Large-scale genetic correlation studies explore the causal relationship and potential mechanism between gut microbiota and COVID-19-associated risks
et al., BMC Microbiology, doi:10.1186/s12866-024-03423-0, Aug 2024
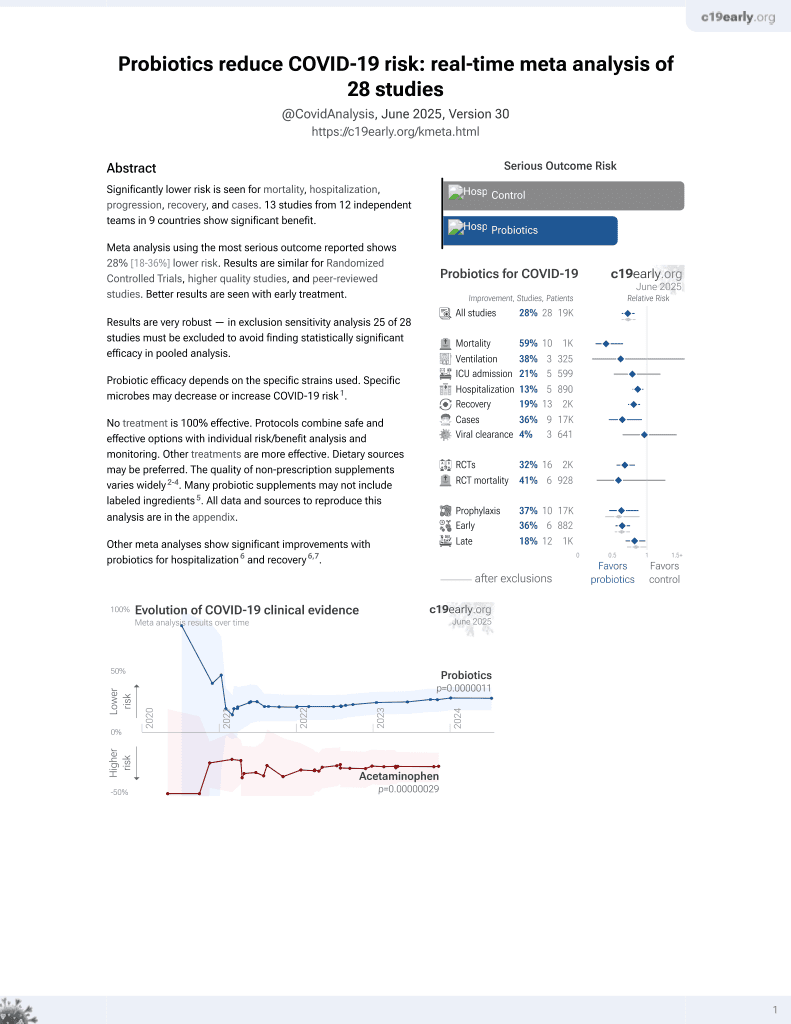
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
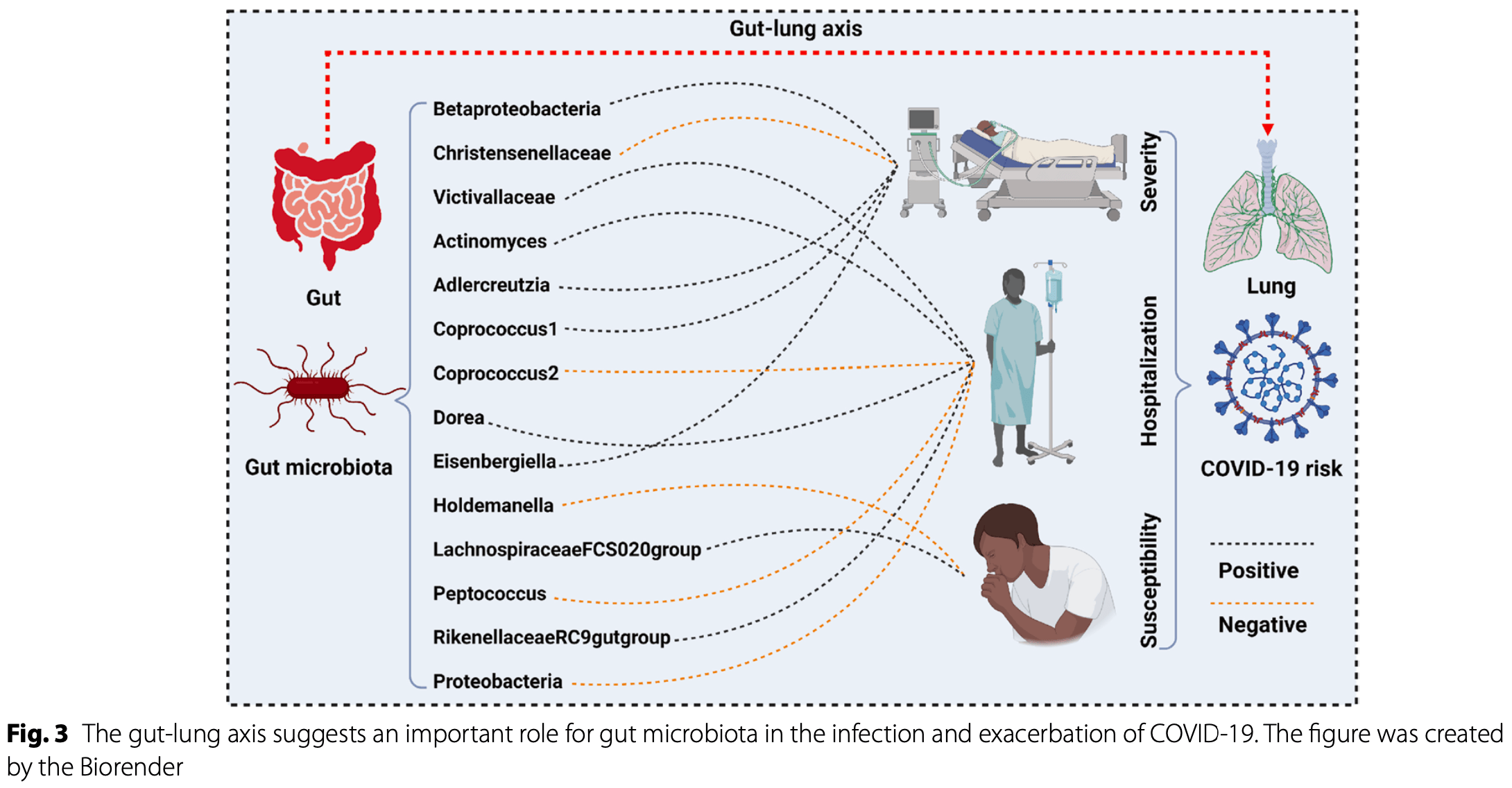
Mendelian randomization study based on large-scale GWAS data from 18,340 individuals showing a causal relationship between 14 gut microbiota taxa and reduced or increased risk of COVID-19 severity, hospitalization, or susceptibility. The study also identified plasma proteins, metabolites, and immune factors as potential mediators linking gut microbiota with COVID-19 outcomes. Results suggest that probiotic treatment may have potential benefits for COVID-19, however efficacy would likely depend on the specific bacterial strains used.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk1.
Li et al., 5 Aug 2024, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
Contact: luopeng@smu.edu.cn, xyyyzjw@csu.edu.cn.
Large-scale genetic correlation studies explore the causal relationship and potential mechanism between gut microbiota and COVID-19-associated risks
BMC Microbiology, doi:10.1186/s12866-024-03423-0
Recent observational studies suggest that gut microorganisms are involved in the onset and development of coronavirus disease 2019 , but the potential causal relationship behind them remains unclear. Exposure data were derived from the MiBioGen consortium, encompassing 211 gut microbiota (n = 18,340). The outcome data were sourced from the COVID-19 host genetics initiative (round 7), including COVID-19 severity (n = 1,086,211), hospitalization (n = 2,095,324), and susceptibility (n = 2,597,856). First, a two-sample Mendelian randomization (TSMR) was performed to investigate the causal effect between gut microbiota and COVID-19 outcomes. Second, a two-step MR was used to explore the potential mediators and underlying mechanisms. Third, several sensitivity analyses were performed to verify the robustness of the results. Five gut microbes were found to have a potential causality with COVID-19 severity, namely Betaproteobacteria (beta = 0.096, p = 0.034), Christensenellaceae (beta = -0.092, p = 0.023), Adlercreutzia (beta = 0.072, p = 0.048), Coprococcus 1 (beta = 0.089, p = 0.032), Eisenbergiella (beta = 0.064, p = 0.024). Seven gut microbes were found to have a potential causality with COVID-19 hospitalization, namely Victivallaceae (beta = 0.037, p = 0.028), Actinomyces (beta = 0.047, p = 0.046), Coprococcus 2 (beta = -0.061, p = 0.031), Dorea (beta = 0.067, p = 0.016), Peptococcus (beta = -0.035, p = 0.049), Rikenellaceae RC9 gut group (beta = 0.034, p = 0.018), and Proteobacteria (beta = -0.069, p = 0.035). Two gut microbes were found to have a potential causality with COVID-19 susceptibility, namely Holdemanella (beta = -0.024, p = 0.023) and Lachnospiraceae FCS020 group (beta = 0.026, p = 0.027). Multi-omics mediation analyses indicate that numerous plasma proteins, metabolites, and immune factors are critical mediators linking gut microbiota with COVID-19 outcomes. Sensitivity analysis suggested no significant heterogeneity or pleiotropy. These findings revealed the causal correlation and potential mechanism between gut microbiota and COVID-19 outcomes, which may improve our understanding of the gut-lung axis in the etiology and pathology of COVID-19 in the future.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1186/ s12866-024-03423-0. Supplementary Material 1.
Supplementary Material 2. Authors' contributions JW-Z and PL conceived, designed, and funded the research. JW-Z and JW wrote the first draft of the manuscript. HL, JW-Z, JW, XB-Z, ZY-D, HZ, NZ, RY-L, PL, and MR-L contributed to data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation. HL, JW-Z, JW,XB-Z, ZY-D, HZ, NZ, RY-L, PL, and MR-L contributed to the revision of the paper. All authors contributed to the article and approved the final manuscript.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate All data used by this study were publicly available from participant studies with the approvement of the ethical standards committee related to human experimentation. No additional ethical approval was required in this study.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Al-Aly, Bowe, Xie, Long COVID after breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-022-01840-0
Araf, Akter, Tang, Fatemi, Parvez et al., Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2: genomics, transmissibility, and responses to current COVID-19 vaccines, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27588
Ayoubkhani, Bermingham, Pouwels, Glickman, Nafilyan et al., Trajectory of long covid symptoms after covid-19 vaccination: community based cohort study, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-069676
Bernard-Raichon, Venzon, Klein, Axelrad, Zhang et al., Gut microbiome dysbiosis in antibiotic-treated COVID-19 patients is associated with microbial translocation and bacteremia, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-33395-6
Bowden, Greco, Minelli, Zhao, Lawlor et al., Improving the accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: moving beyond the NOME assumption, Int J Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/ije/dyy258
Bowden, Smith, Burgess, Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression, Int J Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/ije/dyv080
Bowden, Smith, Haycock, Burgess, Consistent estimation in Mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator, Genet Epidemiol, doi:10.1002/gepi.21965
Burgess, Foley, Allara, Staley, Howson, A robust and efficient method for Mendelian randomization with hundreds of genetic variants, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-019-14156-4
Burgess, Foley, Zuber, Inferring causal relationships between risk factors and outcomes from genome-wide association study data, Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet, doi:10.1146/annurev-genom-083117-021731
Burgess, Thompson, Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method, Eur J Epidemiol, doi:10.1007/s10654-017-0255-x
Chen, Lu, Pettersson-Kymmer, Stewart, Butler-Laporte et al., Genomic atlas of the plasma metabolome prioritizes metabolites implicated in human diseases, Nat Genet, doi:10.1038/s41588-022-01270-1
Cuesta, Burdisso, Segev, Kourrich, Sperandio, Gut colonization by Proteobacteria alters host metabolism and modulates cocaine neurobehavioral responses, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2022.09.014
Davies, Holmes, Davey, Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.k601
Davis, Mccorkell, Vogel, Topol, Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00846-2
Douaud, Lee, Alfaro-Almagro, Arthofer, Wang et al., SARS-CoV-2 is associated with changes in brain structure in UK Biobank, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04569-5
Ferkingstad, Sulem, Atlason, Sveinbjornsson, Magnusson et al., Large-scale integration of the plasma proteome with genetics and disease, Nat Genet, doi:10.1038/s41588-021-00978-w
Gao, Wang, Luo, Sun, Wang et al., Characterization of the human oropharyngeal microbiomes in SARS-CoV-2 infection and recovery patients, Adv Sci (Weinh), doi:10.1002/advs.202102785
Garcia-Garcia, Diez-Echave, Yuste, Chueca, Garcia et al., Gut microbiota composition can predict colonization by multidrugresistant bacteria in SARS-CoV-2 patients in intensive care unit: a pilot study, Antibiotics, doi:10.3390/antibiotics12030498
Ghorbani, Al-Manei, Naud, Healy, Gabarrini et al., Persistence of salivary antibody responses after COVID-19 vaccination is associated with oral microbiome variation in both healthy and people living with HIV, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1079995
Gu, Chen, Wu, Chen, Gao et al., Alterations of the gut microbiota in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 or H1N1 influenza, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa709
Gupta, Karyakarte, Joshi, Das, Jani et al., Nasopharyngeal microbiome reveals the prevalence of opportunistic pathogens in SARS-CoV-2 infected individuals and their association with host types, Microbes Infect, doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2021.104880
Hemani, Tilling, Davey, Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data, PLoS Genet, doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1007081
Hernandez-Teran, Mejia-Nepomuceno, Herrera, Barreto, Garcia et al., Dysbiosis and structural disruption of the respiratory microbiota in COVID-19 patients with severe and fatal outcomes, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-00851-0
Huang, Lin, He, Wang, Zhan, Association between COVID-19 and telomere length: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28008
Kaplan, Wang, Usyk, Sotres-Alvarez, Daviglus et al., Gut microbiome composition in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos is shaped by geographic relocation, environmental factors, and obesity, Genome Biol, doi:10.1186/s13059-019-1831-z
Ke, Weiss, Liu, Dissecting the role of the human microbiome in COVID-19 via metagenome-assembled genomes, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-32991-w
Kononen, Wade, Actinomyces and related organisms in human infections, Clin Microbiol Rev, doi:10.1128/CMR.00100-14
Kurilshikov, Medina-Gomez, Bacigalupe, Radjabzadeh, Wang et al., Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition, Nat Genet, doi:10.1038/s41588-020-00763-1
Leung, Interaction between gut microbiota and COVID-19 and its vaccines, World J Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5801
Li, Jing, Li, Hua, Di et al., Assessment of microbiota in the gut and upper respiratory tract associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Microbiome, doi:10.1186/s40168-022-01447-0
Li, Zhang, Wen, Liu, Liu et al., Large-scale genome-wide association study to identify causal relationships and potential mediators between education and autoimmune diseases, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1249017
Liu, Huang, Yang, Zhou, Chen et al., Conventional dendritic cell 2 links the genetic causal association from allergic asthma to COVID-19: a Mendelian randomization and transcriptomic study, Abstr J Big Data, doi:10.1186/s40537-024-00881-1
Mankowska-Wierzbicka, Zuraszek, Wierzbicka, Gabryel, Mahadea et al., Alterations in gut microbiota composition in patients with COVID-19: a pilot study of whole hypervariable 16S rRNA gene sequencing, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines11020367
Maruo, Sakamoto, Ito, Toda, Benno, Adlercreutzia equolifaciens gen. nov., sp. nov., an equol-producing bacterium isolated from human faeces, and emended description of the genus Eggerthella, Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65404-0
Merenstein, Bushman, Collman, Alterations in the respiratory tract microbiome in COVID-19: current observations and potential significance, Microbiome, doi:10.1186/s40168-022-01342-8
Miao, Li, Zhao, Dai, Chen et al., HSP90 inhibitors stimulate DNAJB4 protein expression through a mechanism involving N(6)-methyladenosine, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-019-11552-8
Nagata, Takeuchi, Masuoka, Aoki, Ishikane et al., Human gut microbiota and its metabolites impact immune responses in COVID-19 and its complications, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.09.024
Natarajan, Zlitni, Brooks, Vance, Dahlen et al., Gastrointestinal symptoms and fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 RNA suggest prolonged gastrointestinal infection, Med, doi:10.1016/j.medj.2022.04.001
Orru, Steri, Sidore, Marongiu, Serra et al., Complex genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and inform therapy, Nat Genet, doi:10.1038/s41588-020-0684-4
Petakh, Kamyshna, Nykyforuk, Yao, Imbery et al., Immunoregulatory intestinal microbiota and COVID-19 in patients with type two diabetes: a double-edged sword, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14030477
Ren, Wang, Cui, Lu, Wang et al., Alterations in the human oral and gut microbiomes and lipidomics in COVID-19, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323826
Ren, Wang, Zhong, Li, Xiao et al., Dynamics of the upper respiratory tract microbiota and its association with mortality in COVID-19, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.202103-0814OC
Righi, Lambertenghi, Gorska, Sciammarella, Ivaldi et al., Impact of COVID-19 and antibiotic treatments on gut microbiome: a role for Enterococcus spp, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10112786
Sanderson, Glymour, Holmes, Kang, Morrison et al., Mendelian randomization, Nat Rev Methods Primers, doi:10.1038/s43586-021-00092-5
Sanna, Van Zuydam, Mahajan, Kurilshikov, Vila et al., Causal relationships among the gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids and metabolic diseases, Nat Genet, doi:10.1038/s41588-019-0350-x
Sodsai, Ittiwut, Ruenjaiman, Ittiwut, Jantarabenjakul et al., TIGIT monoallelic nonsense variant in patient with severe COVID-19 infection, Thailand Emerg Infect Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2811.220914
Thursby, Juge, Introduction to the human gut microbiota, Biochem J, doi:10.1042/BCJ20160510
Troseid, Holter, Holm, Vestad, Sazonova et al., Gut microbiota composition during hospitalization is associated with 60-day mortality after severe COVID-19, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-023-04356-2
Verbanck, Chen, Neale, Do, Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases, Nat Genet, doi:10.1038/s41588-018-0099-7
Wakita, Shimomura, Kitada, Yamamoto, Ohashi et al., Taxonomic classification for microbiome analysis, which correlates well with the metabolite milieu of the gut, BMC Microbiol, doi:10.1186/s12866-018-1311-8
Weihl, Topf, Bengoechea, Duff, Charlton et al., Loss of function variants in DNAJB4 cause a myopathy with early respiratory failure, Acta Neuropathol, doi:10.1007/s00401-022-02510-8
Wen, Zhang, Zhang, Zhang, Lei et al., Large-scale genome-wide association studies reveal the genetic causal etiology between air pollutants and autoimmune diseases, J Transl Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-04928-y
Wu, Hu, Xu, Chen, Guo et al., clusterProfiler 4.0: a universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data, Innovation (Camb), doi:10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100141
Xie, Xu, Bowe, Al-Aly, Long-term cardiovascular outcomes of COVID-19, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-022-01689-3
Xu, Zhang, Guo, Xiao, Fu et al., Integrated analysis of gut microbiome and host immune responses in COVID-19, Front Med, doi:10.1007/s11684-022-0921-6
Yang, Shan, Shi, Li, Li, Coprococcus eutactus, a potent probiotic, alleviates colitis via acetate-mediated IgA response and microbiota restoration, J Agric Food Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06697
Yeoh, Zuo, Lui, Zhang, Liu et al., Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323020
Yu, Hu, enrichplot: Visualization of Functional Enrichment Result
Yu, Wang, Yan, He, DOSE: an R/Bioconductor package for disease ontology semantic and enrichment analysis, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu684
Yu, Yang, Cao, Bo, Lei, The causal role of gut microbiota in development of osteoarthritis, Osteoarthritis Cartilage, doi:10.1016/j.joca.2021.08.003
Zhang, Lau, Liu, Su, Chan et al., Gut microbiota in COVID-19: key microbial changes, potential mechanisms and clinical applications, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, doi:10.1038/s41575-022-00698-4
Zollner, Koch, Jukic, Pfister, Meyer et al., Postacute COVID-19 is characterized by gut viral antigen persistence in inflammatory bowel diseases, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.04.037
Zuo, Liu, Zhang, Lui, Tso et al., Depicting SARS-CoV-2 faecal viral activity in association with gut microbiota composition in patients with COVID-19, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322294
Zuo, Zhang, Lui, Yeoh, Li et al., Alterations in gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12866-024-03423-0",
"ISSN": [
"1471-2180"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12866-024-03423-0",
"alternative-id": [
"3423"
],
"article-number": "292",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "5 July 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "10 July 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "5 August 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "All data used by this study were publicly available from participant studies with the approvement of the ethical standards committee related to human experimentation. No additional ethical approval was required in this study."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "He",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wen",
"given": "Jie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Xiangbin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dai",
"given": "Ziyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Mingren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Nan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lei",
"given": "Ruoyan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "Peng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Jingwei",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "BMC Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "BMC Microbiol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-05T10:05:59Z",
"timestamp": 1722852359000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-05T10:06:24Z",
"timestamp": 1722852384000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-06T00:23:02Z",
"timestamp": 1722903782814
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1722816000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1722816000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12866-024-03423-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12866-024-03423-0/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12866-024-03423-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27588",
"author": "Y Araf",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1825",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "3423_CR1",
"unstructured": "Araf Y, Akter F, Tang YD, Fatemi R, Parvez MSA, Zheng C, et al. Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2: genomics, transmissibility, and responses to current COVID-19 vaccines. J Med Virol. 2022;94(5):1825–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.27588.",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medj.2022.04.001",
"author": "A Natarajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "371",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Med",
"key": "3423_CR2",
"unstructured": "Natarajan A, Zlitni S, Brooks EF, Vance SE, Dahlen A, Hedlin H, et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms and fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 RNA suggest prolonged gastrointestinal infection. Med. 2022;3(6):371–87 e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medj.2022.04.001.",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2022.04.037",
"author": "A Zollner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "495",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "3423_CR3",
"unstructured": "Zollner A, Koch R, Jukic A, Pfister A, Meyer M, Rossler A, et al. Postacute COVID-19 is characterized by gut viral antigen persistence in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(2):495–506 e8. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2022.04.037.",
"volume": "163",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj-2021-069676",
"author": "D Ayoubkhani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "3423_CR4",
"unstructured": "Ayoubkhani D, Bermingham C, Pouwels KB, Glickman M, Nafilyan V, Zaccardi F, et al. Trajectory of long covid symptoms after covid-19 vaccination: community based cohort study. BMJ. 2022;377:e069676. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj-2021-069676.",
"volume": "377",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00846-2",
"author": "HE Davis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "133",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "3423_CR5",
"unstructured": "Davis HE, McCorkell L, Vogel JM, Topol EJ. Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2023;21(3):133–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-022-00846-2.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01840-0",
"author": "Z Al-Aly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1461",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "3423_CR6",
"unstructured": "Al-Aly Z, Bowe B, Xie Y. Long COVID after breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med. 2022;28(7):1461–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-01840-0.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04569-5",
"author": "G Douaud",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "697",
"issue": "7907",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "3423_CR7",
"unstructured": "Douaud G, Lee S, Alfaro-Almagro F, Arthofer C, Wang C, McCarthy P, et al. SARS-CoV-2 is associated with changes in brain structure in UK Biobank. Nature. 2022;604(7907):697–707. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04569-5.",
"volume": "604",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01689-3",
"author": "Y Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "583",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "3423_CR8",
"unstructured": "Xie Y, Xu E, Bowe B, Al-Aly Z. Long-term cardiovascular outcomes of COVID-19. Nat Med. 2022;28(3):583–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-01689-3.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BCJ20160510",
"author": "E Thursby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1823",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Biochem J",
"key": "3423_CR9",
"unstructured": "Thursby E, Juge N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem J. 2017;474(11):1823–36. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160510.",
"volume": "474",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12866-018-1311-8",
"author": "Y Wakita",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "188",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Microbiol",
"key": "3423_CR10",
"unstructured": "Wakita Y, Shimomura Y, Kitada Y, Yamamoto H, Ohashi Y, Matsumoto M. Taxonomic classification for microbiome analysis, which correlates well with the metabolite milieu of the gut. BMC Microbiol. 2018;18(1):188. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-018-1311-8.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2022.09.024",
"author": "N Nagata",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "272",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "3423_CR11",
"unstructured": "Nagata N, Takeuchi T, Masuoka H, Aoki R, Ishikane M, Iwamoto N, et al. Human gut microbiota and its metabolites impact immune responses in COVID-19 and its complications. Gastroenterology. 2023;164(2):272–88. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2022.09.024.",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323020",
"author": "YK Yeoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "698",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "3423_CR12",
"unstructured": "Yeoh YK, Zuo T, Lui GC, Zhang F, Liu Q, Li AY, et al. Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19. Gut. 2021;70(4):698–706. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323020.",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323826",
"author": "Z Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1253",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "3423_CR13",
"unstructured": "Ren Z, Wang H, Cui G, Lu H, Wang L, Luo H, et al. Alterations in the human oral and gut microbiomes and lipidomics in COVID-19. Gut. 2021;70(7):1253–65. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323826.",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048",
"author": "T Zuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "944",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "3423_CR14",
"unstructured": "Zuo T, Zhang F, Lui GCY, Yeoh YK, Li AYL, Zhan H, et al. Alterations in gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(3):944–55 e8. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048.",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41575-022-00698-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "3423_CR15",
"unstructured": "Zhang F, Lau RI, Liu Q, Su Q, Chan FKL, Ng SC. Gut microbiota in COVID-19: key microbial changes, potential mechanisms and clinical applications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-022-00698-4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40537-024-00881-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "3423_CR16",
"unstructured": "Liu H, Huang S, Yang L, Zhou H, Chen B, Wu L, et al. Conventional dendritic cell 2 links the genetic causal association from allergic asthma to COVID-19: a Mendelian randomization and transcriptomic study. Abstr J Big Data. 2024;11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-024-00881-1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s43586-021-00092-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "3423_CR17",
"unstructured": "Sanderson E, Glymour MM, Holmes MV, Kang H, Morrison J, Munafò MR, et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2022;2(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-021-00092-5."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28008",
"author": "D Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5345",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "3423_CR18",
"unstructured": "Huang D, Lin S, He J, Wang Q, Zhan Y. Association between COVID-19 and telomere length: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. J Med Virol. 2022;94(11):5345–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.28008.",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.k601",
"author": "NM Davies",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "k601",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "3423_CR19",
"unstructured": "Davies NM, Holmes MV, Davey SG. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ. 2018;362:k601. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k601.",
"volume": "362",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41588-020-00763-1",
"author": "A Kurilshikov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "156",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nat Genet",
"key": "3423_CR20",
"unstructured": "Kurilshikov A, Medina-Gomez C, Bacigalupe R, Radjabzadeh D, Wang J, Demirkan A, et al. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nat Genet. 2021;53(2):156–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-020-00763-1.",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41588-020-0684-4",
"author": "V Orru",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1036",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nat Genet",
"key": "3423_CR21",
"unstructured": "Orru V, Steri M, Sidore C, Marongiu M, Serra V, Olla S, et al. Complex genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and inform therapy. Nat Genet. 2020;52(10):1036–45. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-020-0684-4.",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41588-022-01270-1",
"author": "Y Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "44",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Genet",
"key": "3423_CR22",
"unstructured": "Chen Y, Lu T, Pettersson-Kymmer U, Stewart ID, Butler-Laporte G, Nakanishi T, et al. Genomic atlas of the plasma metabolome prioritizes metabolites implicated in human diseases. Nat Genet. 2023;55(1):44–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-022-01270-1.",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41588-021-00978-w",
"author": "E Ferkingstad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1712",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Nat Genet",
"key": "3423_CR23",
"unstructured": "Ferkingstad E, Sulem P, Atlason BA, Sveinbjornsson G, Magnusson MI, Styrmisdottir EL, et al. Large-scale integration of the plasma proteome with genetics and disease. Nat Genet. 2021;53(12):1712–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-021-00978-w.",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41588-019-0350-x",
"author": "S Sanna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "600",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nat Genet",
"key": "3423_CR24",
"unstructured": "Sanna S, van Zuydam NR, Mahajan A, Kurilshikov A, Vich Vila A, Vosa U, et al. Causal relationships among the gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids and metabolic diseases. Nat Genet. 2019;51(4):600–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0350-x.",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.joca.2021.08.003",
"author": "XH Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1741",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Osteoarthritis Cartilage",
"key": "3423_CR25",
"unstructured": "Yu XH, Yang YQ, Cao RR, Bo L, Lei SF. The causal role of gut microbiota in development of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(12):1741–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2021.08.003.",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-genom-083117-021731",
"author": "S Burgess",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "303",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet",
"key": "3423_CR26",
"unstructured": "Burgess S, Foley CN, Zuber V. Inferring causal relationships between risk factors and outcomes from genome-wide association study data. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2018;19:303–27. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genom-083117-021731.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/gepi.21965",
"author": "J Bowden",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "304",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Genet Epidemiol",
"key": "3423_CR27",
"unstructured": "Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC, Burgess S. Consistent estimation in Mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4):304–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.21965.",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-017-0255-x",
"author": "S Burgess",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "377",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur J Epidemiol",
"key": "3423_CR28",
"unstructured": "Burgess S, Thompson SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32(5):377–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-017-0255-x.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-019-14156-4",
"author": "S Burgess",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "376",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "3423_CR29",
"unstructured": "Burgess S, Foley CN, Allara E, Staley JR, Howson JMM. A robust and efficient method for Mendelian randomization with hundreds of genetic variants. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):376. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14156-4.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41588-018-0099-7",
"author": "M Verbanck",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat Genet",
"key": "3423_CR30",
"unstructured": "Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, Do R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0099-7.",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/dyv080",
"author": "J Bowden",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "512",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int J Epidemiol",
"key": "3423_CR31",
"unstructured": "Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512–25. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyv080.",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/dyy258",
"author": "J Bowden",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "728",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int J Epidemiol",
"key": "3423_CR32",
"unstructured": "Bowden J, Del Greco MF, Minelli C, Zhao Q, Lawlor DA, Sheehan NA, et al. Improving the accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: moving beyond the NOME assumption. Int J Epidemiol. 2019;48(3):728–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyy258.",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1249017",
"author": "Y Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "3423_CR33",
"unstructured": "Li Y, Zhang J, Wen J, Liu M, Liu W, Li Y. Large-scale genome-wide association study to identify causal relationships and potential mediators between education and autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1249017. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1249017.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-024-04928-y",
"author": "J Wen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "392",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Transl Med",
"key": "3423_CR34",
"unstructured": "Wen J, Zhang J, Zhang H, Zhang N, Lei R, Deng Y, et al. Large-scale genome-wide association studies reveal the genetic causal etiology between air pollutants and autoimmune diseases. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):392. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-024-04928-y.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pgen.1007081",
"author": "G Hemani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1007081",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS Genet",
"key": "3423_CR35",
"unstructured": "Hemani G, Tilling K, Davey SG. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet. 2017;13(11):e1007081. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1007081.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100141",
"author": "T Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Innovation (Camb)",
"key": "3423_CR36",
"unstructured": "Wu T, Hu E, Xu S, Chen M, Guo P, Dai Z, et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: a universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation (Camb). 2021;2(3):100141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100141.",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "3423_CR37",
"unstructured": "Yu G, Hu E. enrichplot: Visualization of Functional Enrichment Result. https://yulab-smu.top/biomedical-knowledge-miningbook/. Accessed 14 Dec 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btu684",
"author": "G Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "608",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics",
"key": "3423_CR38",
"unstructured": "Yu G, Wang LG, Yan GR, He QY. DOSE: an R/Bioconductor package for disease ontology semantic and enrichment analysis. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(4):608–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu684.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322294",
"author": "T Zuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "276",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "3423_CR39",
"unstructured": "Zuo T, Liu Q, Zhang F, Lui GC, Tso EY, Yeoh YK, et al. Depicting SARS-CoV-2 faecal viral activity in association with gut microbiota composition in patients with COVID-19. Gut. 2021;70(2):276–84. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322294.",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2022.09.014",
"author": "S Cuesta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1615",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "3423_CR40",
"unstructured": "Cuesta S, Burdisso P, Segev A, Kourrich S, Sperandio V. Gut colonization by Proteobacteria alters host metabolism and modulates cocaine neurobehavioral responses. Cell Host Microbe. 2022;30(11):1615–29 e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2022.09.014.",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202102785",
"author": "M Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Adv Sci (Weinh)",
"key": "3423_CR41",
"unstructured": "Gao M, Wang H, Luo H, Sun Y, Wang L, Ding S, et al. Characterization of the human oropharyngeal microbiomes in SARS-CoV-2 infection and recovery patients. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(20):e2102785. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202102785.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40168-022-01342-8",
"author": "C Merenstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "165",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Microbiome",
"key": "3423_CR42",
"unstructured": "Merenstein C, Bushman FD, Collman RG. Alterations in the respiratory tract microbiome in COVID-19: current observations and potential significance. Microbiome. 2022;10(1):165. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-022-01342-8.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micinf.2021.104880",
"author": "A Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Microbes Infect",
"key": "3423_CR43",
"unstructured": "Gupta A, Karyakarte R, Joshi S, Das R, Jani K, Shouche Y, et al. Nasopharyngeal microbiome reveals the prevalence of opportunistic pathogens in SARS-CoV-2 infected individuals and their association with host types. Microbes Infect. 2022;24(1):104880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micinf.2021.104880.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-33395-6",
"author": "L Bernard-Raichon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5926",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "3423_CR44",
"unstructured": "Bernard-Raichon L, Venzon M, Klein J, Axelrad JE, Zhang C, Sullivan AP, et al. Gut microbiome dysbiosis in antibiotic-treated COVID-19 patients is associated with microbial translocation and bacteremia. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):5926. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33395-6.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/ijs.0.65404-0",
"author": "T Maruo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1221",
"issue": "Pt 5",
"journal-title": "Int J Syst Evol Microbiol.",
"key": "3423_CR45",
"unstructured": "Maruo T, Sakamoto M, Ito C, Toda T, Benno Y. Adlercreutzia equolifaciens gen. nov., sp. nov., an equol-producing bacterium isolated from human faeces, and emended description of the genus Eggerthella. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2008;58(Pt 5):1221–7. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65404-0.",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines11020367",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "3423_CR46",
"unstructured": "Mankowska-Wierzbicka D, Zuraszek J, Wierzbicka A, Gabryel M, Mahadea D, Baturo A, et al. Alterations in gut microbiota composition in patients with COVID-19: a pilot study of whole hypervariable 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Biomedicines. 2023;11(2); https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020367."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5801",
"author": "JSM Leung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5801",
"issue": "40",
"journal-title": "World J Gastroenterol",
"key": "3423_CR47",
"unstructured": "Leung JSM. Interaction between gut microbiota and COVID-19 and its vaccines. World J Gastroenterol. 2022;28(40):5801–6. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5801.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06697",
"author": "R Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Agric Food Chem",
"key": "3423_CR48",
"unstructured": "Yang R, Shan S, Shi J, Li H, An N, Li S, et al. Coprococcus eutactus, a potent probiotic, alleviates colitis via acetate-mediated IgA response and microbiota restoration. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06697.",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa709",
"author": "S Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2669",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "3423_CR49",
"unstructured": "Gu S, Chen Y, Wu Z, Chen Y, Gao H, Lv L, et al. Alterations of the gut microbiota in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 or H1N1 influenza. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(10):2669–78. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa709.",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11684-022-0921-6",
"author": "X Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "263",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Front Med",
"key": "3423_CR50",
"unstructured": "Xu X, Zhang W, Guo M, Xiao C, Fu Z, Yu S, et al. Integrated analysis of gut microbiome and host immune responses in COVID-19. Front Med. 2022;16(2):263–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0921-6.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14030477",
"author": "P Petakh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Viruses.",
"key": "3423_CR51",
"unstructured": "Petakh P, Kamyshna I, Nykyforuk A, Yao R, Imbery JF, Oksenych V, et al. Immunoregulatory intestinal microbiota and COVID-19 in patients with type two diabetes: a double-edged sword. Viruses. 2022;14(3):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030477.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antibiotics12030498",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "3423_CR52",
"unstructured": "Garcia-Garcia J, Diez-Echave P, Yuste ME, Chueca N, Garcia F, Cabeza-Barrera J, et al. Gut microbiota composition can predict colonization by multidrug-resistant bacteria in SARS-CoV-2 patients in intensive care unit: a pilot study. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023;12(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030498."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-32991-w",
"author": "S Ke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5235",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "3423_CR53",
"unstructured": "Ke S, Weiss ST, Liu YY. Dissecting the role of the human microbiome in COVID-19 via metagenome-assembled genomes. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):5235. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32991-w.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13059-019-1831-z",
"author": "RC Kaplan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "219",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Genome Biol",
"key": "3423_CR54",
"unstructured": "Kaplan RC, Wang Z, Usyk M, Sotres-Alvarez D, Daviglus ML, Schneiderman N, et al. Gut microbiome composition in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos is shaped by geographic relocation, environmental factors, and obesity. Genome Biol. 2019;20(1):219. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1831-z.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CMR.00100-14",
"author": "E Kononen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "419",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Rev",
"key": "3423_CR55",
"unstructured": "Kononen E, Wade WG. Actinomyces and related organisms in human infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015;28(2):419–42. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00100-14.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-00851-0",
"author": "A Hernandez-Teran",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21297",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "3423_CR56",
"unstructured": "Hernandez-Teran A, Mejia-Nepomuceno F, Herrera MT, Barreto O, Garcia E, Castillejos M, et al. Dysbiosis and structural disruption of the respiratory microbiota in COVID-19 patients with severe and fatal outcomes. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):21297. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-00851-0.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202103-0814OC",
"author": "L Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1379",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "3423_CR57",
"unstructured": "Ren L, Wang Y, Zhong J, Li X, Xiao Y, Li J, et al. Dynamics of the upper respiratory tract microbiota and its association with mortality in COVID-19. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;204(12):1379–90. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202103-0814OC.",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40168-022-01447-0",
"author": "J Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "38",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Microbiome",
"key": "3423_CR58",
"unstructured": "Li J, Jing Q, Li J, Hua M, Di L, Song C, et al. Assessment of microbiota in the gut and upper respiratory tract associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Microbiome. 2023;11(1):38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-022-01447-0.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.1079995",
"author": "M Ghorbani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1079995",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "3423_CR59",
"unstructured": "Ghorbani M, Al-Manei K, Naud S, Healy K, Gabarrini G, Sobkowiak MJ, et al. Persistence of salivary antibody responses after COVID-19 vaccination is associated with oral microbiome variation in both healthy and people living with HIV. Front Immunol.2022;13:1079995. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1079995.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-023-04356-2",
"author": "M Troseid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "69",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "3423_CR60",
"unstructured": "Troseid M, Holter JC, Holm K, Vestad B, Sazonova T, Granerud BK, et al. Gut microbiota composition during hospitalization is associated with 60-day mortality after severe COVID-19. Crit Care. 2023;27(1):69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-023-04356-2.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10112786",
"author": "E Righi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines.",
"key": "3423_CR61",
"unstructured": "Righi E, Lambertenghi L, Gorska A, Sciammarella C, Ivaldi F, Mirandola M, et al. Impact of COVID-19 and antibiotic treatments on gut microbiome: a role for Enterococcus spp. Biomedicines. 2022;10(11): 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112786.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-019-11552-8",
"author": "W Miao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3613",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "3423_CR62",
"unstructured": "Miao W, Li L, Zhao Y, Dai X, Chen X, Wang Y. HSP90 inhibitors stimulate DNAJB4 protein expression through a mechanism involving N(6)-methyladenosine. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3613. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11552-8.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00401-022-02510-8",
"author": "CC Weihl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "127",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Neuropathol",
"key": "3423_CR63",
"unstructured": "Weihl CC, Topf A, Bengoechea R, Duff J, Charlton R, Garcia SK, et al. Loss of function variants in DNAJB4 cause a myopathy with early respiratory failure. Acta Neuropathol. 2023;145(1):127–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-022-02510-8.",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2811.220914",
"author": "P Sodsai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2350",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Thailand Emerg Infect Dis",
"key": "3423_CR64",
"unstructured": "Sodsai P, Ittiwut C, Ruenjaiman V, Ittiwut R, Jantarabenjakul W, Suphapeetiporn K, et al. TIGIT monoallelic nonsense variant in patient with severe COVID-19 infection. Thailand Emerg Infect Dis. 2022;28(11):2350–2. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2811.220914.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 64,
"references-count": 64,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bmcmicrobiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12866-024-03423-0"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Large-scale genetic correlation studies explore the causal relationship and potential mechanism between gut microbiota and COVID-19-associated risks",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "24"
}