cause of death of invasively ventilated patients with COVID-19 ARDS in Milan. Italy, Crit Care Resusc",
"volume-title": "Characteristics, treatment, outcomes and cause of death of invasively ventilated patients with COVID-19 ARDS in Milan",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/apm.2020.04.25",
"author": "TK Oh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "903",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Ann Palliat Med",
"key": "1666_CR30",
"unstructured": "Oh TK, Song IA (2020) Prior metformin therapy and 30-day mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a nationwide cohort study. Ann Palliat Med 9(3):903–911. https://doi.org/10.21037/apm.2020.04.25",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592-020-01539-z",
"author": "SB Solerte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "779",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Acta Diabetol",
"key": "1666_CR31",
"unstructured": "Solerte SB, Di Sabatino A, Galli M, Fiorina P (2020) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibition in COVID-19. Acta Diabetol 57(7):779–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-020-01539-z",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1521",
"author": "SB Solerte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2999",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "1666_CR32",
"unstructured": "Solerte SB, D’Addio F, Trevisan R et al (2020) Sitagliptin treatment at the time of hospitalization was associated with reduced mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: a multicenter, case-control, retrospective, observational study. Diabetes Care 43(12):2999–3006. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc20-1521",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.044",
"author": "F Qi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "135",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "1666_CR33",
"unstructured": "Qi F, Qian S, Zhang S, Zhang Z (2020) Single cell RNA sequencing of 13 human tissues identify cell types and receptors of human coronaviruses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 526(1):135–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.044",
"volume": "526",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Acta Diabetol"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology",
"General Medicine",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Metformin use and risk of COVID-19 among patients with type II diabetes mellitus: an NHIS-COVID-19 database cohort study"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "58"
}
