Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Muscle Status in Old Patients Recovering from COVID-19 Infection
et al., Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina57101079, Oct 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
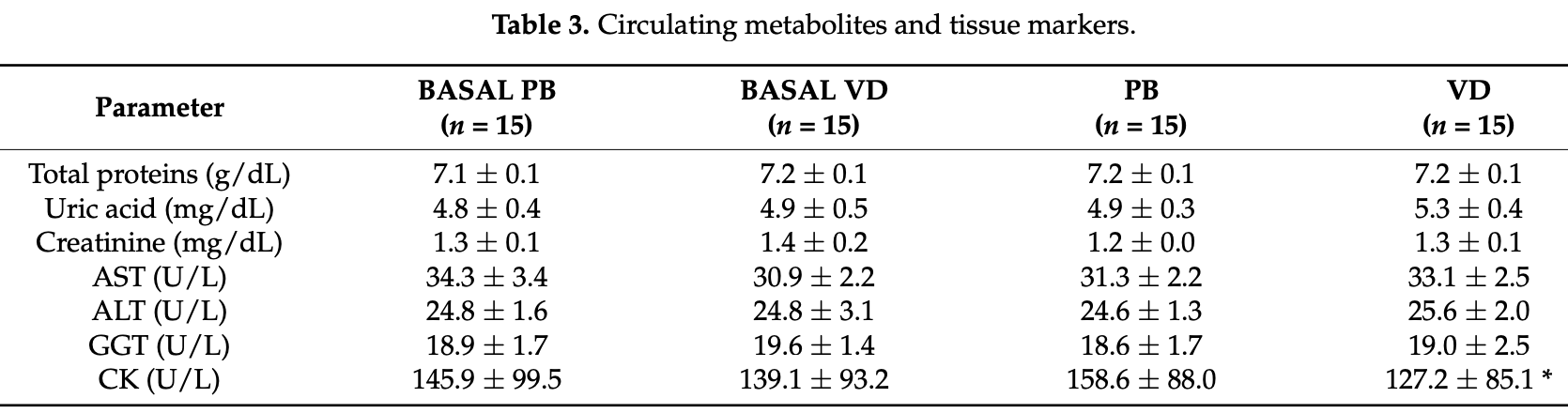
Small RCT with 30 patients examining the effect of vitamin D supplementation on muscle status in elderly recovering COVID-19 patients, showing serum creatine kinase levels returned to optimal values, however there was no significant difference in physical test results.
Caballero-García et al., 9 Oct 2021, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Muscle Status in Old Patients Recovering from COVID-19 Infection
Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina57101079
Background and Objectives: Vitamin D, in addition to its effect on mineral homeostasis, plays a key role in muscle metabolism. Vitamin D supplementation is involved in muscle recovery after damage as a consequence of either pathology or after high-intensity exercise. In this context, the aim of this study was to analyze the effect of vitamin D on muscle fitness in elderly patients in the recovery phase after SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection. Materials and Methods: This pilot study was conducted at the Soria Norte Health Center. The study consisted of a double-blind trial with two groups of men (placebo and vitamin D-supplemented) (n = 15/group). Treatment with vitamin D (cholecalciferol: 2000 IU/day) and placebo was carried out for 6 weeks. Circulating hematological and biochemical parameters (total protein, glucose, vitamin D, urea, uric acid, aspartate aminotransferase/glutamicoxaloacetic transaminase, alanine aminotransferase/glutamic-pyruvic transaminase, creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, aldolase, gamma-glutamyl transferase and myoglobin) and the hormones cortisol and testosterone were determined. As for respiratory function tests, FEV1 and respiratory flow were also studied. For physical fitness tests, the "six-minute walk test" (6MWT) was used. Results: After vitamin D supplementation, we observed that serum creatine kinase levels returned to optimal values. This change suggests a protective role of vitamin D against muscle catabolism compared to placebo. In terms of physical test results, we observed only slight non-significant improvements, although patients reported feeling better. Conclusions: Vitamin D supplementation produces decreases in indicators of muscle damage, which may ultimately contribute to improving the health status and quality of life of patients who have suffered from COVID-19, during the recovery process.
Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
References
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J. Infect. Public Health
Amer, Qayyum, Relation between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and C-reactive protein in asymptomatic adults (from the continuous National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001 to 2006), Am. J. Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2011.08.032
Aronson, Ferner, Biomarkers-A General Review, Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol, doi:10.1002/cpph.19
Baeke, Takiishi, Korf, Gysemans, Mathieu et al., Modulator of the immune system, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.001
Balla, Merugu, Konala, Sangani, Kondakindi et al., Back to basics: Review on vitamin D and respiratory viral infections including COVID-19, J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect, doi:10.1080/20009666.2020.1811074
Bjerk, Edgington, Rector, Kunisaki, Supplemental vitamin D and physical performance in COPD: A pilot randomized trial, Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis, doi:10.2147/COPD.S40885
Caballero-García, Córdova-Martínez, Vicente-Salar, Roche, Pérez-Valdecantos et al., its role in recovery after muscular damage following exercise, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072336
Cai, Huang, Yu, Zhu, Xia et al., COVID-19: Abnormal liver function tests, J. Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.006
Cruz-Jentoft, Bahat, Bauer, Boirie, Bruyère et al., Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2), and the Extended Group for EWGSOP2. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis, Age Ageing, doi:10.1093/ageing/afy169
Córdova, Alvarez De Mon, Inmunidad en el Deporte; Gymnos
Dinarello, Anti-cytokine therapeutics and infections, Vaccine, doi:10.1016/S0264-410X(03)00196-8
Gaudio, Murabito, Agodi, Montineri, Castellino et al., Vitamin D levels are reduced at the rime of hospital admission in Sicilian SARS-CoV-2-positive patients, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18073491
Goyal, Choi, Pinheiro, Schenck, Chen et al., Clinical characteristics of Covid-19 in New York City, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2010419
Guan, Liang, Zhao, Liang, Chen et al., Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: A nationwide analysis, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00547-2020
Guzik, Mohiddin, Dimarco, Patel, Savvatis et al., COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system: Implications for risk assessment, diagnosis, and treatment options, Cardiovasc. Res, doi:10.1093/cvr/cvaa106
Han, Xie, Liu, Yang, Liu et al., Analysis of heart injury laboratory parameters in 273 COVID-19 patients in one hospital in Wuhan, China, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25809
Henry, Lippi, Plebania, Laboratory abnormalities in children with novel coronavirus disease 2019, Clin. Chem. Lab. Med, doi:10.1515/cclm-2020-0272
Hewison, Vitamin D and innate and adaptive immunity, Vitam. Horm, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-386960-9.00002-2
Hornikx, Van Remoortel, Lehouck, Mathieu, Maes et al., Vitamin D supplementation during rehabilitation in COPD: A secondary analysis of a randomized trial, Respir. Res
Jiehao, Jin, Daojiong, Zhi, Lei et al., A case series of children with 2019 novel coronavirus infection: Clinical and epidemiological features, Clin. Infect. Dis
Khan, Rhabdomyolysis: A review of the literature, Neth. J. Med
Knochel, Mechanisms of rhabdomyolysis, Curr. Opin. Rheumatol, doi:10.1097/00002281-199305060-00006
Lee, Nair, Eisman, Center, Vitamin D deficiency in the intensive care unit: An invisible accomplice to morbidity and mortality?, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-009-1642-x
Lippi, Plebani, A modern and pragmatic definition of laboratory medicine, Clin. Chem. Lab. Med, doi:10.1515/cclm-2020-0114
Lippi, Plebani, Laboratory abnormalities in patients with COVID-2019 infection, Clin. Chem. Lab. Med, doi:10.1515/cclm-2020-0198
Malik, Patel, Mehta, Patel, Kelkar et al., Biomarkers and outcomes of COVID-19 hospitalisations: Systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ Evid.-Based Med, doi:10.1136/bmjebm-2020-111536
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sánchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Quesada-Gomez, Entrenas-Castillo, Bouillon, Vitamin D receptor stimulation to reduce acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in patients with coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infections, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105719
Regueiro, López, González, Martínez, Inmunología, Biología y Patología del Sistema Inmunitario
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x
Shi, Liu, Fu, Xu, Wu et al., Vitamin D/VDR signaling attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acutelung injury by maintaining the integrity of the pulmonary epithelial barrier, Mol. Med. Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.4685
Sproston, Ashworth, Role of C-Reactive Protein at sites of inflammation and infection, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.00754
Stegeman, Ochodo, Guleid, Holtman, Yang et al., -19 Diagnostic Test Accuracy Group. Routine laboratory testing to determine if a patient has COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013787
Stockton, Mengersen, Paratz, Kandiah, Bennell, Effect of vitamin D supplementation on muscle strength: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Osteoporos. Int, doi:10.1007/s00198-010-1407-y
Wang, Hou, Luo, Tang, Wu et al., The laboratory tests and host immunity of COVID-19 patients with different severity of illness, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.137799
Yang, Li, Tao, Yang, Wang et al., Infection with SARS-CoV-2 causes abnormal laboratory results of multiple organs in patients, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.103255
Zdrenghea, Makrinioti, Bagacean, Bush, Johnston et al., Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.1909
Zhang, Shan, Minalyan, O'sullivan, Nace, A rare presentation of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) induced viral myositis with subsequent rhabdomyolysis, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.8074
Álvarez-Mon, Ortega, Gasullaet, Fortuny-Profitós, Mazaira-Font et al., A predictive model and risk factors for case fatality of COVID-19, J. Pers. Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina57101079",
"ISSN": [
"1648-9144"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101079",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background and Objectives: Vitamin D, in addition to its effect on mineral homeostasis, plays a key role in muscle metabolism. Vitamin D supplementation is involved in muscle recovery after damage as a consequence of either pathology or after high-intensity exercise. In this context, the aim of this study was to analyze the effect of vitamin D on muscle fitness in elderly patients in the recovery phase after SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection. Materials and Methods: This pilot study was conducted at the Soria Norte Health Center. The study consisted of a double-blind trial with two groups of men (placebo and vitamin D-supplemented) (n = 15/group). Treatment with vitamin D (cholecalciferol: 2000 IU/day) and placebo was carried out for 6 weeks. Circulating hematological and biochemical parameters (total protein, glucose, vitamin D, urea, uric acid, aspartate aminotransferase/glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase, alanine aminotransferase/glutamic-pyruvic transaminase, creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, aldolase, gamma-glutamyl transferase and myoglobin) and the hormones cortisol and testosterone were determined. As for respiratory function tests, FEV1 and respiratory flow were also studied. For physical fitness tests, the “six-minute walk test” (6MWT) was used. Results: After vitamin D supplementation, we observed that serum creatine kinase levels returned to optimal values. This change suggests a protective role of vitamin D against muscle catabolism compared to placebo. In terms of physical test results, we observed only slight non-significant improvements, although patients reported feeling better. Conclusions: Vitamin D supplementation produces decreases in indicators of muscle damage, which may ultimately contribute to improving the health status and quality of life of patients who have suffered from COVID-19, during the recovery process.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"medicina57101079"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caballero-García",
"given": "Alberto",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6916-608X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pérez-Valdecantos",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guallar",
"given": "Pablo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caballero-Castillo",
"given": "Aurora",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5128-1672",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Roche",
"given": "Enrique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noriega",
"given": "David C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0236-2817",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Córdova",
"given": "Alfredo",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicina",
"container-title-short": "Medicina",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-11T01:37:29Z",
"timestamp": 1633916249000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-20T08:50:43Z",
"timestamp": 1634719843000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-06T15:13:07Z",
"timestamp": 1709737987472
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 20,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-09T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633737600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/57/10/1079/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1079",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cvr/cvaa106",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25809",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"author": "Regueiro",
"key": "ref3",
"series-title": "Inmunología, Biología y Patología del Sistema Inmunitario",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"author": "Córdova",
"key": "ref4",
"series-title": "Inmunidad en el Deporte",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0264-410X(03)00196-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-386960-9.00002-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.1909",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105719",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/20009666.2020.1811074",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2015.4685",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18073491",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ageing/afy169",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00547-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2010419",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjebm-2020-111536",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpph.19",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0114",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jpm11010036",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0272",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0198",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.137799",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103255",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.00754",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa198",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjcard.2011.08.032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD013787",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"article-title": "Rhabdomyolysis: A review of the literature",
"author": "Khan",
"first-page": "272",
"journal-title": "Neth. J. Med.",
"key": "ref32",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00002281-199305060-00006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.8074",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072336",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1465-9921-13-84",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/COPD.S40885",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-010-1407-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-009-1642-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/57/10/1079"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Muscle Status in Old Patients Recovering from COVID-19 Infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "57"
}
