Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections
et al., Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3, Feb 2015
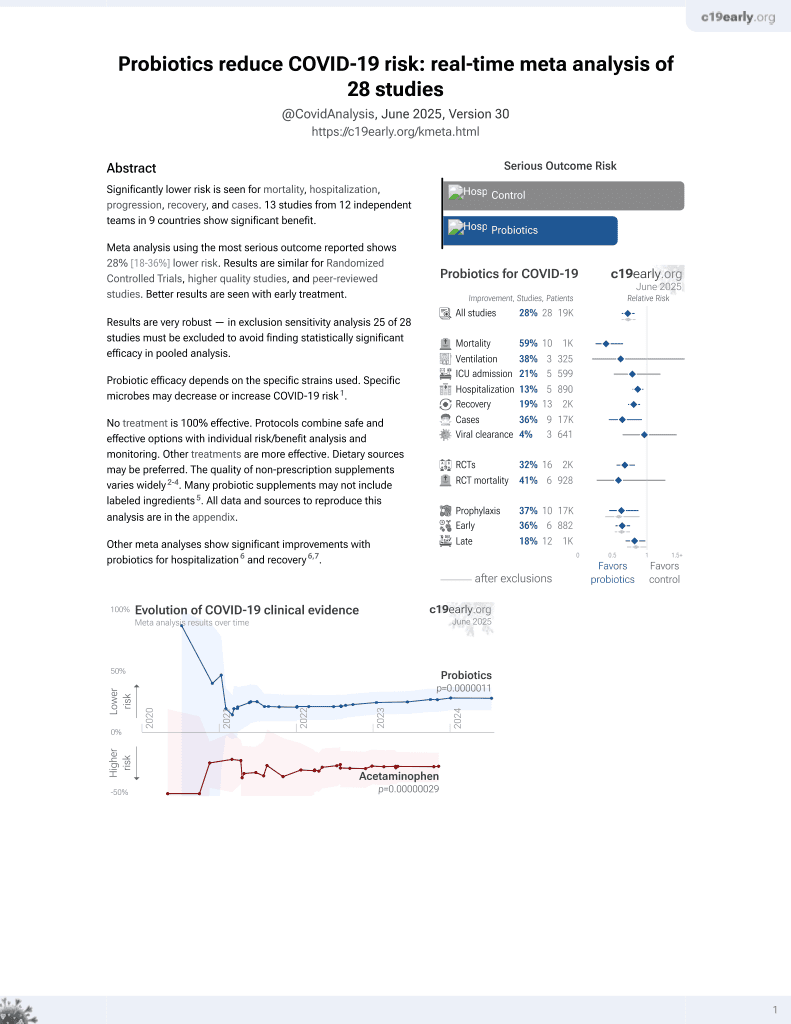
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
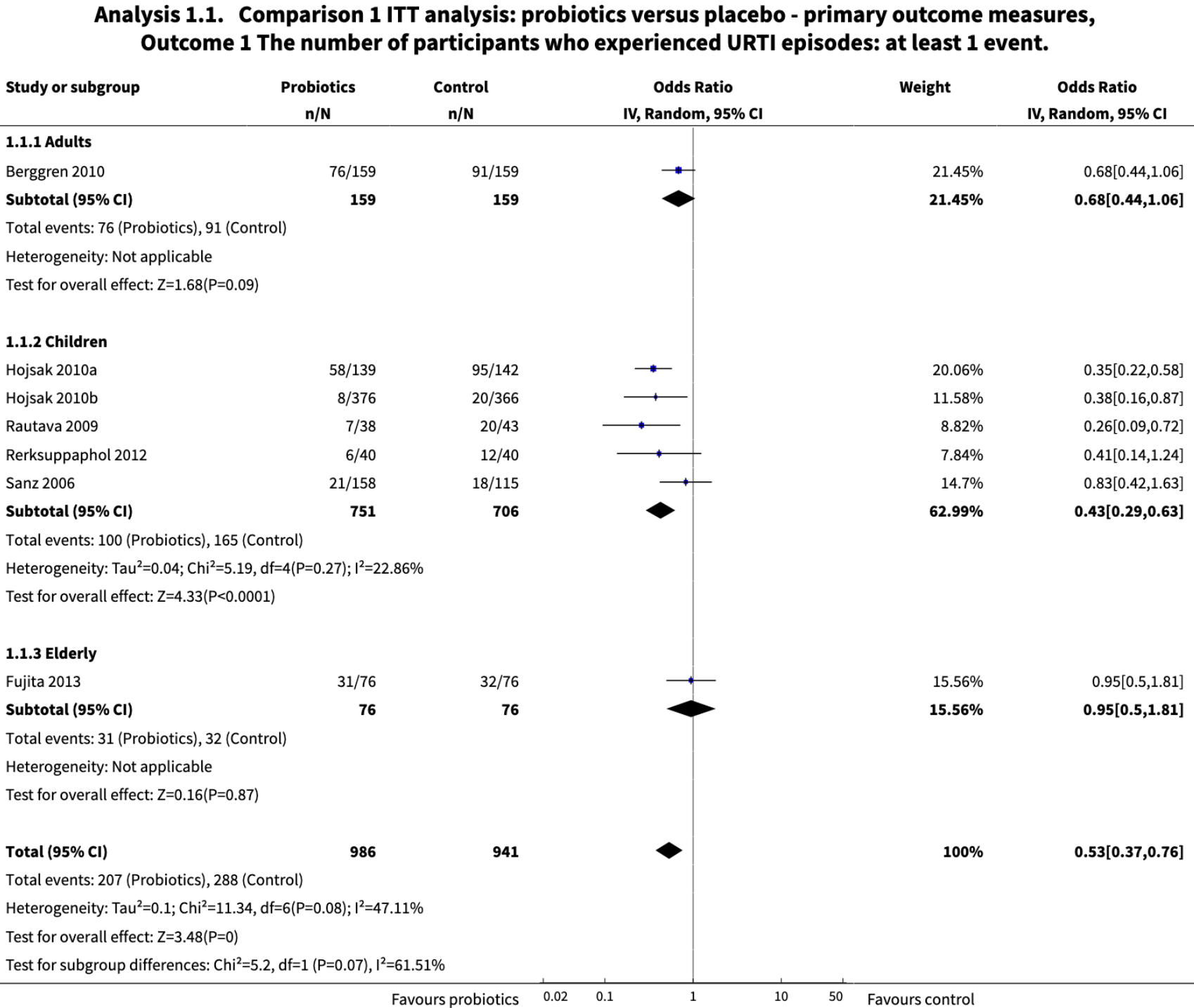
Meta analysis of 12 RCTs with 3,720 patients showing probiotics reduced acute upper respiratory tract infections.
Currently there are 29 probiotics for COVID-19 studies, showing 59% lower mortality [35‑74%], 38% lower ventilation [-87‑79%], 21% lower ICU admission [-20‑48%], 13% lower hospitalization [5‑21%], and 36% fewer cases [7‑55%].
Hao et al., 3 Feb 2015, preprint, 3 authors.
Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, doi:10.1002/14651858.cd006895.pub3
Trusted evidence. Informed decisions. Better health.
Cochrane
Library Trusted evidence. Informed decisions. Better health.
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Age: aged 18 to 65 Inclusion criteria: healthy volunteers Exclusion criteria: known intolerance or allergy to any ingredient included in the formulations, medically treated allergy, current treatment for severe gastrointestinal disorders, pregnancy or lactation, vaccination against influenza within the last 12 months or smoking
Interventions Treatment group: Lactobacillus plantarum HEAL 9 and Lactobacillus paracasei 8700:2 (1 × 10 9 CFU/day) for 12 weeks Control group: placebo: an identical-looking and tasting control product Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 3. Symptom score (burden) Notes -
Risk of bias
C O N T R I B U T I O N S O F A U T H O R S Qiukui Hao (QH) searched for trials, assessed the quality of trials, extracted data, analysed data and dra ed the review. Bi Rong Dong (BD) advised and assisted in writing the protocol and the review, searched for trials and developed the review.
Cochrane
Library Trusted evidence. Informed decisions. Better health.
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Taixiang Wu (TW) contributed to the development of the methods of the review and assisted with data extraction and analysis.
D E C L A R A T I O N S O F I N T E R E S T Qiukui Hao: none known. Bi Rong Dong: none known. Taixiang Wu: none known.
S O U R C E S O F S U P P O R T Internal sources • Chinese Cochrane Center, West China Hospital of..
References
Agustina, Kok, Van De Rest, Fahmida, Firmansyah et al., Early dietary intervention with a mixture of prebiotic oligosaccharides reduces the incidence of allergic manifestations and infections during the first two years of life, Journal of Nutrition
Gil-Campos, López, Rodriguez-Benítez, Romero, Roncero et al., Consumption of a fermented dairy product containing the probiotic Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 reduces the duration of respiratory infections in the elderly in a randomised controlled trial, International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism
Gutierrez-Castrellon ; Gutierrez-Castrellon, Lopez-Velazquez, Diaz-Garcia, Jimenez-Gutierrez, Mancilla-Ramirez et al., Long-term safety and impact on infection rates of postnatal probiotic and prebiotic (synbiotic) treatment: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, International Journal of Sport Nutrition & Exercise Metabolism, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000022.pub2
H A R A C T E R I S T I C S O F S T U D I E S, with 2 parallel arms Method of randomisation: not clearly stated Blinding: double-blind
Hao, Lu, Dong, Huang, Wu, Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub2
Link-Amster, Rochat, Saudan, Mignot, Aeschlimann et al., Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG supplementation for preventing respiratory infections in children: a meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials, Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition
Lu 2008 Lu, Dong, Huang, Wu, Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006895
Othman ; Othman, Meilson, Alfirevic, Pelto, Isolauri et al., Probiotic bacteria down-regulate the milk-induced inflammatory response in milk-hypersensitive subjects but have an immunostimulatory e ect in healthy subjects, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, doi:10.1002/14651858
Perdigon, Alvarez, Rachid, Aguero, Gobbato et al., New scientific paradigms for probiotics and prebiotics, Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology
Pierro, Colombo, Zanvit, Risso, Rottoli, Use of Streptococcus salivarius K12 in the prevention of streptococcal and viral pharyngotonsillitis in children, Drug, Healthcare and Patient Safety
Valente 2009 Valente, Jr, Alexander, Tomas, Evancho-Chapman et al., Immunologic function in the elderly a er injury--the neutrophil and innate immunity, Journal of Trauma
Witard ; Witard, Turner, Jackman, Tipton, Jeukendrup et al., High-intensity training reduces CD8+ T-cell redistribution in response to exercise, Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise
Wu 2007 Wu, Liu, The concepts, design, practice and reports of allocation concealment and blinding, Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine
Yamanaka, Hotomi, Shimada, Togawa, Immunological deficiency in "otitis-prone" children, Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
Yasui 1999 Yasui, Kiyosima, Hori, Shida, Protection against influenza infection of mice fed Bifido bacterium breve YIT 4064, Clinical and Diagnostic Laboratory Immunology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.cd006895.pub3",
"ISSN": [
"1465-1858"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "West China Hospital, Sichuan University; Center of Geriatrics and Gerontology; No. 37, Guo Xue Xiang Chengdu Sichuan China 610041"
}
],
"family": "Hao",
"given": "Qiukui",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "West China Hospital, Sichuan University; Center of Geriatrics and Gerontology; No. 37, Guo Xue Xiang Chengdu Sichuan China 610041"
}
],
"family": "Dong",
"given": "Bi Rong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "West China Hospital, Sichuan University; Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, Chinese Ethics Committee of Registering Clinical Trials; No. 37, Guo Xue Xiang Chengdu Sichuan China 610041"
}
],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Taixiang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"wiley.com",
"cochranelibrary.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2015,
2,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2015-02-04T07:00:04Z",
"timestamp": 1423033204000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-09T22:04:53Z",
"timestamp": 1628546693000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "Cochrane Acute Respiratory Infections Group",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-15T06:31:42Z",
"timestamp": 1715754702898
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 164,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2015,
2,
3
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/wol1/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3/fullpdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2015,
2,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2015,
2,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0001|cit1",
"unstructured": "Berggren A Lazou Ahren I Larsson N Onning G Randomised, double-blind and placebo-controlled study using new probiotic lactobacilli for strengthening the body immune defence against viral infections European Journal of Nutrition"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 on acute respiratory infections and intestinal secretory IgA in children",
"author": "Caceres",
"first-page": "353",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Journal of Pediatric Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0002|cit2",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajic.2013.04.005",
"article-title": "Decreased duration of acute upper respiratory tract infections with daily intake of fermented milk: a multicenter, double-blinded, randomized comparative study in users of day care facilities for the elderly population",
"author": "Fujita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1231",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "American Journal of Infection Control",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0003|cit3",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2009.09.008",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus GG in the prevention of gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infections in children who attend day care centers: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Hojsak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "312",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0004|cit4",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2009-2568",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus GG in the prevention of nosocomial gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infections",
"author": "Hojsak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1171",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0005|cit5",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S000711451000173X",
"article-title": "Reducing the risk of infection in the elderly by dietary intake of yoghurt fermented with Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1",
"author": "Makino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "998",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0006|cit6",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ejcn.2010.65",
"article-title": "Use of a fermented dairy probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus casei (DN-114 001) to decrease the rate of illness in kids: the DRINK study. A patient-oriented, double-blind, cluster-randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial",
"author": "Merenstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "669",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "European Journal of Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0007|cit7",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114508116282",
"article-title": "Specific probiotics in reducing the risk of acute infections in infancy--a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study",
"author": "Rautava",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1722",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0008|cit8",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1442-200X.2012.03647.x",
"article-title": "Randomized controlled trial of probiotics to reduce common cold in schoolchildren",
"author": "Rerksuppaphol",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "682",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics International",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0009|cit9",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "The nutritional status change the effectiveness of a dietary supplement of lactic bacteria on the emerging of respiratory tract diseases in children",
"author": "Rio",
"first-page": "29",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Archivos Latinoamericanos de Nutricion",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0010|cit10",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of Lactobacillus casei on the incidence of infectious conditions in children",
"author": "Sanz",
"first-page": "547",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutricion Hospitalaria",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0011|cit11",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114512004138",
"article-title": "Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus LGGw and Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis BB-12w on health-related quality of life in college students affected by upper respiratory infections",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1999",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0012|cit12",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2005.02.006",
"article-title": "Effect of Lactobacillus gasseri PA 16/8, Bifidobacterium longum SP 07/3, B. bifidum MF 20/5 on common cold episodes: a double blind, randomized, controlled trial",
"author": "Vrese",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "481",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0013|cit13",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.05.048",
"article-title": "Probiotic bacteria reduced duration and severity but not the incidence of common cold episodes in a double blind, randomized, controlled trial",
"author": "Vrese",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6670",
"issue": "44-6",
"journal-title": "Vaccine",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0014|cit14",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5414/CPP43318",
"article-title": "Effect of a dietary supplement containing probiotic bacteria plus vitamins and minerals on common cold infections and cellular immune parameters",
"author": "Winkler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "318",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0015|cit15",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2011-1379",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of probiotics and calcium on diarrhea and respiratory tract infections in Indonesian children",
"author": "Agustina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1155",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0016|cit16",
"volume": "129",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/138.6.1091",
"article-title": "Early dietary intervention with a mixture of prebiotic oligosaccharides reduces the incidence of allergic manifestations and infections during the first two years of life",
"author": "Arslanoglu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1091",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Journal of Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0017|cit17",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/DHPS.S59665",
"article-title": "Use of Streptococcus salivarius K12 in the prevention of streptococcal and viral pharyngotonsillitis in children",
"author": "Pierro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Drug, Healthcare and Patient Safety",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0018|cit18",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2011.11.016",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus fermentum CECT 5716 is safe and well tolerated in infants of 1-6 months of age: a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Gil-Campos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "231",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Pharmacological Research",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0019|cit19",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1123/ijsnem.21.1.55",
"article-title": "Daily probiotic's (Lactobacillus casei Shirota) reduction of infection incidence in athletes",
"author": "Gleeson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Sport Nutrition & Exercise Metabolism",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0020|cit20",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1123/ijsnem.22.4.235",
"article-title": "Effects of a Lactobacillus salivarius probiotic intervention on infection, cold symptom duration and severity, and mucosal immunity in endurance athletes",
"author": "Gleeson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "235",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0021|cit21",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114509991395",
"article-title": "Consumption of a fermented dairy product containing the probiotic Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 reduces the duration of respiratory infections in the elderly in a randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Guillemard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0022|cit22",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2013-0652",
"article-title": "Diarrhea in preschool children and Lactobacillus reuteri: a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Gutierrez-Castrellon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e904",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0023|cit23",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.322.7298.1327",
"article-title": "Effect of long term consumption of probiotic milk on infections in children attending day care centres: double blind, randomised trial",
"author": "Hatakka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1327",
"issue": "1298",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0024|cit24",
"volume": "322",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2007.01.003",
"article-title": "Treatment of acute otitis media with probiotics in otitis-prone children-a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised study",
"author": "Hatakka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "314",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0025|cit25",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsams.2013.08.004",
"article-title": "Probiotic supplementation reduces the duration and incidence of infections but not severity in elite rugby union players",
"author": "Haywood",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "356",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0026|cit26",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1123/ijsnem.17.4.352",
"article-title": "The effect of probiotics on respiratory infections and gastrointestinal symptoms during training in marathon runners",
"author": "Kekkonen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "352",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Sport Nutrition & Exercise Metabolism",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0027|cit27",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2007-1192",
"article-title": "Long-term safety and impact on infection rates of postnatal probiotic and prebiotic (synbiotic) treatment: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Kukkonen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0028|cit28",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ejcn.2012.62",
"article-title": "Milk containing probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and respiratory illness in children: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Kumpu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1020",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "European Journal of Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0029|cit29",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.23623",
"article-title": "The use of the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and viral findings in the nasopharynx of children attending day care",
"author": "Kumpu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1632",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0030|cit30",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijporl.2011.10.025",
"article-title": "Human bocavirus in the nasopharynx of otitis-prone children",
"author": "Lehtoranta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "206",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0031|cit31",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2008-2666",
"article-title": "Probiotic effects on cold and influenza-like symptom incidence and duration in children",
"author": "Leyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e172",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0032|cit32",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.11.114",
"article-title": "Different effects of probiotic species/strains on infections in preschool children: a double-blind, randomized, controlled study",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1073",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Vaccine",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0033|cit33",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2013.08.020",
"article-title": "Prebiotic and probiotic supplementation prevents rhinovirus infections in preterm infants: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Luoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "405",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0034|cit34",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S000711451000173X",
"article-title": "Reducing the risk of infection in the elderly by dietary intake of yoghurt fermented with Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1",
"author": "Makino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "998",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0035|cit35",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MPG.0b013e3182333f18",
"article-title": "Human milk probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 reduces the incidence of gastrointestinal and upper respiratory tract infections in infants",
"author": "Maldonado",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0036|cit36",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/acm.2009.0310",
"article-title": "Immunogenic yeast-based fermentate for cold/flu-like symptoms in nonvaccinated individuals",
"author": "Moyad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "213",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0037|cit37",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0038|cit38",
"unstructured": "Pitkaranta A Hatakka K Blomgren K Pohjavuori S Korpela R Probiotics in prevention of acute otitis media in otitis prone children 8th International Symposium on Recent Advances in Otitis Media 2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCG.0b013e31817e1c91",
"article-title": "A new chance of preventing winter diseases by the administration of symbiotic formulations",
"author": "Pregliasco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "224",
"issue": "Suppl 3 Pt 2",
"journal-title": "Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0039|cit39",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08910600801924928",
"article-title": "Effect of a probiotic milk product on gastrointestinal and respiratory infections in children attending day-care",
"author": "Kloster Smerud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "80",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0040|cit40",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetic, bacteriological, and clinical studies on SY5555 in children",
"author": "Tajima",
"first-page": "31",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Japanese Journal of Antibiotics",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0041|cit41",
"volume": "48",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7205/MILMED.172.9.1006",
"article-title": "Effect of a probiotics supplementation on respiratory infections and immune and hormonal parameters during intense military training",
"author": "Tiollier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1006",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Military Medicine",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0042|cit42",
"volume": "172",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of fermented milk containing the probiotic Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 on winter infections in free-living elderly subjects: a randomised, controlled pilot study",
"author": "Turchet",
"first-page": "75",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of Nutrition, Health and Aging",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0043|cit43",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1475-2891-10-30",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus fermentum (PCC) supplementation and gastrointestinal and respiratory-tract illness symptoms: a randomised control trial in athletes",
"author": "West",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrition Journal",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0044|cit44",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2013.10.002",
"article-title": "Probiotic supplementation for respiratory and gastrointestinal illness symptoms in healthy physically active individuals",
"author": "West",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "581",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0045|cit45",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Therapeutic effectiveness and clinical tolerance in children of a medication combining in the same preparation of a tetracycline base with lyophilized lactobacillus",
"author": "Kaplan",
"first-page": "1889",
"issue": "28",
"journal-title": "Semaine des Hopitaux",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0046|cit46",
"volume": "44",
"year": "1968"
},
{
"article-title": "The development of a treatment method for streptococcal tonsillitis in children",
"author": "Marushko",
"first-page": "79",
"journal-title": "Likarska Sprava",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0047|cit47",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0048|cit48",
"unstructured": "The effect of a probiotic on protection against upper respiratory tract infections in children Ongoing study August 2013"
},
{
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0049|cit49",
"unstructured": "Probiotics in prevention of common cold Ongoing study October 2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600938",
"article-title": "Enhancement of natural immune function by dietary consumption of Bifidobacterium lactis (HN019)",
"author": "Arunachalam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "263",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "European Journal of Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0050|cit50",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.12-1745",
"article-title": "Impact of the administration of probiotics on mortality in critically ill adult patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Barraud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "646",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0051|cit51",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD007401.pub3",
"article-title": "Probiotics for treating persistent diarrhoea in children",
"author": "Bernaola Aponte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0052|cit52",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "National ambulatory medical care survey: 2001 summary",
"author": "Cherry",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Advance Data",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0053|cit53",
"volume": "337",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.324.7350.1361",
"article-title": "Probiotics in preventing of antibiotic associated diarrhoea: meta-analysis",
"author": "D'Souza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1361",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0054|cit54",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(99)75304-X",
"article-title": "Modulation of nonspecific mechanisms of defense by lactic acid bacteria: effective dose",
"author": "Donnet-Hughes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "863",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Journal of Dairy Science",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0055|cit55",
"volume": "82",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/IAI.72.6.3299-3309.2004",
"article-title": "Bacterial probiotic modulation of dendritic cell",
"author": "Drakes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3299",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Infection and Immunity",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0056|cit56",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD003124.pub3",
"article-title": "Acetylcysteine and carbocysteine for acute upper and lower respiratory tract infections in paediatric patients without chronic broncho-pulmonary disease",
"author": "Duijvestijn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0057|cit57",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0149-2918(01)80137-5",
"article-title": "Diagnosis and treatment of upper respiratory tract infections in the primary care setting",
"author": "Fendrick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1683",
"journal-title": "Clinical Therapeutics",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0058|cit58",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0958-6946(98)00074-0",
"article-title": "Stimulation of the immune system by lactic cultures",
"author": "Gill",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "535",
"journal-title": "International Dairy Journal",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0059|cit59",
"volume": "8",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0060|cit60",
"unstructured": "Brozek J Oxman A GRADEpro 2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.12-0679",
"article-title": "Lack of efficacy of probiotics in preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia probiotics for ventilator-associated pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "859",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0061|cit61",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0002-9343(01)01059-2",
"article-title": "Clinical significance and pathogenesis of viral respiratory infections",
"author": "Gwaltney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"issue": "Suppl",
"journal-title": "American Journal of Medicine",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0062|cit62",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557",
"article-title": "Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses",
"author": "Higgins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "557",
"issue": "7414",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0063|cit63",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0064|cit64",
"unstructured": "Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011 Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD006821.pub2",
"article-title": "Saline nasal irrigation for acute upper respiratory tract infections",
"author": "Kassel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0065|cit65",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Nutrition and the tooth system",
"author": "Kollath",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "Deutsche Zahnarztliche Zeitschrift",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0066|cit66",
"volume": "8",
"year": "1953"
},
{
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0067|cit67",
"unstructured": "Lefebvre C Manheimer E Glanville J Chapter 6: Searching for studies In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD000022.pub2",
"article-title": "Antibiotic prophylaxis to reduce respiratory tract infections and mortality in adults receiving intensive care",
"author": "Liberati",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0068|cit68",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1574-695X.1994.tb00011.x",
"article-title": "Modulation of a specific humoral immune response and changes in intestinal flora mediated through fermented milk intake",
"author": "Link-Amster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Immunology and Medical Microbiology",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0069|cit69",
"volume": "10",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13312-013-0123-z",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG supplementation for preventing respiratory infections in children: a meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Indian Pediatrics",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0070|cit70",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00005176-199504000-00012",
"article-title": "Lactic acid bacteria in the treatment of acute rotavirus gastroenteritis",
"author": "Majamaa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "333",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0071|cit71",
"volume": "20",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/71.4.861",
"article-title": "Immunologic effects of yogurt",
"author": "Meydani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "861",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "American Journal of Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0072|cit72",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD005941.pub2",
"article-title": "Probiotics for preventing preterm labour",
"author": "Othman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0073|cit73",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2222.1998.00449.x",
"article-title": "Probiotic bacteria down-regulate the milk-induced inflammatory response in milk-hypersensitive subjects but have an immunostimulatory effect in healthy subjects",
"author": "Pelto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1474",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Clinical and Experimental Allergy",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0074|cit74",
"volume": "28",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(95)76784-4",
"article-title": "Immune system stimulation by probiotics",
"author": "Perdigon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1597",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Journal of Dairy Science",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0075|cit75",
"volume": "78",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00004836-200308000-00004",
"article-title": "New scientific paradigms for probiotics and prebiotics",
"author": "Reid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0076|cit76",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0077|cit77",
"unstructured": "The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager (RevMan) 2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(95)76659-0",
"article-title": "Immunomodulation of human blood cells following the ingestion of lactic acid bacteria",
"author": "Schiffrin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "491",
"journal-title": "Journal of Dairy Science",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0078|cit78",
"volume": "78",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM199708143370701",
"article-title": "The effect of changes in the consumption of macrolide antibiotics on erythromycin resistance in group A streptococci in Finland",
"author": "Seppala",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "441",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "New England Journal of Medicine",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0079|cit79",
"volume": "337",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.2001.10719027",
"article-title": "Systemic immunity-enhancing effects in healthy subjects following dietary consumption of the lactic acid bacterium lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001",
"author": "Sheih",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "149",
"issue": "Suppl 2",
"journal-title": "Journal of the American College of Nutrition",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0080|cit80",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-138-7-200304010-00008",
"article-title": "Changing use of antibiotics in community-based outpatient practice, 1991-1999",
"author": "Steinman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "525",
"journal-title": "Annals of Internal Medicine",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0081|cit81",
"volume": "738",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.1996.03530280052036",
"article-title": "The challenges of emerging infections disease: development and spread of multiply-resistant bacterial pathogens",
"author": "Tenover",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "300",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0082|cit82",
"volume": "275",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/TA.0b013e3181b84279",
"article-title": "Immunologic function in the elderly after injury--the neutrophil and innate immunity",
"author": "Valente",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "968",
"journal-title": "Journal of Trauma",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0083|cit83",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1249/MSS.0b013e318257d2db",
"article-title": "High-intensity training reduces CD8+ T-cell redistribution in response to exercise",
"author": "Witard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1689",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0084|cit84",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "The concepts, design, practice and reports of allocation concealment and blinding",
"author": "Wu",
"first-page": "222",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0085|cit85",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb51880.x",
"article-title": "Immunological deficiency in \"otitis-prone\" children",
"author": "Yamanaka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "70",
"journal-title": "Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0086|cit86",
"volume": "830",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CDLI.6.2.186-192.1999",
"article-title": "Protection against influenza infection of mice fed Bifido bacterium breve YIT 4064",
"author": "Yasui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "186",
"journal-title": "Clinical and Diagnostic Laboratory Immunology",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0087|cit87",
"volume": "6",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub2",
"article-title": "Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections",
"author": "Hao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0088|cit88",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895",
"article-title": "Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"key": "10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3-BIB0089|cit89",
"year": "2008"
}
],
"reference-count": 89,
"references-count": 89,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/14651858.CD006895.pub3"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"update-to": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.cd006895.pub2",
"label": "New version",
"type": "new_version",
"updated": {
"date-parts": [
[
2015,
2,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2015-02-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1422921600000
}
}
]
}