Probiotic improves symptomatic and viral clearance in Covid19 outpatients: a randomized, quadruple-blinded, placebo-controlled trial
et al., Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.2018899, NCT04517422, May 2021 (preprint)
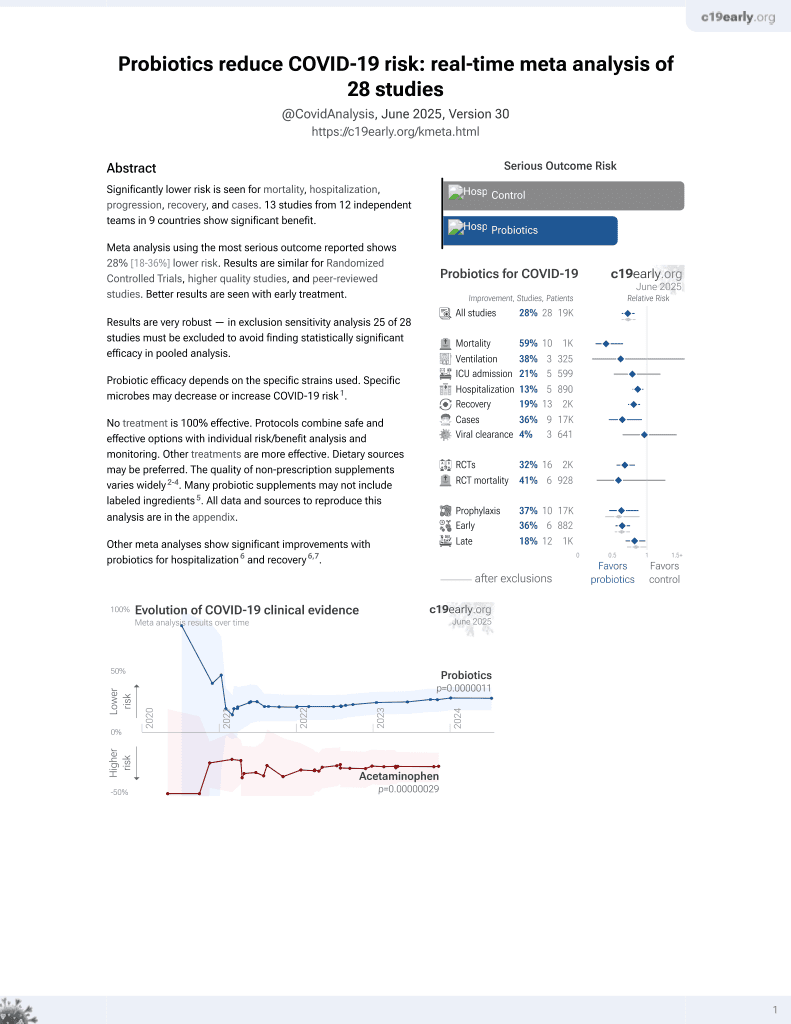
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
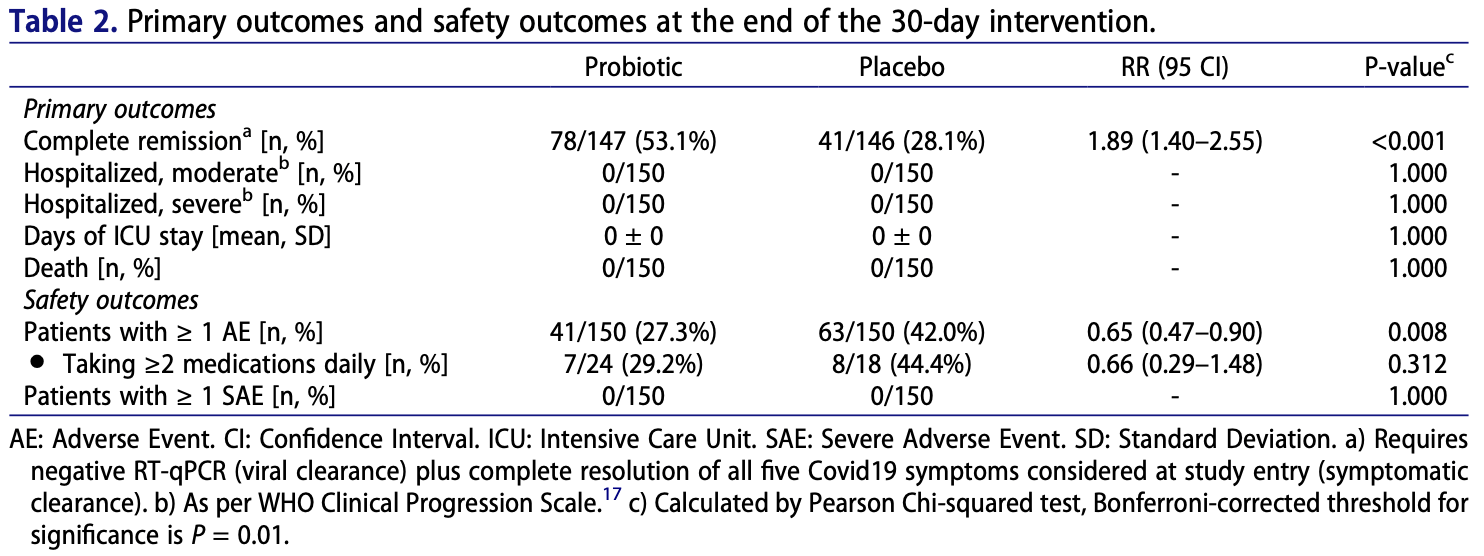
RCT 293 outpatients in Mexico, 147 treated with a probiotic composed of three L. plantarum strains (KABP022, KABP023 and KABP033) and one P. acidilacti strain (KABP021), showing improved recovery with treatment. There were no hospitalizations or deaths.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk1.
|
risk of no recovery, 34.7% lower, RR 0.65, p < 0.001, treatment 69 of 147 (46.9%), control 105 of 146 (71.9%), NNT 4.0.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Gutiérrez-Castrellón et al., 24 May 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Mexico, peer-reviewed, 9 authors, study period 19 August, 2020 - 2 February, 2021, average treatment delay 4.0 days, trial NCT04517422 (history).
Probiotic improves symptomatic and viral clearance in Covid19 outpatients: a randomized, quadruple-blinded, placebo-controlled trial
Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.2018899
Intestinal bacteria may influence lung homeostasis via the gut-lung axis. We conducted a singlecenter, quadruple-blinded, randomized trial in adult symptomatic Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid19) outpatients. Subjects were allocated 1:1 to probiotic formula (strains Lactiplantibacillus plantarum KABP022, KABP023, and KAPB033, plus strain Pediococcus acidilactici KABP021, totaling 2 × 10 9 colony-forming units (CFU)) or placebo, for 30 days. Co-primary endpoints included: i) proportion of patients in complete symptomatic and viral remission; ii) proportion progressing to moderate or severe disease with hospitalization, or death; and iii) days on Intensive Care Unit (ICU). Three hundred subjects were randomized (median age 37.0 years [range 18 to 60], 161 [53.7%] women, 126 [42.0%] having known metabolic risk factors), and 293 completed the study (97.7%). Complete remission was achieved by 78 of 147 (53.1%) in probiotic group compared to 41 of 146 (28.1%) in placebo (RR: 1.89 [95 CI 1.40-2.55]; P < .001), significant after multiplicity correction. No hospitalizations or deaths occurred during the study, precluding the assessment of remaining coprimary outcomes. Probiotic supplementation was well-tolerated and reduced nasopharyngeal viral load, lung infiltrates and duration of both digestive and non-digestive symptoms, compared to placebo. No significant compositional changes were detected in fecal microbiota between probiotic and placebo, but probiotic supplementation significantly increased specific IgM and IgG against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) compared to placebo. It is thus hypothesized this probiotic primarily acts by interacting with the host's immune system rather than changing colonic microbiota composition. Future studies should replicate these findings and elucidate its mechanism of action (Registration: NCT04517422).
Author contributions PGC, JEM, and ATAA designed the study. TGM, CDNR, and IJE performed patient procedures. ELO and GLV performed laboratory analyses. CJG and PGC collected and curate the data. PGC conducted the statistical analyses. PGC and JEM drafted the manuscript. ATAA critically revised the manuscript.
Disclosure statement ATAA reports receiving speaker fees from AB-Biotics SA (Kaneka Group). JEM is a staff scientist with no stock options or shares at AB-Biotics SA (Kaneka Group). Other authors report their institution was sponsored by AB-Biotics SA (Kaneka Group) for the submitted work.
References
Abt, Osborne, Monticelli, Doering, Alenghat et al., Commensal bacteria calibrate the activation threshold of innate antiviral immunity, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2012.04.011
Anand, Prévost, Nayrac, Beaudoin-Bussières, Benlarbi et al., Longitudinal analysis of humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2 spike in convalescent individuals up to 8 months post-symptom onset, Cell Reports Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100290
Baud, Agri, Gibson, Reid, Giannoni, Using probiotics to flatten the curve of coronavirus disease COVID-2019 pandemic, Front Public Heal, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2020.00186
Belkaid, Harrison, Homeostatic immunity and the microbiota, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2017.04.008
Boni, Lemey, Jiang, Lam, Perry et al., Evolutionary origins of the SARS-CoV-2 sarbecovirus lineage responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, Nat Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0771-4
Borghesi, Zigliani, Golemi, Carapella, Maculotti et al., Chest X-ray severity index as a predictor of in-hospital mortality in coronavirus disease 2019: a study of 302 patients from Italy, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.021
Bradley, Finsterbusch, Schnepf, Crotta, Llorian et al., Microbiota-driven tonic interferon signals in lung stromal cells protect from influenza virus infection, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.105
Budden, Gellatly, Wood, Cooper, Morrison et al., Emerging pathogenic links between microbiota and the gut-lung axis, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2016.142
Ceccarelli, Borrazzo, Pinacchio, Santinelli, Pietro et al., Oral bacteriotherapy in patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2020.613928
Colosimo, Kohn, Luo, Piscotta, Han et al., Mapping interactions of microbial metabolites with Human G-protein-coupled receptors, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2019.07.002
Corman, Landt, Kaiser, Molenkamp, Meijer et al., Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045
Dan, Mateus, Kato, Hastie, Yu et al., Immunological memory to SARS-CoV-2 assessed for up to 8 months after infection, Science
Dang, Marsland, Microbes, metabolites, and the gut-lung axis, Mucosal Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41385-019-0160-6
Didari, Solki, Mozaffari, Nikfar, Abdollahi, A systematic review of the safety of probiotics, Expert Opin. Drug Saf, doi:10.1517/14740338.2014.872627
Dispinseri, Secchi, Pirillo, Tolazzi, Borghi et al., Neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in symptomatic COVID-19 is persistent and critical for survival, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-22958-8
Donaldson, Lee, Mazmanian, Gut biogeography of the bacterial microbiota, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/nrmicro3552
Earle, Ambrosino, Fiore-Gartland, Goldblatt, Gilbert et al., Evidence for antibody as a protective correlate for COVID-19 vaccines, Vaccine, doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.05.063
Falony, Joossens, Vieira-Silva, Wang, Darzi et al., Population-level analysis of gut microbiome variation, Science, doi:10.1126/science.aad3503
Falony, Vieira-Silva, Raes, Richness and ecosystem development across faecal snapshots of the gut microbiota, Nat. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-018-0143-5
Feld, Kandel, Biondi, Kozak, Zahoor et al., Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of outpatients with COVID-19: a phase 2, placebo-controlled randomised trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30566-X
Gold, Rossen, Ahmad, Sutton, Li et al., Race, ethnicity, and age trends in persons who died from COVID-19 -United States, May, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6942e1
Gottlieb, Nirula, Chen, Boscia, Heller et al., Effect of Bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with Etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0202
Gutierrez-Merino, Isla, Combes, Martinez-Estrada, Motes, Beneficial bacteria activate type-I interferon production via the intracellular cytosolic sensors STING and MAVS, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2019.1707015
Hao, Dong, Wu, Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3
Hill, Guarner, Reid, Gibson, Merenstein et al., Expert consensus document: the international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66
Jagannathan, Andrews, Bonilla, Hedlin, Jacobson et al., Peginterferon Lambda-1a for treatment of outpatients with uncomplicated COVID-19: a randomized placebo-controlled trial, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20168-2
Kastl, Terry, Wu, Albenberg, The structure and function of the human small intestinal microbiota, Curr Understanding Future Directions
Khunti, Davies, Kosiborod, Nauck, Long COVID -metabolic risk factors and novel therapeutic management, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-021-00495-0
King, Glanville, Sanders, Fitzgerald, Varley, Effectiveness of probiotics on the duration of illness in healthy children and adults who develop common acute respiratory infectious conditions: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114514000075
Koutsoumanis, Allende, Alvarez-Ordóñez, Bolton, Bover-Cid et al., Update of the list GUT MICROBES
Lavezzo, Franchin, Ciavarella, Cuomo-Dannenburg, Barzon et al., Suppression of a SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in the Italian municipality of Vo, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2488-1
Ledford, COVID antibody treatments show promise for preventing severe disease, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-021-00650-7
Lozupone, Stombaugh, Gordon, Jansson, Knight, Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature11550
Lynn, Benson, Lynn, Pulendran, Modulation of immune responses to vaccination by the microbiota: implications and potential mechanisms, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-00486-8
López-Medina, López, Hurtado, Dávalos, Ramirez et al., Effect of Ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3071
Ma, Zhang, Chen, Jiang, Shen et al., Probiotic consumption influences universal adaptive mutations in indigenous human and mouse gut microbiota, Commun Biol, doi:10.1038/s42003-021-02724-8
Marshall, Murthy, Diaz, Adhikari, Angus et al., A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7
Martínez-Romero, Aguirre-Noyola, Bustamante-Brito, González-Román, Hernández-Oaxaca et al., We and herbivores eat endophytes, Microb Biotechnol
Meijerink, Van Hemert, Taverne, Wels, De Vos et al., Identification of genetic loci in Lactobacillus plantarum that modulate the immune response of dendritic cells using comparative genome hybridization, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010632
Mullish, Marchesi, Mcdonald, Pass, Masetti et al., Probiotics reduce self-reported symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection in overweight and obese adults: should we be considering probiotics during viral pandemics?, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.1900997
Mörbe, Jørgensen, Fenton, Burg, Riis et al., Human gut-associated lymphoid tissues (GALT); diversity, structure, and function, Mucosal Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41385-021-00389-4
Nugroho, Wardhana, Maghfirah, Mulia, Rachmi et al., Relationship of D-dimer with severity and mortality in SARS-CoV-2 patients : a meta-analysis, Int J Lab Hematol, doi:10.1111/ijlh.13336
Paineau, Carcano, Leyer, Darquy, Alyanakian et al., Effects of seven potential probiotic strains on specific immune responses in healthy adults: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial, FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol, doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2008.00413.x
Panigrahi, Parida, Nanda, Satpathy, Pradhan et al., A randomized synbiotic trial to prevent sepsis among infants in rural India, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature23480
Peng, Zhang, Yao, Kwok, Zhang, Probiotics as adjunctive treatment for patients contracted COVID-19: current understanding and future needs, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.669808
Quast, Pruesse, Yilmaz, Gerken, Schweer et al., The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools, Nucleic Acids Res
Reis, Silva, Silva, Thabane, Singh et al., Effect of early treatment with hydroxychloroquine or Lopinavir and Ritonavir on risk of hospitalization among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.6468
Roager, Hansen, Bahl, Frandsen, Carvalho et al., Colonic transit time is related to bacterial metabolism and mucosal turnover in the gut, Nat Microbiol
Rockstroh, Wolf, Fertey, Kalbitz, Schroth et al., Correlation of humoral immune responses to different SARS-CoV-2 antigens e2018899-14 P. GUTIÉRREZ-CASTRELLÓN ET AL. with virus neutralizing antibodies and symptomatic severity in a German COVID-19 cohort, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/2222175120211913973
Schloss, Reintroducing mothur: 10 years later, Appl Environ Microbiol
Seow, Graham, Merrick, Acors, Pickering et al., Longitudinal observation and decline of neutralizing antibody responses in the three months following SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans, Nat Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-020-00813-8
Singh, Stellrecht, Arunachalam, Barman, Robek et al., Lack of active SARS-CoV-2 virus in a subset of PCR-positive COVID-19 congregate care patients, J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104879
Smilowitz, Kunichoff, Garshick, Shah, Pillinger et al., C-reactive protein and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19, Eur Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa1103
Suez, Zmora, Segal, Elinav, The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0439-x
Svedlund, Sjödin, Dotevall, GSRS-A clinical rating scale for gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and peptic ulcer disease, Dig Dis Sci, doi:10.1007/BF01535722
Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Wolski, Wang et al., Effect of high-dose Zinc and Ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
Van Hemert, Meijerink, Molenaar, Bron, De Vos et al., Identification of Lactobacillus plantarum genes modulating the cytokine response of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, BMC Microbiol, doi:10.1186/1471-2180-10-293
Wang, Nair, Liu, Iketani, Luo et al., Antibody resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1, Nat, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03398-2
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Ali, Gao et al., REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035002
Weiss, Rasmussen, Zeuthen, Nielsen, Jarmer et al., Lactobacillus acidophilus induces virus immune defence genes in murine dendritic cells by a Toll-like receptor-2-dependent mechanism, Immunology, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03301.x
Wiersinga, Rhodes, Cheng, Peacock, Prescott, Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.12839
Wieërs, Belkhir, Enaud, Leclercq, De Foy et al., How probiotics affect the microbiota, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2019.00454
Yelin, Flett, Merakou, Mehrotra, Stam et al., Genomic and epidemiological evidence of bacterial transmission from probiotic capsule to blood in ICU patients, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0626-9
Yeoh, Zuo, Lui, Zhang, Liu et al., Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323020
Zhao, Peng, Sakandar, Kwok, Zhang, Meta-analysis: randomized trials of Lactobacillus plantarum on immune regulation over the last decades, Front Immunol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2021.2018899",
"ISSN": [
"1949-0976",
"1949-0984"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2021.2018899",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1080/19490976.2021.2018899"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Peer Review Statement",
"name": "peerreview_statement",
"order": 1,
"value": "The publishing and review policy for this title is described in its Aims & Scope."
},
{
"URL": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=kgmi20",
"label": "Aim & Scope",
"name": "aims_and_scope_url",
"order": 2,
"value": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=kgmi20"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-07-15"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-11-03"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-11-22"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2022-01-11"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9885-9635",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro de Investigación Translacional en Ciencias de la Salud, Hospital General Dr. Manuel Gea Gonzalez, Ciudad de México, (CDMX), México"
},
{
"name": "International Scientific Council for Probiotics, Ciudad de México, (CDMX), México"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gutiérrez-Castrellón",
"given": "Pedro",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro de Investigación Translacional en Ciencias de la Salud, Hospital General Dr. Manuel Gea Gonzalez, Ciudad de México, (CDMX), México"
}
],
"family": "Gandara-Martí",
"given": "Tania",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Digestive Unit, Hospital Angeles Pedregal, Ciudad de México, (CDMX), México"
}
],
"family": "Abreu Y Abreu",
"given": "Ana T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro de Investigación Translacional en Ciencias de la Salud, Hospital General Dr. Manuel Gea Gonzalez, Ciudad de México, (CDMX), México"
}
],
"family": "Nieto-Rufino",
"given": "Cesar D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "DiagnoMol SA de CV, Ciudad de México (CDMX), México"
}
],
"family": "López-Orduña",
"given": "Eduardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro de Investigación Translacional en Ciencias de la Salud, Hospital General Dr. Manuel Gea Gonzalez, Ciudad de México, (CDMX), México"
}
],
"family": "Jiménez-Escobar",
"given": "Irma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro de Investigación Translacional en Ciencias de la Salud, Hospital General Dr. Manuel Gea Gonzalez, Ciudad de México, (CDMX), México"
}
],
"family": "Jiménez-Gutiérrez",
"given": "Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Scientific Council for Probiotics, Ciudad de México, (CDMX), México"
}
],
"family": "López-Velazquez",
"given": "Gabriel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0128-8363",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "R&D Department, AB-Biotics SA (KANEKA Group) Sant Cugat, (Barcelona) Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Espadaler-Mazo",
"given": "Jordi",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Gut Microbes"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.tandfonline.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-11T12:15:27Z",
"timestamp": 1641903327000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-11T12:16:57Z",
"timestamp": 1641903417000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "AB-Biotics SA"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-12T06:49:27Z",
"timestamp": 1641970167251
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1949-0976"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1949-0984"
}
],
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
31
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1641859200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/19490976.2021.2018899",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "301",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1080",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
11
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Informa UK Limited",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0771-4",
"author": "Boni MF",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1408",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "cit0001",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2488-1",
"author": "Lavezzo E",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "425",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "cit0002",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12839",
"author": "Wiersinga WJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "782",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "cit0003",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66",
"author": "Hill C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "506",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "cit0004",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro.2016.142",
"author": "Budden KF",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "cit0005",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41385-019-0160-6",
"author": "Dang AT",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "843",
"journal-title": "Mucosal Immunol",
"key": "cit0006",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114514000075",
"author": "King S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr",
"key": "cit0007",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"author": "Hao Q",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "cit0008",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1574-695X.2008.00413.x",
"author": "Paineau D",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol",
"key": "cit0009",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2180-10-293",
"author": "van Hemert S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "BMC Microbiol",
"key": "cit0010",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0010632",
"author": "Meijerink M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e10632",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "cit0011",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"author": "Zhao W",
"first-page": "728",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "cit0012",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2020.00186",
"author": "Baud D",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "186",
"journal-title": "Front Public Heal",
"key": "cit0013",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2021.1900997",
"author": "Mullish BH",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Gut Microbes",
"key": "cit0014",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.669808",
"author": "Peng J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "669808",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "cit0015",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2020.613928",
"author": "Ceccarelli G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "613928",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "cit0016",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"author": "Marshall JC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e192",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "cit0017",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"author": "Weinreich DM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "cit0018",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.0202",
"author": "Gottlieb RL",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "632",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "cit0019",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.3071",
"author": "López-Medina E",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1426",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "cit0020",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30566-X",
"author": "Feld JJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "498",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "cit0021",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-22177-1",
"author": "Jagannathan P",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "cit0022",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.6468",
"author": "Reis G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e216468",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw open",
"key": "cit0023",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"author": "Thomas S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e210369",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "cit0024",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-00650-7",
"author": "Ledford H",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "513",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "cit0025",
"volume": "591",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03398-2",
"author": "Wang P",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "130",
"journal-title": "Nat",
"key": "cit0026",
"volume": "593",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-021-00495-0",
"author": "Khunti K",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "379",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Endocrinol",
"key": "cit0027",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.021",
"author": "Borghesi A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "291",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "cit0028",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104879",
"author": "Singh A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104879",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "cit0029",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-00813-8",
"author": "Seow J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1598",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "cit0030",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-22958-8",
"author": "Dispinseri S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2670",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "cit0031",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2021.1913973",
"author": "Rockstroh A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "774",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "cit0032",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.05.063",
"author": "Earle K",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4423",
"journal-title": "Vaccine",
"key": "cit0033",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100290",
"author": "Anand SP",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100290",
"journal-title": "Cell Reports Med",
"key": "cit0034",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Dan JM",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "cit0035",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2012.04.011",
"author": "Abt M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "158",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "cit0036",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.105",
"author": "Bradley KC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "245",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "cit0037",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature23480",
"author": "Panigrahi P",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "407",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "cit0038",
"volume": "548",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"author": "Martínez-Romero E",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Microb Biotechnol",
"key": "cit0039",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323020",
"author": "Yeoh YK",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "698",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "cit0040",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-018-0143-5",
"author": "Falony G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "526",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol",
"key": "cit0041",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"author": "Roager HM",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "cit0042",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro3552",
"author": "Donaldson GP",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol",
"key": "cit0043",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"author": "Kastl AJ",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "Curr Understanding Future Directions",
"key": "cit0044",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2019.00454",
"author": "Wieërs G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "454",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "cit0045",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41385-021-00389-4",
"author": "Mörbe UM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "793",
"journal-title": "Mucosal Immunol",
"key": "cit0046",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2019.1707015",
"author": "Gutierrez-Merino J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "771",
"journal-title": "Gut Microbes",
"key": "cit0047",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03301.x",
"author": "Weiss G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "268",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "cit0048",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature11550",
"author": "Lozupone C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "220",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "cit0049",
"volume": "489",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-020-01566-0",
"author": "Ma C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Commun Biol",
"key": "cit0050",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2019.07.002",
"author": "Colosimo DA",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "cit0051",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2017.04.008",
"author": "Belkaid Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "562",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "cit0052",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-00486-8",
"author": "Lynn DJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "cit0053",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa1103",
"author": "Smilowitz NR",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2270",
"journal-title": "Eur Heart J",
"key": "cit0054",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijlh.13336",
"author": "Nugroho J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Int J Lab Hematol",
"key": "cit0055",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Koutsoumanis K",
"first-page": "e06174",
"journal-title": "EFSA J",
"key": "cit0056",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-019-0439-x",
"author": "Suez J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "716",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med",
"key": "cit0057",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-019-0626-9",
"author": "Yelin I",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1728",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "cit0058",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1517/14740338.2014.872627",
"author": "Didari T",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin. Drug Saf",
"key": "cit0059",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6942e1",
"author": "Gold JAW",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1517",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "cit0060",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.aad3503",
"author": "Falony G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "560",
"journal-title": "Science (80-)",
"key": "cit0061",
"volume": "352",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"author": "Corman VM",
"first-page": "2000045",
"journal-title": "Eurosurveillance",
"key": "cit0062",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF01535722",
"author": "Svedlund J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Dig Dis Sci",
"key": "cit0063",
"volume": "33",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"author": "Schloss PD",
"journal-title": "Appl Environ Microbiol",
"key": "cit0064",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Quast C",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "cit0065",
"year": "2013"
}
],
"reference-count": 65,
"references-count": 65,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Gut Microbes"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Gastroenterology",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Probiotic improves symptomatic and viral clearance in Covid19 outpatients: a randomized, quadruple-blinded, placebo-controlled trial"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/tandf_crossmark_01",
"volume": "14"
}