Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis
et al., Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324, Oct 2024
Diet for COVID-19
26th treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2021, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 30 studies, recognized in 4 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
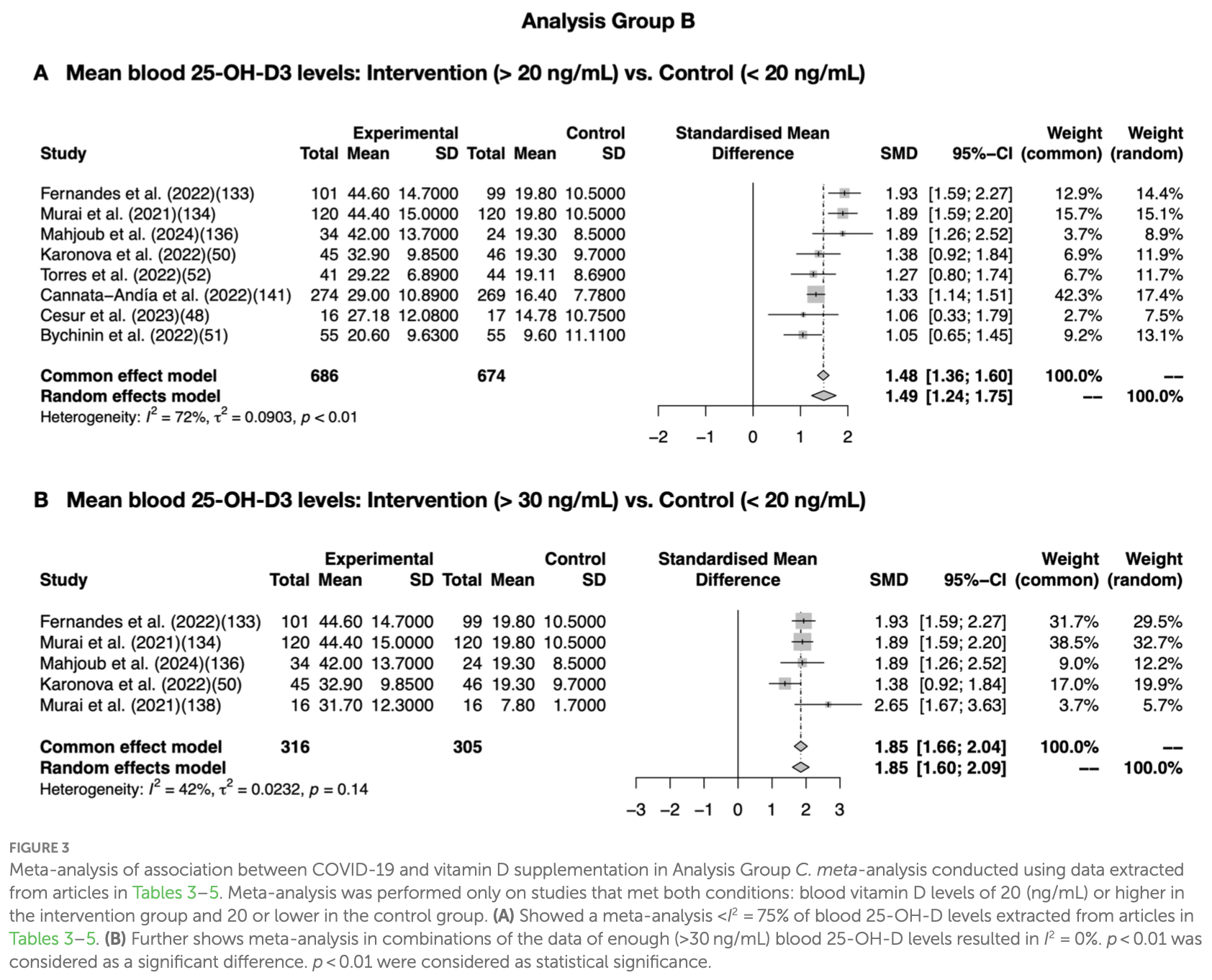
Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa, focusing on diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality. Authors conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the unexpectedly low COVID-19 mortality rates in Africa despite challenging health conditions. They found that a healthy diet rich in phytochemicals, particularly polyphenols and flavonoids, was effective against COVID-19. Blood vitamin D levels were associated with COVID-19 mortality, with Africa having higher average levels than many other regions. The gut microbiota was also linked to COVID-19 outcomes, with African populations showing a more diverse and healthier gut microbiome. Authors highlight the potential protective effects of these factors in Africa's lower COVID-19 mortality rates compared to developed countries. They note that the Japanese diet, similar to the Mediterranean diet, is associated with lower rates of underlying lifestyle-related diseases, potentially contributing to better COVID-19 outcomes. The review also examined the effects of vitamin D supplementation, finding statistically significant differences in vitamin D levels, hospitalization time, and cases. Authors suggest that maintaining adequate blood vitamin D levels and consuming phytochemicals are associated with a healthy gut microbiota and improved immune responses, correlating with lower COVID-19 mortality rates.
2 meta-analyses show significant improvements with diet for hospitalization7,
severity8, and
cases7,8.
Review covers diet, vitamin D, and probiotics.
1.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
2.
Tassakos et al., The Impact of Diet Quality on COVID-19 Severity and Outcomes—A Scoping Review, Current Nutrition Reports, doi:10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3.
3.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
4.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
5.
Halim et al., Relevance of Mediterranean diet as a nutritional strategy in diminishing COVID-19 risk: A systematic review, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.03.24.24304597.
6.
Kahleova et al., The Role of Nutrition in COVID-19: Taking a Lesson from the 1918 H1N1 Pandemic, American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, doi:10.1177/15598276221097621.
Santa et al., 6 Oct 2024, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis
Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324
Background: As the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic subsides, the clinical sequelae are becoming more problematic. Interestingly, the statistical data indicate that Africa has experienced the lowest number of cases and deaths, with an unexpected phenomenon where the number of deaths from COVID-19 has not increased significantly. Several studies have investigated the relationship between diet and coronavirus. However, no systematic review/ meta-analysis has conclusively linked diet (phytochemicals and vitamin D) and the gut microbiota in the context of COVID-19. Methods: This study examined the responses to COVID-19 in Japan and Africa, formulating the following hypotheses: (1) a healthy diet is effective against COVID-19, (2) blood vitamin D levels are associated with COVID-19 mortality, and (3) COVID-19 is associated with the gut microbiota. To investigate these hypotheses, a keyword search and meta-analysis were conducted using PubMed, and each hypothesis was tested. Results: This study found that a healthy diet, particularly rich in phytochemicals such as polyphenols and flavonoids, is effective against COVID-19. An association was detected between blood vitamin D levels and COVID-19 mortality. The gut microbiota was linked to COVID-19 and its amelioration. These findings may have significant implications for not only understanding COVID-19 but also future prevention of pneumonia.
Ethics statement Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because all data used are publicly available. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/ next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements because all data used are publicly available.
Author contributions
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324/ full#supplementary-material Frontiers in Nutrition 20 frontiersin.org
References
Aborode, Ogunsola, Adeyemo, A crisis within a crisis: COVID-19 and hunger in African children, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-1213
Adebayo, Itkonen, Öhman, Skaffari, Saarnio et al., Vitamin D intake, serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status and response to moderate vitamin D3 supplementation: a randomised controlled trial in east African and Finnish women, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S000711451700397X
Adom, Villiers, Puoane, Kengne, A scoping review of policies related to the prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Africa, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13114028
Ahmadi, Mehrabi, Zare, Ghadir, Masoumi, Efficacy of Nanocurcumin as an add-on treatment for patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a double-blind, randomized clinical trial, Int J Clin Pract, doi:10.1155/2023/5734675
Annweiler, Beaudenon, Gautier, Gonsard, Boucher et al., High-dose versus standard-dose vitamin D supplementation in older adults with COVID-19 (COVIT-TRIAL): a multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled superiority trial, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003999
Ao, Kikuta, Ishii, The effects of vitamin D on immune system and inflammatory diseases, Biomol Ther, doi:10.3390/biom11111624
Aparicio, Gold, Weiss, Litonjua, Lee-Sarwar et al., Association of vitamin D Level and maternal gut microbiome during pregnancy: findings from a randomized controlled trial of antenatal vitamin D supplementation, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15092059
Arabnezhad, Mohammadifard, Rahmani, Majidi, Ferns et al., Effects of curcumin supplementation on vitamin D levels in women with premenstrual syndrome and dysmenorrhea: a randomized controlled study, BMC Complement Med Ther, doi:10.1186/s12906-022-03515-2
Aryan, Farahani, Chamanara, Elyasi, Jaafari et al., Evaluation of the efficacy of oral nano-silymarin formulation in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial, Phytother Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7537
Asano, Kushida, Yamamoto, Tomata, Tsuji et al., Abdominal fat in individuals with overweight reduced by consumption of a 1975 Japanese diet: a randomized controlled trial, Obesity, doi:10.1002/oby.22448
Babszky, Torma, Aczel, Bakonyi, Gombos et al., COVID-19 infection alters the microbiome: elite athletes and sedentary patients have similar bacterial Flora, Genes, doi:10.3390/genes12101577
Bell, Schultz, Relative burdens of the COVID-19, malaria, tuberculosis, and HIV/AIDS epidemics in sub-Saharan Africa, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.21-0899
Bellerba, Serrano, Johansson, Pozzi, Segata et al., Colorectal cancer, vitamin D and microbiota: a double-blind phase II randomized trial (ColoViD) in colorectal cancer patients, Neoplasia, doi:10.1016/j.neo.2022.100842
Blackett, Sun, Purpura, Margolis, Elkind et al., Decreased gut microbiome tryptophan metabolism and serotonergic signaling in patients with persistent mental health and gastrointestinal symptoms after COVID-19, Clin Transl Gastroenterol, doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000524
Bouillon, Marcocci, Carmeliet, Bikle, White et al., Skeletal and extraskeletal actions of vitamin D: current evidence and outstanding questions, Endocr Rev, doi:10.1210/er.2018-00126
Brunvoll, Nygaard, Ellingjord-Dale, Holland, Istre et al., Prevention of covid-19 and other acute respiratory infections with cod liver oil supplementation, a low dose vitamin D supplement: quadruple blinded, randomised placebo controlled trial, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-071245
Bychinin, Klypa, Mandel, Yusubalieva, Baklaushev et al., Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on cellular immunity and inflammatory markers in COVID-19 patients admitted to the ICU, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-22045-y
Caballero-García, Pérez-Valdecantos, Guallar, Caballero-Castillo, Roche et al., Effect of vitamin D supplementation on muscle status in old patients recovering from COVID-19 infection, Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina57101079
Cannata-Andía, Díaz-Sottolano, Fernández, Palomo-Antequera, Herrero-Puente et al., A single-oral bolus of 100,000 IU of cholecalciferol at hospital admission did not improve outcomes in the COVID-19 disease: the COVID-VIT-D-a randomised multicentre international clinical trial, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-022-02290-8
Carlberg, Nutrigenomics of vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11030676
Carrouel, Valette, Gadea, Esparcieux, Illes et al., Use of an antiviral mouthwash as a barrier measure in the SARS-CoV-2 transmission in adults with asymptomatic to mild COVID-19: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind controlled trial, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028
Cashman, Kiely, Andersen, Grønborg, Madsen et al., Individual participant data (IPD)-level meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials with vitamin D-fortified foods to estimate dietary reference values for vitamin D, Eur J Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-020-02298-x
Cesur, Atasever, Özoran, Impact of vitamin D3 supplementation on COVID-19 vaccine response and immunoglobulin G antibodies in deficient women: a randomized controlled trial, Vaccine, doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.03.046
Chilamakuri, Agarwal, COVID-19: characteristics and therapeutics, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells10020206
D'ascanio, Vitelli, Cingolani, Maranzano, Brenner et al., Randomized clinical trial "olfactory dysfunction after COVID-19: olfactory rehabilitation therapy vs. intervention treatment with Palmitoylethanolamide and frontiersin.org Luteolin": preliminary results, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, doi:10.26355/eurrev_202106_26059
D'ecclesiis, Gavioli, Martinoli, Raimondi, Chiocca et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396
De Filippo, Cavalieri, Paola, Ramazzotti, Poullet et al., Correlation analysis between gut microbiota alterations and the cytokine response in patients with coronavirus disease during hospitalization, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1128/spectrum.01689-21
De Ligt, Hesselink, Jorgensen, Hoebers, Blaak et al., Resveratrol supplementation reduces ACE2 expression in human adipose tissue, Adipocytes, doi:10.1080/21623945.2021.1965315
De Luca, Camaioni, Marra, Salzano, Carriere et al., Effect of ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Luteolin on olfaction and memory in patients with long COVID: results of a longitudinal study, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells11162552
Elamir, Amir, Lim, Rana, Lopez et al., Impact of vitamin D supplementation on the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 pneumonia patients: a single-center randomized controlled trial, BMC Complement. Med. Ther, doi:10.1186/s12906-024-04393-6
Entrenas, Costa, Barrios, Díaz, López et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Faber, Malan, Kruger, Asare, Visser et al., Potential of egg as complementary food to improve nutrient intake and dietary diversity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14163396
Federico, Dallio, Masarone, Sarno, Tuccillo et al., Evaluation of the effect derived from Silybin with vitamin D and vitamin E administration on clinical, metabolic, endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress parameters, and serological worsening markers in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients, Oxidative Med Cell Longev, doi:10.1155/2019/8742075
Fernandes, Murai, Reis, Sales, Santos et al., Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on cytokines, chemokines, and growth factor in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab426
Fincham, Hohlfeld, Clarke, Kredo, Mccaul, Exploring trial publication and research waste in COVID-19 randomised trials of hydroxychloroquine, corticosteroids, and vitamin D: a meta-epidemiological cohort study, BMC Med Res Methodol, doi:10.1186/s12874-023-02110-4
Forsgård, Rode, Lobenius-Palmér, Kamm, Patil et al., Limosilactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 supplementation and SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody response in healthy adults: a randomized, triple-blinded, placebo-controlled trial, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2023.2229938
Gao, Ye, Lei, Zhang, Luo et al., Dendrobium officinale aqueous extract influences the immune response following vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114702
Ghareghani, Reiter, Zibara, Farhadi, Latitude et al., melatonin, and gut microbiota act in concert to initiate multiple sclerosis: a New mechanistic pathway, Front Immunol, doi:10.1038/nature05414
Gill, Mwananyanda, Leod, Kwenda, Pieciak et al., What is the prevalence of COVID-19 detection by PCR among deceased individuals in Lusaka, Zambia? A postmortem surveillance study, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-066763
Golabi, Ghasemi, Adelipour, Bagheri, Suzuki et al., Oxidative stress and inflammatory status in COVID-19 outpatients: a health center-based analytical cross-sectional study, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11040606
Greene, Roberts, Frugé, Negative association between Mediterranean diet adherence and COVID-19 cases and related deaths in Spain and 23 OECD countries: an ecological study, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.591964
Gualtieri, Marchetti, Frank, Smeriglio, Trombetta et al., Antioxidant-enriched diet on oxidative stress and inflammation gene expression: a randomized controlled trial, Genes, doi:10.3390/genes14010206
Gutiérrez-Castrellón, Gandara-Martí, Abreu, Ay, Nieto-Rufino et al., Probiotic improves symptomatic and viral clearance in COVID 19 outpatients: a randomized, quadruple-blinded, placebo-controlled trial, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.2018899
Haas, Brandl, Schinhammer, Skurk, Individualized supplementation of Immunoactive micronutrients and severity of upper respiratory infection symptoms-a randomized intervention study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16101400
Halfmann, Hatta, Chiba, Maemura, Fan et al., Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in domestic cats, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2013400
Hanel, Carlberg, Skin colour and vitamin D: an update, Exp Dermatol, doi:10.1111/exd.14142
Hosseini, El Abd, Ducharme, Effects of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 related outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102134
Houeze, Wang, Zhou, Zhang, Wang, Comparison study of Beninese and Chinese herbal medicines in treating COVID-19, J Ethnopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116172
Hurtado-Barroso, Trius-Soler, Lamuela-Raventós, Zamora-Ros, Vegetable and fruit consumption and prognosis among Cancer survivors: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of cohort studies, Adv Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmaa082
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Itkonen, Andersen, Björk, Brugård, Eneroth et al., Vitamin D status and current policies to achieve adequate vitamin D intake in the Nordic countries, Scand J Public Health, doi:10.1177/1403494819896878
Jamieson, Smart, Bouranis, Choi, Danczak et al., Gut enterotype-dependent modulation of gut microbiota and their metabolism in response to xanthohumol supplementation in healthy adults, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2024.2315633
Jastrzębska, Skalska, Radzimiński, López-Sánchez, Weiss et al., Changes of 25(OH)D concentration, bone resorption markers and physical performance as an effect of Sun exposure, supplementation of vitamin D and lockdown among young soccer players during a one-year training season, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030521
Jolliffe, Vivaldi, Chambers, Cai, Li et al., Vitamin D supplementation does not influence SARS-CoV-2 vaccine efficacy or immunogenicity: sub-studies nested within the CORONAVIT randomised controlled trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14183821
Kalichuran, Van Blydenstein, Venter, Omar, Vitamin D status and COVID-19 severity, S Afr J Infect Dis, doi:10.4102/sajid.v37i1.359
Kamer, Rinott, Tsaban, Kaplan, Yaskolka et al., Successful weight regain attenuation by autologous fecal microbiota transplantation is associated with non-core gut microbiota changes during weight loss; randomized controlled trial, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2023.2264457
Karonova, Chernikova, Golovatyuk, Bykova, Grant et al., Vitamin D intake may reduce SARS-CoV-2 infection morbidity in health care workers, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030505
Kawaguchi, Kikuchi, Hasunuma, Maruyama, Yoshikawa et al., A citrus flavonoid hesperidin suppresses infection-induced endotoxin shock in mice, Biol Pharm Bull, doi:10.1248/bpb.27.679
Klein, Wood, Jaycox, Dhodapkar, Lu et al., Distinguishing features of long COVID identified through immune profiling, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06651-y
Kogan, Gantt, Swerdlow, Viboud, Semakula et al., Leveraging Serosurveillance and postmortem surveillance to quantify the impact of coronavirus disease 2019 in Africa, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac897
Kumazawa, Takimoto, Matsumoto, Kawaguchi, Potential use of dietary natural products, especially polyphenols, for improving type-1 allergic symptoms, Curr Pharm Des, doi:10.2174/138161282006140220120344
Kushida, Sugawara, Asano, Yamamoto, Fukuda et al., Effects of the 1975 Japanese diet on the gut microbiota in younger adults, J Nutr Biochem, doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.10.011
Lackner, Mahnert, Moissl-Eichinger, Madl, Habisch et al., Interindividual differences in aronia juice tolerability linked to gut microbiome and metabolome changes-secondary analysis of a randomized placebocontrolled parallel intervention trial, Microbiome, doi:10.1186/s40168-024-01774-4
Lacy, Khan, Deb, Das, Igoe et al., Geographic disparities and predictors of COVID-19 vaccination in Missouri: a retrospective ecological study, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2024.1329382
Lau, Su, Lau, Ching, Wong et al., A synbiotic preparation (SIM01) for post-acute COVID-19 syndrome in Hong Kong (RECOVERY): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00685-0
Lee, Park, Kang, Choi, Park et al., High dose intramuscular vitamin D3 supplementation impacts the gut microbiota of patients with Clostridioides difficile infection, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.904987
Li, Watanabe, Kawashima, Plichta, Wang et al., Identification of trypsin-degrading commensals in the large intestine, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05181-3
Losso, Losso, Toc, Inungu, Finley, The young age and plant-based diet hypothesis for low SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 pandemic in sub-Saharan Africa, Plant Foods Hum Nutr, doi:10.1007/s11130-021-00907-6
Lowe, Maiyar, Norman, Vitamin D-mediated gene expression, Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Jamalimoghadamsiahkali, Asadi, Zarei et al., Treatment with 25-Hydroxyvitamin D(3) (Calcifediol) is associated with a reduction in the blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio marker of disease severity in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a pilot multicenter, randomized, placebocontrolled, double-blinded clinical trial, Endocr Pract, doi:10.3390/nu15071736
Mahjoub, Youssef, Yaakoubi, Salah, Jaballah et al., Melatonin, vitamins and minerals supplements for the treatment of COVID-19 and COVID-like illness: a prospective, randomized, double-blind multicenter study, Explore, doi:10.1016/j.explore.2023.06.009
Mariani, Antonietti, Tajer, Ferder, Inserra et al., High-dose vitamin D versus placebo to prevent complications in COVID-19 patients: multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2022.111899
Marseglia, Licari, Leonardi, Papale, Zicari et al., A polycentric, randomized, parallel-group, study on Lertal ® , a multicomponent nutraceutical, as preventive treatment in children with allergic rhinoconjunctivitis: phase II, Ital J Pediatr, doi:10.1186/s13052-019-0678-y
Mathrani, Yip, Sequeira-Bisson, Barnett, Stevenson et al., Effect of a 12-week polyphenol Rutin intervention on markers of pancreatic β-cell function and gut microbiota in adults with overweight without diabetes, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15153360
Mc, Schnell, Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled proof-of-concept trial of resveratrol for outpatient treatment of mild coronavirus disease (COVID-19), Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-13920-9
Middelkoop, Stewart, Walker, Delport, Jolliffe et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent tuberculosis infection in South African schoolchildren: multicenter phase 3 double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial (ViDiKids), Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2023.05.010
Miller, Imel, Rickets, vitamin D, and ca/P metabolism, Horm Res Paediatr, doi:10.1159/000527011
Miyamoto, Kawakami, Hanafusa, Nakanishi, Miyasaka et al., Determination of a serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D reference ranges in Japanese adults using fully automated liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, J Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.tjnut.2023.01.036
Mogire, Mutua, Kimita, Kamau, Bejon et al., Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet Glob Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30457-7
Mullish, Marchesi, Mcdonald, Pass, Masetti et al., Probiotics reduce self-reported symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection in overweight and obese adults: should we be considering probiotics during viral pandemics?, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.1900997
Murai, Fernandes, Antonangelo, Gualano, Pereira, Effect of a single high-dose vitamin D3 on the length of hospital stay of severely 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-deficient patients with COVID-19, Clinics, doi:10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Murakami, Shinozaki, Livingstone, Yuan, Tajima et al., Associations of food choice values and food literacy with overall diet quality: a nationwide cross-sectional study in Japanese adults, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S000711452300082X
Naderpoor, Mousa, Gomez Arango, Barrett, Dekker et al., Effect of vitamin D supplementation on Faecal microbiota: a randomised clinical trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11122888
Nagai, Moriyama, Ishii, Mori, Watanabe et al., Acute and subacute oral toxicity characterization and safety assessment of COVID organics ® (Madagascar's anti-COVID herbal tea) in animal models, Environ Sci Pollut Res Int
Nagaoka, Tamura, Reich, Therapeutic potential of cathelicidin peptide LL-37, an antimicrobial agent, in a murine Sepsis model, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms21175973
Nagata, Takeuchi, Masuoka, Aoki, Ishikane et al., Human gut microbiota and its metabolites impact immune responses in COVID-19 and its complications, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.09.024
Niet, Trémège, Coffiner, Rousseau, Calmes et al., Vitamin D3 supplementation at 5000 IU daily for the prevention of influenza-like illness in healthcare workers: a pragmatic randomized clinical trial, Placebo-Controlled Trial Nutr, doi:10.3390/nu15010180
Nogrady, How kids' immune systems can evade COVID, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-020-03496-7
Odai, Terauchi, Kato, Hirose, Miyasaka, Effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on vascular endothelial function in participants with prehypertension: a randomized, double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Study Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11122844
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Pham, Fehlbaum, Seifert, Richard, Bruins et al., Effects of colon-targeted vitamins on the composition and metabolic activity of the human gut microbiome-a pilot study, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.1875774
Rabbi, Oláh, Popp, Máté, Kovács, Food security and the COVID-19 crisis from a consumer buying behaviour perspective-the case of Bangladesh, Food Secur, doi:10.3390/foods10123073
Reuben, Beugnon, Jurburg, COVID-19 alters human microbiomes: a meta-analysis, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2023.1211348
Riccia, Cafaro, John, Van Helmond, Mitrev et al., Healthcare costs and healthcare utilization outcomes of vitamin D3 supplementation at 5000 IU daily during a 10.9 month observation period within a pragmatic randomized clinical trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15204435
Rodríguez-Argente, Alba-Domínguez, Díaz-Martínez, Vergara, Díaz-Márques et al., Buccopharyngeal route administered high polyphenolic olive oil and COVID-19: a pilot clinical trial, Immun Inflamm Dis, doi:10.1002/iid3.1054
Sabico, Enani, Sheshah, Aljohani, Aldisi et al., Effects of a 2-week 5000 IU versus 1000 IU vitamin D3 supplementation on recovery of symptoms in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072170
Santa, Healthy diet, grape phytochemicals, and vitamin D: preventing chronic inflammation and keeping good microbiota, Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1871530323666221017151705
Santa, Kumazawa, Nagaoka, The potential use of grape phytochemicals for preventing the development of intestine-related and subsequent inflammatory diseases, Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1871530319666190529105226
Santa, Kumazawa, Watanabe, Nagaoka, The potential use of vitamin D3 and phytochemicals for their anti-ageing effects, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms25042125
Santa, Kumazawa, Watanabe, Nagaoka, The recommendation of the Mediterranean-styled Japanese diet for healthy longevity, Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/0118715303280097240130072031
Santa, Watanabe, Kumazawa, Nagaoka, Phytochemicals and vitamin D for a healthy life and prevention of diseases, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms241512167
Sarhan, Warda, Sarhan, Boshra, Mostafa-Hedeab et al., Evidence for the efficacy of a high dose of vitamin D on the hyperinflammation state in moderate-to-severe COVID-19 patients: a randomized clinical trial, Medicina
Sayama, Okamoto, Saito, Tamaki, Saito-Obata et al., Lack of zoonotic coronavirus species detected among children hospitalized with pneumonia in the Philippines, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad430
Scaturro, Vitagliani, Tomasello, Sconza, Respizzi et al., Combined rehabilitation with alpha lipoic acid, acetyl-L-carnitine, resveratrol, and cholecalciferolin discogenic sciatica in young people: a randomized clinical trial, Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina59122197
Sevillano-Jiménez, Romero-Saldaña, Carrascal-Laso, García-Rodríguez, Molina-Luque et al., Impact of high prebiotic and probiotic dietary education in the SARS-CoV-2 era: improved cardio-metabolic profile in schizophrenia spectrum disorders, BMC Psychiatr, doi:10.1186/s12888-022-04426-9
Shin-Ya, Nakashio, Ohgitani, Suganami, Kawamoto et al., Effects of tea, catechins and catechin derivatives on omicron subvariants of SARS-CoV-2, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-43563-3
Shohan, Nashibi, Mahmoudian-Sani, Abolnezhadian, Ghafourian et al., The therapeutic efficacy of quercetin in combination with antiviral drugs in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a randomized controlled trial, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174615
Stadio, 'ascanio, Vaira, Cantone, Luca et al., Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Luteolin supplement combined with olfactory training to treat post-COVID-19 olfactory impairment: a multi-center doubleblinded randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial, Curr Neuropharmacol, doi:10.2174/1570159X20666220420113513
Stadio, Gallina, Cocuzza, Luca, Ingrassia et al., Treatment of COVID-19 olfactory dysfunction with olfactory training, palmitoylethanolamide with luteolin, or combined therapy: a blinded controlled multicenter randomized trial, Eur Arch Otorrinolaringol, doi:10.1007/s00405-023-08085-8
Sugawara, Kushida, Iwagaki, Asano, Yamamoto et al., The 1975 type Japanese diet improves lipid metabolic parameters in younger adults: a randomized controlled trial, J Oleo Sci, doi:10.5650/jos.ess17259
Tadayon, Rayner, Shokraee, Shokraie, Panahi et al., Obesity as an independent risk factor for COVID-19 severity and mortality, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD015201
Takabayashi, Okada, Hirata, Takimoto, Nakamura et al., Nutritional adequacy assessment of the Japanese diet using the number of dishes compared to existing dietary diversity indices: a cross-sectional analysis from the 2012 national health and nutrition survey, Japan, J Nutr Sci Vitaminol, doi:10.3906/sag-2108-239
Takagi, Inoue, Oshima, Sakazume, Ogawa et al., Typing of the gut microbiota community in Japanese subjects, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms10030664
Tiwari, Dicks, Popov, Karaseva, Ermakov et al., Probiotics at war against viruses: what is missing from the picture?, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.01877
Torres, Casado, Vigón, Rodríguez-Mora, Mateos et al., Multidisciplinary group of study of COVID-19 (MGS-COVID); contributing members of the multidisciplinary group of study of COVID-19 (in alphabetical order). Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965
Tosi, Favari, Bresciani, Flanagan, Hornberger et al., Unravelling phenolic metabotypes in the frame of the COMBAT study, a randomized, controlled trial with cranberry supplementation, Food Res Int, doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113187
Van Brummelen, Van Brummelen, The potential role of resveratrol as supportive antiviral in treating conditions such as COVID-19-a formulator's perspective, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112767
Versace, Ortelli, Dezi, Ferrazzoli, Alibardi et al., Coultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide/luteolin normalizes GABA(B)-ergic activity and cortical plasticity in long COVID-19 syndrome, Clin Neurophysiol, doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2022.10.017
Villasis-Keever, López-Alarcón, Miranda-Novales, Zurita-Cruz, Barrada-Vázquez et al., Effect of cholecalciferol supplementation on the clinical features and inflammatory markers in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a randomized, open-label, Single-Center Study Nutr, doi:10.3390/nu14132602
Watanabe, The COVID-19 pandemic in Japan, Surg Today, doi:10.1007/s00595-020-02033-3
Watson, Alhaffar, Mehchy, Whittaker, Akil et al., Why is COVID-19 less severe in children? A review of the proposed mechanisms underlying the age-related difference in severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections, Arch Dis Child, doi:10.1136/archdischild-2020-320338
Wattanathorn, Tong-Un, Thukham-Mee, Paholpak, Rangseekhajee, A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of an anthocyanin-rich functional ingredient on cognitive function and eye dryness in late adulthood volunteers: roles of epigenetic and gut microbiome modulations, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15163499
Weisberg, Connors, Zhu, Baldwin, Lin et al., Distinct antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in children and adults across the COVID-19 clinical spectrum, Nat Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-020-00826-9
Wong, Zaw, Xian, Howe, Regular supplementation with resveratrol improves bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: a randomized. Placebo-Controlled Trial, J Bone Miner Res, doi:10.1002/jbmr.4115
Wong, Zhang, Ching, Mak, Huang et al., Effects of gut microbiome modulation on reducing adverse health outcomes among elderly and diabetes patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (IMPACT study), Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15081982
Worldometer, Population
Wu, Le, Maeda-Minami, Yoshino, Horiba et al., Relationship between conventional medicine chapters in ICD-10 and Kampo pattern diagnosis: a crosssectional study, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.751403
Xue, Honda, Hibi, Mechanisms of gastrointestinal barrier dysfunction in COVID-19 patients, World J Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2283
Yaskolka, Keller, Hoffmann, Rinott, Tsaban et al., The effect of polyphenols on DNA methylation-assessed biological age attenuation: the DIRECT PLUS randomized controlled trial, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-023-03067-3
Yuki, Nojima, Hosono, Tanaka, Kimura et al., Oral MucoRice-CTB vaccine for safety and microbiota-dependent immunogenicity in humans: a phase 1 randomised trial, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30196-8
Zekeya, Mamiro, Ndossi, Kilonzo, Kisingo et al., Screening and evaluation of cytotoxicity and antiviral effects of secondary metabolites from water extracts of Bersama abyssinica against SARS-CoV-2 Delta, BMC Complement. Med. Ther, doi:10.1186/s12906-022-03754-3
Zhang, Verma, Feng, Melo, Mcquillan et al., Impact of natural selection on global patterns of genetic variation and association with clinical phenotypes at genes involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22168912