Effect of High-Dose Zinc and Ascorbic Acid Supplementation vs Usual Care on Symptom Length and Reduction Among Ambulatory Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The COVID A to Z Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369, COVIDAtoZ, NCT04342728, Feb 2021
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
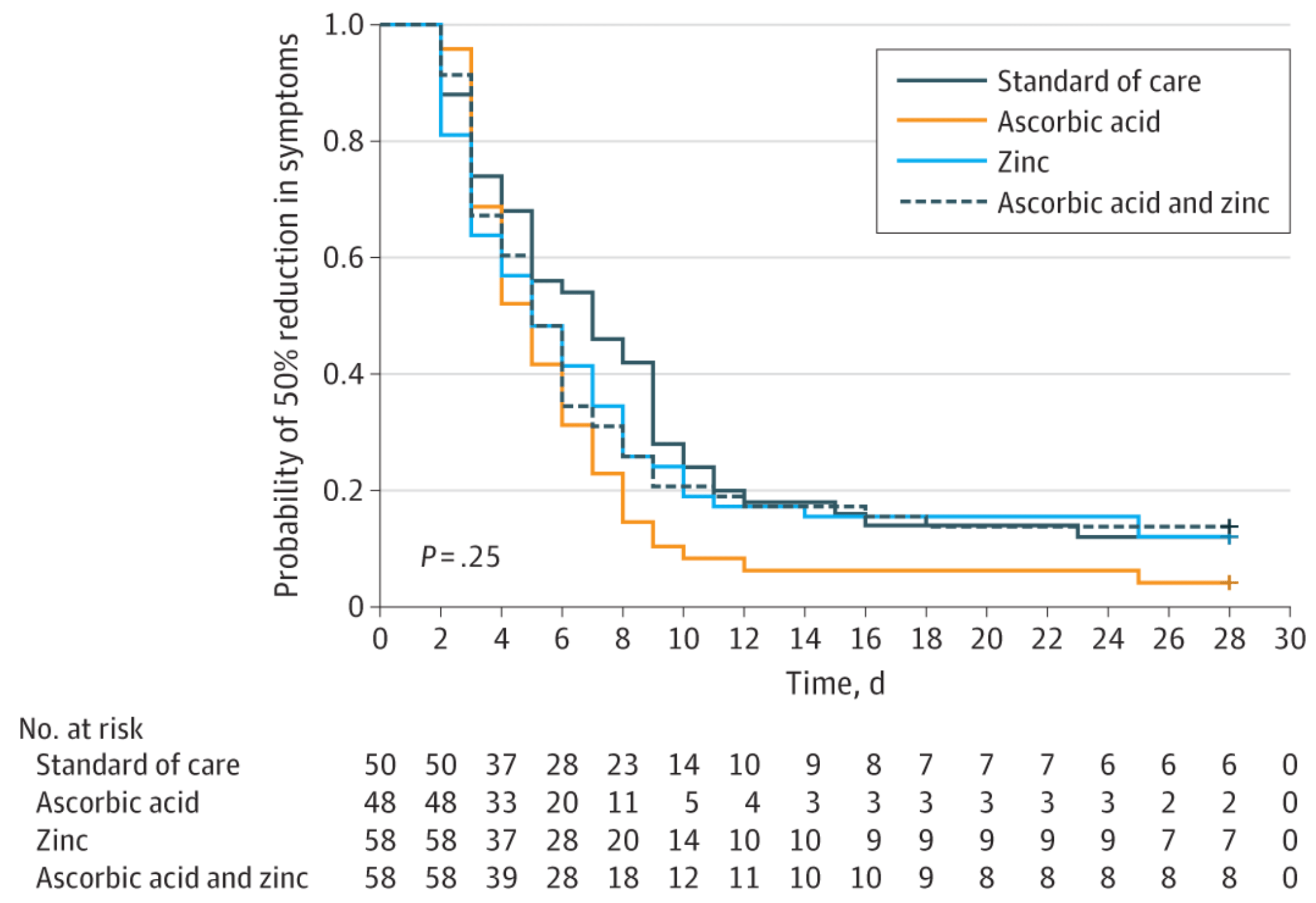
Small 214 low-risk outpatient RCT showing non-statistically significant faster recovery with zinc and with vitamin C. Study performed in the USA where zinc deficiency is relatively uncommon. The zinc dosage is relatively low, 50mg zinc gluconate (7mg elemental zinc), one tenth of that shown to reduce the duration of colds in other studies1.
The 'both' (combination) treatment group had much higher rates of diabetes (29.3% vs 6.0% in SOC), hypertension (46.6% vs 28.0%), and dyslipidemia (41.4% vs 18.0%), yet the statistical analysis did not adjust for these major confounders. This likely biased the results against the active treatment arm and undermined the futility stopping criteria. The treatment groups were also older, with the combination group mean age of 48.7 vs. 42 for the control group.
The reported mean 'Time to 50% reduction' in Table 2 appears to only include patients who successfully achieved the reduction, effectively excluding the worst outcomes (treatment failures) from the primary continuous measure. Using ANOVA on this truncated time-to-event data is statistically inappropriate and introduces selection bias.
Table 2 reports the mean (SD) for 'no shortness of breath' in the standard of care group as 3.6 (45) days. An SD of 45 days is not possible in a 28-day study and may be a typographical error for 4.5.
Table 1 (footnote c) indicates the 12-component score was collected for 78 patients (20 SOC, 14 AA, 21 zinc, 23 both). However, Table 2 reports outcomes for only 75 patients (19 SOC, 14 AA, 21 zinc, 21 both) with no explanation provided for the 3 missing patients.
An author reports receiving consulting fees from Gilead, the maker of remdesivir.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments2.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted differences between groups.
Study covers vitamin C and zinc.
|
risk of hospitalization, 43.7% higher, RR 1.44, p = 0.72, treatment 5 of 58 (8.6%), control 3 of 50 (6.0%).
|
|
recovery time, 11.9% lower, relative time 0.88, p = 0.38, treatment mean 5.9 (±4.9) n=58, control mean 6.7 (±4.4) n=50, mean time to a 50% reduction in symptoms, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Thomas et al., 12 Feb 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period 8 April, 2020 - 11 February, 2021, trial NCT04342728 (history) (COVIDAtoZ).
Effect of High-Dose Zinc and Ascorbic Acid Supplementation vs Usual Care on Symptom Length and Reduction Among Ambulatory Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection
JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
IMPORTANCE There is limited evidence regarding early treatment of novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection to mitigate symptom progression. OBJECTIVE To examine whether high-dose zinc and/or high-dose ascorbic acid reduce the severity or duration of symptoms compared with usual care among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS This multicenter, single health system randomized clinical factorial open-label trial enrolled 214 adult patients with a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection confirmed with a polymerase chain reaction assay who received outpatient care in sites in Ohio and
ARTICLE INFORMATION Additional Contributions: Serpil Erzurum, MD, James Young, MD, Daniel Culver, MD, Joan Booth, RN, Nancy Obuchowski, MPH, and John Petrich, RPh (Cleveland Clinic), were members of the operational and safety monitoring board. They were not compensated for their time. We would like to thank Samantha Xu, BS (Cleveland Clinic), for help with logistics of study set-up and coordination. She was compensated for her time.
References
Carr, Vitamin C administration in the critically ill: a summary of recent meta-analyses, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-019-2538-y
Eby, Davis, Halcomb, Reduction in duration of common colds by zinc gluconate lozenges in a double-blind study, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.25.1.20
Gammoh, Rink, Zinc in infection and inflammation, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu9060624
Hemilä, Chalker, Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000980.pub4
Hemilä, Vitamin C and infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu9040339
Hemilä, Vitamin C, respiratory infections and the immune system, Trends Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.it.2003.09.004
Hemilä, Zinc lozenges and the common cold: a meta-analysis comparing zinc acetate and zinc gluconate, and the role of zinc dosage, JRSM Open, doi:10.1177/2054270417694291
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Krenn, Gaudernak, Holzer, Lanke, Van Kuppeveld et al., Antiviral activity of the zinc ionophores pyrithione and hinokitiol against picornavirus infections, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01543-08
Li, Moore, Vasilieva, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature02145
Singh, Das, Zinc for the common cold, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001364.pub3
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Wang, Il'giovine, Mehra, Nissen, Desai, None
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jama.2020.2648&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"ISSN": [
"2574-3805"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Suma",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Divyang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Bittel",
"given": "Barbara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Wolski",
"given": "Kathy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Qiuqing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Anirudh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Il’Giovine",
"given": "Zachary J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio"
},
{
"name": "Neurologic Institute, Respiratory Institute, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Mehra",
"given": "Reena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Cleveland Clinic Florida, Weston"
}
],
"family": "McWilliams",
"given": "Carla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Nissen",
"given": "Steve E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Desai",
"given": "Milind Y.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"container-title-short": "JAMA Netw Open",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-13T01:40:31Z",
"timestamp": 1613180431000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-17T04:10:12Z",
"timestamp": 1671250212000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T12:59:44Z",
"timestamp": 1712321984982
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 254,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/articlepdf/2776305/thomas_2021_oi_210024_1612460884.60692.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e210369",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China.",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "zoi210024r1",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1239",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "zoi210024r3",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9060624",
"article-title": "Zinc in infection and inflammation.",
"author": "Gammoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "zoi210024r4",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9040339",
"article-title": "Vitamin C and infections.",
"author": "Hemilä",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "zoi210024r5",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold.",
"author": "Hemilä",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "zoi210024r6",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD001364.pub3",
"article-title": "Zinc for the common cold.",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "zoi210024r7",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.25.1.20",
"article-title": "Reduction in duration of common colds by zinc gluconate lozenges in a double-blind study.",
"author": "Eby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "zoi210024r8",
"volume": "25",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2054270417694291",
"article-title": "Zinc lozenges and the common cold: a meta-analysis comparing zinc acetate and zinc gluconate, and the role of zinc dosage.",
"author": "Hemilä",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JRSM Open",
"key": "zoi210024r9",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-019-2538-y",
"article-title": "Vitamin C administration in the critically ill: a summary of recent meta-analyses.",
"author": "Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "265",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "zoi210024r10",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"article-title": "Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture.",
"author": "te Velthuis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "zoi210024r11",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature02145",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "450",
"issue": "6965",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "zoi210024r12",
"volume": "426",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01543-08",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of the zinc ionophores pyrithione and hinokitiol against picornavirus infections.",
"author": "Krenn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "58",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "zoi210024r13",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.it.2003.09.004",
"article-title": "Vitamin C, respiratory infections and the immune system.",
"author": "Hemilä",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "579",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Trends Immunol",
"key": "zoi210024r14",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/03079459208418879",
"article-title": "Ascorbic acid and infectious bronchitis infections in broilers.",
"author": "Davelaar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "581",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Avian Pathol",
"key": "zoi210024r15",
"volume": "21",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc gluconate lozenges for common cold: a double-blind clinical trial.",
"author": "Weismann",
"first-page": "279",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Dan Med Bull",
"key": "zoi210024r16",
"volume": "37",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results.",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "zoi210024r17",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "zoi210024r2",
"unstructured": "US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19. Accessed January 12, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/index.html"
}
],
"reference-count": 17,
"references-count": 17,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2776305"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [
"The COVID A to Z Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Effect of High-Dose Zinc and Ascorbic Acid Supplementation vs Usual Care on Symptom Length and Reduction Among Ambulatory Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "4"
}
